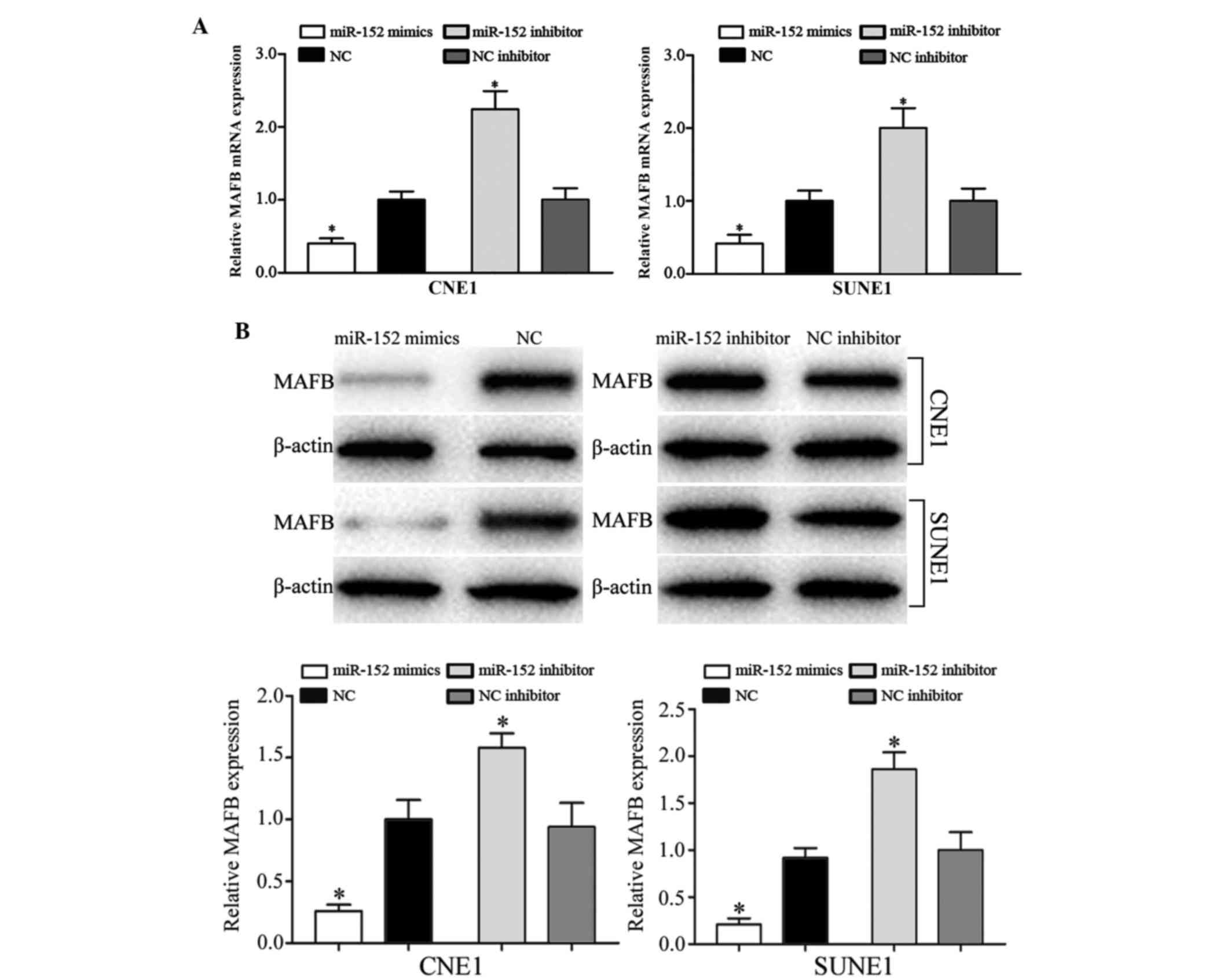
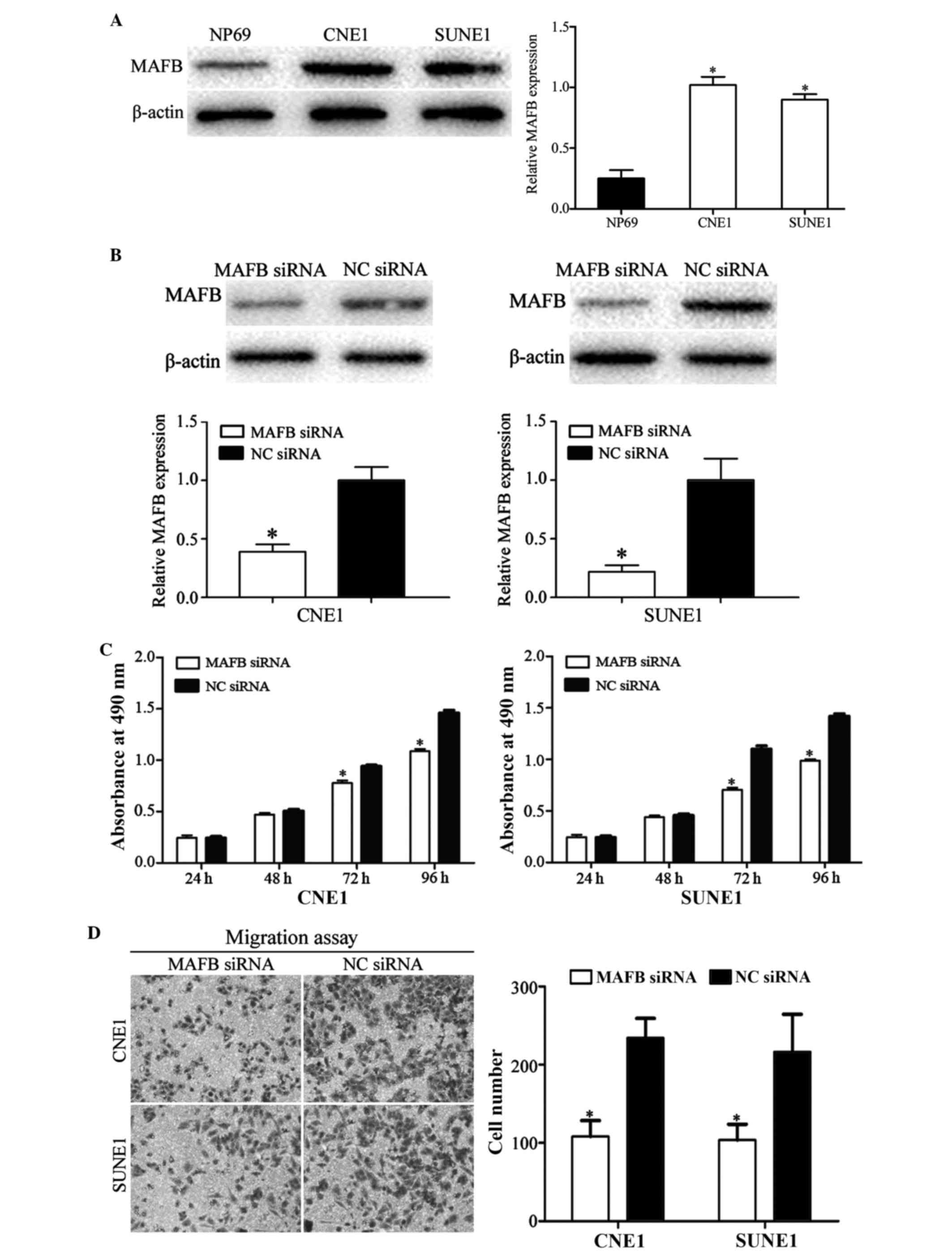
|
1
|
Tao Q and Chan AT: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: Molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic developments.
