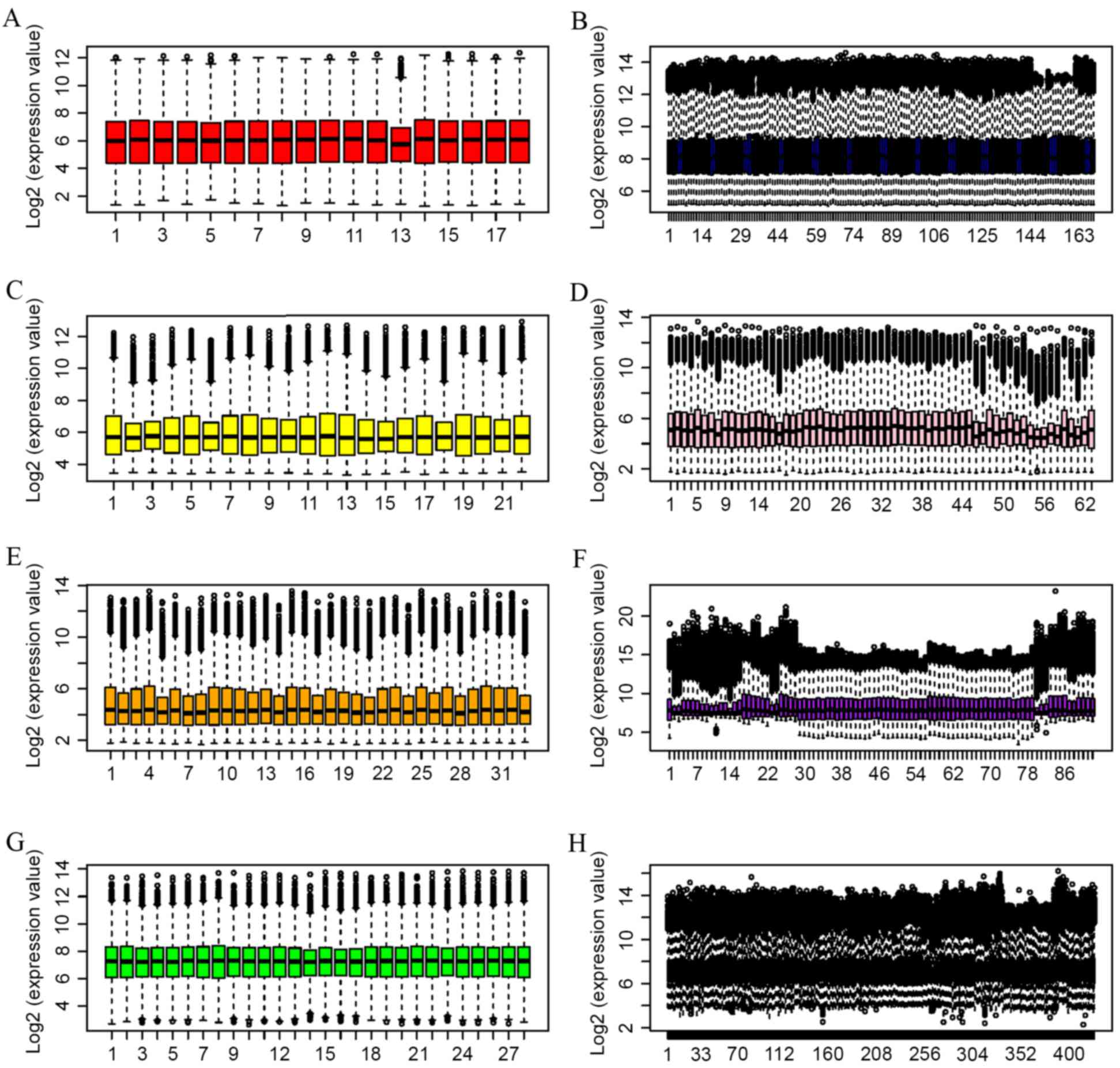
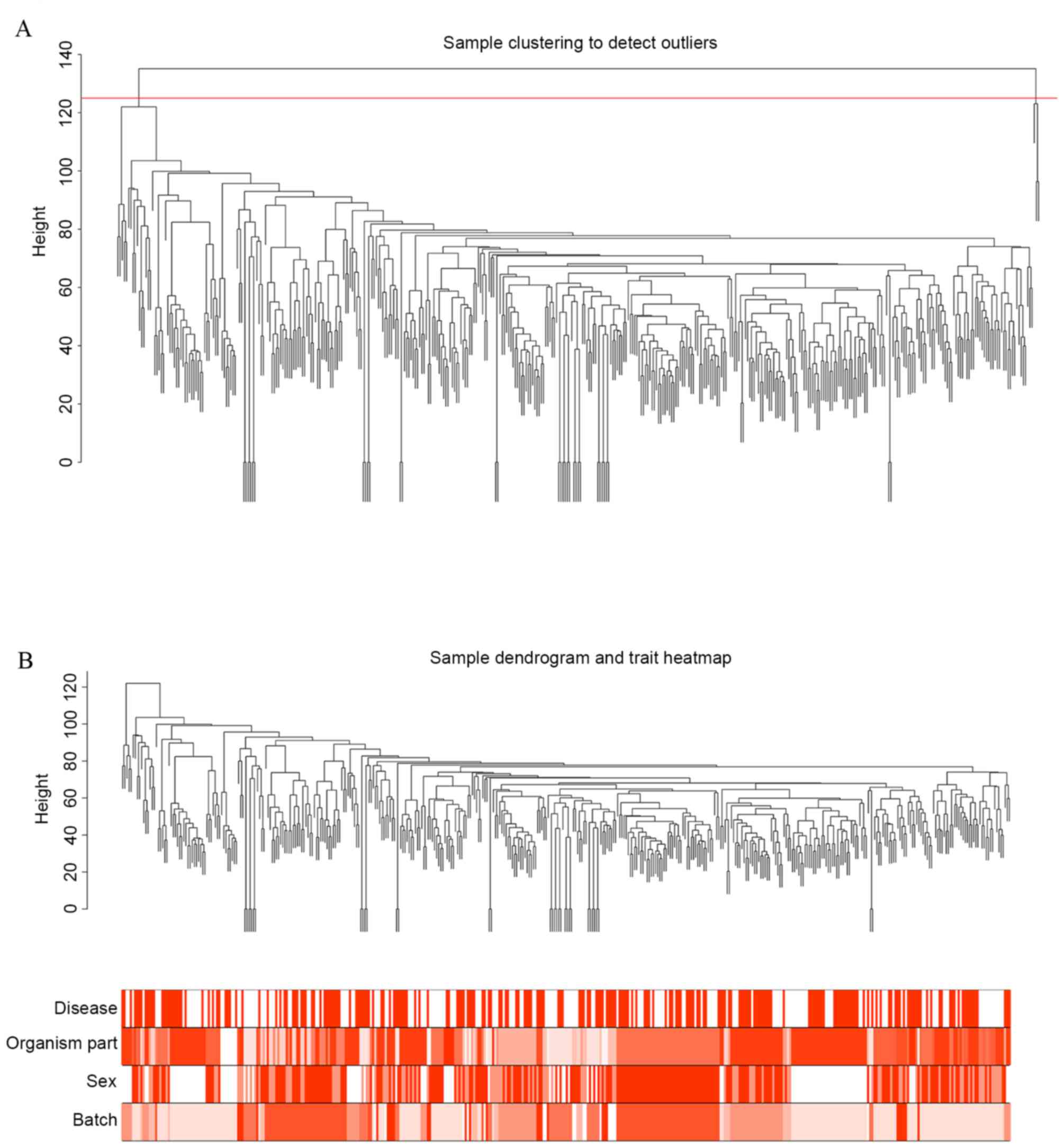
