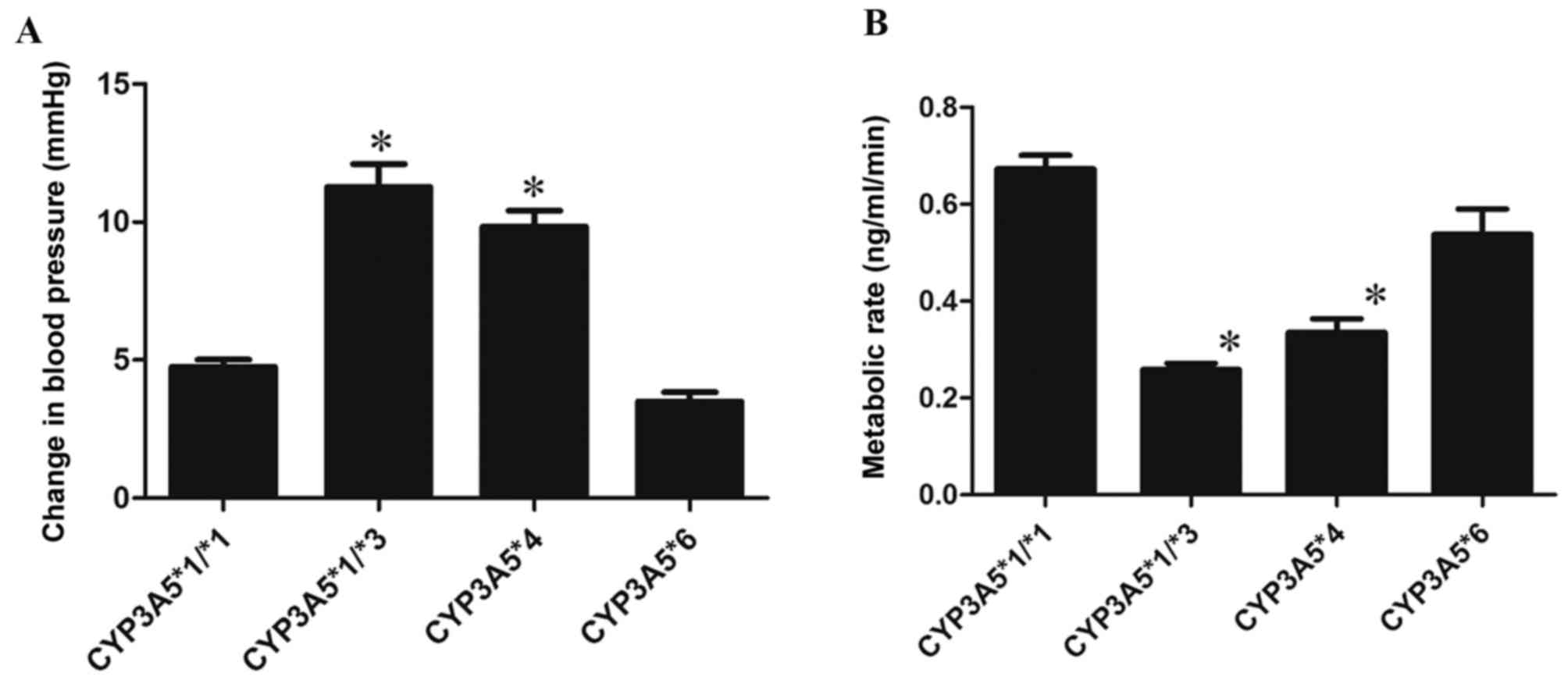
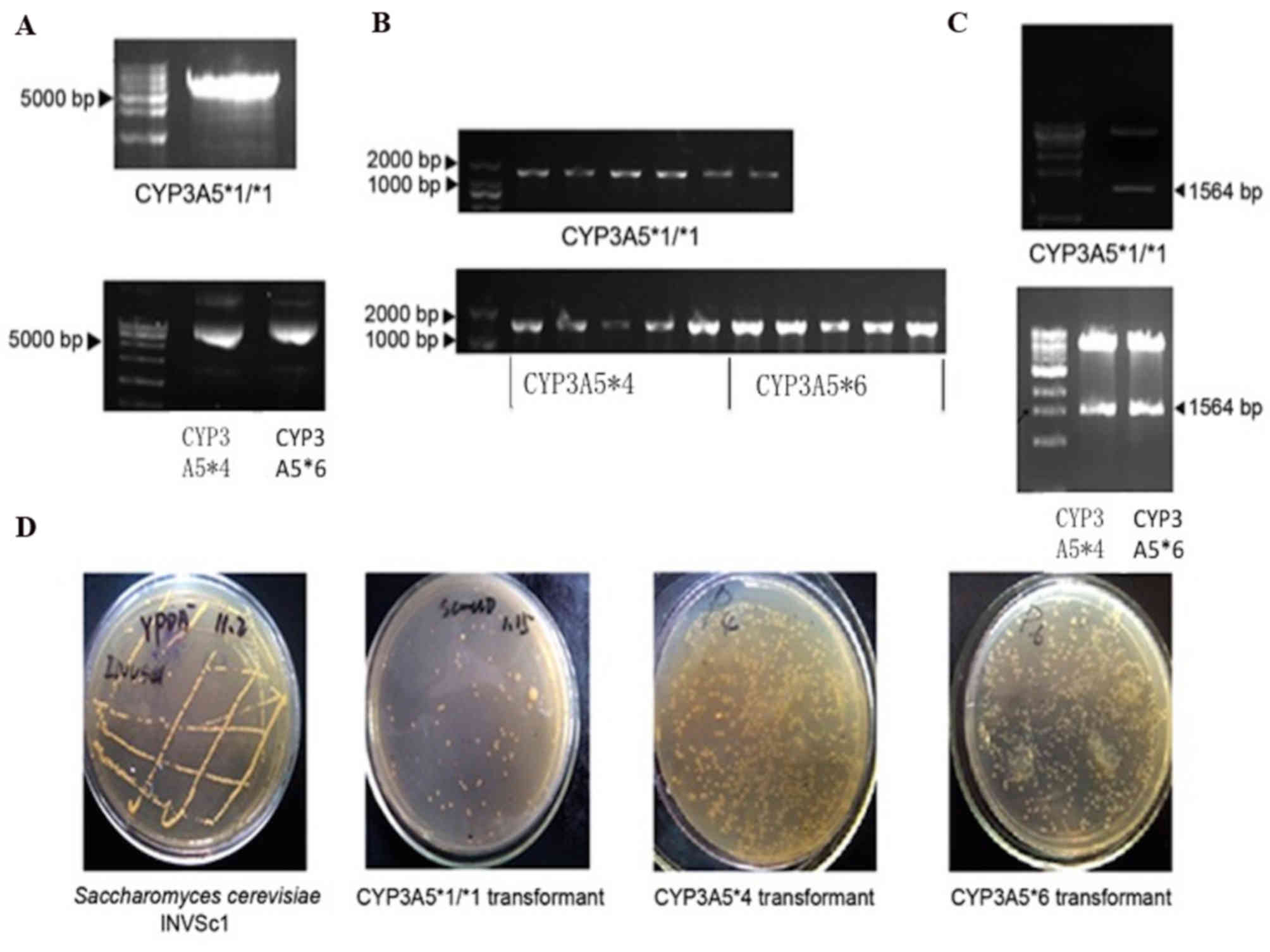
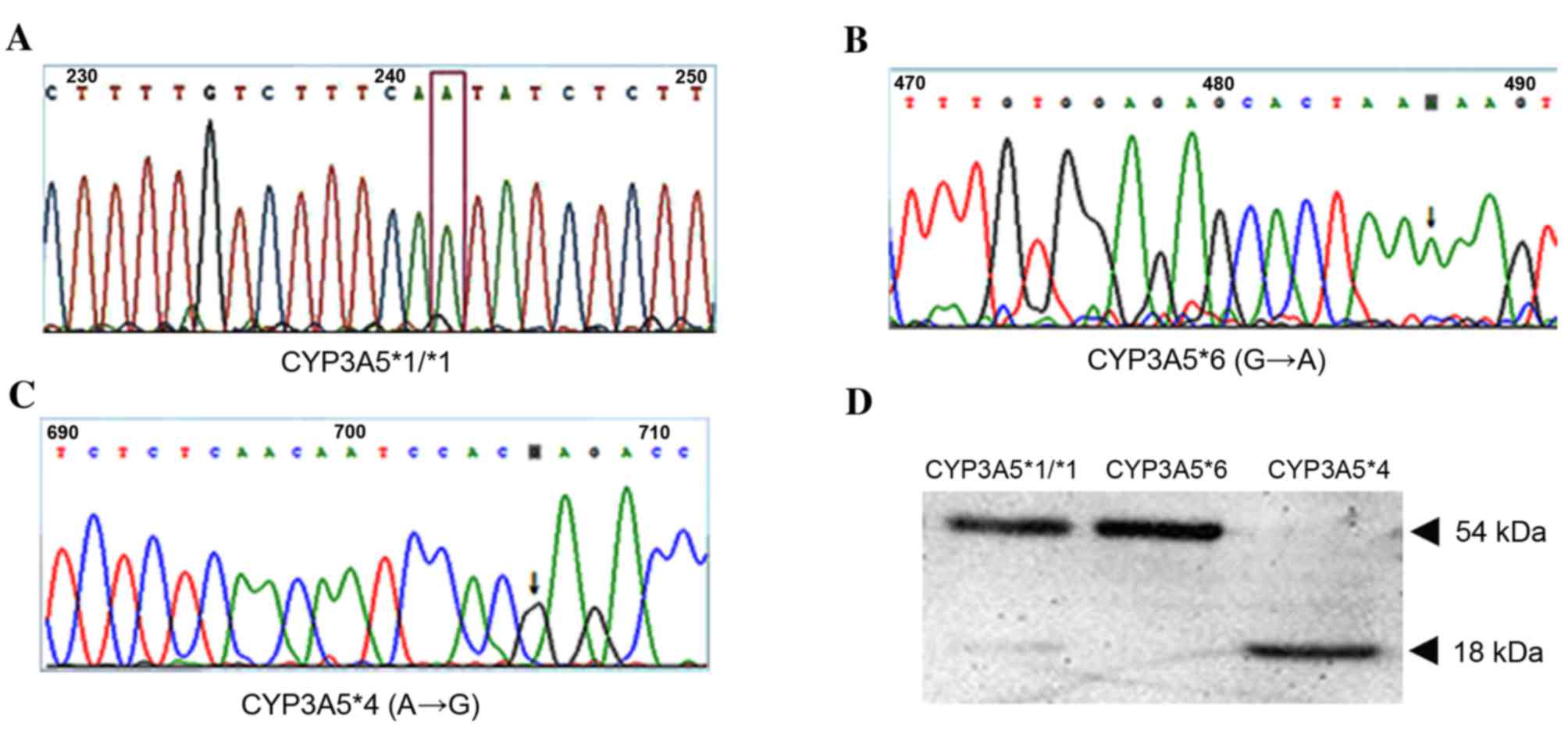
|
1
|
Emoto C and Iwasaki K: Approach to predict
the contribution of cytochrome P450 enzymes to drug metabolism in
the early drug-discovery stage: The effect of the expression of
cytochrome b(5) with recombinant P450 enzymes. Xenobiotica.
37:986–999. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang YP, Zuo XC, Huang ZJ, Cai JJ, Wen J,
Duan DD and Yuan H: CYP3A5 polymorphism, amlodipine and
hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 28:145–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin YS, Dowling AL, Quigley SD, Farin FM,
Zhang J, Lamba J, Schuetz EG and Thummel KE: Co-regulation of
CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 and contribution to hepatic and intestinal
midazolam metabolism. Mol Pharmacol. 62:162–172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shin J, Pauly DF, Pacanowski MA, Langaee
T, Frye RF and Johnson JA: Effect of cytochrome P450 3A5 genotype
on atorvastatin pharmacokinetics and its interaction with
clarithromycin. Pharmacotherapy. 31:942–950. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kuehl P, Zhang J, Lin Y, Lamba J, Assem M,
