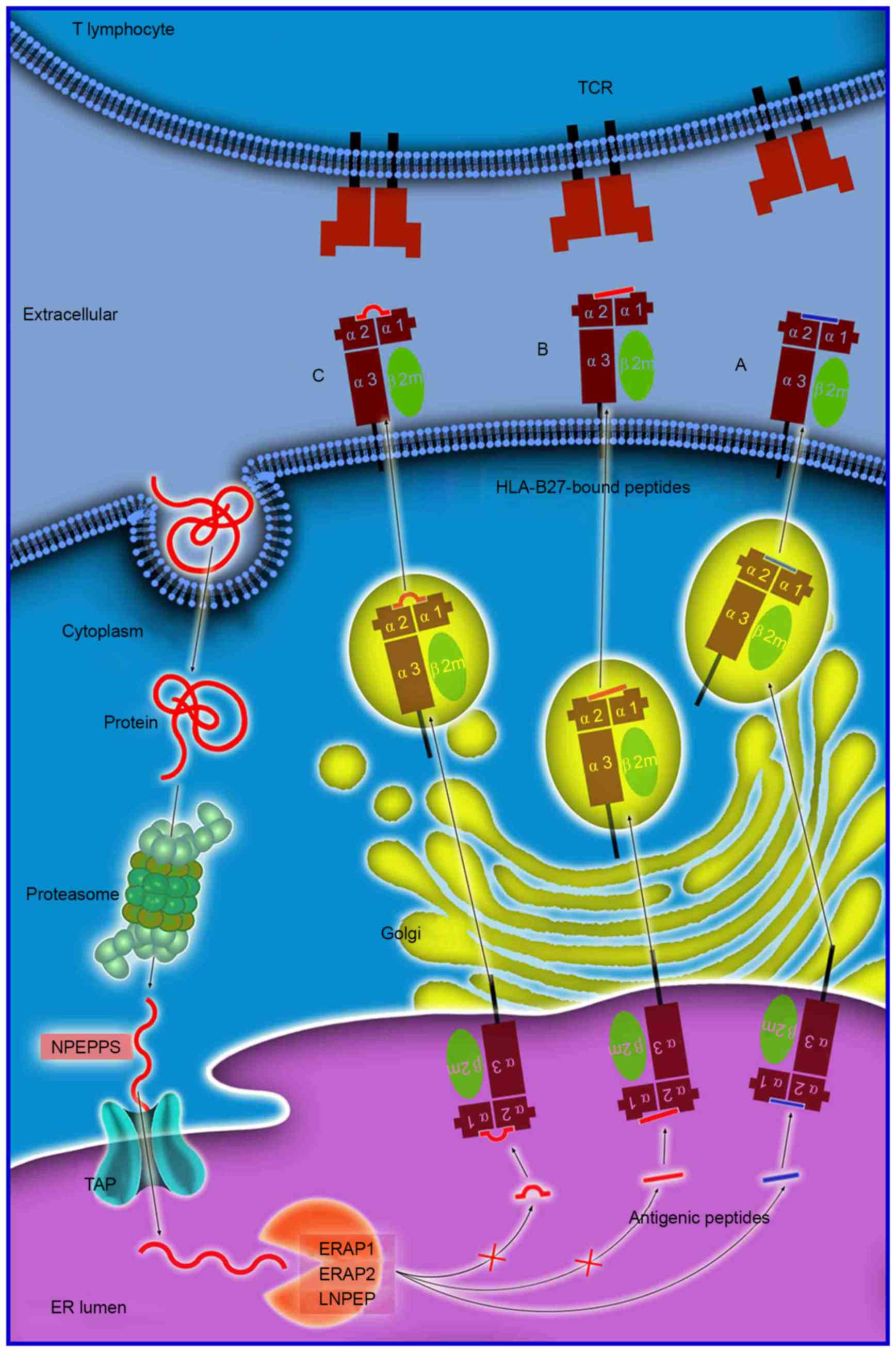
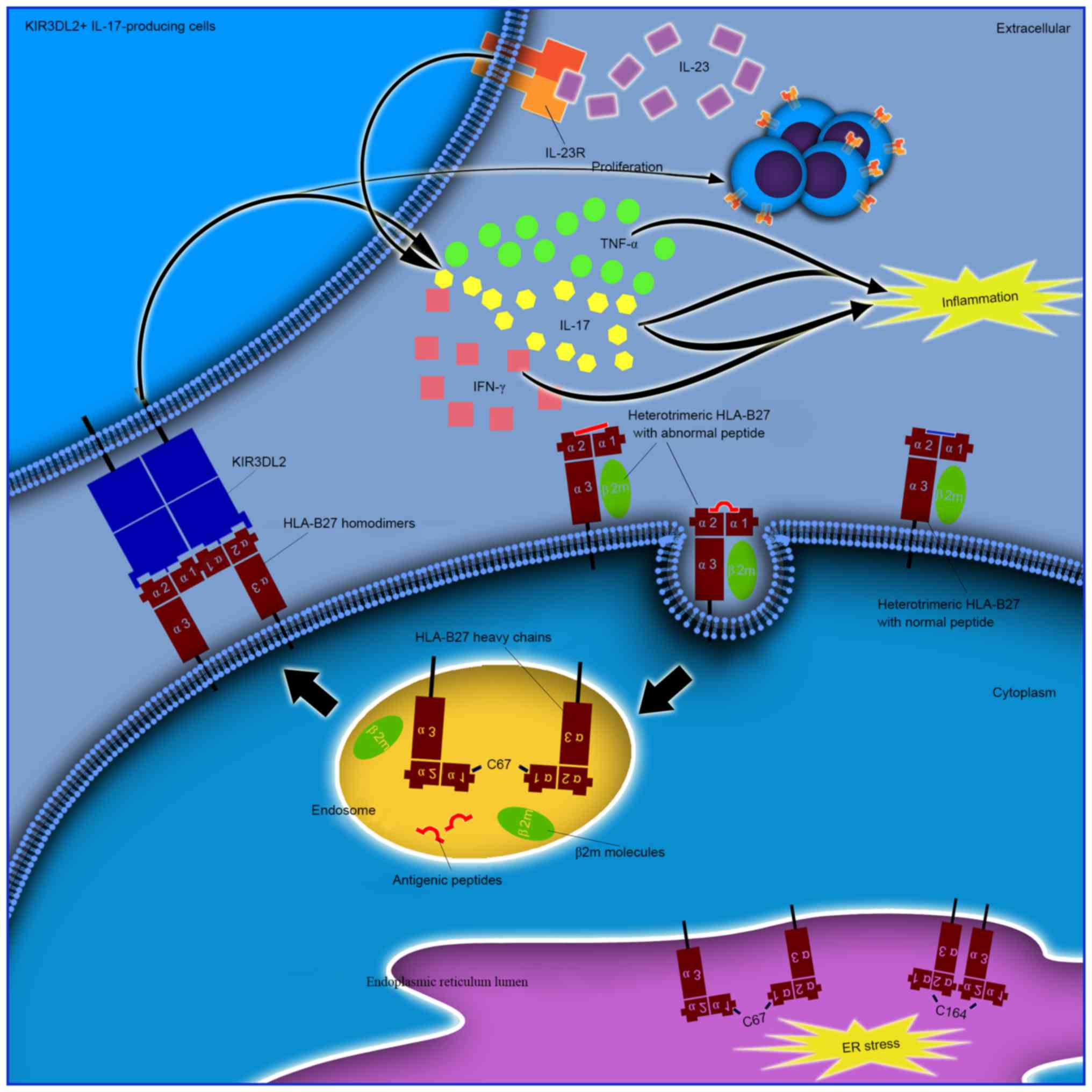
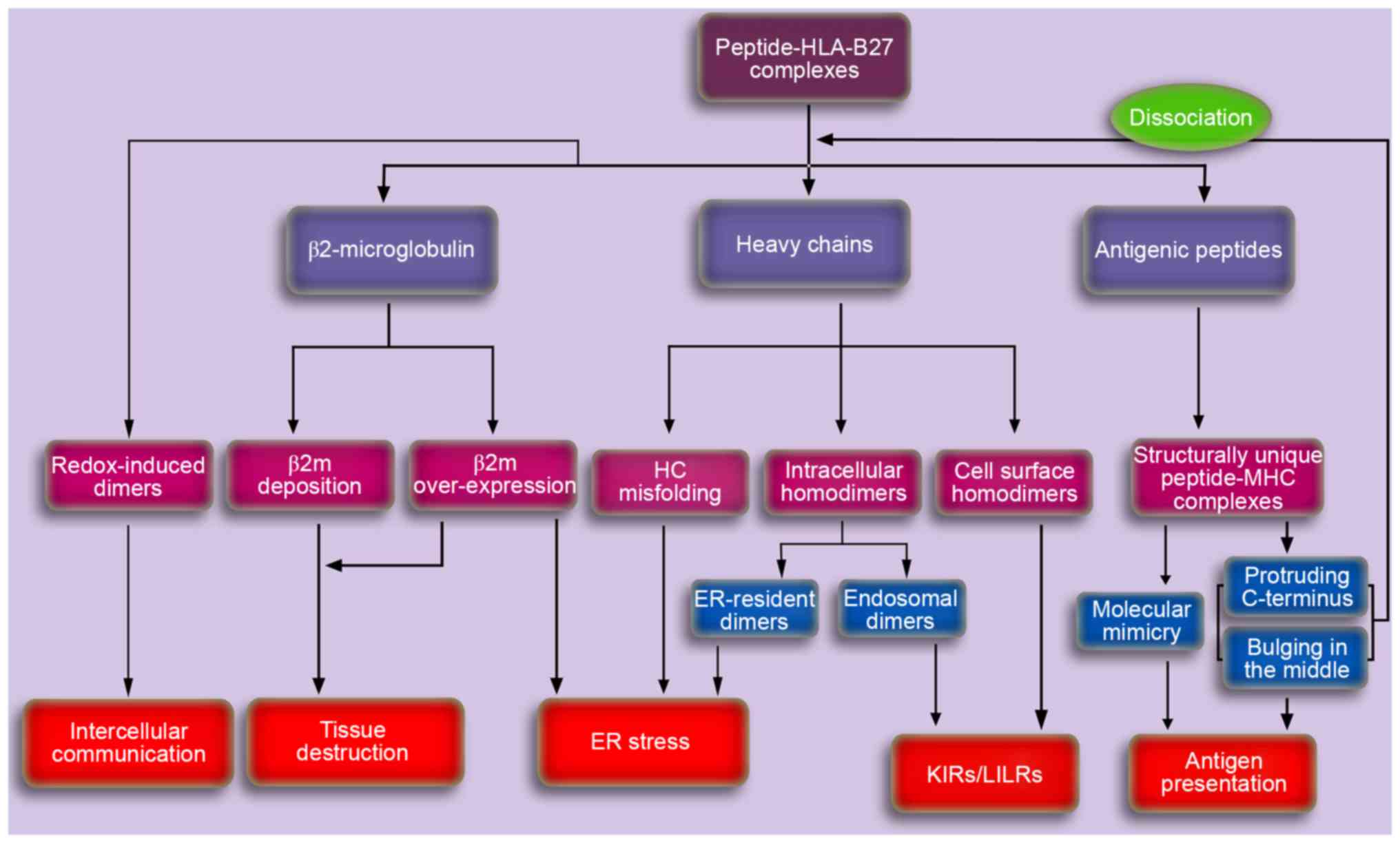
|
1
|
Dougados M and Baeten D:
Spondyloarthritis. Lancet. 377:2127–2137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cho H, Kim T, Kim TH, Lee S and Lee KH:
Spinal mobility, vertebral squaring, pulmonary function, pain,
fatigue, and quality of life in patients with ankylosing
spondylitis. Ann Rehabil Med. 37:675–682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Braun J and Sieper J: Ankylosing
spondylitis. Lancet. 369:1379–1390. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Végvári A, Szabó Z, Szántó S, Glant TT,
Mikecz K and Szekanecz Z: The genetic background of ankylosing
spondylitis. Joint Bone Spine. 76:623–628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brewerton DA, Hart FD, Nicholls A, Caffrey
M, James DC and Sturrock RD: Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27.
Lancet. 1:904–907. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chatzikyriakidou A, Voulgari PV and Drosos
AA: What is the role of HLA-B27 in spondyloarthropathies? Autoimmun
Rev. 10:464–468. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
International Genetics of Ankylosing
Spondylitis Consortium (IGAS), ; Cortes A, Hadler J, Pointon JP,
Robinson PC, Karaderi T, Leo P, Cremin K, Pryce K, Harris J, et al:
Identification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis
through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat Genet.