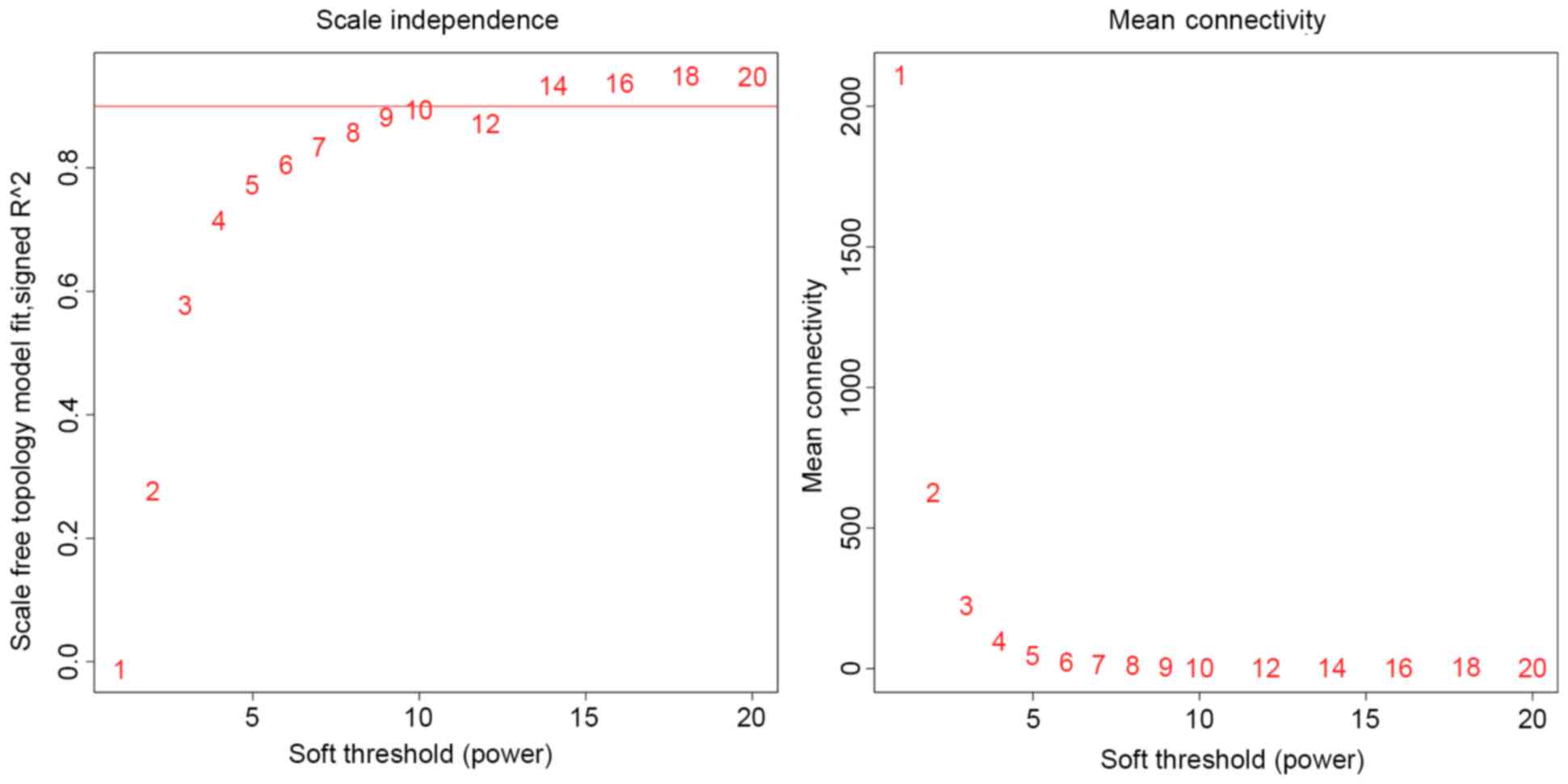
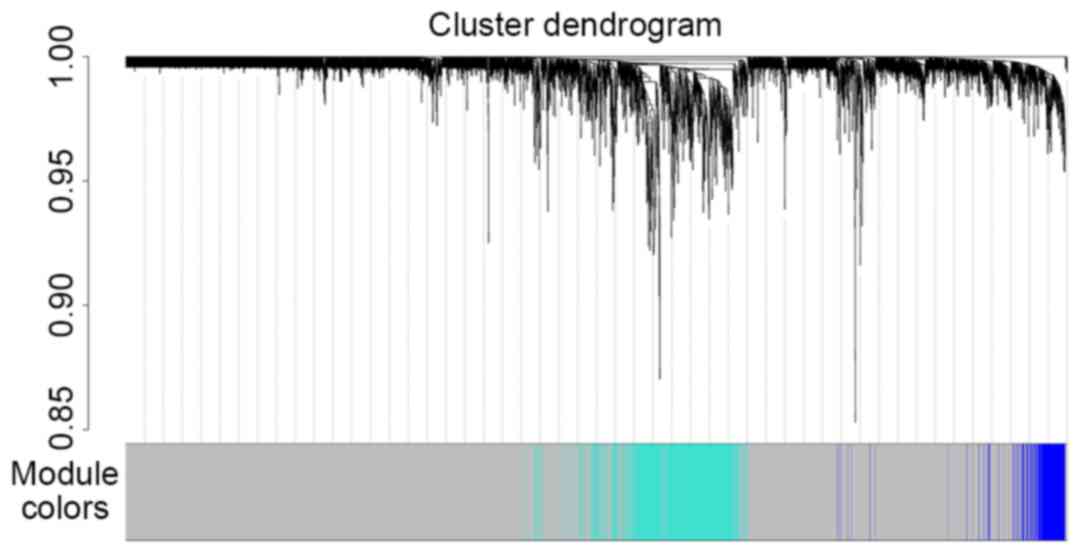
