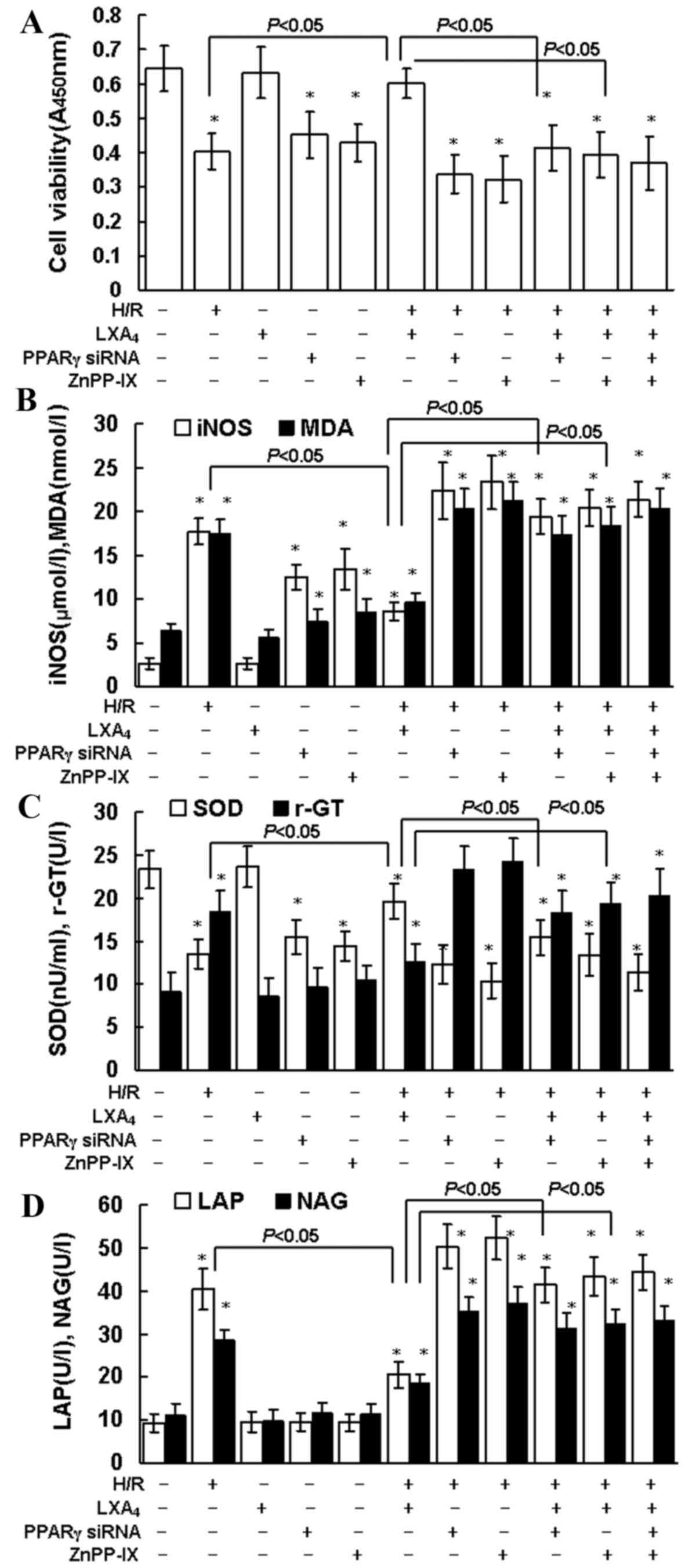
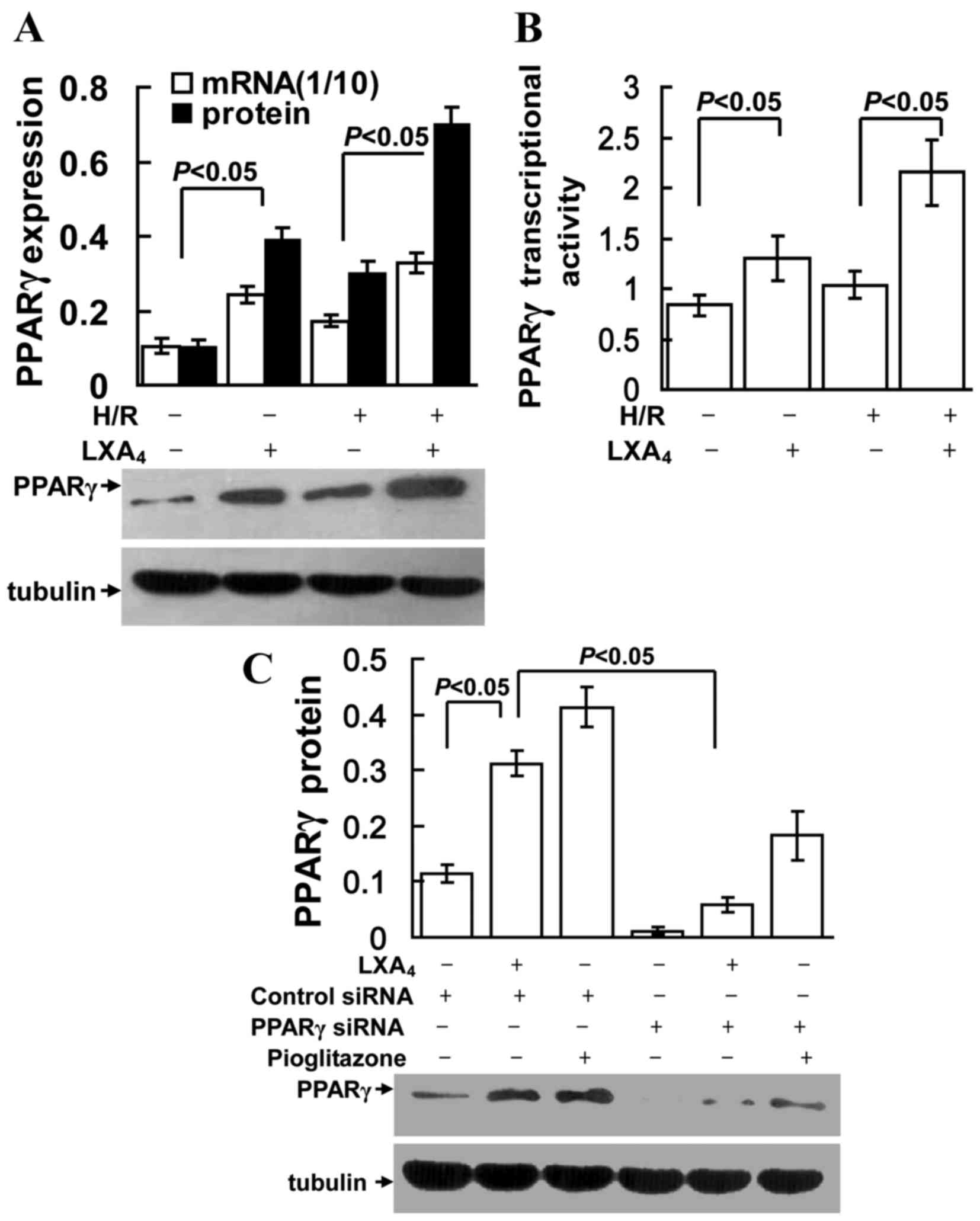
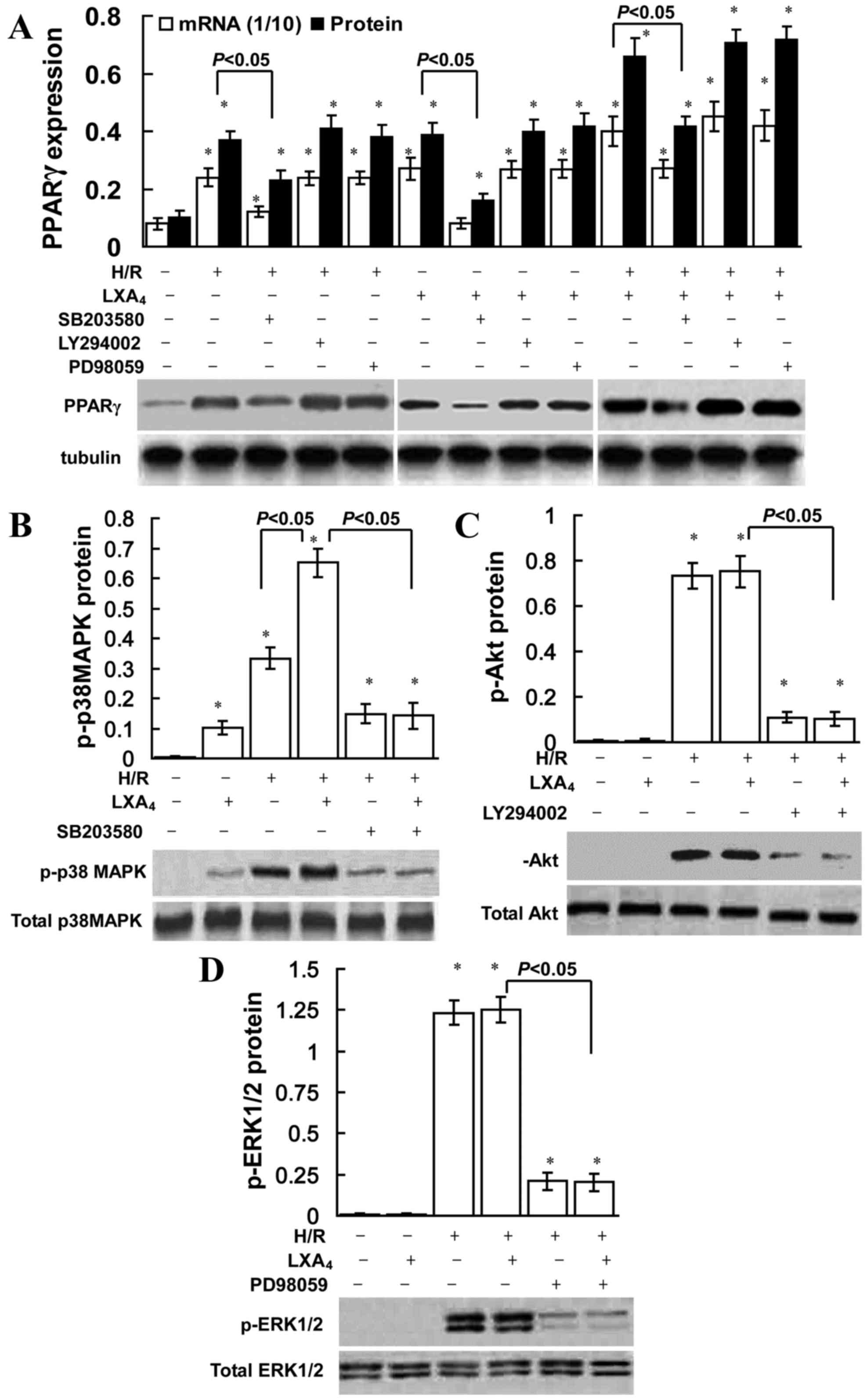
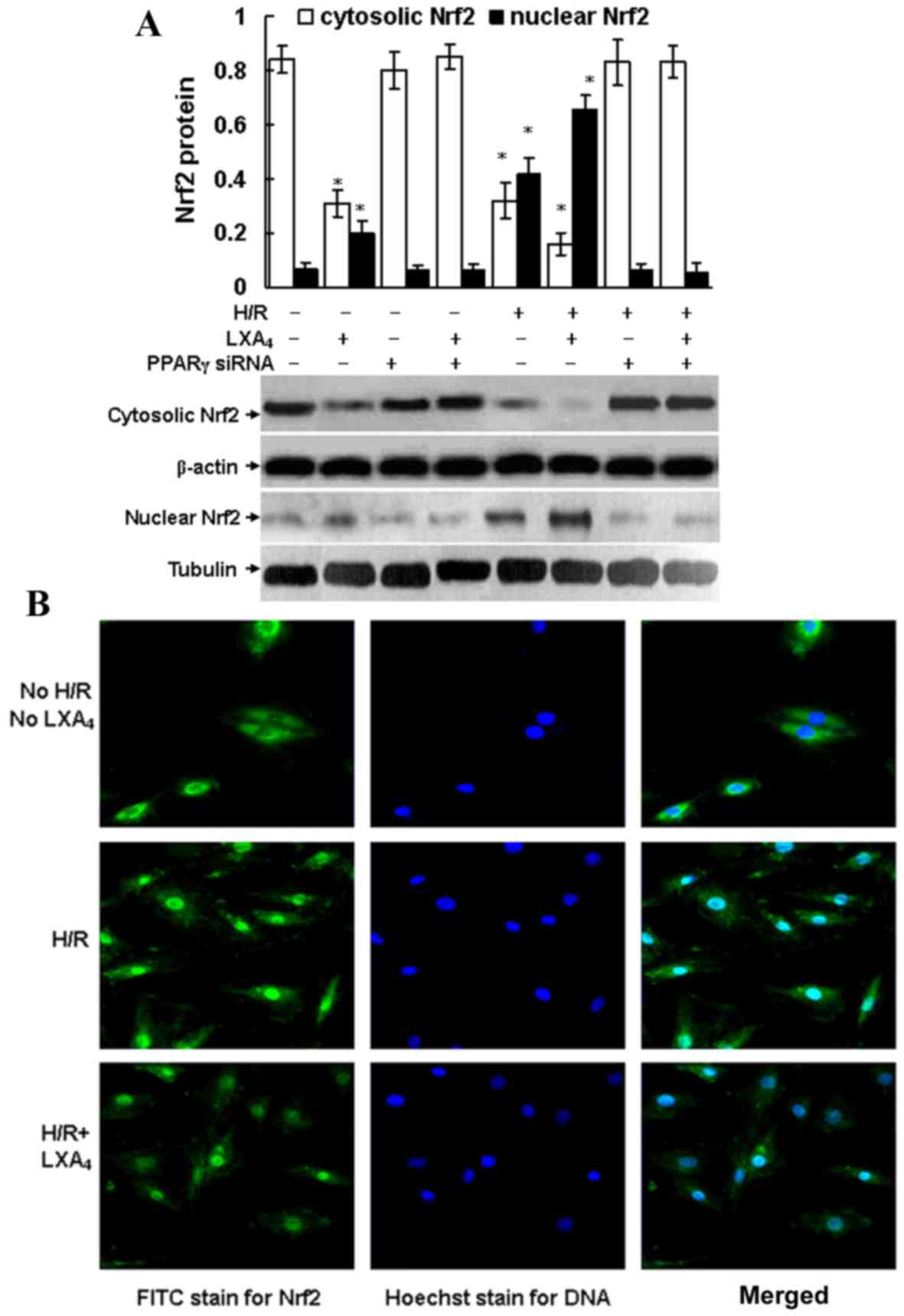
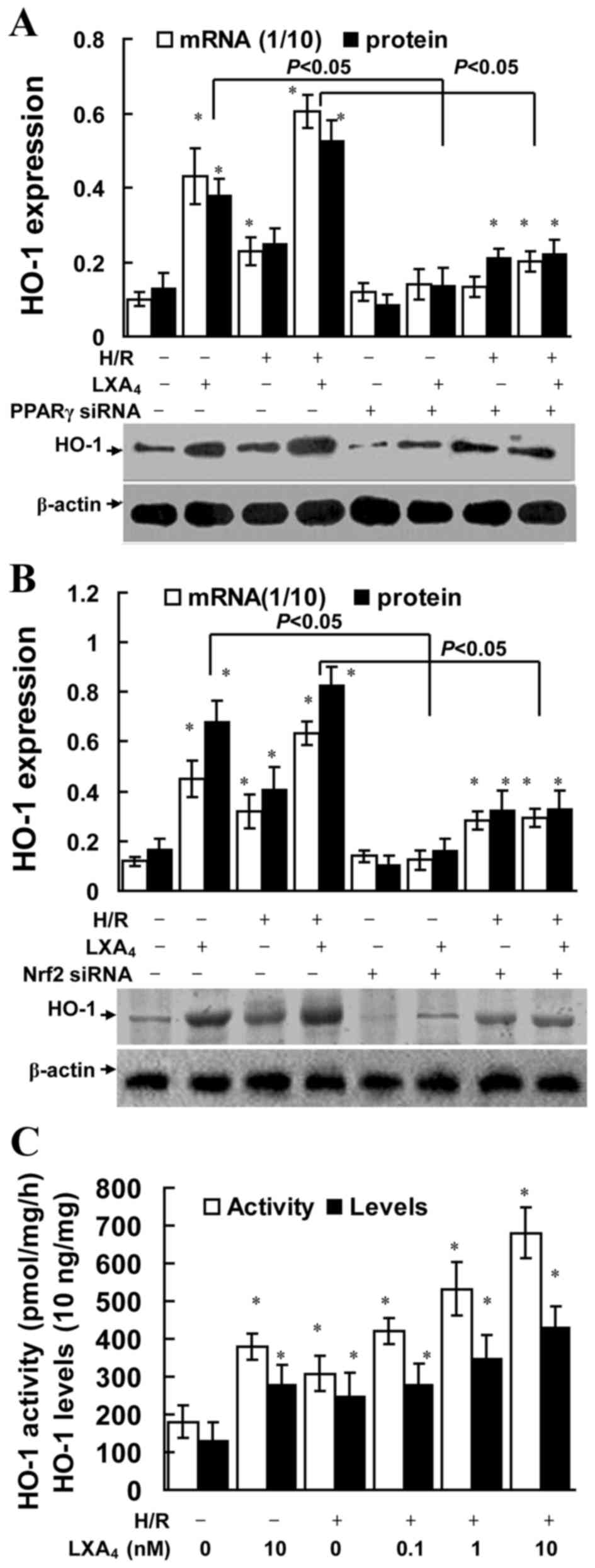
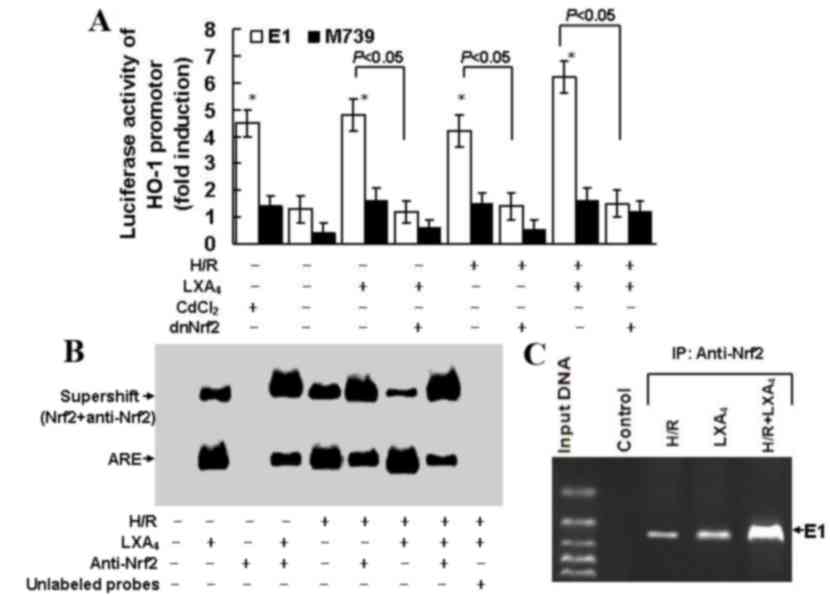
|
1
|
Wen X, Murugan R, Peng Z and Kellum JA:
Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury: A new perspective. Contrib
