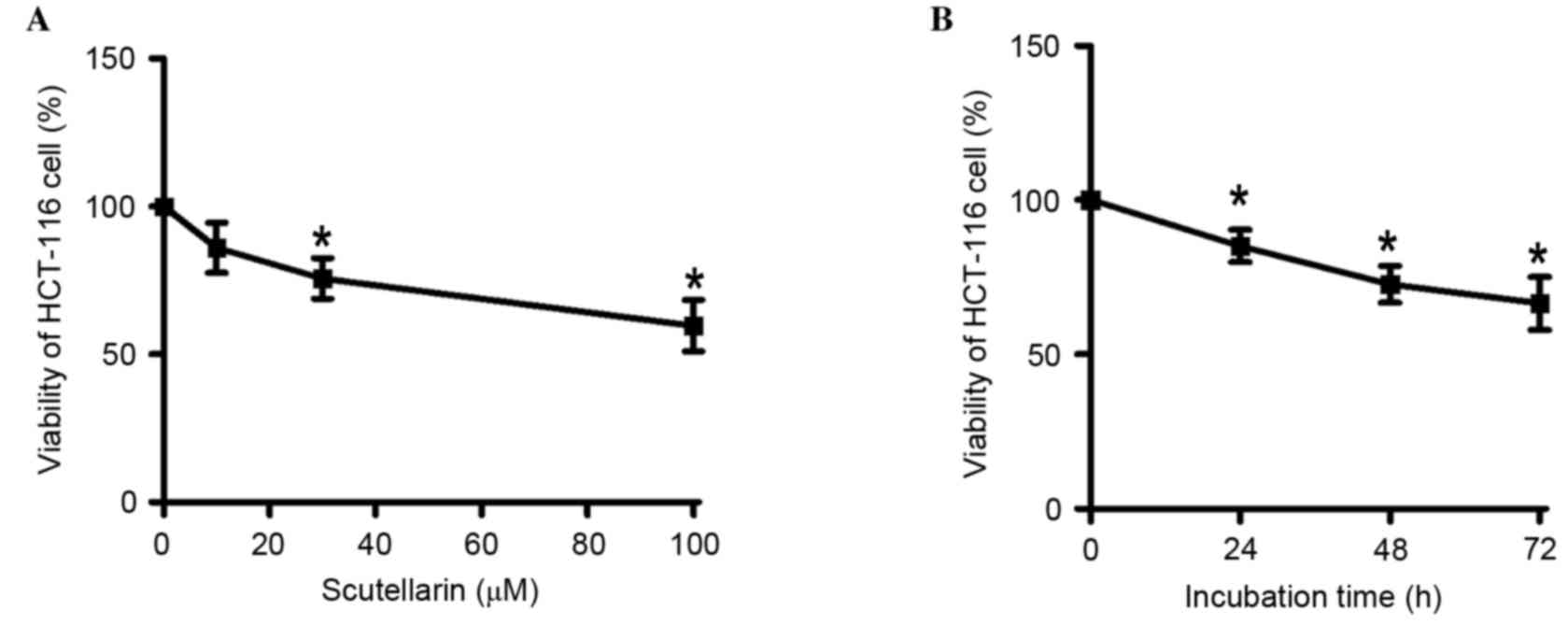
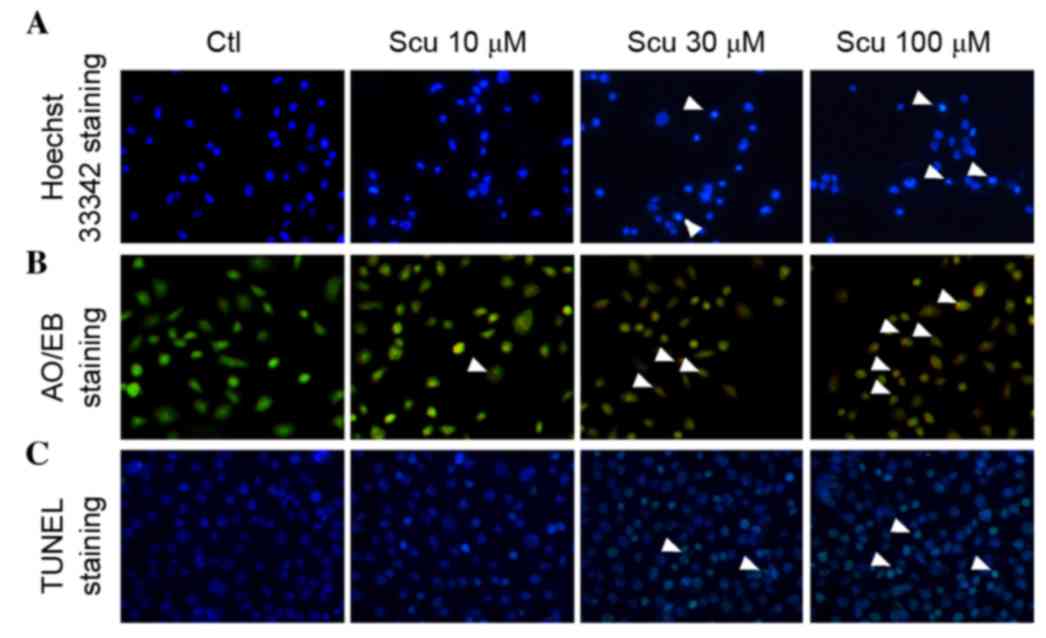
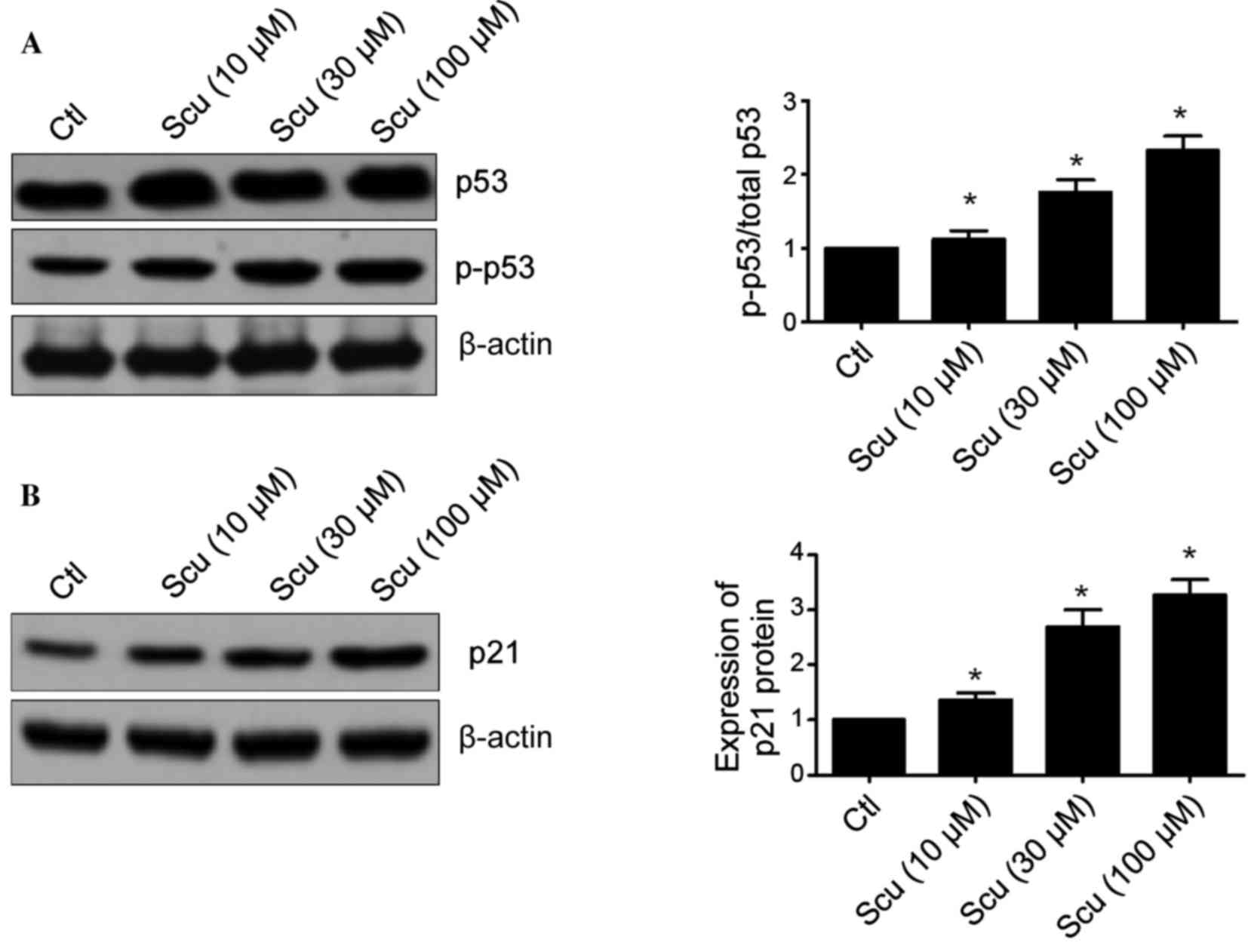
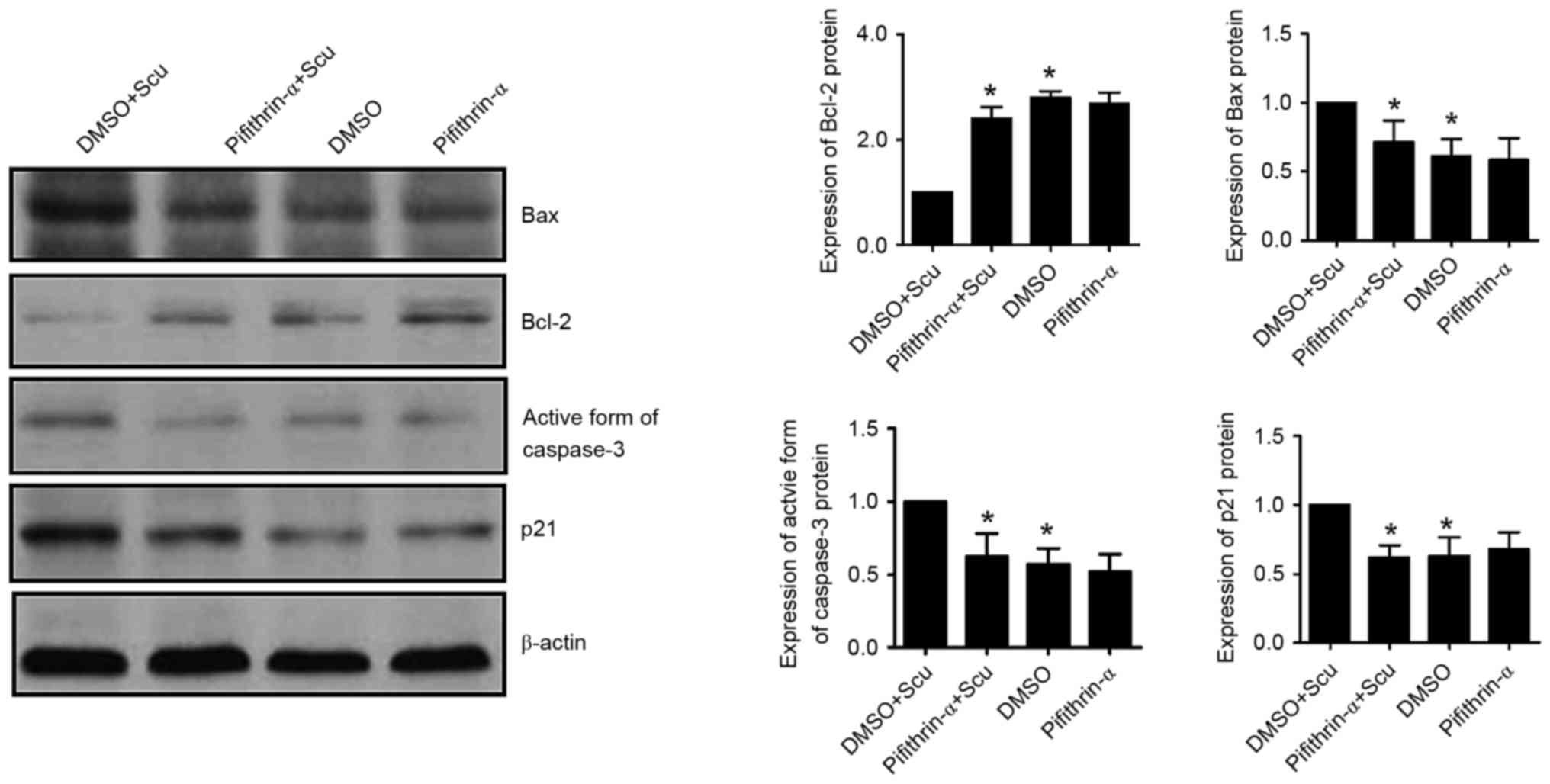
|
1
|
Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, Fuchs
CS, Ramanathan RK, Williamson SK, Findlay BP, Pitot HC and Alberts
SR: A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin,
irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with
previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
22:23–30. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sadahiro S, Suzuki T, Ishikawa K, Nakamura
T, Tanaka Y, Masuda T, Mukoyama S, Yasuda S, Tajima T, Makuuchi H
and Murayama C: Recurrence patterns after curative resection of
colorectal cancer in patients followed for a minimum of ten years.