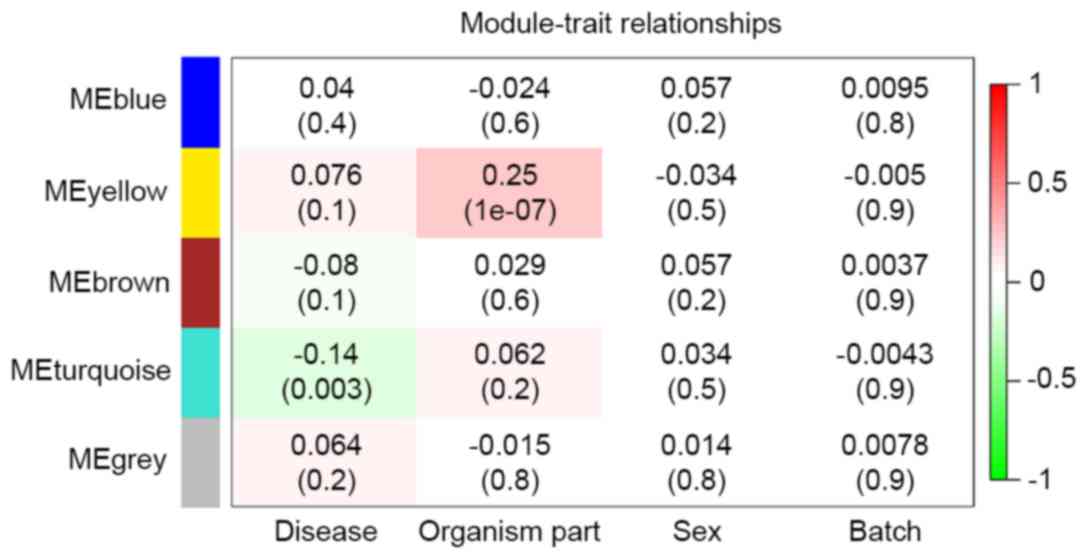
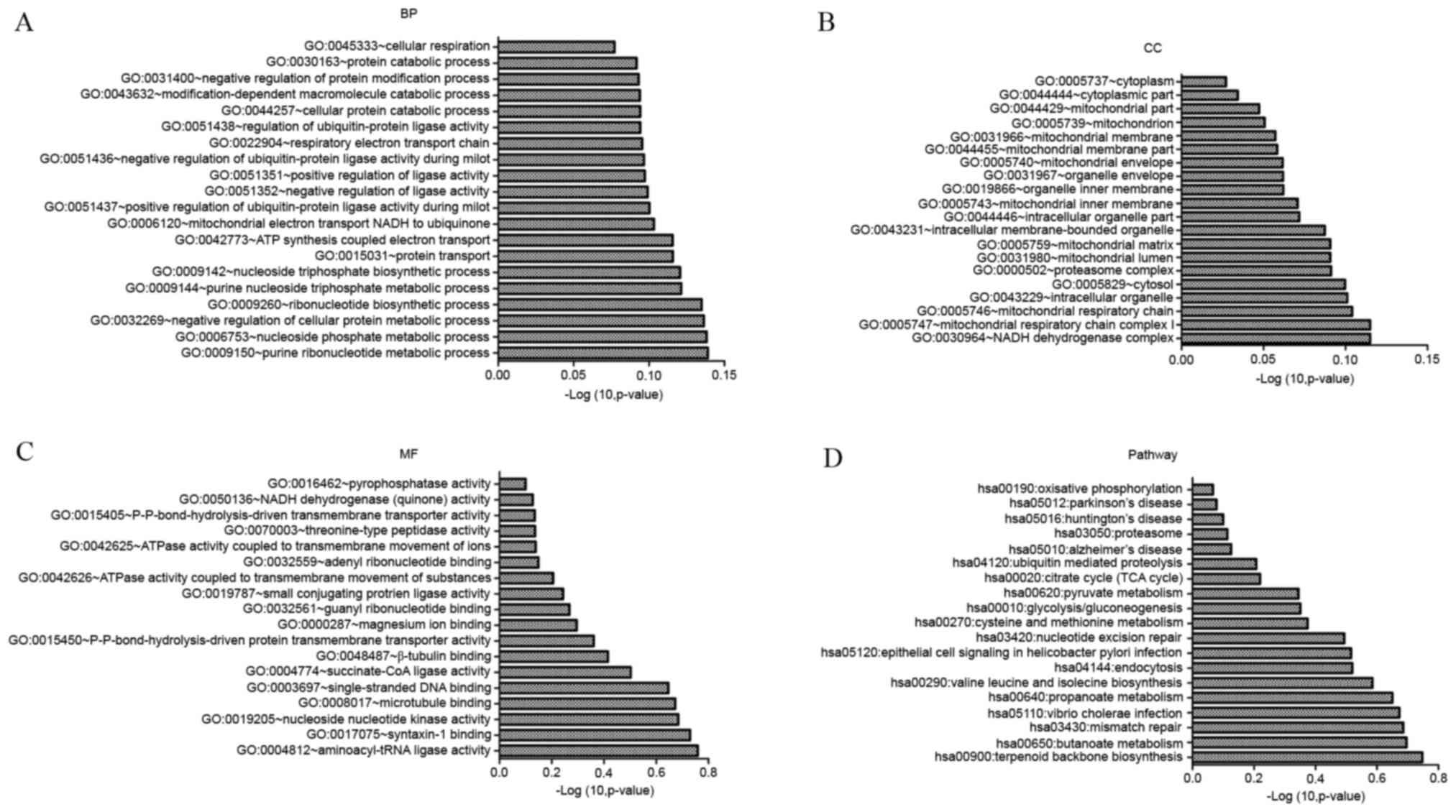
