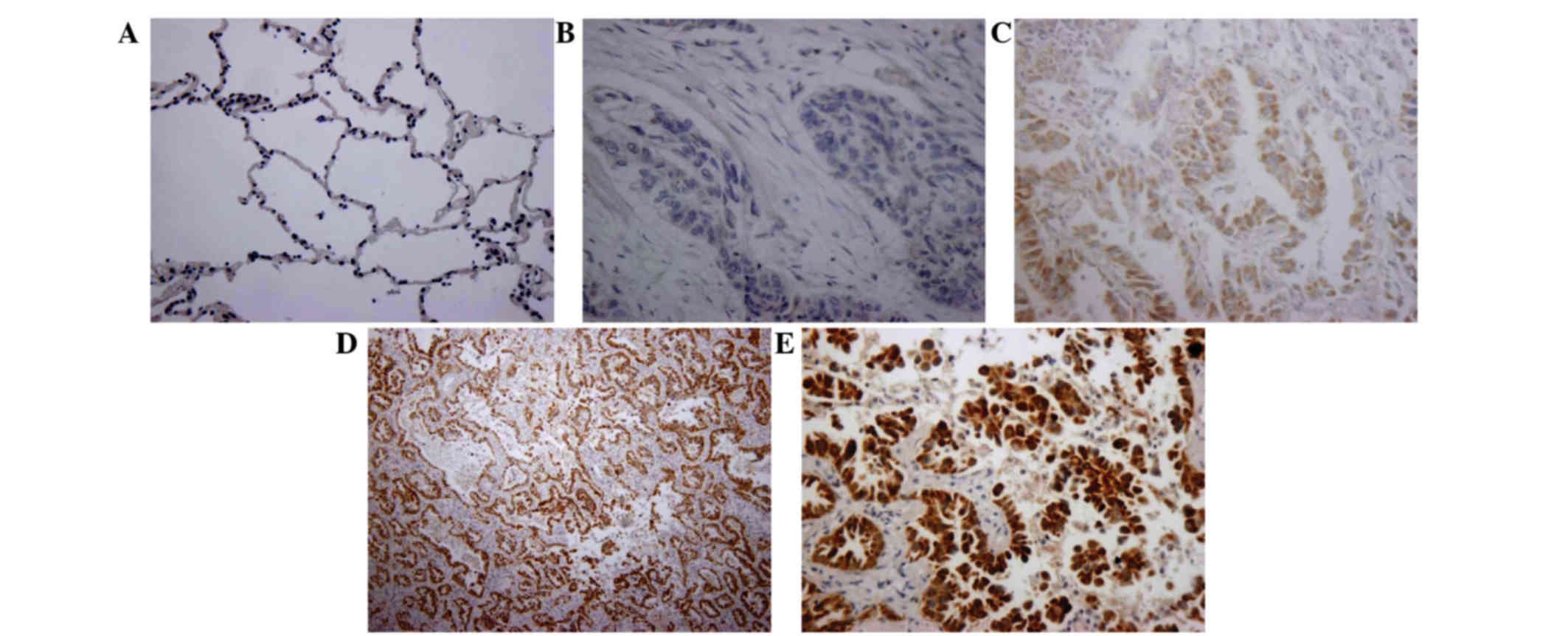
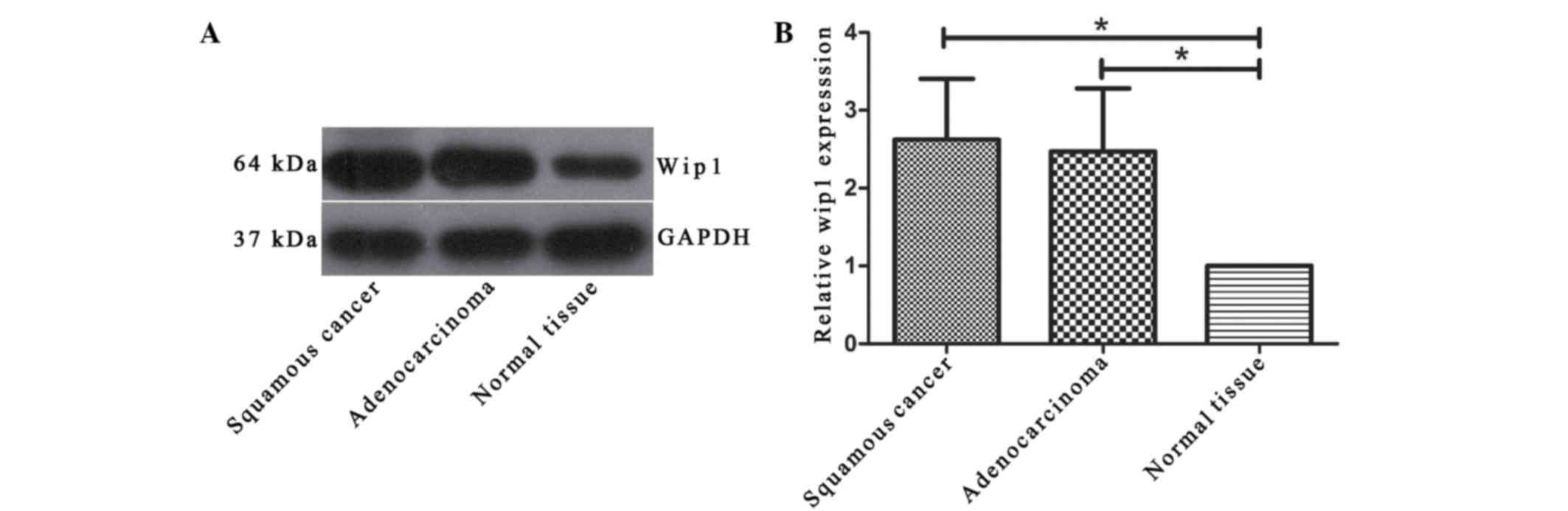
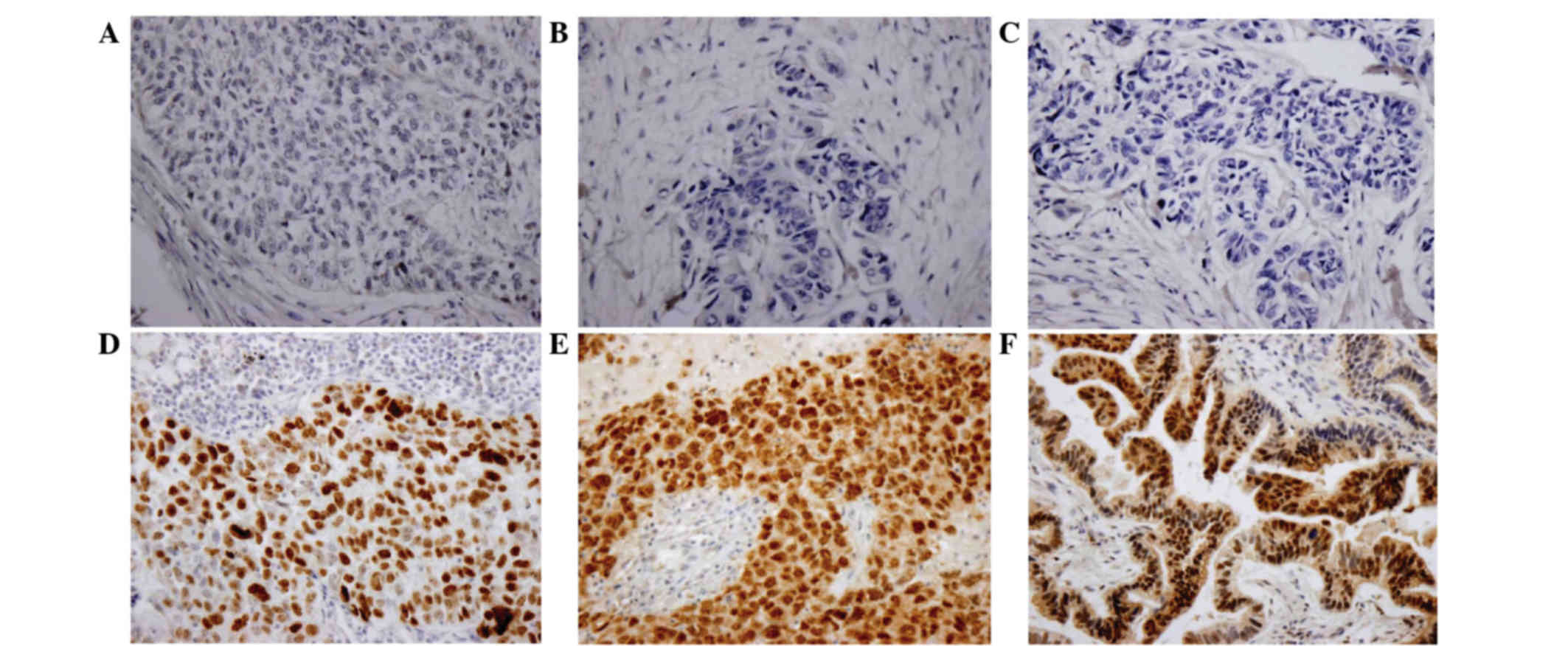
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K,
Shen S, Mercer WE, Van De Woude GF, O'Connor PM and Appella E:
Wip1, a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response
to ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:6048–6053. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Buss MC, Remke M, Lee J, Gandhi K,
Schniederjan MJ, Kool M, Northcott PA, Pfister SM, Taylor MD and
Castellino RC: The WIP1 oncogene promotes progression and invasion
of aggressive medulloblastoma variants. Oncogene. 34:1126–1140.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu S, Qi L, Han W, Wan X, Jiang S, Li Y,
Xie Y, Liu L, Zeng F, Liu Z and Zu X: Overexpression of wip1 is
associated with biologic behavior in human clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e1102182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li ZT, Zhang L, Gao XZ, Jiang XH and Sun
LQ: Expression and significance of the Wip1 proto-oncogene in
colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:1975–1979. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruark E, Snape K, Humburg P, Loveday C,
Bajrami I, Brough R, Rodrigues DN, Renwick A, Seal S, Ramsay E, et
al: Mosaic PPM1D mutations are associated with predisposition to
breast and ovarian cancer. Nature. 493:406–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bulavin DV, Demidov ON, Saito S,
Kauraniemi P, Phillips C, Amundson SA, Ambrosino C, Sauter G,
Nebreda AR, Anderson CW, et al: Amplification of PPM1D in human
tumors abrogates p53 tumor-suppressor activity. Nat Genet.
