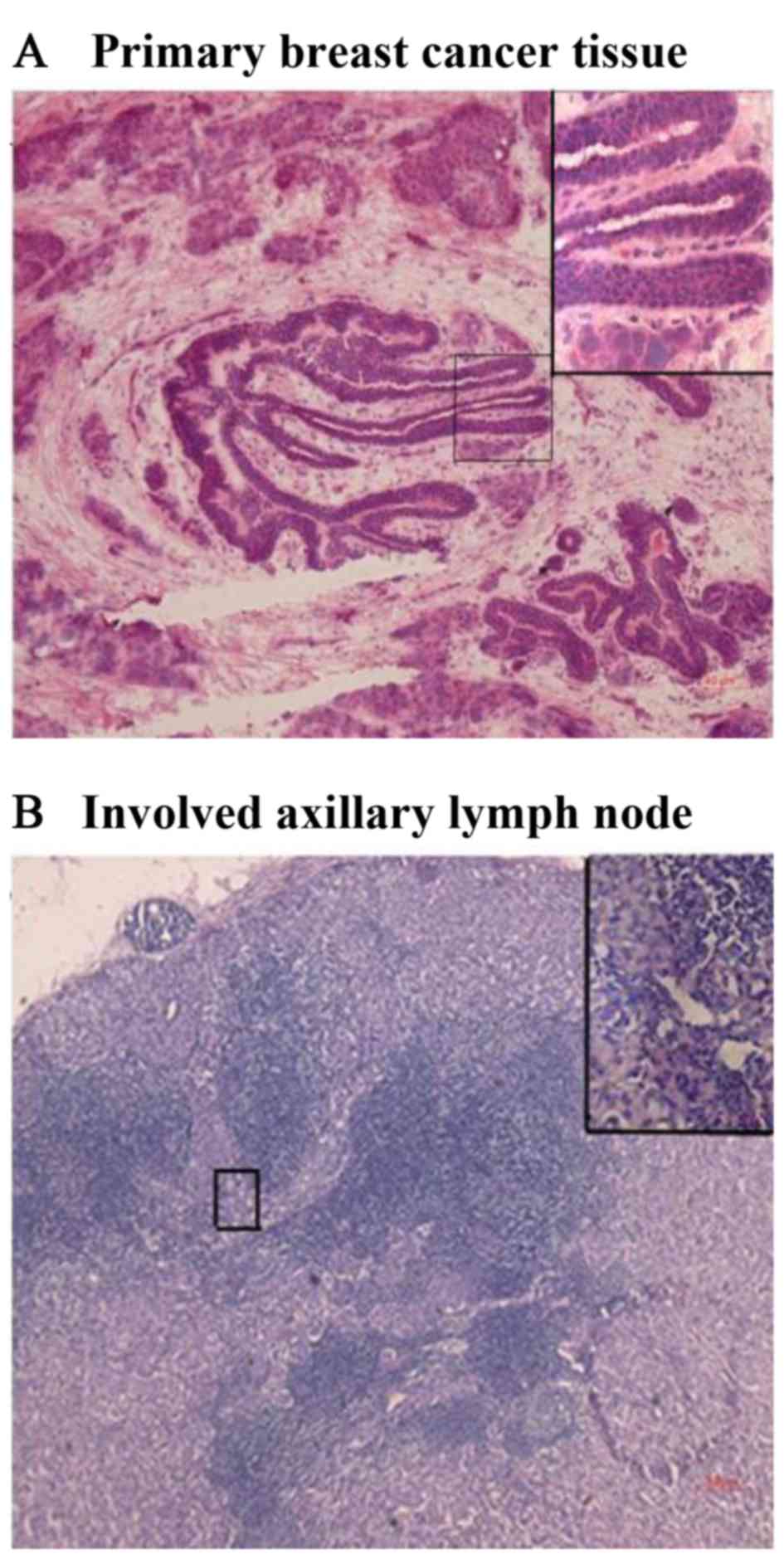
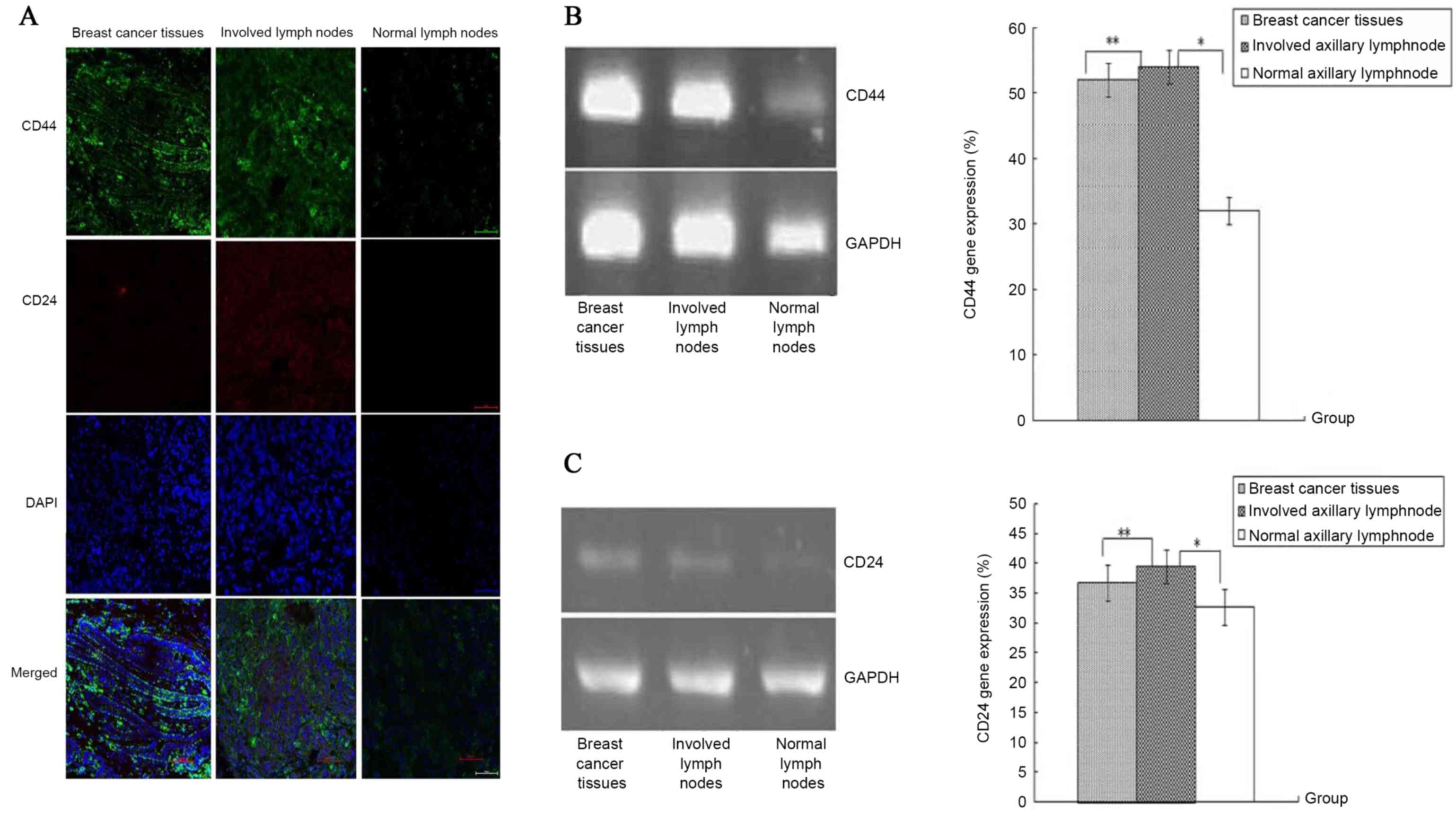
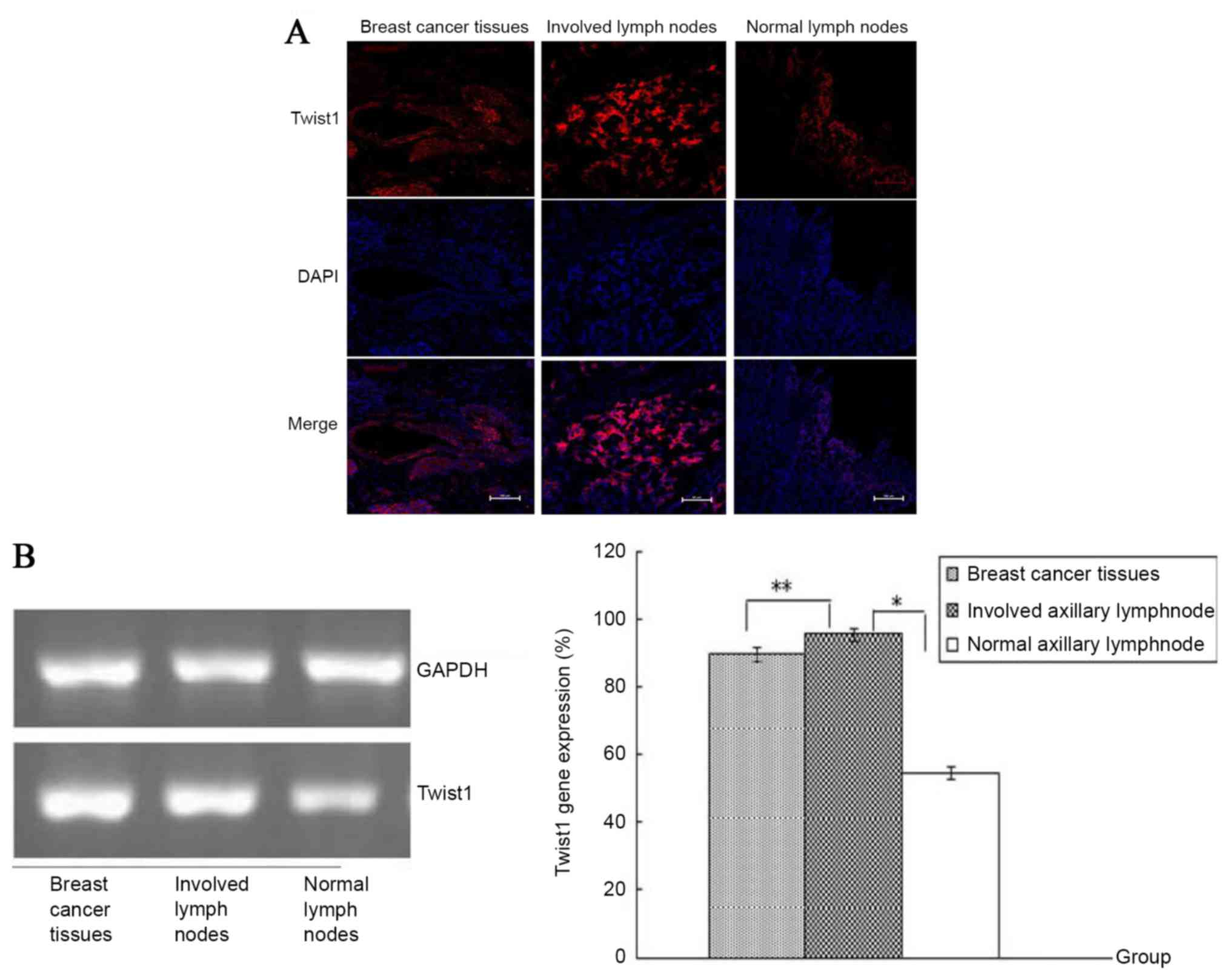
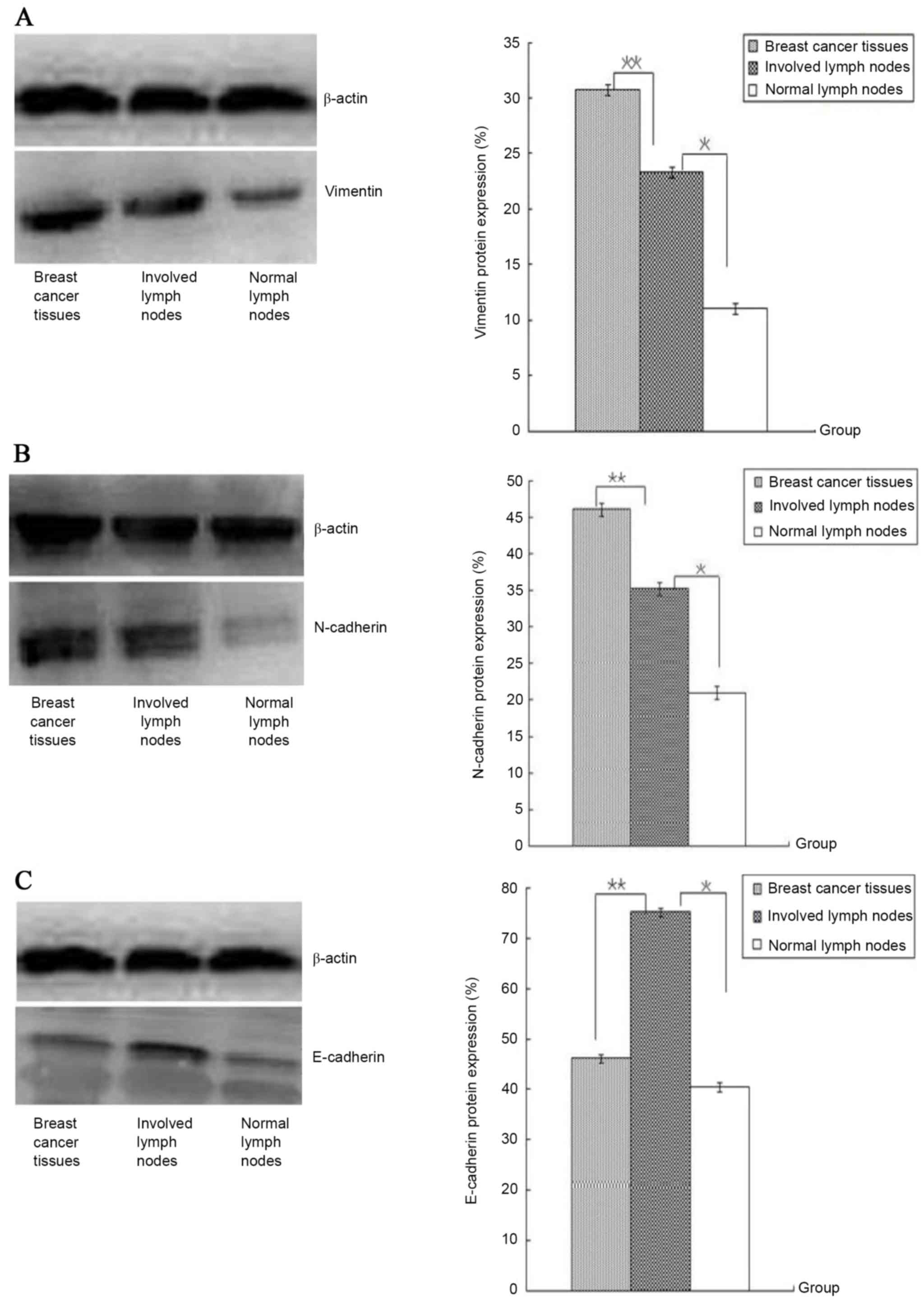
|
1
|
Velasco-Velázquez MA, Homsi N, De La
Fuente M and Pestell RG: Breast cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 44:573–577. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C,
Cufí S, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B and Menendez JA: Metformin
regulates breast cancer stem cell ontogeny by transcriptional
regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) status.
Cell Cycle. 9:3807–3814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li J and Zhou BP: Activation of β-catenin
and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT
associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer. 11:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ru GQ, Wang HJ, Xu WJ and Zhao ZS:
Upregulation of twist in gastric carcinoma associated with tumor
invasion and poor prognosis. Pathol Oncol Res. 17:341–347. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li S, Kendall SE, Raices R, Finlay J,
Covarrubias M, Liu Z, Lowe G, Lin YH, Teh YH, Leigh V, et al:
TWIST1 associates with NF-κB subunit RELA via carboxyl-terminal WR
domain to promote cell autonomous invasion through IL8 production.
BMC Biol. 10:732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kong Y, Wang J, Liu W, Chen Q, Yang J, Wei
W, Wu M, Yang L, Xie X, Lv N, et al: Cytokeratin19-2g2, a novel
fragment of cytokeratin19 in serum, indicating a more invasive
behavior and worse prognosis in breast cancer patients. PLoS One.