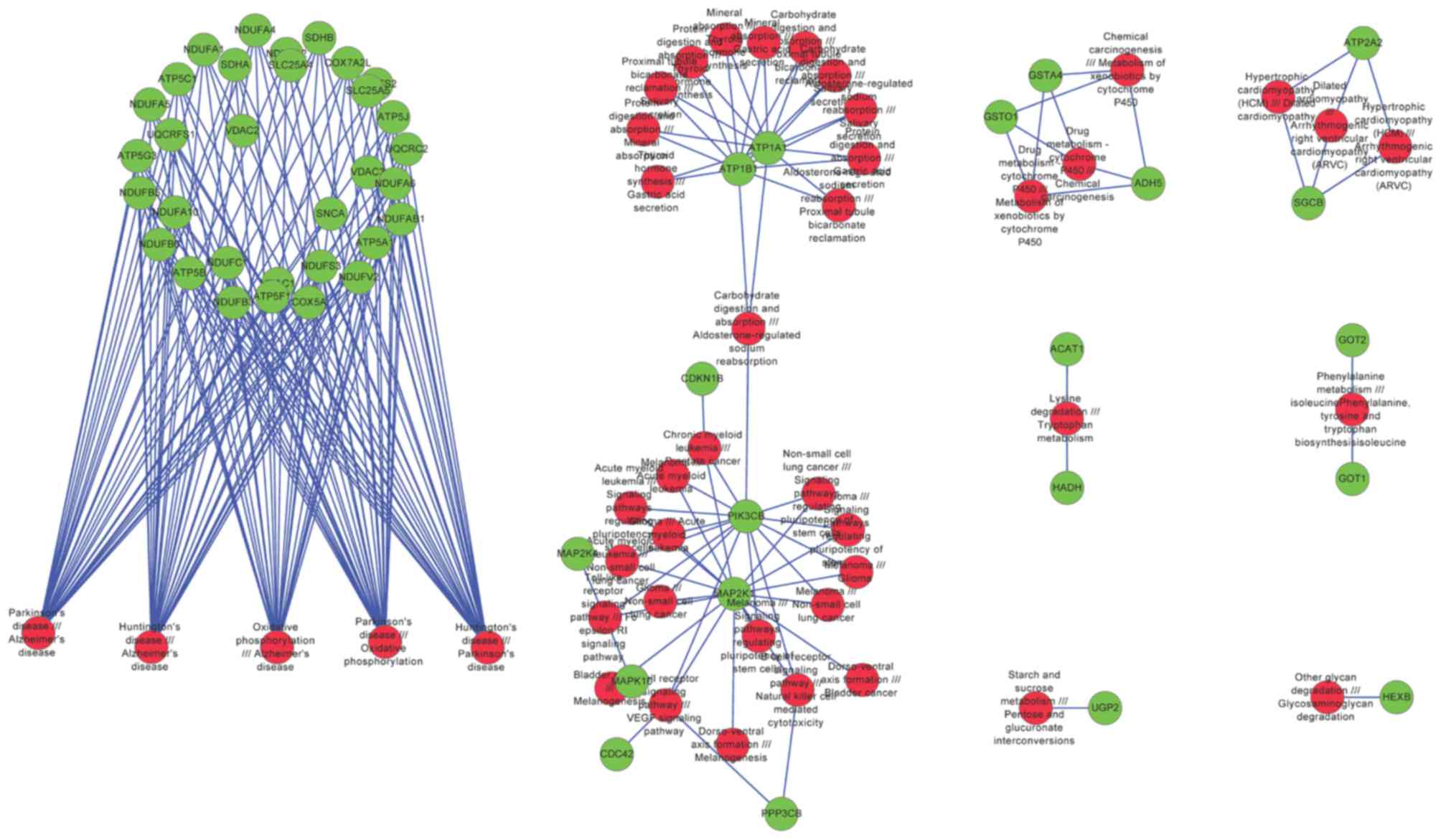
|
1
|
Ma CL, Su L, Xie JJ, Long JX, Wu P and Gu
L: The prevalence and incidence of Parkinson's disease in China: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neural Transm (Vienna).