Hepatogastroenterology. 50:1362–1366. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim DI, Lee TK, Lim IS, Kim H, Lee YC and
Kim CH: Regulation of IGF-I production and proliferation of human
leiomyomal smooth muscle cells by Scutellaria barbata D. Don in
vitro: Isolation of flavonoids of apigenin and luteolin as acting
compounds. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 205:213–224. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dai ZJ, Wang XJ, Li ZF, Ji ZZ, Ren HT,
Tang W, Liu XX, Kang HF, Guan HT and Song LQ: Scutellaria barbate
extract induces apoptosis of hepatoma H22 cells via the
mitochondrial pathway involving caspase-3. World J Gastroenterol.
14:7321–7328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hong H and Liu GQ: Protection against
hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by
scutellarin. Life Sci. 74:2959–2973. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang GH, Wang Q, Chen JJ, Zhang XM, Tam
SC and Zheng YT: The anti-HIV-1 effect of scutellarin. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 334:812–816. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pan Z, Zhao W, Zhang X, Wang B, Wang J,
Sun X, Liu X, Feng S, Yang B and Lu Y: Scutellarin alleviates
interstitial fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction of infarct rats by
inhibiting TGFβ1 expression and activation of p38-MAPK and ERK1/2.
Br J Pharmacol. 162:688–700. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li H, Huang D, Gao Z, Lv Y, Zhang L, Cui H
and Zheng J: Scutellarin inhibits cell migration by regulating
production of αvβ6 integrin and E-cadherin in human tongue cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 24:1153–1160. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chan JY, Tan BK and Lee SC: Scutellarin
sensitizes drug-evoked colon cancer cell apoptosis through enhanced
caspase-6 activation. Anticancer Res. 29:3043–3047. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Korsmeyer SJ: BCL-2 gene family and the
regulation of programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 59 Suppl
7:1693S–1700S. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M,
Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC: Tumor
suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harris SL and Levine AJ: The p53 pathway:
Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Müller M, Wilder S, Bannasch D, Israeli D,
Lehlbach K, Li-Weber M, Friedman SL, Galle PR, Stremmel W, Oren M
and Krammer PH: p53 activates the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) gene in response
to DNA damage by anticancer drugs. J Exp Med. 188:2033–2045. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boyle P and Ferlay J: Cancer incidence and
mortality in Europe, 2004. Ann Oncol. 16:481–488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schrag D, Cramer LD, Bach PB and Begg CB:
Age and adjuvant chemotherapy use after surgery for stage III colon
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:850–857. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng Y, Zhang S, Tu J, Cao Z, Pan Y, Shang
B, Liu R, Bao M, Guo P and Zhou Q: Novel function of scutellarin in
inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing cell apoptosis of human
Burkitt lymphoma Namalwa cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 53:2456–2464. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li H, Fan H, Wang Z, Zheng J and Cao W:
Potentiation of scutellarin on human tongue carcinoma xenograft by
low-intensity ultrasound. PLoS One. 8:e594732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ling YH, Liebes L, Jiang JD, Holland JF,
Elliott PJ, Adams J, Muggia FM and Perez-Soler R: Mechanisms of
proteasome inhibitor PS-341-induced G(2)-M-phase arrest and
apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:1145–1154. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barlev NA, Liu L, Chehab NH, Mansfield K,
Harris KG, Halazonetis TD and Berger SL: Acetylation of p53
activates transcription through recruitment of coactivators/histone
acetyltransferases. Mol Cell. 8:1243–1254. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin XM, Oltvai ZN, Veis-Novack DJ, Linette
GP and Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 gene family and the regulation of
programmed cell death. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol.
59:387–393. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Swanton E, Savory P, Cosulich S, Clarke P
and Woodman P: Bcl-2 regulates a caspase-3/caspase-2 apoptotic
cascade in cytosolic extracts. Oncogene. 18:1781–1787. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Drygin D, O'Brien SE, Hannan RD, McArthur
GA and Von Hoff DD: Targeting the nucleolus for cancer-specific
activation of p53. Drug Discov Today. 19:259–265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|