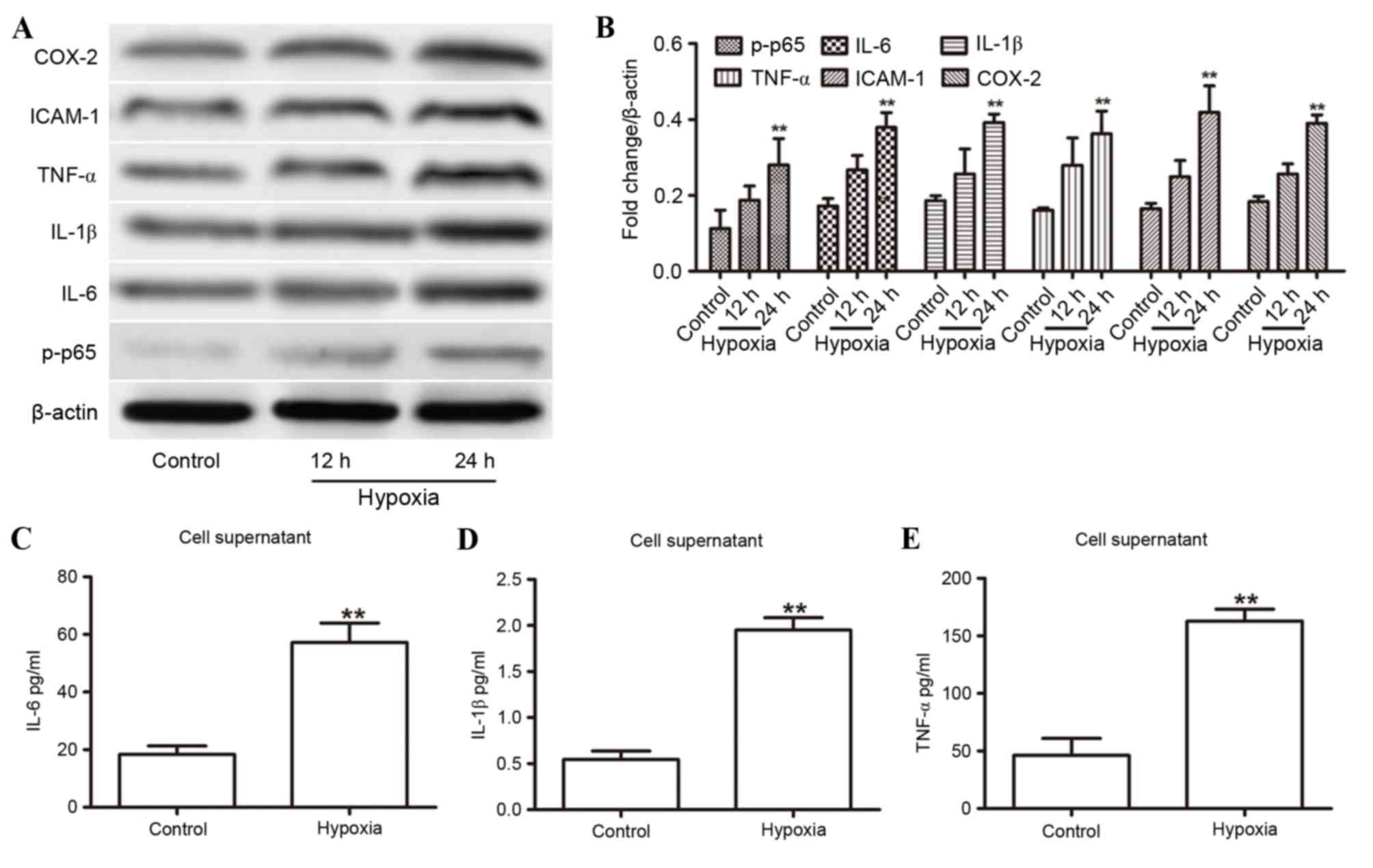
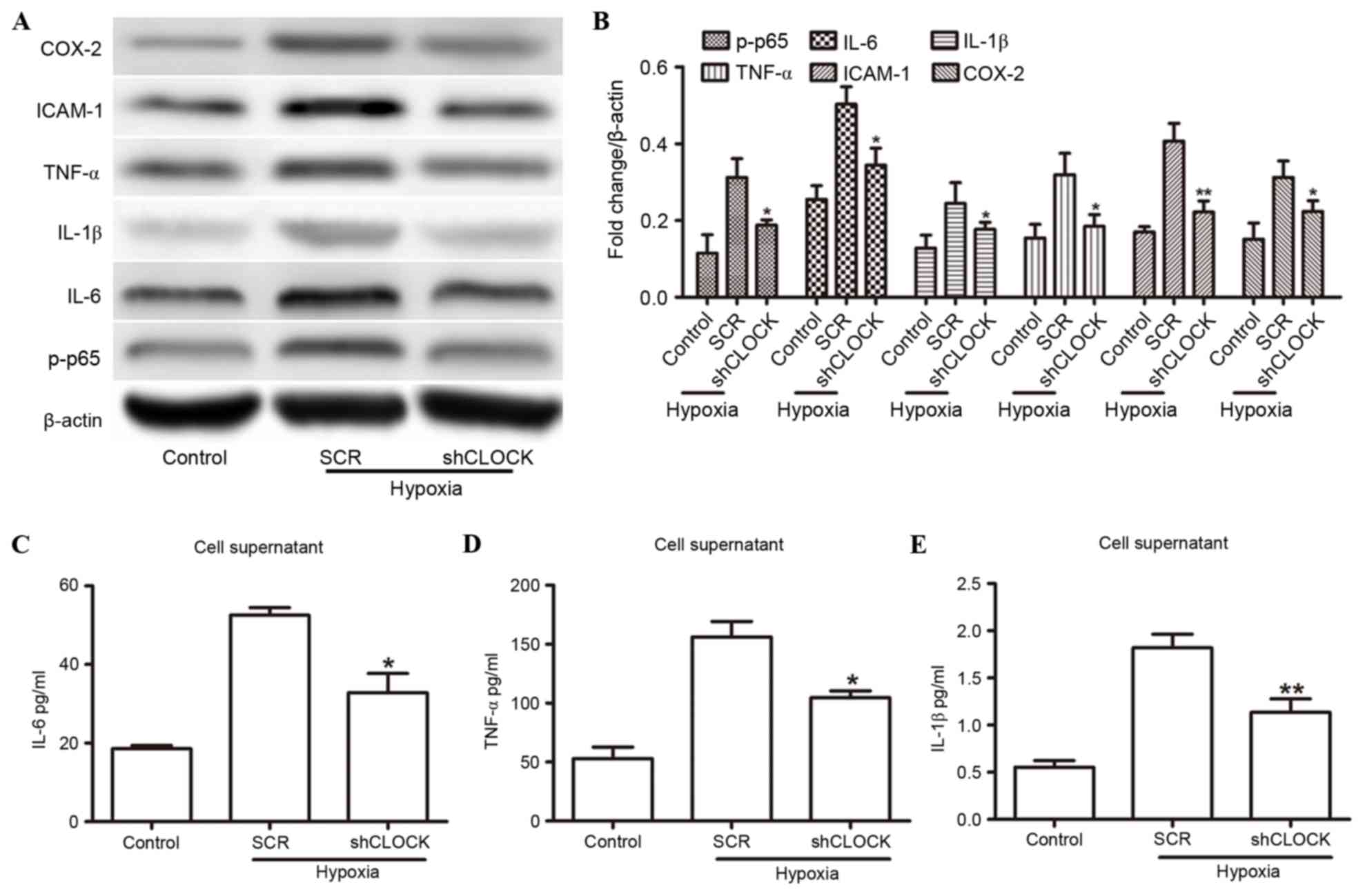
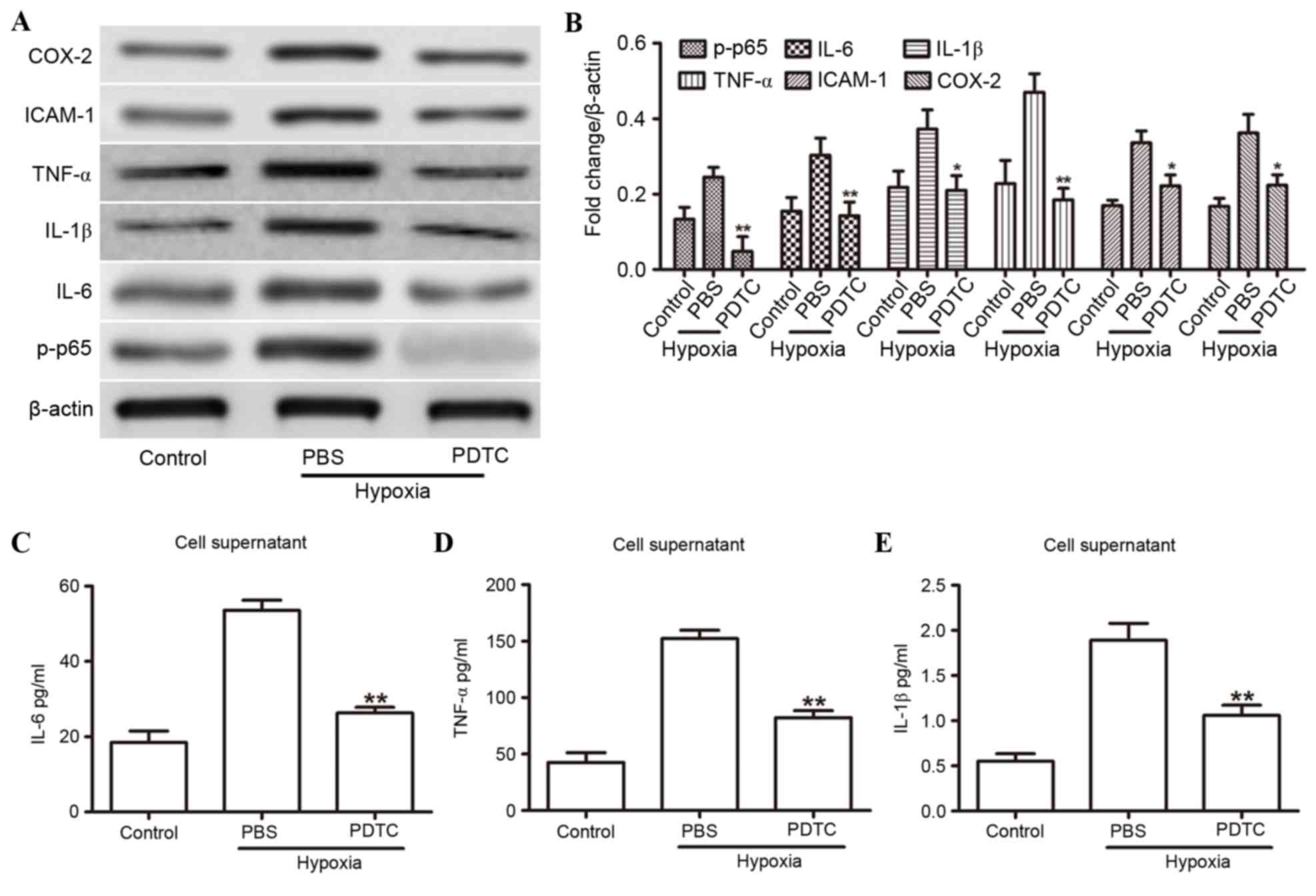
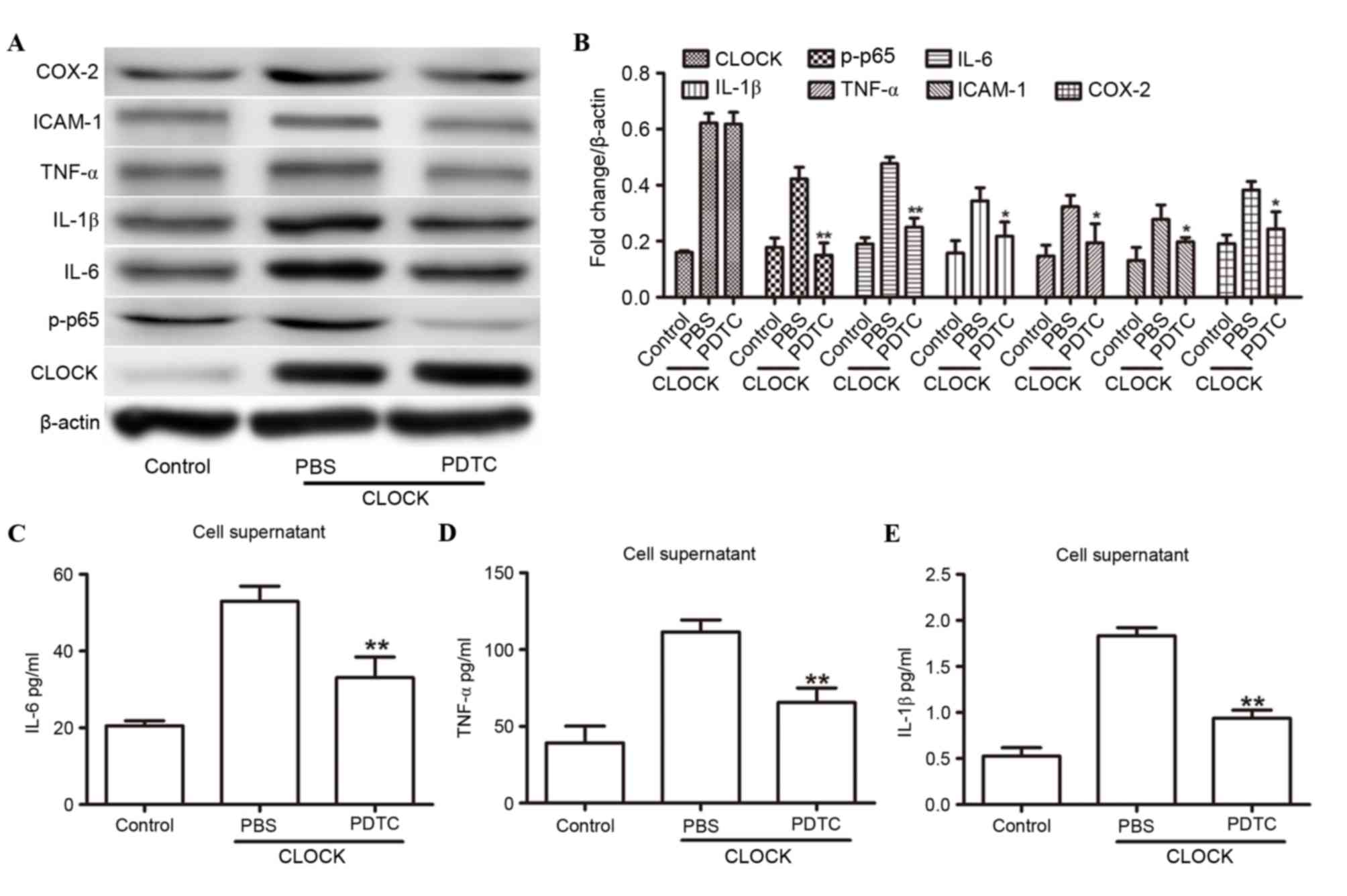
|
1
|
Xu C, Lu C, Hua L, Jin H, Yin L, Chen S
and Qian R: Rhythm changes of clock genes, apoptosis-related genes
and atherosclerosis-related genes in apolipoprotein E knockout
mice. Can J Cardiol. 25:473–479. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takeda N and Maemura K: The role of clock
genes and circadian rhythm in the development of cardiovascular
diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:3225–3234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reppert SM and Weaver DR: Coordination of
circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 418:935–941. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ramin C, Devore EE, Pierre-Paul J, Duffy
JF, Hankinson SE and Schernhammer ES: Chronotype and breast cancer
risk in a cohort of US nurses. Chronobiol Int. 30:1181–1186. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Savvidis C and Koutsilieris M: Circadian
rhythm disruption in cancer biology. Mol Med. 18:1249–1260. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anea CB, Zhang M, Stepp DW, Simkins GB,