Nephrol. 165:39–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chok MK, Ferlicot S, Conti M, Almolki A,
Dürrbach A, Loric S, Benoît G, Droupy S and Eschwège P:
Renoprotective potency of heme oxygenase-1 induction in rat renal
ischemia-reperfusion. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 8:252–259.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nath KA: Heme oxygenase-1: A provenance
for cytoprotective pathways in the kidney and other tissues. Kidney
Int. 70:432–443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Volti G, Sorrenti V, Murabito P,
Galvano F, Veroux M, Gullo A, Acquaviva R, Stacchiotti A, Bonomini
F, Vanella L and Di Giacomo C: Pharmacological induction of heme
oxygenase-1 inhibits iNOS and oxidative stress in renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc. 39:2986–2991. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iglesias P and Diez JJ: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists in renal disease.
Eur J Endocrinol. 154:613–621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reel B, Guzeloglu M, Bagriyanik A, Atmaca
S, Aykut K, Albayrak G and Hazan E: The effects of PPAR-γ agonist
pioglitazone on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg
Res. 182:176–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miglio G, Rosa AC, Rattazzi L, Grange C,
Collino M, Camussi G and Fantozzi R: The subtypes of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors expressed by human podocytes and
their role in decreasing podocyte injury. Br J Pharmacol.