Schuetz J, Watkins PB, Daly A, Wrighton SA, Hall SD, et al:
Sequence diversity in CYP3A promoters and characterization of the
genetic basis of polymorphic CYP3A5 expression. Nat Genet.
27:383–391. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Williams JA, Ring BJ, Cantrell VE, Jones
DR, Eckstein J, Ruterbories K, Hamman MA, Hall SD and Wrighton SA:
Comparative metabolic capabilities of CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7.
Drug Metab Dispos. 30:883–891. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Walker DK, Humphrey MJ and Smith DA:
Importance of metabolic stability and hepatic distribution to the
pharmacokinetic profile of amlodipine. Xenobiotica. 24:243–250.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sugimoto K, Uno T and Tateishi T: Effects
of the CYP3A5 genotype on omeprazole sulfoxidation in CYP2C19 PMs.
Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 64:583–587. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim KA, Park PW, Lee OJ, Choi SH, Min BH,
Shin KH, Chun BG, Shin JG and Park JY: Effect of CYP3A5*3 genotype
on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of amlodipine in
healthy Korean subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 80:646–656. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Elmachad M, Elkabbaj D, Elkerch F, Laarabi
FZ, Barkat A, Oualim Z and Sefiani A: Frequencies of CYP3A5*1/*3
variants in a Moroccan population and effect on tacrolimus daily
dose requirements in renal transplant patients. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 16:644–647. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Provenzani A, Notarbartolo M, Labbozzetta
M, Poma P, Vizzini G, Salis P, Caccamo C, Bertani T, Palazzo U,
Polidori P, et al: Influence of CYP3A5 and ABCB1 gene polymorphisms
and other factors on tacrolimus dosing in Caucasian liver and
kidney transplant patients. Int J Mol Med. 28:1093–1102.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Amundsen R, Åsberg A, Ohm IK and
Christensen H: Cyclosporine A- and tacrolimus-mediated inhibition
of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos. 40:655–661. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo C, Pei QI, Tan H, Huang Z, Yuan H and
Yang G: Effects of genetic factors on the pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of amlodipine in primary hypertensive patients.
