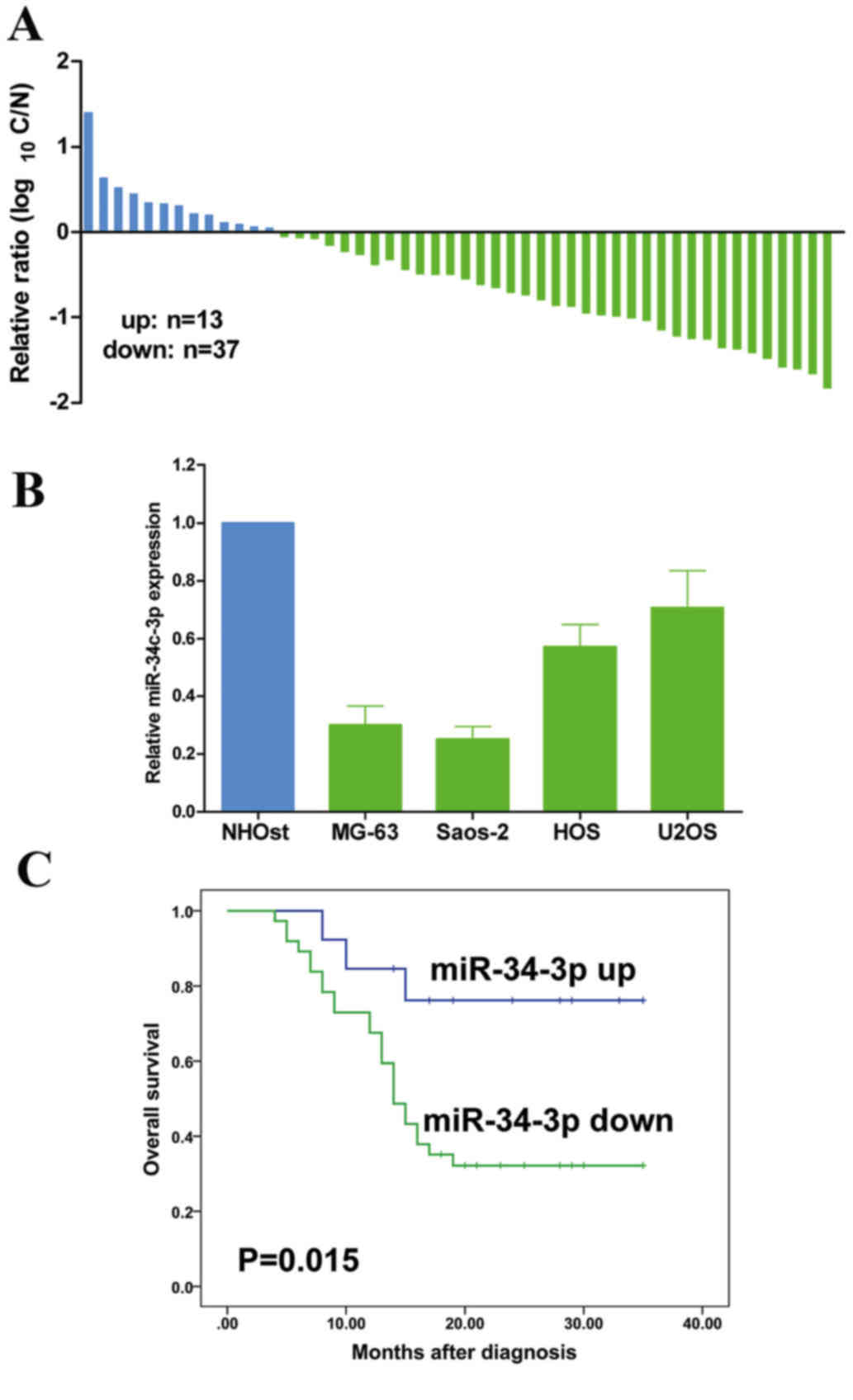
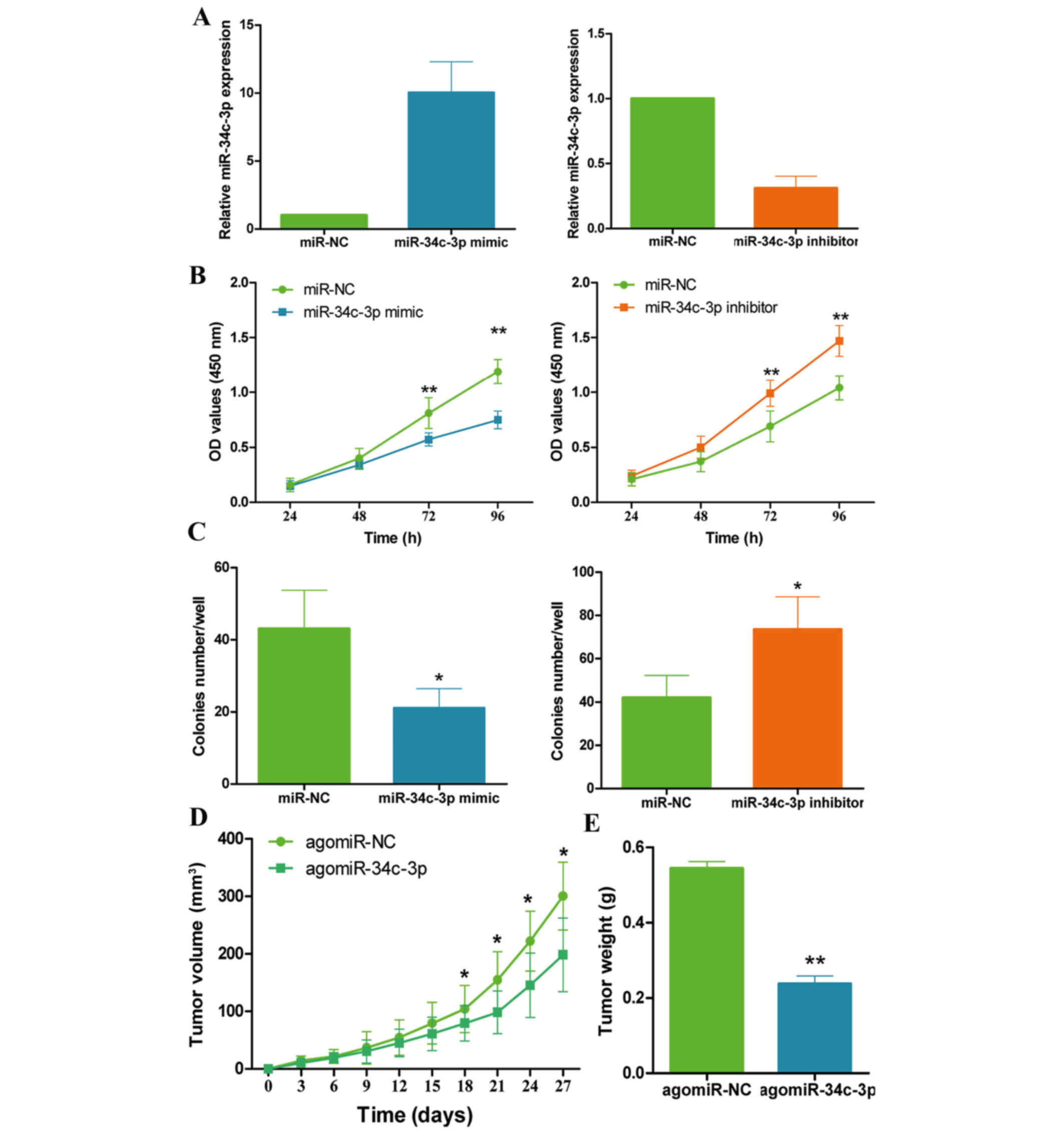
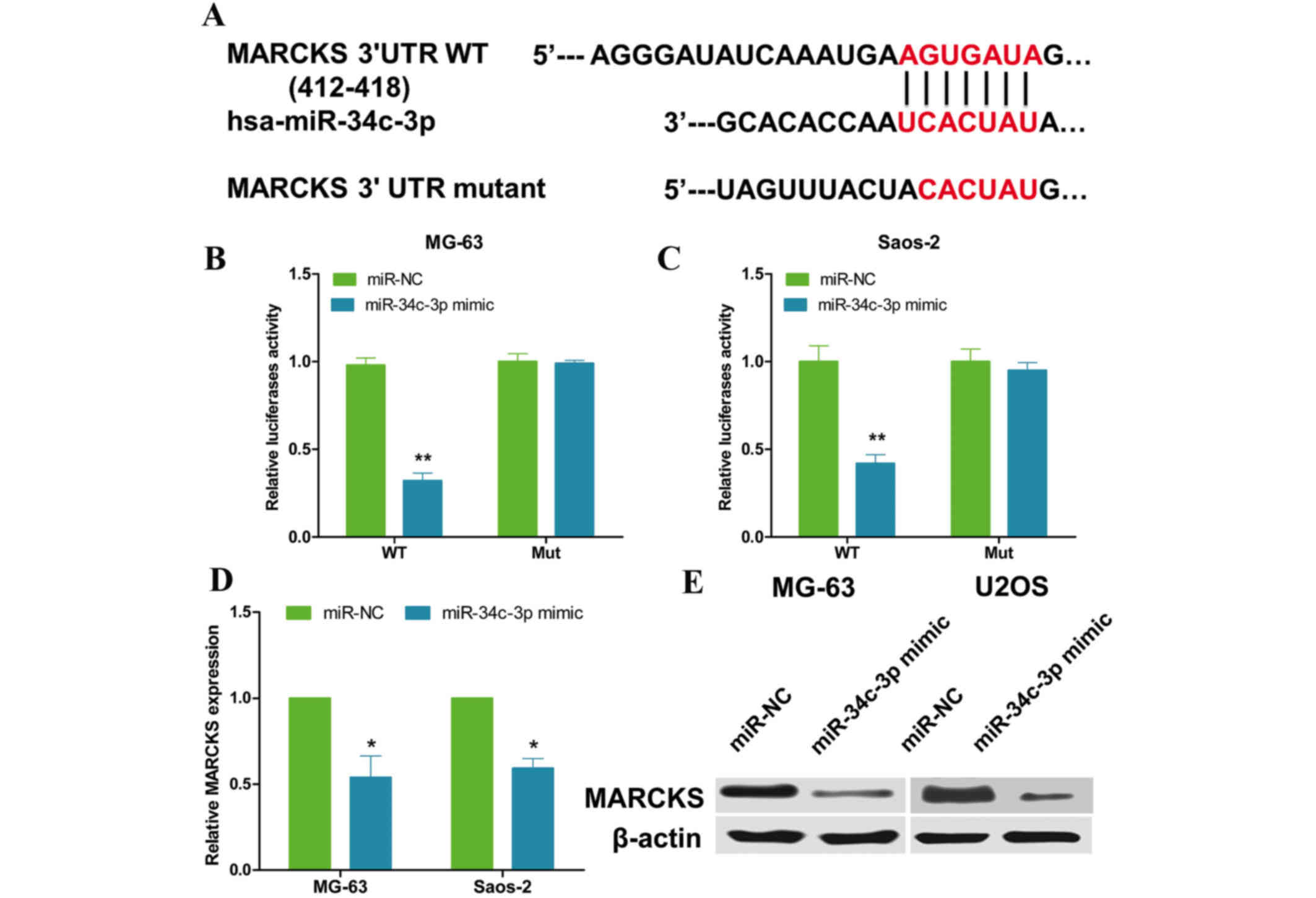
|
1
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Benjamin RS: Osteosarcoma: Better
treatment through better trial design. Lancet Oncol. 16:12–13.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li F, Li S and Cheng T: TGF-β1 promotes
osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion through the
miR-143-versican pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:2169–2179. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Berindan-Neagoe I, Pdel Monroig C,
Pasculli B and Calin GA: MicroRNAome genome: A treasure for cancer
diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:311–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou YL, Xu YJ and Qiao CW: MiR-34c-3p
suppresses the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) by inhibiting PAC1/MAPK pathway. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6312–6322. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu F, Wang X, Li J, Gu K, Lv L, Zhang S,
Che D, Cao J, Jin S and Yu Y: miR-34c-3p functions as a tumour
suppressor by inhibiting eIF4E expression in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cell Prolif. 48:582–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lopez JA and Alvarez-Salas LM:
Differential effects of miR-34c-3p and miR-34c-5p on SiHa cells
proliferation apoptosis, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 409:513–519. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Z, Wu Y, Tian Y, Sun X, Liu J, Ren H,
Liang C, Song L, Hu H, Wang L and Jiao B: Differential effects of
miR-34c-3p and miR-34c-5p on the proliferation, apoptosis and
invasion of glioma cells. Oncol Lett. 6:1447–1452. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang C, Chen H, Shao L and Wang Q:
MicroRNA-1 functions as a potential tumor suppressor in
osteosarcoma by targeting Med1 and Med31. Oncol Rep. 32:1249–1256.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Swierczynski SL and Blackshear PJ:
Membrane association of the myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase
substrate (MARCKS) protein. Mutational analysis provides evidence
for complex interactions. J Biol Chem. 270:13436–13445. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yarmola EG, Edison AS, Lenox RH and Bubb
MR: Actin filament cross-linking by MARCKS: Characterization of two
actin-binding sites within the phosphorylation site domain. J Biol
Chem. 276:22351–22358. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arbuzova A, Schmitz AA and Vergéres G:
Cross-talk unfolded: MARCKS proteins. Biochem J. 362:1–12. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rombouts K, Lottini B, Caligiuri A, Liotta
F, Mello T, Carloni V, Marra F and Pinzani M: MARCKS is a
downstream effector in platelet-derived growth factor-induced cell
motility in activated human hepatic stellate cells. Exp Cell Res.
314:1444–1454. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Masaki T, Tokuda M, Yoshida S, Nakai S,
Morishita A, Uchida N, Funaki T, Kita Y, Funakoshi F, Nonomura T,
et al: Comparison study of the expressions of myristoylated
alanine-rich C kinase substrate in hepatocellular carcinoma, liver
cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, and normal liver. Int J Oncol.
26:661–671. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stensman H and Larsson C: Protein kinase
Cepsilon is important for migration of neuroblastoma cells. BMC
cancer. 8:3652008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen CH, Cheng CT, Yuan Y, Zhai J, Arif M,
Fong LW, Wu R and Ann DK: Elevated MARCKS phosphorylation
contributes to unresponsiveness of breast cancer to paclitaxel
treatment. Oncotarget. 6:15194–15208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|