45:730–738. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sheehan NJ: HLA-B27: What's new?
Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:621–631. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khan MA: Polymorphism of HLA-B27: 105
subtypes currently known. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 15:3622013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brown MA: Progress in the genetics of
ankylosing spondylitis. Brief Funct Genomics. 10:249–257. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Warde N: Spondyloarthropathies: HLA-B27
and ERAP1 contribute to ankylosing spondylitis via aberrant peptide
processing and presentation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 7:4982011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Evans DM, Spencer CC, Pointon JJ, Su Z,
Harvey D, Kochan G, Oppermann U, Dilthey A, Pirinen M, Stone MA, et
al: Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis
implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease
susceptibility. Nat Genet. 43:761–767. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nguyen TT, Chang SC, Evnouchidou I, York
IA, Zikos C, Rock KL, Goldberg AL, Stratikos E and Stern LJ:
Structural basis for antigenic peptide precursor processing by the
endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
18:604–613. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yewdell JW: DRiPs solidify: Progress in
understanding endogenous MHC class I antigen processing. Trends
Immunol. 32:548–558. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Madden DR: The three-dimensional structure
of peptide-MHC complexes. Annu Rev Immunol. 13:587–622. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Colbert RA, Tran TM and Layh-Schmitt G:
HLA-B27 misfolding and ankylosing spondylitis. Mol Immunol.
57:44–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lenart I, Guiliano DB, Burn G, Campbell
EC, Morley KD, Fussell H, Powis SJ and Antoniou AN: The MHC Class I
heavy chain structurally conserved cysteines 101 and 164
participate in HLA-B27 dimer formation. Antioxid Redox Signal.
16:33–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alvarez-Navarro C and López de Castro JA:
ERAP1 structure, function and pathogenetic role in ankylosing
spondylitis and other MHC-associated diseases. Mol Immunol.
57:12–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Colbert RA: The immunobiology of HLA-B27:
Variations on a theme. Curr Mol Med. 4:21–30. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raposo G and Stoorvogel W: Extracellular
vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol.
200:373–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lynch S, Santos SG, Campbell EC, Nimmo AM,
Botting C, Prescott A, Antoniou AN and Powis SJ: Novel MHC class I
structures on exosomes. J Immunol. 183:1884–1891. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lorente E, Infantes S, Abia D, Barnea E,
Beer I, García R, Lasala F, Jiménez M, Mir C, Morreale A, et al: A
viral, transporter associated with antigen processing
(TAP)-independent, high affinity ligand with alternative
interactions endogenously presented by the nonclassical human
leukocyte antigen E class I molecule. J Biol Chem. 287:34895–34903.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen B, Li D and Xu W: Association of
ankylosing spondylitis with HLA-B27 and ERAP1: Pathogenic role of
antigenic peptide. Med Hypotheses. 80:36–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lévy F, Burri L, Morel S, Peitrequin AL,
Lévy N, Bachi A, Hellman U, Van den Eynde BJ and Servis C: The
final N-terminal trimming of a subaminoterminal proline-containing
HLA class I-restricted antigenic peptide in the cytosol is mediated
by two peptidases. J Immunol. 169:4161–4171. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Antoniou AN, Lenart I and Guiliano DB:
Pathogenicity of misfolded and dimeric HLA-B27 molecules. Int J
Rheumatol. 2011:4868562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dakwar E, Reddy J, Vale FL and Uribe JS: A
review of the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Neurosurg
Focus. 24:E22008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Taurog JD, Dorris ML, Satumtira N, Tran
TM, Sharma R, Dressel R, van den Brandt J and Reichardt HM:
Spondylarthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2-microglobulin-transgenic
rats is not prevented by lack of CD8. Arthritis Rheum.
60:1977–1984. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Collins EJ, Garboczi DN and Wiley DC:
Three-dimensional structure of a peptide extending from one end of
a class I MHC binding site. Nature. 371:626–629. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Probst-Kepper M, Hecht HJ, Herrmann H,
Janke V, Ocklenburg F, Klempnauer J, van den Eynde BJ and Weiss S:
Conformational restraints and flexibility of 14-meric peptides in
complex with HLA-B*3501. J Immunol. 173:5610–5616. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Green KJ, Miles JJ, Tellam J, van Zuylen
WJ, Connolly G and Burrows SR: Potent T cell response to a class
I-binding 13-mer viral epitope and the influence of HLA
micropolymorphism in controlling epitope length. Eur J Immunol.