Biomed Rep. 3:195–200. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi M, Eren-Dogu ZF, Colangelo C,
Cottrell J, Hoopmann MR, Kapp EA, Kim S, Lam H, Neubert TA,
Palmblad M, et al: ABRF proteome informatics research group (iPRG)
2015 study: Detection of differentially abundant proteins in
label-free quantitative LC-MS/MS experiments. J Proteome Res Jan.
3:2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
15
|
Beresford AP, Macrae PV, Alker D and
Kobylecki RJ: Biotransformation of amlodipine. Identification and
synthesis of metabolites found in rat, dog and human
urine/confirmation of structures by gas chromatography-mass
spectrometry and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Arzneimittelforschung. 39:201–209. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chennuru LN, Choppari T, Nandula RP, Zhang
T and Franco P: Direct separation of pregabalin enantiomers using a
zwitterionic chiral selector by high performance liquid
chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry and ultraviolet
detection. Molecules. 21:E15782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Colson CA, Cornelis PE, Digneffe CS and
Walon C: Genetically engineered microorganisms for massive
production of amylolytic enzymes and process for preparing same. US
Patend 4469791 A. Filed February 13, 1981; issued September 4.
1984.
|
|
18
|
Narita V, Widyanto RM, Pambudi S and
Sudiro TM: Cloning of dengue virus type 3 (Indonesian Strain
D3-1703) non structural-1 gene into pYES2/CT vector. Makara Sains.
15:173–178. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Costa IM, Schultz L, de Araujo Bianchi
Pedra B, Leite MS, Farsky SH, De Oliveira MA, Pessoa A and Monteiro
G: Recombinant L-asparaginase 1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: An
allosteric enzyme with antineoplastic activity. Sci Rep.
6:362392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang Y, Liu XL, Wen J, Huang LH, Lu Y,
Miao RJ, Liu X, Li Y, Xing XW and Yuan H: Downregulation of the β1
adrenergic receptor in the myocardium results in insensitivity to
metoprolol and reduces blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Mol Med Rep. 15:703–711. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guengerich FP, Brian WR, Iwasaki M, Sari
MA, Bäärnhielm C and Berntsson P: Oxidation of dihydropyridine
calcium channel blockers and analogues by human liver cytochrome
P-450 IIIA4. J Med Chem. 34:1838–1844. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ha HR, Chen J, Freiburghaus AU and Follath
F: Metabolism of theophylline by cDNA-expressed human cytochromes
P-450. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 39:321–326. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ho H, Pinto A, Hall SD, Flockhart DA, Li
L, Skaar TC, Cadman P, O'Connor DT, Wagner U, Fineberg NS and
Weinberger MH: Association between the CYP3A5 genotype and blood
pressure. Hypertension. 45:294–298. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Granvil CP, Yu AM, Elizondo G, Akiyama TE,
Cheung C, Feigenbaum L, Krausz KW and Gonzalez FJ: Expression of
the human CYP3A4 gene in the small intestine of transgenic mice: In
vitro metabolism and pharmacokinetics of midazolam. Drug Metab
Dispos. 31:548–558. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang L, Miyaki K, Wang W and Muramatsu M:
CYP3A5 polymorphism and sensitivity of blood pressure to dietary
salt in Japanese men. J Hum Hypertens. 24:345–350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stopher DA, Beresford AP, Macrae PV and
Humphrey MJ: The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of amlodipine in
humans and animals. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 12 Suppl 7:S55–S59.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Faulkner JK, McGibney D, Chasseaud LF,
Perry JL and Taylor IW: The pharmacokinetics of amlodipine in
healthy volunteers after single intravenous and oral doses and
after 14 repeated oral doses given once daily. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
22:21–25. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Balram C, Zhou Q, Cheung YB and Lee EJ:
CYP3A5*3 and *6 single nucleotide polymorphisms in three distinct
Asian populations. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 59:123–126. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fukuen S, Fukuda T, Maune H, Ikenaga Y,
Yamamoto I, Inaba T and Azuma J: Novel detection assay by PCR-RFLP
and frequency of the CYP3A5 SNPs, CYP3A5*3 and *6, in a Japanese
population. Pharmacogenetics. 12:331–334. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thompson EE, Kuttab-Boulos H, Witonsky D,
Yang L, Roe BA and Di Rienzo A: CYP3A variation and the evolution
of salt-sensitivity variants. Am J Hum Genet. 75:1059–1069. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|