Reed G, Fulton DJ and Rudic RD: Vascular disease in mice with a
dysfunctional circadian clock. Circulation. 119:1510–1517. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paschos GK and FitzGerald GA: Circadian
clocks and vascular function. Circ Res. 106:833–841. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang X, Guo D, Lin C, Shi Z, Qian R, Fu W,
Liu J, Li X and Fan L: Upregulation of the gene expression of CLOCK
is correlated with hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in advanced varicose
lesions. Mol Med Rep. 12:6164–6170. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghosh S, May MJ and Kopp EB: NF-kappa B
and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:225–260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pahl HL: Activators and target genes of
Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene. 18:6853–6866. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pasparakis M, Luedde T and
Schmidt-Supprian M: Dissection of the NF-kappaB signalling cascade
in transgenic and knockout mice. Cell Death Differ. 13:861–872.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JH and Sancar A: Regulation of
apoptosis by the circadian clock through NF-kappaB signaling. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:12036–12041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Monje FJ, Cabatic M, Divisch I, Kim EJ,
Herkner KR, Binder BR and Pollak DD: Constant darkness induces
IL-6-dependent depression-like behavior through the NF-κB signaling
pathway. J Neurosci. 31:9075–9083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang X, Guo D, Lin C, Shi Z, Qian R, Fu W,
Liu J, Li X and Fan L: hCLOCK causes Rho-Kinase-Mediated
endothelial dysfunction and NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:6718392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Labrecque N and Cermakian N: Circadian
clocks in the immune system. J Biol Rhythms. 30:277–290. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Keller M, Mazuch J, Abraham U, Eom GD,
Herzog ED, Volk HD, Kramer A and Maier B: A circadian clock in
macrophages controls inflammatory immune responses. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:21407–21412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sato S, Sakurai T, Ogasawara J, Takahashi
M, Izawa T, Imaizumi K, Taniguchi N, Ohno H and Kizaki T: A
circadian clock gene, Rev-erbα, modulates the inflammatory function