8:e570922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eckert MA, Lwin TM, Chang AT, Kim J, Danis
E, Ohno-Machado L and Yang J: Twist1-induced invadopodia formation
promotes tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell. 19:372–386. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qin Q, Xu Y, He T, Qin C and Xu J: Normal
and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying
molecular mechanisms. Cell Res. 22:90–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sleeman JP, Cady B and Pantel K: The
connectivity of lymphogenous and hematogenous tumor cell
dissemination: Biological insights and clinical implications. Clin
Exp Metastasis. 29:737–746. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Markiewicz A, Ahrends T,
Wełnicka-Jaśkiewicz M, Seroczyńska B, Skokowski J, Jaśkiewicz J,
Szade J, Biernat W and Zaczek AJ: Expression of epithelial to
mesenchymal transition-related markers in lymph node metastases as
a surrogate for primary tumor metastatic potential in breast
cancer. J Transl Med. 10:2262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sell S: Cancer-associated carbohydrates
identified by monoclonal antibodies. Hum Pathol. 21:1003–1019.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hilkens J, Buijs F, Hilgers J, Hageman P,
Calafat J, Sonnenberg A and van der Valk M: Monoclonal antibodies
against human milk-fat globule membranes detecting differentiation
antigens of the mammary gland and its tumors. Int J Cancer.
34:197–206. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Duffy MJ, Evoy D and McDermott EW: CA
15–3: Uses and limitation as a biomarker for breast cancer. Clin
Chim Acta. 411:1869–1874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou J, Zhang L, Gu Y, Li K, Nie Y, Fan D
and Feng Y: Dynamic expression of CEACAM7 in precursor lesions of
gastric carcinoma and its prognostic value in combination with CEA.
World J Surg Oncol. 9:1722011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sobin LH, Hermanek P and Hutter RV: TNM
classification of malignant tumors. A comparison between the new
(1987) and the old editions. Cancer. 61:2310–2314. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elston CW and Ellis IO: Pathological
prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological
grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with
long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 19:403–410. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Montgomery N, Hill A, McFarlane S, Neisen
J, O'Grady A, Conlon S, Jirstrom K, Kay EW and Waugh DJ: CD44
enhances invasion of basal-like breast cancer cells by upregulating
serine protease and collagen-degrading enzymatic expression and
activity. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C,
Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X and Perou CM: Phenotypic and
molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM,
Neumeister VM, Sjolund A, Rimm DL, Wong H, Rodriguez A,
Herschkowitz JI, et al: Residual breast cancers after conventional
therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13820–13825. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhong Y, Shen S, Zhou Y, Mao F, Guan J,
Lin Y, Xu Y and Sun Q: ALDH1 is a better clinical indicator for
relapse of invasive ductal breast cancer than the CD44+/CD24-
phenotype. Med Oncol. 31:8642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sung WJ, Park KS, Kwak SG, Hyun DS, Jang
JS and Park KK: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in patients of
pulmonary adenocarcinoma: Correlation with cancer stem cell markers
and prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8997–9009. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vesuna F, Lisok A, Kimble B and Raman V:
Twist modulates breast cancer stem cells by transcriptional.
Neoplasia. 11:1318–1328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li J and Zhou BP: Activation of β-catenin
and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT
associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer. 11:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kalluri R: EMT: When epithelial cells
decide to become mesenchymal-like cells. J Clin Invest.
119:1417–1419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huber MA, Kraut N and Beug H: Molecular
requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor
progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vesuna F, Lisok A, Kimble B, Domek J, Kato
Y, Groep P vander, Artemov D, Kowalski J, Carraway H, van Diest P
and Raman V: Twist contributes to hormone resistance in breast
cancer by downregulating estrogen receptor-α. Oncogene.
31:3223–3234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ri G, Ohno S, Yamamoto T, Ito E, Furutani
M, Furutani Y, Umeda Y, Tsukahara T, Hagita N and Matsuoka R: Serum
levels of CA15-3, KL-6 and BCA225 are positively correlated with
each other in the general population. Anticancer Res. 29:4239–4242.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bidard FC, Hajage D, Bachelot T, Delaloge
S, Brain E, Campone M, Cottu P, Beuzeboc P, Rolland E, Mathiot C
and Pierga JY: Assessment of circulating tumor cells and serum
markers for progression-free survival prediction in metastatic
breast cancer: A prospective observational study. Breast Cancer
Res. 14:R292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|