162:111–125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ragab D, Abdallah DM and El-Abhar HS:
Cilostazol renoprotective effect: Modulation of PPAR-γ, NGAL, KIM-1
and IL-18 underlies its novel effect in a model of
ischemia-reperfusion. PLoS One. 9:e953132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh JP, Singh AP and Bhatti R: Explicit
role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in gallic
acid-mediated protection against ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute
kidney injury in rats. J Surg Res. 187:631–639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu QQ, Wang Y, Senitko M, Meyer C, Wigley
WC, Ferguson DA, Grossman E, Chen J, Zhou XJ, Hartono J, et al:
Bardoxolone methyl (BARD) ameliorates ischemic AKI and increases
expression of protective genes Nrf2, PPARγ and HO-1. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 300:F1180–F1192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Serhan CN and Chiang N: Endogenous
pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators: A new
pharmacologic genus. Br J Pharmacol. 153 Suppl 1:S200–S215. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nascimento-Silva V, Arruda MA,
Barja-Fidalgo C and Fierro IM: Aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 blocks
reactive oxygen species generation in endothelial cells: A novel
antioxidative mechanism. Thromb Haemost. 97:88–98. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leonard MO, Nannan K, Burne MJ, Lappin DW,
Doran P, Coleman P, Stenson C, Taylor C, Daniels F, Godson C, et
al: 15-Epi-15-(para-fluorophenoxy)-lipoxin A(4)-methyl ester, a
synthetic analogue of 15-epi-lipoxin A(4), is protective in
experimental ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol.
13:1657–1662. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kieran NE, Doran PP, Connolly SB, Greenan
MC, Higgins DF, Leonard M, Godson C, Taylor CT, Henger A, Kretzler
M, et al: Modification of the transcriptomic response to renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury by lipoxin analog. Kidney Int.
64:480–492. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nascimento-Silva V, Arruda MA,
Barja-Fidalgo C, Villela CG and Fierro IM: Novel lipid mediator
aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 induces heme oxygenase-1 in
endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 289:C557–C563. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Biteman B, Hassan IR, Walker E, Leedom AJ,
Dunn M, Seta F, Laniado-Schwartzman M and Gronert K:
Interdependence of lipoxin A4 and heme-oxygenase in
counter-regulating inflammation during corneal wound healing. FASEB
J. 21:2257–2266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin SW, Zhang L, Lian QQ, Liu D, Wu P, Yao
SL and Ye DY: Posttreatment with aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4
analog attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in
mice: The role of heme oxygenase-1. Anesth Analg. 104:369–377.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen XQ, Wu SH, Zhou Y and Tang YR:
Lipoxin A4-induced heme oxygenase-1 protects cardiomyocytes against
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via p38 MAPK activation and Nrf2/ARE
complex. PLoS One. 8:e671202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen XQ, Wu SH, Zhou Y and Tang YR:
Involvement of K+ channel-dependent pathways in lipoxin A4-induced
protective effects on hypoxia/reoxygenation injury of
cardiomyocytes. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
88:391–397. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sobrado M, Pereira MP, Ballesteros I,
Hurtado O, Fernández-López D, Pradillo JM, Caso JR, Vivancos J,
Nombela F, Serena J, et al: Synthesis of lipoxin A4 by
5-lipoxygenase mediates PPARgamma-dependent, neuroprotective
effects of rosiglitazone in experimental stroke. J Neurosci.
29:3875–3884. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weinberger B, Quizon C, Vetrano AM, Archer
F, Laskin JD and Laskin DL: Mechanisms mediating reduced
responsiveness of neonatal neutrophils to lipoxin A4. Pediatr Res.
64:393–398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alam J and Cook JL: Transcriptional
regulation of the heme oxygenase-1 gene via the stress response
element pathway. Curr Pharm Des. 9:2499–2511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen JC, Huang KC and Lin WW: HMG-CoA
reductase inhibitors upregulate heme oxygenase-1 expression in
murine RAW264.7 macrophages via ERK, p38 MAPK and protein kinase G
pathways. Cell Signal. 18:32–39. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Masuya Y, Hioki K, Tokunaga R and Taketani
S: Involvement of the tyrosine phosphorylation pathway in induction
of human heme oxygenase-1 by hemin, sodium arsenite, and cadmium
chloride. J Biochem. 124:628–633. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu XM, Peyton KJ, Ensenat D, Wang H,
Hannink M, Alam J and Durante W: Nitric oxide stimulates heme
oxygenase-1 gene transcription via the Nrf2/ARE complex to promote
vascular smooth muscle cell survival. Cardiovasc Res. 75:381–389.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McMahon B, Stenson C, McPhillips F,
Fanning A, Brady HR and Godson C: Lipoxin A4 antagonizes the
mitogenic effects of leukotriene D4 in human renal mesangial cells.
