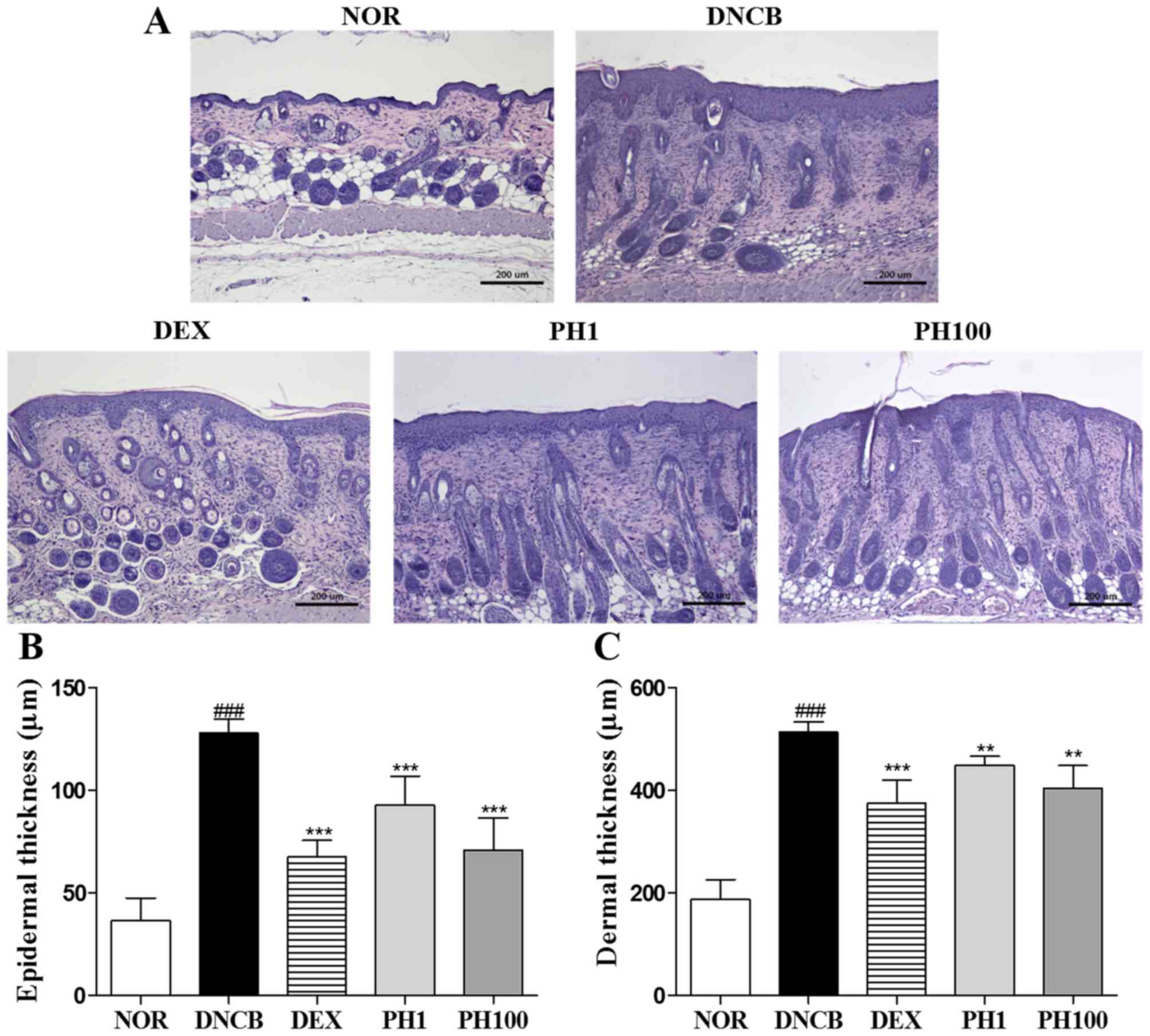
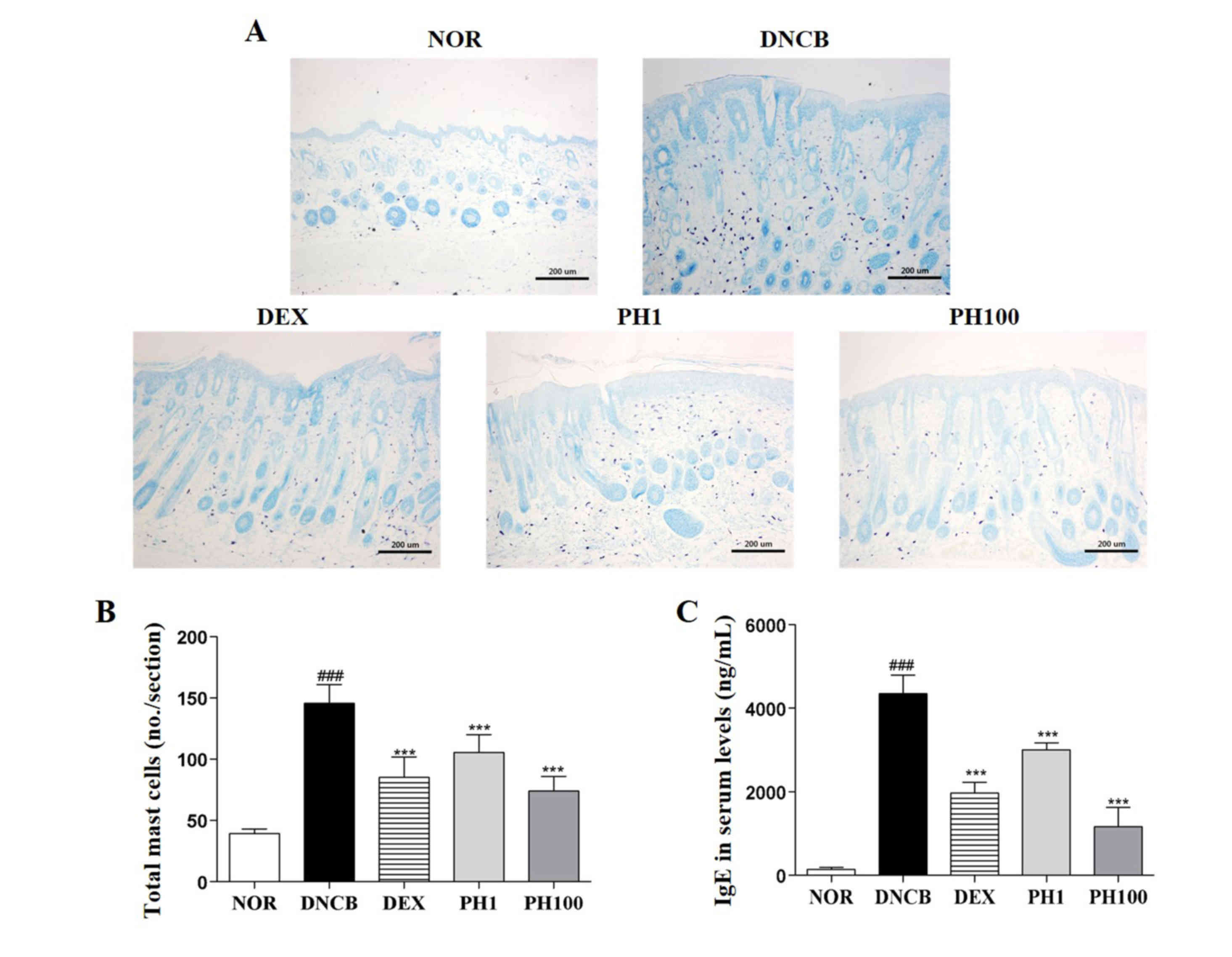
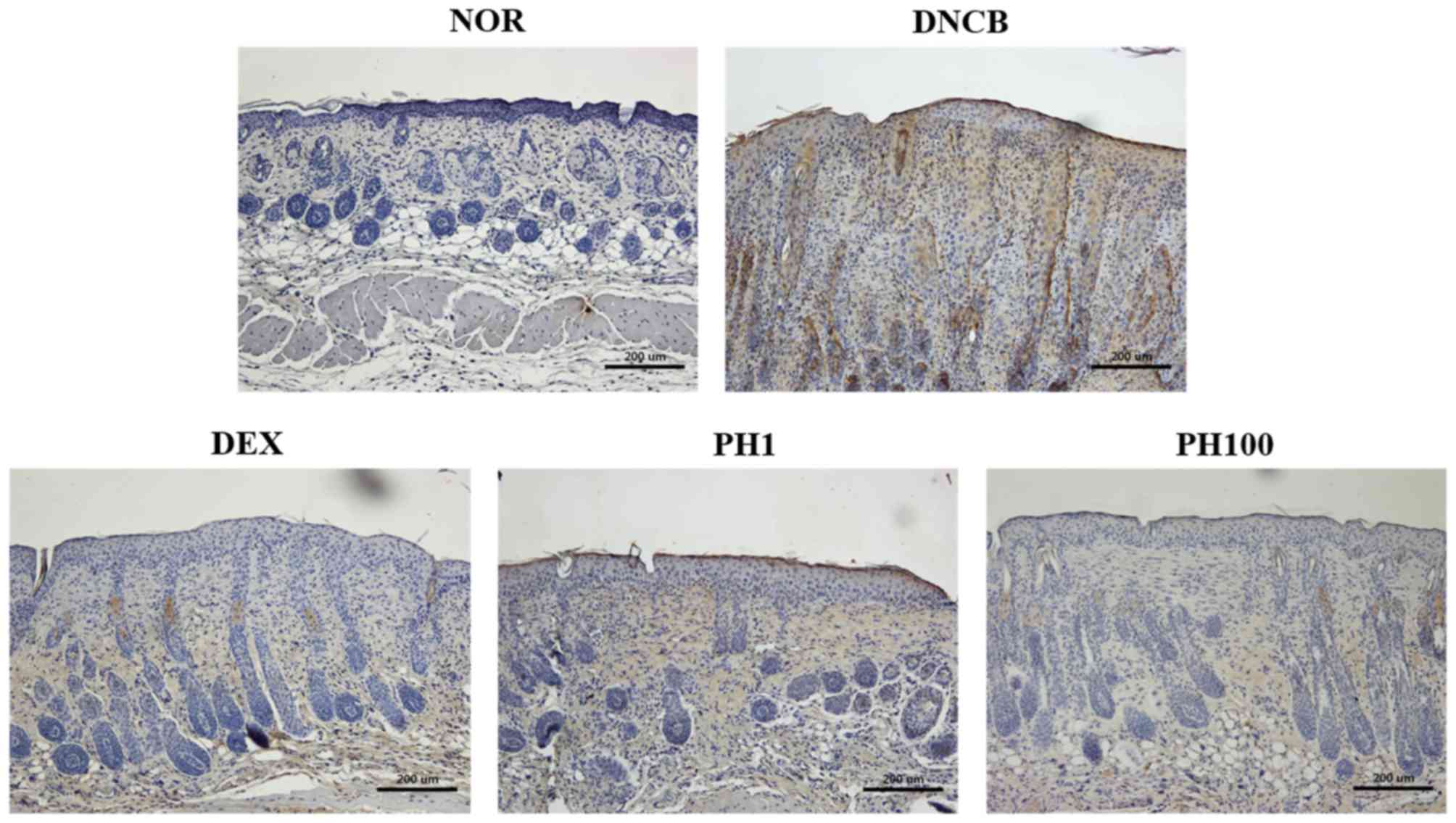
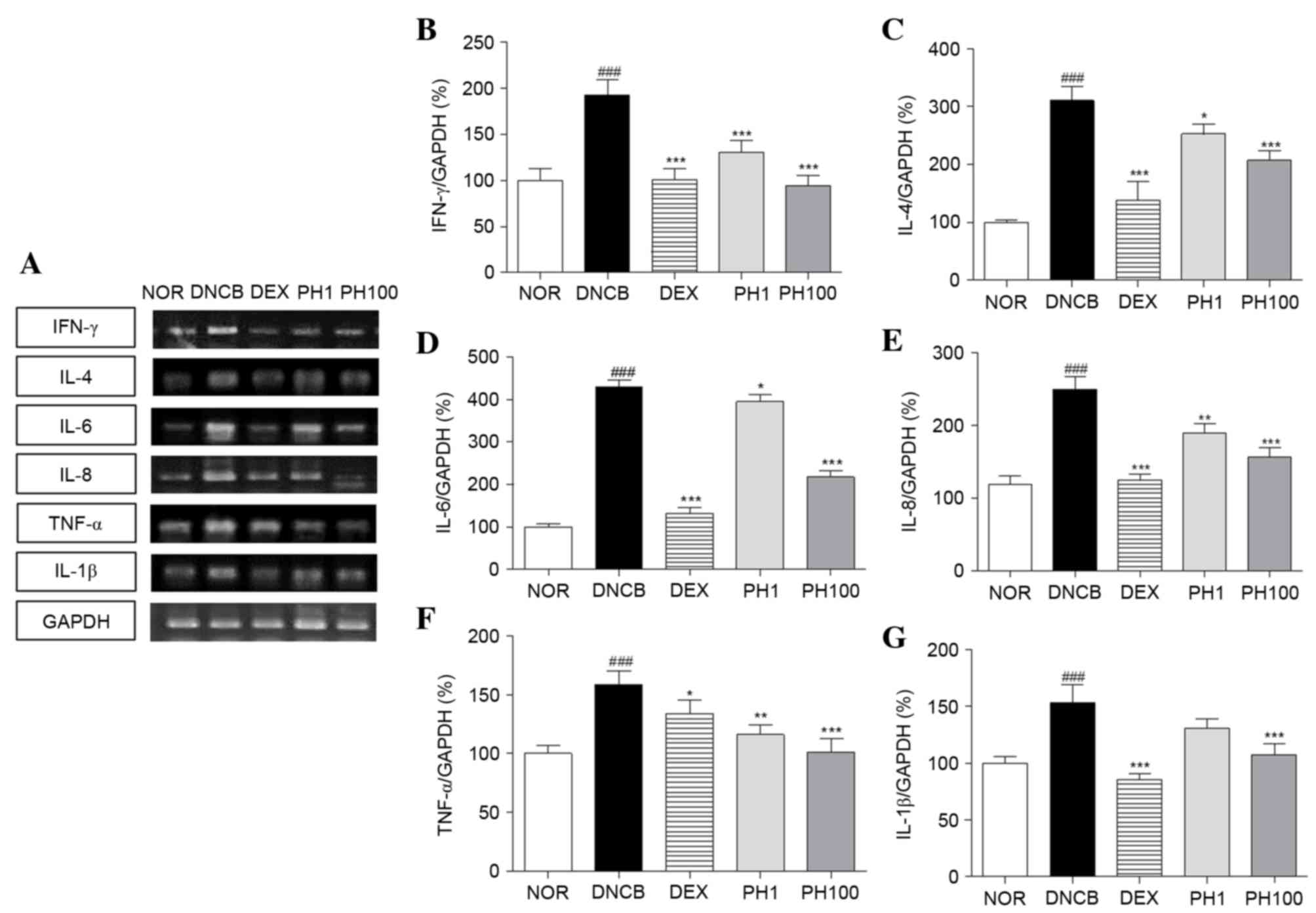
|
1
|
Levy ML: Atopic dermatitis: Understanding
the disease and its management. Curr Med Res Opin. 23:3091–3103.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Minnicozzi M, Sawyer RT and Fenton MJ:
Innate immunity in allergic disease. Immunol Rev. 242:106–127.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mosmann TR and Coffman RL: Th1 and th2
cells: Different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different
functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 7:145–173. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leung DY, Boguniewicz M, Howell MD, Nomura
I and Hamid QA: New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest.
113:651–657. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakamura K: Pathogenesis and treatment of
allergic skin disease-atopic dermatitis. Arerugi. 64:703–706.
