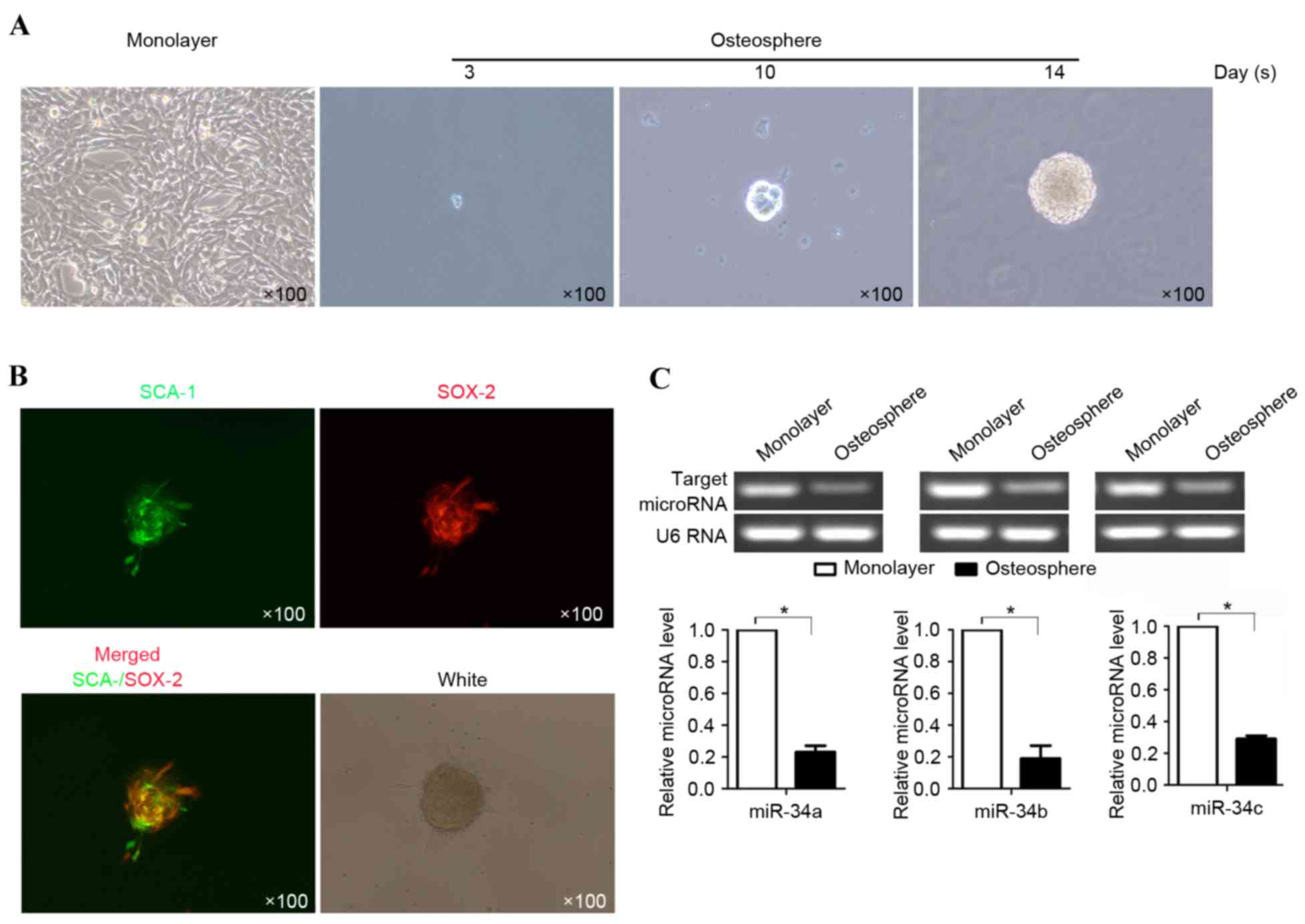
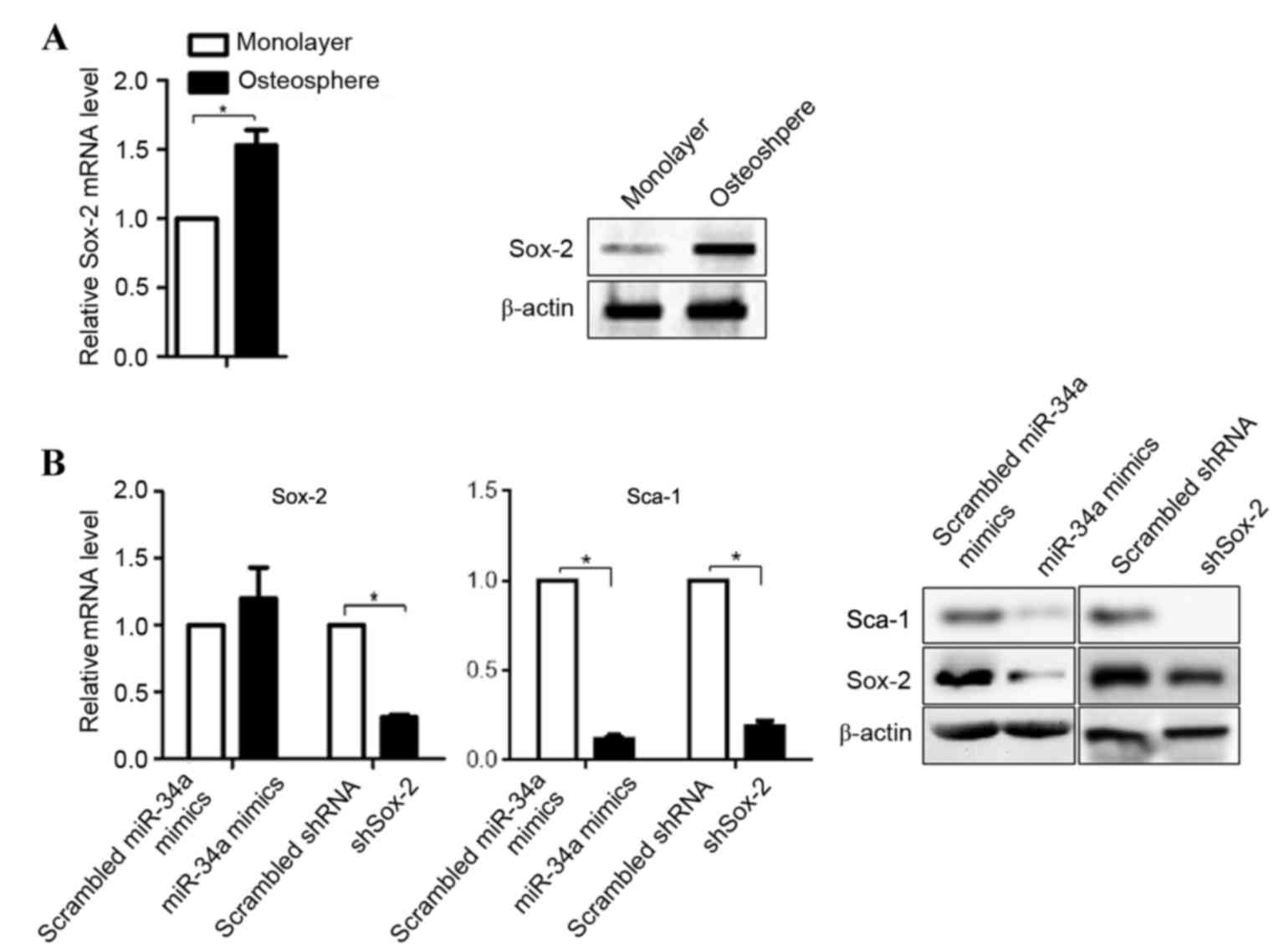
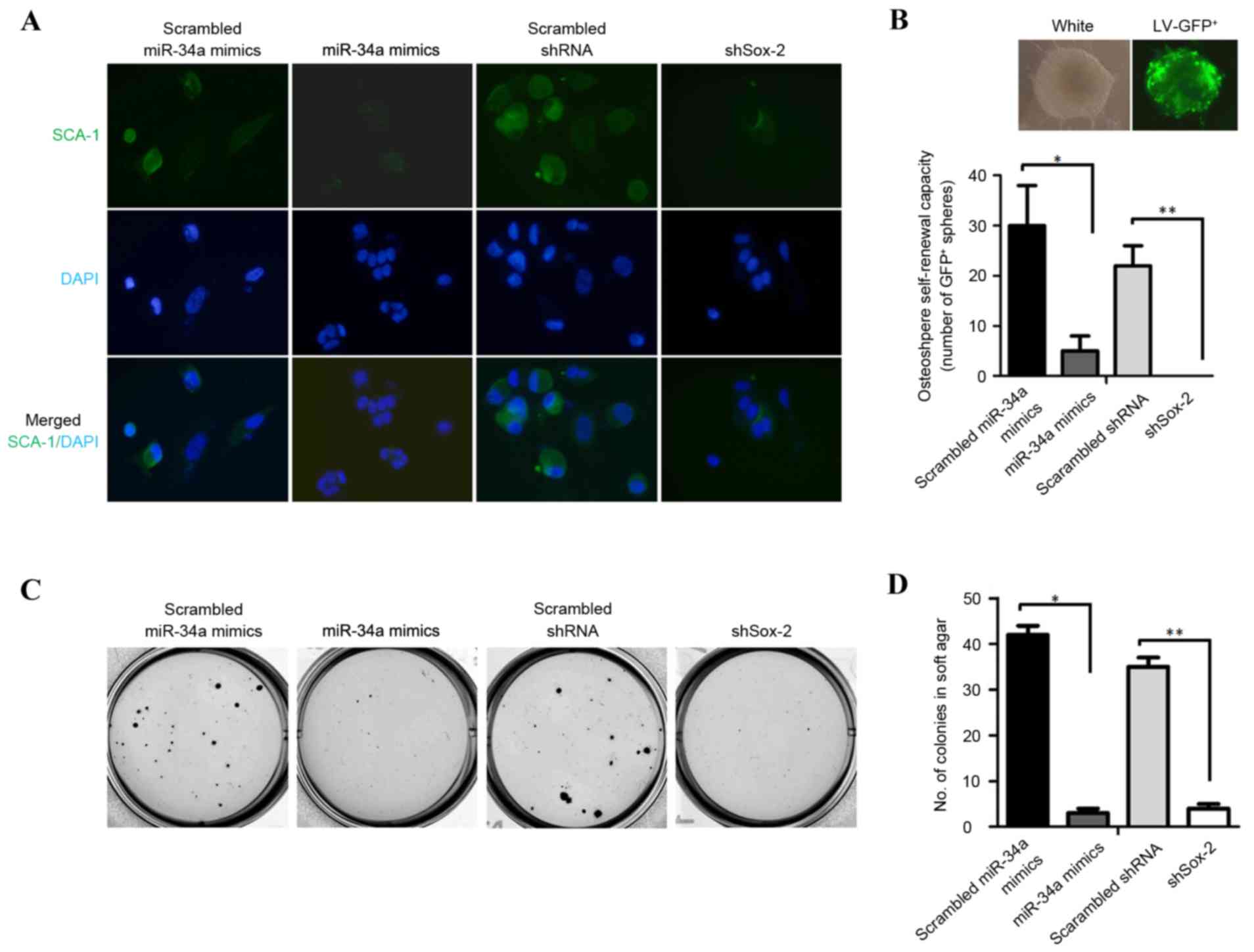
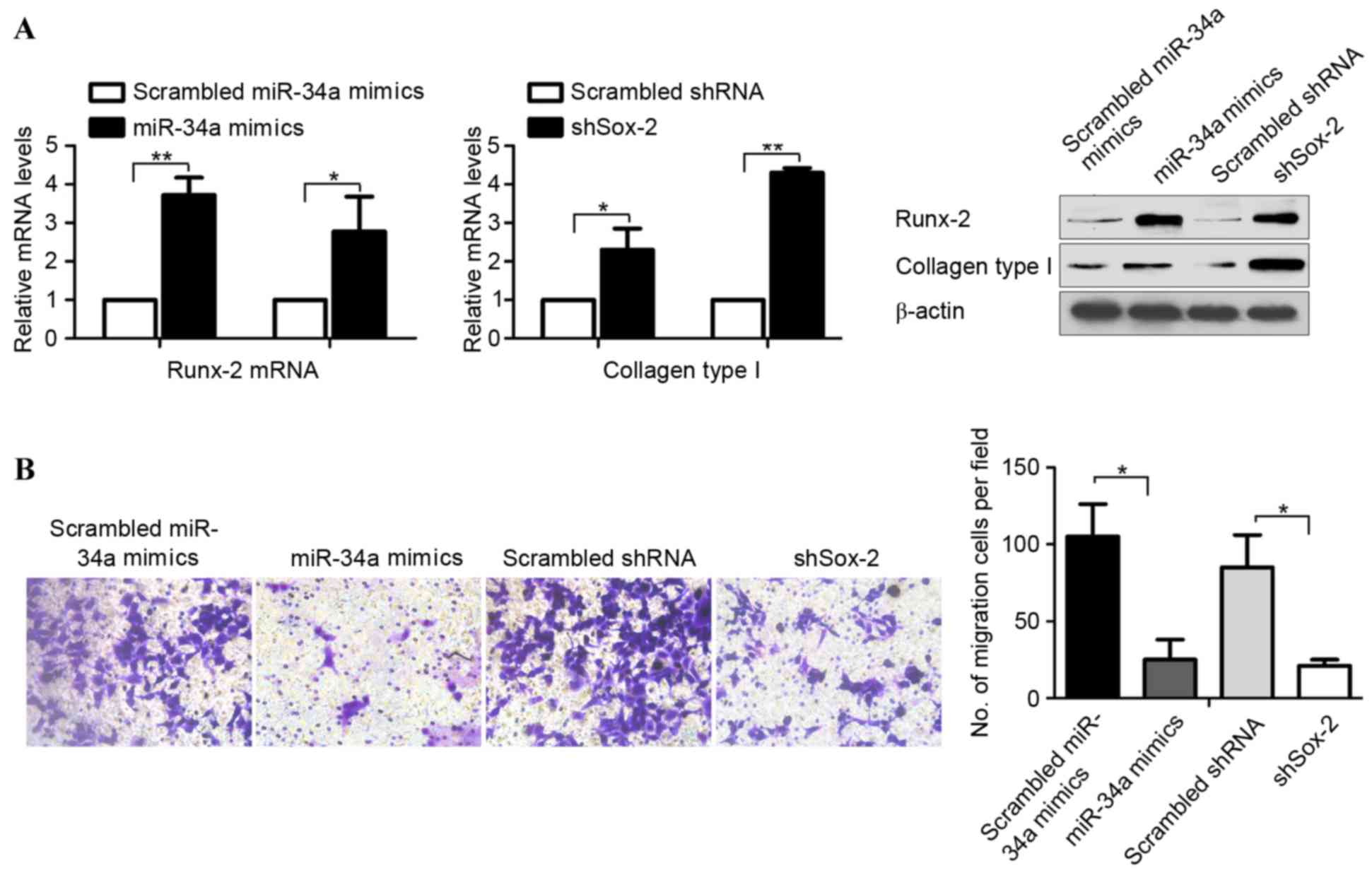
|
1
|
Ek ET, Dass CR and Choong PF: Commonly
used mouse models of osteosarcoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 60:1–8.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo MD, Healey
JH, Bernstein ML, Betcher D, Ferquson WS, Gebhardt MC, Goorin AM,
Harris M, et al: Osteosarcoma: The addition of muramyl tripeptide
to chemotherapy improves overall survival-a report from the
Children's oncology group. J Clin Oncol. 26:633–638. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma Y, Ren Y, Han EQ, Li H, Chen D, Jacobs
JJ, Gitelis S, O'Keefe RJ, Konttinen YT, Yin G and Li TF:
Inhibition of the Wnt-β-catenin and Notch signaling pathways
sensitizes osteosarcoma cells to chemotherapy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 431:274–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Y, Duan G and Feng S: MicroRNA-301a