Differential activation of MAP kinases through distinct receptors.
J Biol Chem. 275:27566–27575. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu SH, Wu XH, Lu C, Dong L and Chen ZQ:
Lipoxin A4 inhibits proliferation of human lung fibroblasts induced
by connective tissue growth factor. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
34:65–72. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu SH, Wu XH, Lu C, Dong L, Zhou GP and
Chen ZQ: Lipoxin A4 inhibits connective tissue growth
factor-induced production of chemokines in rat mesangial cells.
Kidney Int. 69:248–256. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu SH, Liao PY, Dong L and Chen ZQ: Signal
pathway involved in inhibition by lipoxin A(4) of production of
interleukins in endothelial cells by lipopolysaccharide. Inflamm
Res. 57:430–437. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu SH, Zhang YM, Tao HX and Dong L:
Lipoxin A(4) inhibits transition of epithelial to mesenchymal cells
in proximal tubules. Am J Nephrol. 32:122–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pang H, Yi P, Wu P, Liu Z, Liu Z, Gong J,
Hao H, Cai L, Ye D and Huang Y: Effect of lipoxin A4 on
lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial hyperpermeability. Sci World
Journal. 11:1056–1067. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhao X, Gonzales N and Aronowski J:
Pleiotropic role of PPARγ in intracerebral hemorrhage: An intricate
system involving Nrf2, RXR, and NF-κB. CNS Neurosci Ther.
21:357–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kronke G, Kadl A, Ikonomu E, Bluml S,
Fürnkranz A, Sarembock IJ, Bochkov VN, Exner M, Binder BR and
Leitinger N: Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human vascular cells
is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:1276–1282. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ptasinska A, Wang S, Zhang J, Wesley RA
and Danner RL: Nitric oxide activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma through a p38 MAPK signaling
pathway. FASEB J. 21:950–961. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta deltaC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kieran NE, Maderna P and Godson C:
Lipoxins: Potential anti-inflammatory, proresolution and
antifibrotic mediators in renal disease. Kidney Int. 65:1145–1154.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ohse T, Ota T, Kieran N, Godson C, Yamada
K, Tanaka T, Fujita T and Nangaku M: Modulation of
interferon-induced genes by lipoxin analogue in anti-glomerular
membrane nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:919–927. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Börgeson E, Docherty NG, Murphy M, Rodgers
K, Ryan A, O'Sullivan TP, Guiry PJ, Goldschmeding R, Higgins DF and
Godson C: Lipoxin A4 and benzo-lipoxin A4 attenuate experimental
renal fibrosis. FASEB J. 25:2967–2979. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brennan EP, Nolan KA, Börgeson E, Gough
OS, McEvoy CM, Docherty NG, Higgins DF, Murphy M, Sadlier DM,
Ali-Shah ST, et al: Lipoxins attenuate renal fibrosis by inducing
let-7c and suppressing TGFβR1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:627–637. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng LL, Zhong L, Lei JR, Tang L, Liu L,
Xie SQ and Liao XH: Protective effect of lipoxin A4 against
rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Xi Bao Yu Fen
Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:907–910. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu SH, Wu XH, Liao PY and Dong L: Signal
transduction involved in protective effects of
15(R/S)-methyl-lipoxin A(4) on mesangioproliferative nephritis in
rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 76:173–180. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park SY, Bae JU, Hong KW and Kim CD: HO-1
induced by cilostazol protects against TNF-α-associated
cytotoxicity via a PPAR-γ-dependent pathway in human endothelial
cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 15:83–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mann GE, Niehueser-Saran J, Watson A, Gao
L, Ishii T, de Winter P and Siow RC: Nrf2/ARE regulated antioxidant
gene expression in endothelial and smooth muscle cells in oxidative
stress: Implications for atherosclerosis and preeclampsia. Sheng Li
Xue Bao. 59:117–127. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N and Biswal S:
Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the
Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:89–116.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|