31:210–215. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dudgeon C, Shreeram S, Tanoue K, Mazur SJ,
Sayadi A, Robinson RC, Appella E and Bulavin DV: Genetic variants
and mutations of PPM1D control the response to DNA damage. Cell
Cycle. 12:2656–2664. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Filipponi D, Muller J, Emelyanov A and
Bulavin DV: Wip1 controls global heterochromatin silencing via
ATM/BRCA1-dependent DNA methylation. Cancer Cell. 24:528–541. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Casanovas O, Miró F, Estanyol JM, Itarte
E, Agell N and Bachs O: Osmotic stress regulates the stability of
cyclin D1 in a p38SAPK2-dependent manner. J Biol Chem.
275:35091–35097. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee JS, Lee MO, Moon BH, Shim SH, Fornace
AJ Jr and Cha HJ: Senescent growth arrest in mesenchymal stem cells
is bypassed by Wip1-mediated downregulation of intrinsic stress
signaling pathways. Stem Cells. 27:1963–1975. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao Q, Guo X, Li X, Xiong W, Li X, Yang
J, Chen P, Zhang W, Yu H, Tang H, et al: Prohibitin is an important
biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and prognosis.
Eur J Cancer Prev. 22:68–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux
DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V and Sobin L:
Internation Association for the Study of Lung Cancer: The IASLC
Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of the TNM
stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM
classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koom WS, Park SY, Kim W, Kim M, Kim JS,
Kim H, Choi IK, Yun CO and Seong J: Combination of radiotherapy and
adenovirus-mediated p53 gene therapy for MDM2-overexpressing