34:2510–2519. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
York IA, Brehm MA, Zendzian S, Towne CF
and Rock KL: Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) trims
MHC class I-present edpeptides in vivo and plays an important role
in immunodominance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:9202–9207. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hammer GE, Gonzalez F, James E, Nolla H
and Shastri N: In the absence of aminopeptidase ERAAP, MHC class I
molecules present many unstable and highly immunogenic peptides.
Nat Immunol. 8:101–108. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lorente E, García R, Mir C, Barriga A,
Lemonnier FA, Ramos M and López D: Role of metalloproteases in
vaccinia virus epitope processing for transporter associated with
antigen processing (TAP)-independent human leukocyte antigen
(HLA)-B7 class I antigen presentation. J Biol Chem. 287:9990–10000.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schwarz K, De Giuli R, Schmidtke G, Kostka
S, van den Broek M, Kim KB, Crews CM, Kraft R and Groettrup M: The
selective proteasome inhibitors lactacystin and epoxomicin can be
used to either up- or down-regulate antigen presentation at
nontoxic doses. J Immunol. 164:6147–6157. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Allen RL and Trowsdale J: Recognition of
classical and heavy chain forms of HLA-B27 by leukocyte receptors.
Curr Mol Med. 4:59–65. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kollnberger S, Chan A, Sun MY, Chen LY,
Wright C, di Gleria K, McMichael A and Bowness P: Interaction of
HLA-B27 homodimers with KIR3DL1 and KIR3DL2, unlike HLA-B27
heterotrimers, is independent of the sequence of bound peptide. Eur
J Immunol. 37:1313–1322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Allen RL, Raine T, Haude A, Trowsdale J
and Wilson MJ: Leukocyte receptor complex-encoded immunomodulatory
receptors show differing specificity for alternative HLA-B27
structures. J Immunol. 167:5543–5547. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chan AT, Kollnberger SD, Wedderburn LR and
Bowness P: Expansion and enhanced survival of natural killer cells
expressing the killer immunoglobulin-like receptor KIR3DL2 in
spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 52:3586–3595. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bowness P, Ridley A, Shaw J, Chan AT,
Wong-Baeza I, Fleming M, Cummings F, McMichael A and Kollnberger S:
Th17 cells expressing KIR3DL2+ and responsive to HLA-B27 homodimers
are increased in ankylosing spondylitis. J Immunol. 186:2672–2680.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Giles J, Shaw J, Piper C, Wong-Baeza I,
McHugh K, Ridley A, Li D, Lenart I, Antoniou AN, DiGleria K, et al:
HLA-B27 homodimers and free H chains are stronger ligands for
leukocyte Ig-like receptor B2 than classical HLA class I. J
Immunol. 188:6184–6193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wong-Baeza I, Ridley A, Shaw J, Hatano H,
Rysnik O, McHugh K, Piper C, Brackenbridge S, Fernandes R, Chan A,
et al: KIR3DL2 binds to HLA-B27 dimers and free H chains more
strongly than other HLA class I and promotes the expansion of T
cells in ankylosing spondylitis. J Immunol. 190:3216–3224. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dangoria NS, DeLay ML, Kingsbury DJ, Mear
JP, Uchanska-Ziegler B, Ziegler A and Colbert RA: HLA-B27
misfolding is associated with aberrant intermolecular disulfide
bond formation (dimerization) in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol
Chem. 277:23459–23468. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Campbell EC, Antoniou AN and Powis SJ: The
multi-faceted nature of HLA class I dimer molecules. Immunology.
136:380–384. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cauli A, Shaw J, Giles J, Hatano H, Rysnik
O, Payeli S, McHugh K, Dessole G, Porru G, Desogus E, et al: The
arthritis-associated HLA-B*27:05 allele forms more cell surface B27
dimer and free heavy chain ligands for KIR3DL2 than HLA-B*27:09.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 52:1952–1962. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kuśnierczyk P and Majorczyk E: Pas de
quatre: An interaction of HLA-B*27:05 and KIR3DL2 homodimers in
spondyloarthropathies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 52:1931–1912. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rajagopalan S and Long EO: KIR2DL4
(CD158d): An activation receptor for HLA-G. Front Immunol.