2015.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu J, Pei M, Zheng C, Li Y, Wang Y, Lu A
and Yang L: A systems-pharmacology analysis of herbal medicines
used in health improvement treatment: Predicting potential new
drugs and targets. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:9387642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ng TB, Liu F and Wang HX: The antioxidant
effects of aqueous and organic extracts of panax quinquefolium,
panax notoginseng, codonopsis pilosula, pseudostellaria
heterophylla and glehnia littoralis. J Ethnopharmacol. 93:285–288.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pang W, Lin S, Dai Q, Zhang H and Hu J:
Antitussive activity of pseudostellaria heterophylla (miq.) pax
extracts and improvement in lung function via adjustment of
multi-cytokine levels. Molecules. 16:3360–3370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li X, Chen Y, Lai Y, Yang Q, Hu H and Wang
Y: Sustainable utilization of traditional chinese medicine
resources: Systematic evaluation on different production modes.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:2189012015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y and Yang XW: Studies on chemical
constituents of root tuber of cultivated pseudostellaria
heterophylla (Zheshen No1). Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
33:2353–2355. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wong CK, Leung KN, Fung MC, Fung KP and
Choy YM: The induction of cytokine gene expression in murine
peritoneal macrophages by pseudostellaria heterophylla.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 16:347–357. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choi YY, Kim MH, Hong J, Kim K and Yang
WM: Effect of Dangguibohyul-Tang, a mixed extract of astragalus
membranaceus and angelica sinensis, on allergic and inflammatory
skin reaction compared with single extracts of astragalus
membranaceus or angelica sinensis. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2016:59363542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shin HS, See HJ, Jung SY, Choi DW, Kwon
DA, Bae MJ, Sung KS and Shon DH: Turmeric (curcuma longa)
attenuates food allergy symptoms by regulating type 1/type 2 helper
t cells (th1/th2) balance in a mouse model of food allergy. J
Ethnopharmacol. 175:21–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang H, Lee CH, Kim JR, Kwon JY, Seo SG,
Han JG, Kim BG, Kim JE and Lee KW: Chlorella vulgaris attenuates
dermatophagoides farinae-induced atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in
nc/nga mice. Int J Mol Sci. 16:21021–21034. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park S, Kim da S, Kang S and Shin BK:
Synergistic topical application of salt-processed phellodendron
amurense and sanguisorba officinalis linne alleviates atopic
dermatitis symptoms by reducing levels of immunoglobulin e and
pro-inflammatory cytokines in nc/nga mice. Mol Med Rep.
12:7657–7664. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vocanson M, Hennino A, Chavagnac C,
Saint-Mezard P, Dubois B, Kaiserlian D and Nicolas JF: Contribution
of cd4(+)and cd8(+) T-cells in contact hypersensitivity and
allergic contact dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 1:75–86.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang EY, Chen AY and Zhu BT: Mechanism of
dinitrochlorobenzene-induced dermatitis in mice: Role of specific
antibodies in pathogenesis. PLoS One. 4:e77032009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee HS, Kim SK, Han JB, Choi HM, Park JH,
Kim EC, Choi MS, An HJ, Um JY, Kim HM and Min BI: Inhibitory
effects of Rumex japonicus Houtt. On the development of atopic
dermatitis-like skin lesions in Nc/Nga mice. Br J Dermatol.
155:33–38. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen L, Martinez O, Overbergh L, Mathieu
C, Prabhakar BS and Chan LS: Early up-regulation of Th2 cytokines
and late surge of Th1 cytokines in an atopic dermatitis model. Clin
Exp Immunol. 138:375–387. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee HJ, Lee HP, Ha SJ, Byun DG and Kim JW:
Spontaneous expression of mrna for iL-10, GM-CSF, TGF-beta,
TGF-alpha, and IL-6 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from
atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 84:553–558. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szegedi K, Lutter R, Res PC, Bos JD,
Luiten RM, Kezic S and Middelkamp-Hup MA: Cytokine profiles in
interstitial fluid from chronic atopic dermatitis skin. J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. 29:2136–2144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li W, Zhao Y, Xu X, Ma W, Gao P, Wang Y,
Liang K and Li R: Rebamipide suppresses TNF-α mediated inflammation
in vitro and attenuates the severity of dermatitis in mice. FEBS J.
282:2317–2326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee J, Choi YY, Kim MH, Han JM, Lee JE,
Kim EH, Hong J, Kim J and Yang WM: Topical application of angelica
sinensis improves pruritus and skin inflammation in mice with
atopic dermatitis-like symptoms. J Med Food. 19:98–105. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mishra S, Tripathi A, Chaudhari BP,
Dwivedi PD, Pandey HP and Das M: Deoxynivalenol induced mouse skin
cell proliferation and inflammation via MAPK pathway. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 279:186–197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|