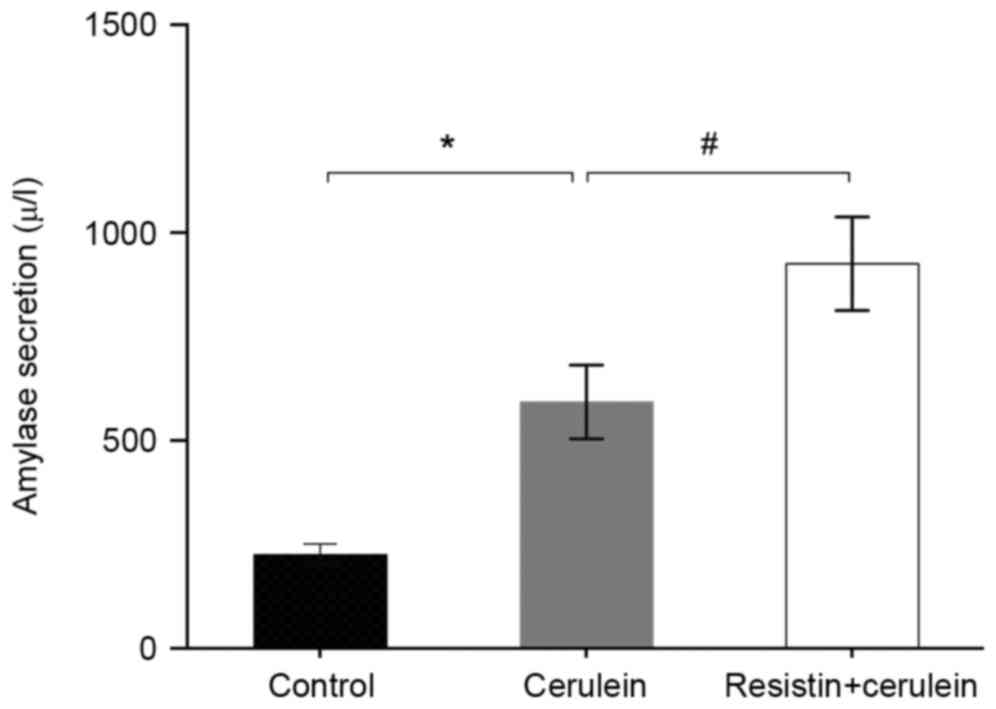
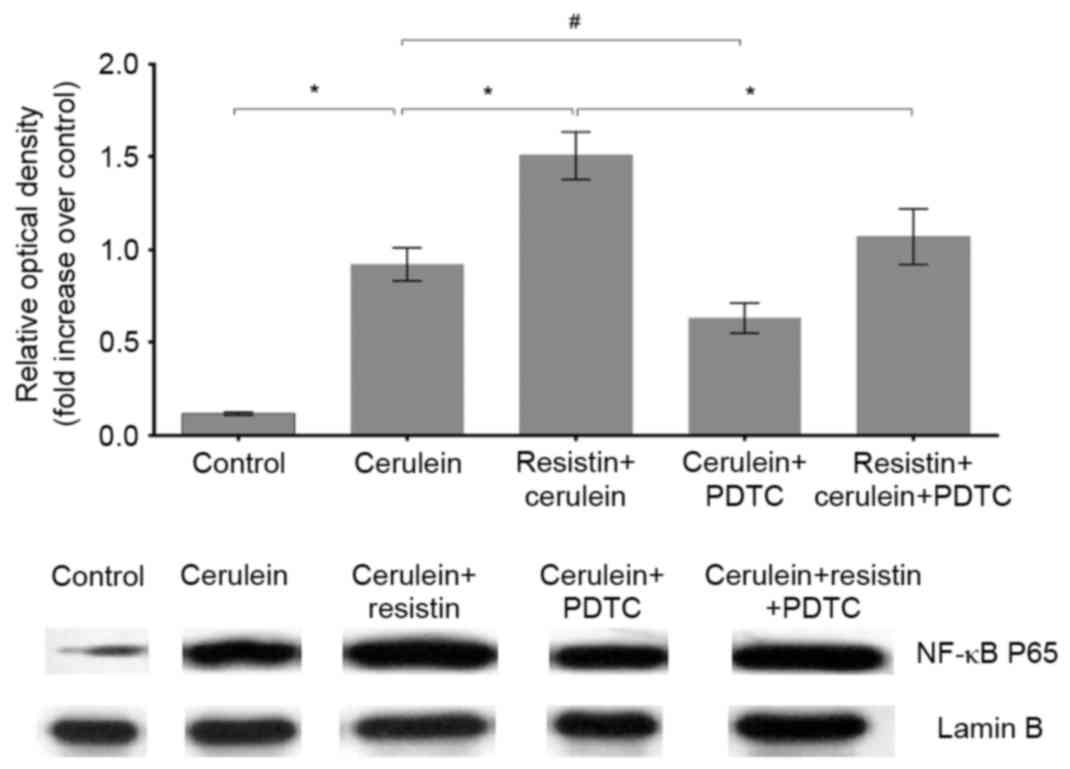
|
1
|
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK and Flegal
KM: Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States,
2011–2012. Jama. 311:806–814. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abu Hilal M and Armstrong T: The impact of
obesity on the course and outcome of acute pancreatitis. Obes Surg.