modulates doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma cells by targeting
AMP-activated protein kinase alpha 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
459:367–373. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clarke MF: Self-renewal and solid-tumor
stem cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 11(2 Suppl 2): S14–S16.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krutovskikh VA and Herceg Z: Oncogenic
miroRNAs (OncomiRs) as a new class of cancer biomarkers. Bioessays.
32:894–904. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: MicroRNAs in cancer.
Annu Rev Pathol. 4:199–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baashah S and Soleimani M: The oncogenic
and tumour suppressive roles of microRNAs in cancer and apoptosis.
Eur J Cancer. 47:1127–1137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, De Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hermeking H: p53 enters the microRNA
world. Cancer Cell. 12:414–418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan K, Gao J, Yang T, Ma Q, Qiu X, Fan Q
and Ma B: MicroRNA-34a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
7:e337782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Avilion AA, Nicolis SK, Pevny LH, Perez L,
Vivian N and Lovell-Badge R: Multipotent cell lineages in early
mouse development depend on SOX2 function. Genes Dev. 17:126–140.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lefebvre V, Dumitriu B, Penzo-Méndez A,
Han Y and Pallavi B: Control of cell fate and differentiation by
Sry-related high-mobility-group box (Sox) transcription factors.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:2195–2214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Basu-Roy U, Seo E, Ramanathapuram L, Rapp
TB, Perry JA, Orkin SH, Mansukhani A and Basilico C: Sox2 maintains