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Radiat Res. 53:202–210. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saito-Ohara F, Imoto I, Inoue J, Hosoi H,
Nakagawara A, Sugimoto T and Inazawa J: PPM1D is a potential target
for 17q gain in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 63:1876–1883.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang DH, He JA, Li J, Ma WF, Hu XH, Xin SJ
and Duan ZQ: Expression of proto-oncogene Wip1 in breast cancer and
its clinical significance. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 90:519–522.
2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sculier JP: Nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur
Respir Rev. 22:33–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tarulli GA, De Silva D, Ho V, Kunasegaran
K, Ghosh K, Tan BC, Bulavin DV and Pietersen AM: Hormone-sensing
cells require Wip1 for paracrine stimulation in normal and
premalignant mammary epithelium. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu H, Liu C, Zhao Z, Gao N, Chen G, Wang Y
and Cui J: Clinical implications of GRHL3 protein expression in
breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:1827–1831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang D, Zhang H, Hu X, Xin S and Duan Z:
Abnormality of pl6/p38MAPK/p53/Wipl pathway in papillary thyroid
cancer. Gland Surg. 1:33–38. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bulavin DV, Phillips C, Nannenga B,
Timofeev O, Donehower LA, Anderson CW, Appella E and Fornace AJ Jr:
Inactivation of the Wip1 phosphatase inhibits mammary tumorigenesis
through p38 MAPK-mediated activation of the p16 (Ink4a)-p19 (Arf)
pathway. Nat Genet. 36:343–350. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|