of macrophages through the negative regulation of Ccl2 expression.
J Immunol. 192:407–417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lawrence T and Fong C: The resolution of
inflammation: Anti-inflammatory roles for NF-kappaB. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 42:519–523. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hayden MS, West AP and Ghosh S: NF-kappaB
and the immune response. Oncogene. 25:6758–6780. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Spengler ML, Kuropatwinski KK, Comas M,
Gasparian AV, Fedtsova N, Gleiberman AS, Gitlin II, Artemicheva NM,
Deluca KA, Gudkov AV and Antoch MP: Core circadian protein CLOCK is
a positive regulator of NF-κB-mediated transcription. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:E2457–E2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
González-Miranda JM: On the effect of
circadian oscillations on biochemical cell signaling by NF-κB. J
Theor Biol. 335:283–294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Yu W and Zheng L: The dynamics of
NF-κB pathway regulated by circadian clock. Math Biosci. 260:47–53.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cuzzocrea S, Chatterjee PK, Mazzon E, Dugo
L, Serraino I, Britti D, Mazzullo G, Caputi AP and Thiemermann C:
Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates the development of acute and
chronic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 135:496–510. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu SF and Malik AB: NF-kappa B activation
as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L622–L645. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Németh ZH, Haskó G and Vizi ES:
Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate augments IL-10, inhibits TNF-alpha,
MIP-1alpha, IL-12, and nitric oxide production and protects from
the lethal effect of endotoxin. Shock. 10:49–53. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roy A, Jana A, Yatish K, Freidt MB, Fung
YK, Martinson JA and Pahan K: Reactive oxygen species up-regulate
CD11b in microglia via nitric oxide: Implications for
neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:686–699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Alonso-Fernández P and De la Fuente M:
Role of the immune system in aging and longevity. Curr Aging Sci.
4:78–100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|