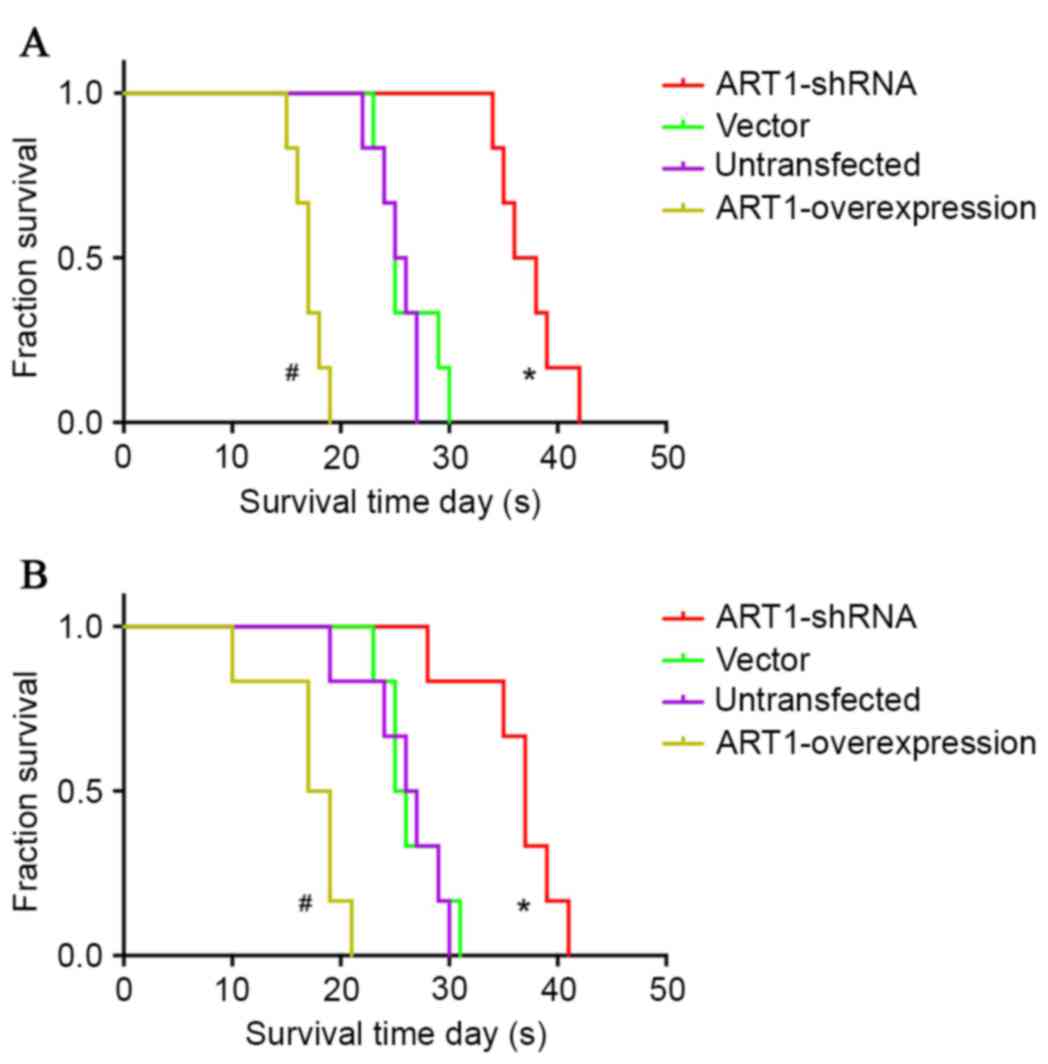
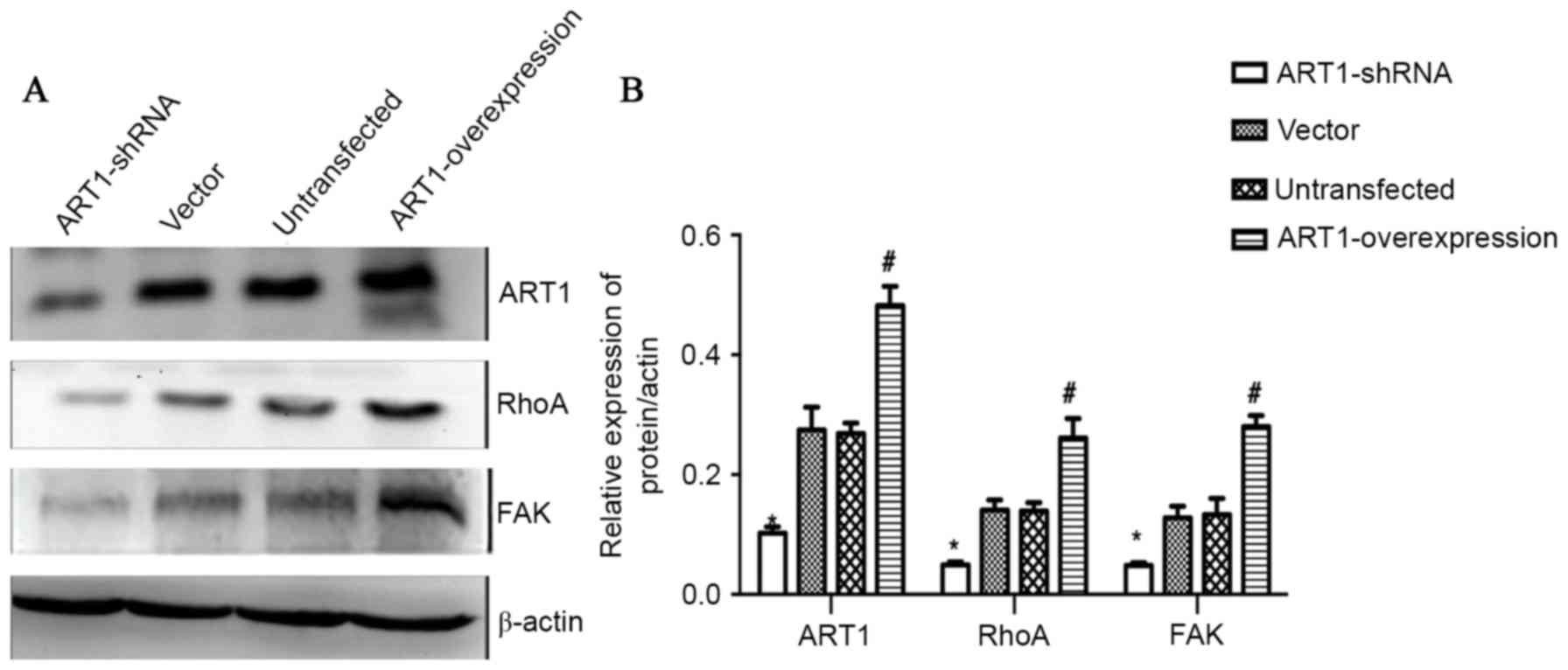
|
1
|
Hassa PO, Haenni SS, Elser M and Hottiger
MO: Nuclear ADP-ribosylation reactions in mammalian cells: Where
are we today and where are we going? Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
70:789–829. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Laing S, Unger M, Koch-Nolte F and Haag F:
ADP-ribosylation of arginine. Amino Acids. 41:257–269. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stevens LA, Levine RL, Gochuico BR and
Moss J: ADP-ribosylation of human defensin HNP-1 results in the
replacement of the modified arginine with the noncoded amino acid
ornithine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:19796–19800. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Corda D and Di Girolamo M: Functional
aspects of protein mono-ADP-ribosylation. EMBO J. 22:1953–1958.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yau L, Litchie B, Thomas S, Storie B,
Yurkova N and Zahradka P: Endogenous mono-ADP-ribosylation mediates
smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via protein kinase
N-dependent induction of c-fos expression. Eur J Biochem.
270:101–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yau L, Molnar P, Moon MC, Buhay S, Werner
JP, Molnar K, Saward L, Rizzo DD and Zahradka P:
Meta-iodobenzylguanidine, an inhibitor of arginine-dependent
mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation, prevents neointimal hyperplasia. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 326:717–724. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang Y, Wang YL, Yang L, Xu JX, Xiong W,
Xiao M and Li M: Inhibition of arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase 1
reduces the expression of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in colon
carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 32:130–136. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuang J, Wang YL, Xiao M, Tang Y, Chen WW,
Song GL, Yang X and Li M: Synergistic effect of arginine-specific
ADP-ribosyltransferase 1 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 on
apoptosis induced by cisplatin in CT26 cells. Oncol Rep.
31:2335–2343. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang W, Wu YL, Zhong J, Jiang FX, Tian XL
and Yu LF: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist suppress
angiogenesis and growth of gastric cancer xenografts. Dig Dis Sci.
53:1206–1210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu HY, Huang ZL, Yang GH, Lu WQ and Yu
NR: Inhibitory effect of modified citrus pectin on liver metastases
in a mouse colon cancer model. World J Gastroenterol. 14:7386–7391.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang L, Wang YL, Sheng YT, Xiong W, Xu JX,
Tang Y and Li X: The correlation of ART1 expression with
angiogenesis in colorectal carcinoma and it relationship with VEGF
and integrin αVβ3 expressions. Basic Clin Med. 9:1064–1069.