121:123–134. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang W, Phillips K, Wielgus AR, Liu J,
Albertini A, Zucca FA, Faust R, Qian SY, Miller DS, Chignell CF, et
al: Neuromelanin activates microglia and induces degeneration of
dopaminergic neurons: Implications for progression of Parkinson's
disease. Neurotox Res. 19:63–72. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wakabayashi K, Tanji K, Odagiri S, Miki Y,
Mori F and Takahashi H: The Lewy body in Parkinson's disease and
related neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurobiol. 47:495–508.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Lau LM, Verbaan D, Marinus J and van
Hilten JJ: Survival in Parkinson's disease. Relation with motor and
non-motor features. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 20:613–616. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Müller B, Assmus J, Herlofson K, Larsen JP
and Tysnes OB: Importance of motor vs. non-motor symptoms for
health-related quality of life in early Parkinson's disease.
Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 19:1027–1032. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng B, Liao Z, Locascio JJ, Lesniak KA,
Roderick SS, Watt ML, Eklund AC, Zhang-James Y, Kim PD, Hauser MA,
et al: PGC-1α, a potential therapeutic target for early
intervention in Parkinson's disease. Sci Transl Med. 2:52ra732010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, James M, Middleton FA and Davis
RL: Transcriptional analysis of multiple brain regions in
Parkinson's disease supports the involvement of specific protein
processing, energy metabolism and signaling pathways, and suggests
novel disease mechanisms. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet.
137:5–16. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Moran LB, Duke DC, Deprez M, Dexter DT,
Pearce RK and Graeber MB: Whole genome expression profiling of the
medial and lateral substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease.
Neurogenetics. 7:1–11. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lesnick TG, Papapetropoulos S, Mash DC,
Ffrench-Mullen J, Shehadeh L, de Andrade M, Henley JR, Rocca WA,
Ahlskog JE and Maraganore DM: A genomic pathway approach to a
complex disease: Axon guidance and Parkinson disease. PLoS Genet.
3:e982007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Keller-McGandy C,
Bouzou B, Asteris G, Clark TW, Frosch MP and Standaert DG: Effects
of gender on nigral gene expression and parkinson disease.
Neurobiol Dis. 26:606–614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Corradini BR, Iamashita P, Tampellini E,
Farfel JM, Grinberg LT and Moreira-Filho CA: Complex network-driven
view of genomic mechanisms underlying Parkinson's disease: Analyses
in dorsal motor vagal nucleus, locus coeruleus, and substantia
nigra. Biomed Res Int. 2014:5436732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Riley BE, Gardai SJ, Emig-Agius D,
Bessarabova M, Ivliev AE, Schüle B, Alexander J, Wallace W,
Halliday GM, Langston JW, et al: Systems-based analyses of brain
regions functionally impacted in Parkinson's disease reveals
underlying causal mechanisms. PloS One. 9:e1029092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garcia-Esparcia P, Schlüter A, Carmona M,
Moreno J, Ansoleaga B, Torrejón-Escribano B, Gustincich S, Pujol A
and Ferrer I: Functional genomics reveals dysregulation of cortical
olfactory receptors in Parkinson disease: Novel putative
chemoreceptors in the human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
72:524–539. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Clarke C, Madden SF, Doolan P, Aherne ST,
Joyce H, O'Driscoll L, Gallagher WM, Hennessy BT, Moriarty M, Crown
J, et al: Correlating transcriptional networks to breast cancer
survival: A large-scale coexpression analysis. Carcinogenesis.
34:2300–2308. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu R, Cheng Y, Yu J, Lv QL and Zhou HH:
Identification and validation of gene module associated with lung
cancer through coexpression network analysis. Gene. 563:56–62.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi K, Bing ZT, Cao GQ, Guo L, Cao YN,
Jiang HO and Zhang MX: Identify the signature genes for diagnose of
uveal melanoma by weight gene co-expression network analysis. Int J
Ophthalmol. 8:269–274. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McCall MN, Bolstad BM and Irizarry RA:
Frozen robust multiarray analysis (fRMA). Biostatistics.