self-renewal of tumor-initiating cells in osteosarcomas. Oncogene.
31:2270–2282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gritti A, Frölichsthal-Schoeller P, Galli
R, Parati EA, Cova L, Pagano SF, Bjornson CR and Vescovi AL:
Epidermal and fibroblast growth factors behave as mitogenic
regulators for a single multipotent stem cell-like population from
the subventricular region of the adult mouse forebrain. J Neurosci.
19:3287–3297. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vanderluit JL, Ferguson KL, Nikoletopoulou
V, Parker M, Ruzhynsky V, Alexson T, McNamara SM, Park DS, Rudnicki
M and Slack RS: p107 regulates neural precursor cells in the
mammalian brain. J Cell Biol. 166:853–863. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng S, Calin GA, Croce CM, Coukos G and
Zhang L: Mechanisms of microRNA deregulation in human cancer. Cell
Cycle. 7:2643–2646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom
M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D and Slack
FJ: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM,
Chuang JC, Coetzee GA and Jones PA: Specific activation of
microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogen BCL6 by
chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell.
9:435–443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chow TF, Mankaruos M, Scorilas A, Youssef
Y, Girgis A, Mossad S, Metias S, Rofael Y, Honey RJ, Stewart R, et
al: The miR-17-92 cluster is over expressed in and has an oncogenic
effect on renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 183:743–751. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Basu-Roy U, Ambrosetti D, Favaro R,
Nicolis SK, Mansukhani A and Basilico C: The transcription factor
Sox2 is required for osteoblast self-renewal. Cell Death Differ.
17:1345–1353. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|