Expert Rev Mol Med. 9:1–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qiu J, Cosmopoulos K, Pegtel M, Hopmans E,
Murray P, Middeldorp J, Shapiro M and Thorley-Lawson DA: A novel
persistence associated EBV miRNA expression profile is disrupted in
neoplasia. PLoS Pathog. 7:e10021932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan G, Tang X and Tang F: The role of
microRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:69–79. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McDermott AL, Dutt SN and Watkinson JC:
The aetiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Otolaryngol Allied
Sci. 26:82–92. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Su SF, Han F, Zhao C, Huang Y, Chen CY,
Xiao WW, Li JX and Lu TX: Treatment outcomes for different
subgroups of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with
intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Chin J Cancer. 30:565–573.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee AW, Foo W, Law SC, Peters LJ, Poon YF,
Chappell R, Sze WM, Tung SY, Lau WH and Ho JH: Total biological
effect on late reactive tissues following reirradiation for
recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
46:865–872. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hui EP, Leung SF, Au JS, Zee B, Tung S,
Chua D, Sze WM, Law CK, Leung TW and Chan AT: Lung metastasis alone
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A relatively favorable prognostic
group. A study by the Hong Kong nasopharyngeal carcinoma study
group. Cancer. 101:300–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wright CM, Dan T, Dicker AP and Simone NL:
microRNAs: The short link between cancer and RT-induced DNA damage
response. Front Oncol. 4:1332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He J, Tang Y and Tian Y: MicroRNA-214
promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis via targeting Bax in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:6286–6292.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen JJ, Liu SX, Chen MZ and Zhao ZY:
Has-miR-125a and 125b are induced by treatment with cisplatin in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibit apoptosis in a p53-dependent
manner by targeting p53 mRNA. Mol Med Rep. 12:3569–3574.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma J, Yao Y, Wang P, Liu Y, Zhao L, Li Z,
Li Z and Xue Y: MiR-152 functions as a tumor suppressor in
glioblastoma stem cells by targeting Kruppel-like factor 4. Cancer
Lett. 355:85–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Allaya N, Khabir A, Sallemi-Boudawara T,
Sellami N, Daoud J, Ghorbel A, Frikha M, Gargouri A,
Mokdad-Gargouri R and Ayadi W: Over-expression of miR-10b in NPC
patients: Correlation with LMP1 and Twist1. Tumour Biol.
36:3807–3814. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su Y, Wang Y, Zhou H, Lei L and Xu L:
MicroRNA-152 targets ADAM17 to suppress NSCLC progression. FEBS
Lett. 588:1983–1988. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsuruta T, Kozaki K, Uesugi A, Furuta M,
Hirasawa A, Imoto I, Susumu N, Aoki D and Inazawa J: miR-152 is a
tumor suppressor microRNA that is silenced by DNA hypermethylation
in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 71:6450–6462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li L, Chen YY, Li SQ, Huang C and Qin YZ:
Expression of miR-148/152 family as potential biomarkers in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Sci Monit. 21:1155–1161. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhai R, Kan X, Wang B, Du H, Long Y, Wu H,
Tao K, Wang G, Bao L, Li F and Zhang W: miR-152 suppresses gastric
cancer cell proliferation and motility by targeting CD151. Tumour
Biol. 35:11367–11373. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dang YW, Zeng J, He RQ, Rong MH, Luo DZ
and Chen G: Effects of miR-152 on cell growth inhibition, motility
suppression and apoptosis induction in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:4969–4976. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu C, Li J, Ding Q, Cheng G, Zhou H, Tao
L, Cai H, Li P, Cao Q, Ju X, et al: miR-152 controls migration and
invasive potential by targeting TGFα in prostate cancer cell lines.
Prostate. 73:1082–1089. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou X, Zhao F, Wang ZN, Song YX, Chang H,
Chiang Y and Xu HM: Altered expression of miR-152 and miR-148a in
ovarian cancer is related to cell proliferation. Oncol Rep.
27:447–454. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang JS, Li BJ, Lu HW, Chen Y, Lu C, Zhu
RX, Liu SH, Yi QT, Li J and Song CH: Serum miR-152, miR-148a,
miR-148b, and miR-21 as novel biomarkers in non-small cell lung
cancer screening. Tumour Biol. 36:3035–3042. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng Z, Ma R, Tan W and Zhang L: MiR-152
suppresses the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells by
inhibiting FGF2. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng X, Chopp M, Lu Y, Buller B and Jiang
F: MiR-15b and miR-152 reduce glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis
via NRP-2 and MMP-3. Cancer Lett. 329:146–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nishizawa M, Kataoka K and Vogt PK: MafA
has strong cell transforming ability but is a weak transactivator.
Oncogene. 22:7882–7890. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Blank V and Andrews NC: The Maf
transcription factors: Regulators of differentiation. Trends
Biochem Sci. 22:437–441. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ring BZ, Cordes SP, Overbeek PA and Barsh
GS: Regulation of mouse lens fiber cell development and
differentiation by the Maf gene. Development. 127:307–317.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Motohashi H, Shavit JA, Igarashi K,
Yamamoto M and Engel JD: The world according to Maf. Nucleic Acids
Res. 25:2953–2959. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zanocco-Marani T, Vignudelli T, Parenti S,
Gemelli C, Condorelli F, Martello A, Selmi T, Grande A and Ferrari
S: TFE3 transcription factor regulates the expression of MAFB
during macrophage differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 315:1798–1808.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eychene A, Rocques N and Pouponnot C: A
new MAFia in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:683–693. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|