11:242–253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carvalho BS and Irizarry RA: A framework
for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics.
26:2363–2367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Fertig EJ,
Jaffe AE and Storey JD: sva: Surrogate Variable Analysis.
Bioconductor. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. Journal of the royal statistical society. Series
B (Methodological). 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang B and Horvath S: A general framework
for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat Appl Genet
Mol Biol. 4:Article172005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin MT and Beal MF: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.
Nature. 443:787–795. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Henchcliffe C and Beal MF: Mitochondrial
biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. Nat
Clin Pract Neurol. 4:600–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schapira AH: Mitochondria in the aetiology
and pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 7:97–109.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Devi L, Raghavendran V, Prabhu BM,
Avadhani NG and Anandatheerthavarada HK: Mitochondrial import and
accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human
dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol
Chem. 283:9089–9100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Olsen JH, Friis S and Frederiksen K:
Malignant melanoma and other types of cancer preceding Parkinson
disease. Epidemiology. 17:582–587. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
West AB, Dawson VL and Dawson TM: To die
or grow: Parkinson's disease and cancer. Trends Neurosci.
28:348–352. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
D'Amelio M, Ragonese P, Sconzo G, Aridon P
and Savettieri G: Parkinson's disease and cancer: Insights for
pathogenesis from epidemiology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1155:324–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kaut O, Schmitt I and Wüllner U:
Genome-scale methylation analysis of Parkinson's disease patients'
brains reveals DNA hypomethylation and increased mRNA expression of
cytochrome P450 2E1. Neurogenetics. 13:87–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morale MC, L'Episcopo F, Tirolo C,
Giaquinta G, Caniglia S, Testa N, Arcieri P, Serra PA, Lupo G,
Alberghina M, et al: Loss of aromatase cytochrome P450 function as
a risk factor for Parkinson's disease? Brain Res Rev. 57:431–443.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McCann SJ, Pond SM, James KM and Le
Couteur DG: The association between polymorphisms in the cytochrome
P-450 2D6 gene and Parkinson's disease: A case-control study and
meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci. 153:50–53. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pan F, Dong H, Ding H, Ye M, Liu W, Wu Y,
Zhang X, Chen Z, Luo Y and Ding X: SNP rs356219 of the α-synuclein
(SNCA) gene is associated with Parkinson's disease in a Chinese Han
population. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 18:632–634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sharma LK, Lu J and Bai Y: Mitochondrial
respiratory complex I: Structure, function and implication in human
diseases. Curr Med Chem. 16:1266–1277. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Peralta S, Torraco A, Wenz T, Garcia S,
Diaz F and Moraes CT: Partial complex I deficiency due to the CNS
conditional ablation of Ndufa5 results in a mild chronic
encephalopathy but no increase in oxidative damage. Hum Mol Genet.
23:1399–1412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sun Y, Vashisht AA, Tchieu J, Wohlschlegel
JA and Dreier L: Voltage-dependent anion channels (VDACs) recruit
Parkin to defective mitochondria to promote mitochondrial
autophagy. J Biol Chem. 287:40652–40660. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chu Y, Goldman JG, Kelly L, He Y, Waliczek
T and Kordower JH: Abnormal alpha-synuclein reduces nigral
voltage-dependent anion channel 1 in sporadic and experimental
Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 69:1–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li YJ, Oliveira SA, Xu P, Martin ER,
Stenger JE, Scherzer CR, Hauser MA, Scott WK, Small GW, Nance MA,
et al: Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 modifies age-at-onset of
Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease. Hum Mol Genet.
12:3259–3267. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li YJ, Scott WK, Zhang L, Lin PI, Oliveira
SA, Skelly T, Doraiswamy MP, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Martin ER, Haines JL,
et al: Revealing the role of glutathione S-transferase omega in
age-at-onset of Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Neurobiol Aging.
27:1087–1093. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|