3:2582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Antoniou AN, Ford S, Taurog JD, Butcher GW
and Powis SJ: Formation of HLA-B27 homodimers and their
relationship to assembly kinetics. J Biol Chem. 279:8895–8902.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Colbert RA, DeLay ML, Layh-Schmitt G and
Sowders DP: HLA-B27 misfolding and spondyloarthropathies. Prion.
3:15–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Turner MJ, Sowders DP, DeLay ML, Mohapatra
R, Bai S, Smith JA, Brandewie JR, Taurog JD and Colbert RA: HLA-B27
misfolding in transgenic rats is associated with activation of the
unfolded protein response. J Immunol. 175:2438–2348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
DeLay ML, Turner MJ, Klenk EI, Smith JA,
Sowders DP and Colbert RA: HLA-B27 misfolding and the unfolded
protein response augment interleukin-23 production and are
associated with Th17 activation in transgenic rats. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:2633–2643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zeng L, Lindstrom MJ and Smith JA:
Ankylosing spondylitis macrophage production of higher levels of
interleukin-23 in response to lipopolysaccharide without induction
of a significant unfolded protein response. Arthritis Rheum.
63:3807–3817. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ciccia F, Accardo-Palumbo A, Rizzo A,
Guggino G, Raimondo S, Giardina A, Cannizzaro A, Colbert RA,
Alessandro R and Triolo G: Evidence that autophagy, but not the
unfolded protein response, regulates the expression of IL-23 in the
gut of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and subclinical gut
inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 73:1566–1574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Neerinckx B, Carter S and Lories R: IL-23
expression and activation of autophagy in synovium and PBMCs of
HLA-B27 positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Response to:
‘Evidence that autophagy, but not the unfolded protein response,
regulates the expression of IL-23 in the gut of patients with
ankylosing spondylitis and subclinical gut inflammation’ by Ciccia.
Ann Rheum Dis. 73:e682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ciccia F, Bombardieri M, Principato A,
Giardina A, Tripodo C, Porcasi R, Peralta S, Franco V, Giardina E,
Craxi A, et al: Overexpression of interleukin-23, but not
interleukin-17, as an immunologic signature of subclinical
intestinal inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum.
60:955–965. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Appel H, Maier R, Bleil J, Hempfing A,
Loddenkemper C, Schlichting U, Syrbe U and Sieper J: In situ
analysis of interleukin-23- and interleukin-12-positive cells in
the spine of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum.
65:1522–1529. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kenna TJ, Lau MC, Keith P, Ciccia F,
Costello ME, Bradbury L, Low PL, Agrawal N, Triolo G, Alessandro R,
et al: Disease-associated polymorphisms in ERAP1 do not alter
endoplasmic reticulum stress in patients with ankylosing
spondylitis. Genes Immun. 16:35–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shaw J, Hatano H and Kollnberger S: The
biochemistry and immunology of non-canonical forms of HLA-B27. Mol
Immunol. 57:52–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Luthra-Guptasarma M and Singh B: HLA-B27
lacking associated beta2-microglobulin rearranges to auto-display
or cross-display residues 169–181: A novel molecular mechanism for
spondyloarthropathies. FEBS Lett. 575:1–8. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Uchanska-Ziegler B and Ziegler A:
Ankylosing spondylitis: A beta2m-deposition disease? Trends
Immunol. 24:73–76. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tran TM, Dorris ML, Satumtira N,
Richardson JA, Hammer RE, Shang J and Taurog JD: Additional human
beta2-microglobulin curbs HLA-B27 misfolding and promotes arthritis
and spondylitis without colitis in male HLA-B27-transgenic rats.
Arthritis Rheum. 54:1317–1327. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yeremenko N, Paramarta JE and Baeten D:
The interleukin-23/interleukin-17 immune axis as a promising new
target in the treatment of spondyloarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
26:361–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jethwa H and Bowness P: The interleukin
(IL)-23/IL-17 axis in ankylosing spondylitis: New advances and
potentials for treatment. Clin Exp Immunol. 183:30–36. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|