18:326–328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen SM, Xiong GS and Wu SM: Is obesity an
indicator of complications and mortality in acute pancreatitis? An
updated meta-analysis. J Dig Dis. 13:244–251. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sadr-Azodi O, Orsini N, Andrén-Sandberg A
and Wolk A: Abdominal and total adiposity and the risk of acute
pancreatitis: A population-based prospective cohort study. Am J
Gastroenterol. 108:133–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Premkumar R, Phillips AR, Petrov MS and
Windsor JA: The clinical relevance of obesity in acute
pancreatitis: Targeted systematic reviews. Pancreatology. 15:25–33.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Acharya C, Navina S and Singh VP: Role of
pancreatic fat in the outcomes of pancreatitis. Pancreatology.
14:403–408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Martínez J, Johnson CD, Sánchez-Paya J, de
Madaria E, Robles-Diaz G and Perez-Mateo M: Obesity is a definitive
risk factor of severity and mortality in acute pancreatitis: An
updated meta-analysis. Pancreatology. 6:206–209. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hong S, Qiwen B, Ying J, Wei A and
Chaoyang T: Body mass index and the risk and prognosis of acute
pancreatitis: A meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
23:1136–1143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Johnson CD, Toh SK and Campbell MJ:
Combination of APACHE-II score and an obesity score (APACHE-O) for
the prediction of severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 4:1–6.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grundy SM: Adipose tissue and metabolic
syndrome: too much, too little or neither. Eur J Clin Invest.
45:1209–1217. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vazquez-Vela ME, Torres N and Tovar AR:
White adipose tissue as endocrine organ and its role in obesity.
Arch Med Res. 39:715–728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao H: Adipocytokines in obesity and
metabolic disease. J Endocrinol. 220:T47–T59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ,
Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS and Lazar MA: The
hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 409:307–312.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L, Smith U
and Tarkowski A: Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory
properties. J Immunol. 174:5789–5795. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qatanani M, Szwergold NR, Greaves DR,
Ahima RS and Lazar MA: Macrophage-derived human resistin
exacerbates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in
mice. J Clin Invest. 119:531–539. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jamaluddin MS, Weakley SM, Yao Q and Chen
C: Resistin: functional roles and therapeutic considerations for
cardiovascular disease. Br J Pharmacol. 165:622–632. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Daniel P, Leśniowski B, Jasińska A,
Pietruczuk M and Malecka-Panas E: Usefulness of assessing
circulating levels of resistin, ghrelin, and IL-18 in alcoholic
acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 55:2982–2987. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Daniel P, Leśniowski B, Mokrowiecka A,
Jasińska A, Pietruczuk M and Małecka-Panas E: Circulating levels of
visfatin, resistin and pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-8 in
acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 10:477–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schäffler A, Hamer O, Dickopf J, Goetz A,
Landfried K, Voelk M, Herfarth H, Kopp A, Büchler C, Schölmerich J
and Brünnler T: Admission resistin levels predict peripancreatic
necrosis and clinical severity in acute pancreatitis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 105:2474–2484. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Filková M, Haluzik M, Gay S and Senolt L:
The role of resistin as a regulator of inflammation: Implications
for various human pathologies. Clin Immunol. 133:157–170. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang CY, Wang W, Tang JX and Yuan ZR: The
adipocytokine resistin stimulates the production of proinflammatory
cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-6 in pancreatic acinar cells via
NF-kappaB activation. J Endocrinol Invest. 36:986–992.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song YZ, Guan J, Wang HJ, Ma W, Li F, Xu
F, Ding LB, Xie L, Liu B, Liu K and Lv Z: Possible involvement of
serum and synovial fluid resistin in knee osteoarthritis: Cartilage
damage, clinical, and radiological links. J Clin Lab Anal.