2012.
|
|
12
|
Xiao M, Tang Y, Wang YL, Yang L, Li X,
Kuang J and Song GL: ART1 silencing enhances apoptosis of mouse
CT26 cells via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
32:1587–1599. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiong W, Tang Y, Wang YL and Xu JX:
Effects of ART1 gene silencing on the ability of CT26 cellular
matrix adhesion and migration. Fudan Univer J Med Sci. 40:328–334.
2013.
|
|
14
|
Xu JX, Wang YL, Tang Y and Xiong W: Effect
of ART1 gene silencing by RNA interference on the proliferation of
mouse colon carcinoma cells and its possible mechanism. Tumor.
32:949–954. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Sawhney RS, Liu W and Brattain MG: A novel
role of ERK5 in integrin-mediated cell adhesion and motility in
cancer cells via Fak signaling. J Cell Physiol. 219:152–161. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Z, Gruszczynska-Biegala J and
Zolkiewska A: ADP-ribosylation of integrin alpha7 modulates the
binding of integrin alpha7beta1 to laminin. Biochem J. 385:309–317.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: Integrin beta
1-focal adhesion kinase signaling directs the proliferation of
metastatic cancer cells disseminated in the lungs. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:10290–10295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR and Schlaepfer DD:
Required role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) for
integrin-stimulated cell migration. J Cell Sci. 112:2677–2691.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gilcrease MZ: Integrin signaling in
epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 247:1–25. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schaller MD: Cellular functions of FAK
kinases: Insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J
Cell Sci. 123:1007–1013. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dorfleutner A, Stehlik C, Zhang J, Gallick
GE and Flynn DC: AFAP-110 is required for actin stress fiber
formation and cell adhesion in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J
Cell Physiol. 213:740–749. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nobes CD and Hall A: Rho, rac, and cdc42
GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes
associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia.
Cell. 81:53–62. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang S, Tang Q, Xu F, Xue Y, Zhen Z, Deng
Y, Liu M, Chen J, Liu S, Qiu M, et al: RhoA regulates G1-S
progression of gastric cancer cells by modulation of multiple INK4
family tumor suppressors. Mol Cancer Res. 7:570–580. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zohrabian VM, Forzani B, Chau Z, Murali R
and Jhanwar-Uniyal M: Rho/ROCK and MAPK signaling pathways are
involved in glioblastoma cell migration and proliferation.
Anticancer Res. 29:119–123. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Levens DL: Reconstructing Myc. Gene Dev.
17:1071–1077. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kamaraju AK and Roberts AB: Role of
Rho/ROCK and p38 MAP kinase pathways in transforming growth
factor-beta-mediated Smad-dependent growth inhibition of human
breast carcinoma cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 280:1024–1036. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song Y, Wu J, Oyesanya RA, Lee Z,
Mukherjee A and Fang X: Sp-1 and c-Myc mediate lysophosphatidic
acid-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in
ovarian cancer cells via a hypoxia-inducible factor-1-independent
mechanism. Clin Cancer Res. 15:492–501. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang X, Ge YL and Tian RH: The knockdown
of c-myc expression by RNAi inhibits cell proliferation in human
colon cancer HT-29 cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
14:305–318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shiu YT, Li S, Yuan S, Wang Y, Nguyen P
and Chien S: Shear stress-induced c-fos activation is mediated by
Rho in a calcium-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
303:548–555. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ueyama T, Sakoda T, Kawashima S, Hiraoka
E, Hirata KI, Akita H and Yokoyama M: Activated RhoA stimulates
c-fos gene expression in myocardial cells. Circ Res. 81:672–678.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jia ZC, Wan YL, Tang JQ, Dai Y, Liu YC,
Wang X and Zhu J: Tissue factor/activated factor VIIa induces
matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression through activation of c-Fos
via ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in human colon cancer
cell. Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:437–445. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pandey MK, Liu G, Cooper TK and Mulder KM:
Knockdown of c-Fos suppresses the growth of human colon carcinoma
cells in athymic mice. Int J Cancer. 130:213–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tulchinsky E: Fos family members:
Regulation, structure and role in oncogenic transformation. Histol
Histopathol. 15:921–928. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Benitah SA, Valerón PF and Lacal JC: ROCK
and nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent activation of cyclooxygenase-2
by Rho GTPases: Effects on tumor growth and therapeutic
consequences. Mol Biol Cell. 14:3041–3054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fosslien E: Biochemistry of cyclooxygenase
(COX)-2 inhibitors and molecular pathology of COX-2 in neoplasia.
Crit Rev Cl Lab Sci. 37:431–502. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Asting AG, Carén H, Andersson M, Lönnroth
C, Lagerstedt K and Lundholm K: COX-2 gene expression in colon
cancer tissue related to regulating factors and promoter
methylation status. BMC Cancer. 11:2382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|