30:437–443. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barnes PJ and Karin M: Nuclear
factor-kappaB: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic
inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 336:1066–1071. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gukovsky I, Li N, Todoric J, Gukovskaya A
and Karin M: Inflammation, autophagy, and obesity: Common features
in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
Gastroenterology. 144:1199–1209, e1194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schreck RMB, Männel DN, Dröge W and
Baeuerle PA: Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear
factor kappa B activation in intact cells. J Exp Med.
175:1181–1194. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang ZY, Jiang CY, Wang L, Wang JC, Zhang
SD, Einarsson C, Eriksson M, Han TQ, Parini P and Eggertsen G:
Increased NPC1L1 and ACAT2 expression in the jejunal mucosa from
Chinese gallstone patients. Biochem Biophy Res Com. 379:49–54.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Logsdon CD, Guthrie J, Alves F and
Rosewicz S: Glucocorticoids have opposite effects on ornithine
decarboxylase and cell growth in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells.
Yale J Biol Med. 65:449–456, 465-449. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gonzalez A, Santofimia-Castaño P and
Salido GM: Culture of pancreatic AR42J cell for use as a model for
acinar cell function. Pancreapedia: Exocrine Pancreas Knowledge
Base; 2011
|
|
30
|
Masamune A, Sakai Y, Satoh A, Fujita M,
Yoshida M and Shimosegawa T: Lysophosphatidylcholine induces
apoptosis in AR42J cells. Pancreas. 22:75–83. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ye H, Zhang HJ, Xu A and Hoo RL: Resistin
production from adipose tissue is decreased in db/db obese mice and
is reversed by rosiglitazone. PLoS one. 8:e655432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Elsayed EY, Mosalam NA and Mohamed NR:
Resistin and insulin resistance: A link between inflammation and
hepatocarcinogenesis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:7139–7142. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Al-Daghri N, Chetty R, McTernan PG,
Al-Rubean K, Al-Attas O, Jones AF and Kumar S: Serum resistin is
associated with C-reactive protein & LDL cholesterol in type 2
diabetes and coronary artery disease in a Saudi population.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 4:102005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Al Hannan F and Culligan KG: Human
resistin and the RELM of Inflammation in diabesity. Diabetol Metab
Syndr. 7:542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Silswal N, Singh AK, Aruna B, Mukhopadhyay
S, Ghosh S and Ehtesham NZ: Human resistin stimulates the
pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-12 in macrophages by
NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
334:1092–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bertolani C, Sancho-Bru P, Failli P,
Bataller R, Aleffi S, DeFranco R, Mazzinghi B, Romagnani P, Milani
S, Ginés P, et al: Resistin as an intrahepatic cytokine:
Overexpression during chronic injury and induction of
proinflammatory actions in hepatic stellate cells. Am J Pathol.
169:2042–2053. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cohen MC and Cohen S: Cytokine function: A
study in biologic diversity. Am J Clin Pathol. 105:589–598. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bhatia M: Inflammatory response on the
pancreatic acinar cell injury. Scand J Surg. 94:97–102.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sunden-Cullberg J, Nyström T, Lee ML,
Mullins GE, Tokics L, Andersson J, Norrby-Teglund A and Treutiger
CJ: Pronounced elevation of resistin correlates with severity of
disease in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med.
35:1536–1542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzuki S, Miyasaka K, Jimi A and Funakoshi
A: Induction of acute pancreatitis by cerulein in human IL-6 gene
transgenic mice. Pancreas. 21:86–92. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rakonczay Z Jr, Hegyi P, Takács T,
McCarroll J and Saluja AK: The role of NF-kappaB activation in the
pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Gut. 57:259–267. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen X, Ji B, Han B, Ernst SA, Simeone D
and Logsdon CD: NF-kappaB activation in pancreas induces pancreatic
and systemic inflammatory response. Gastroenterology. 122:448–457.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|