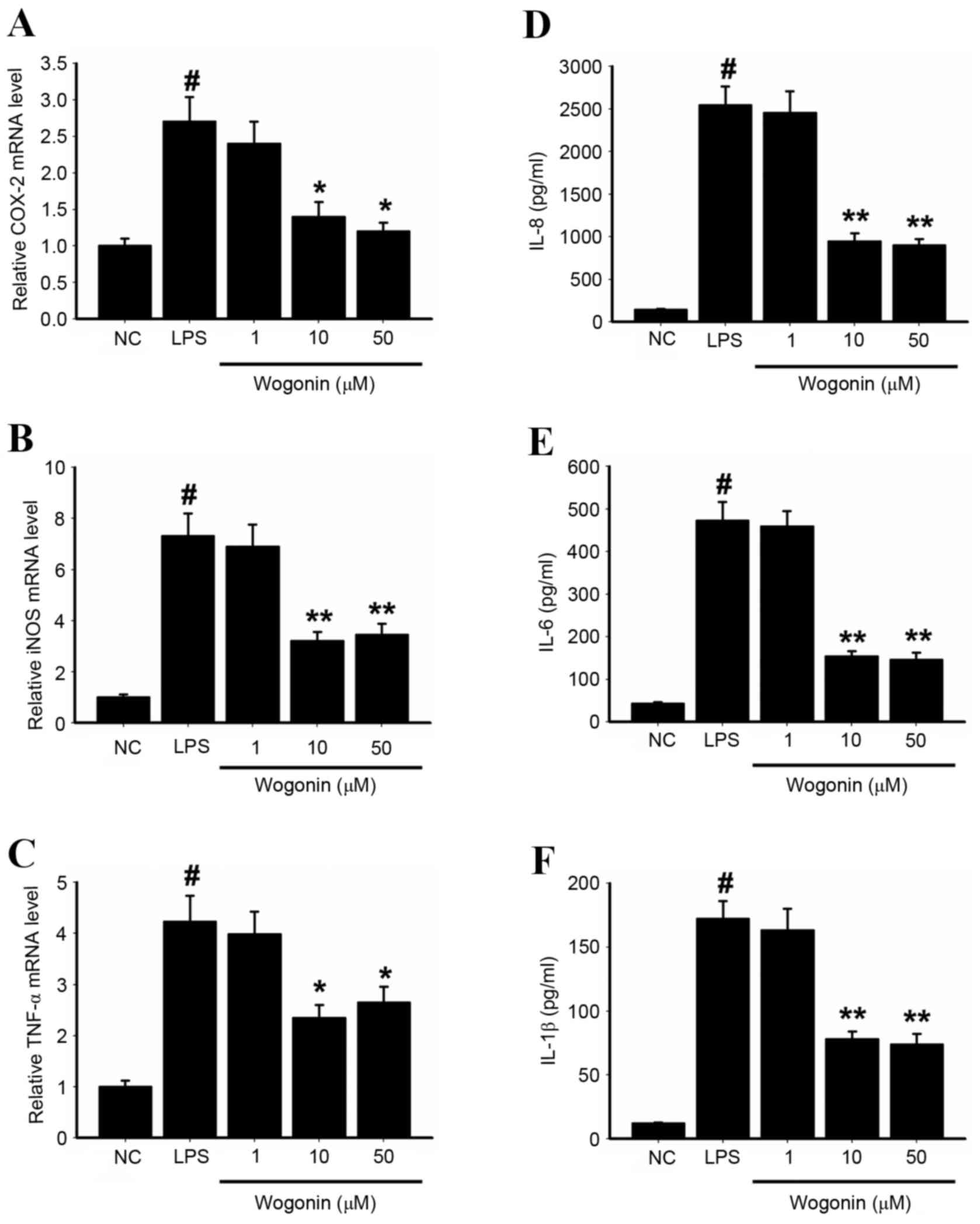
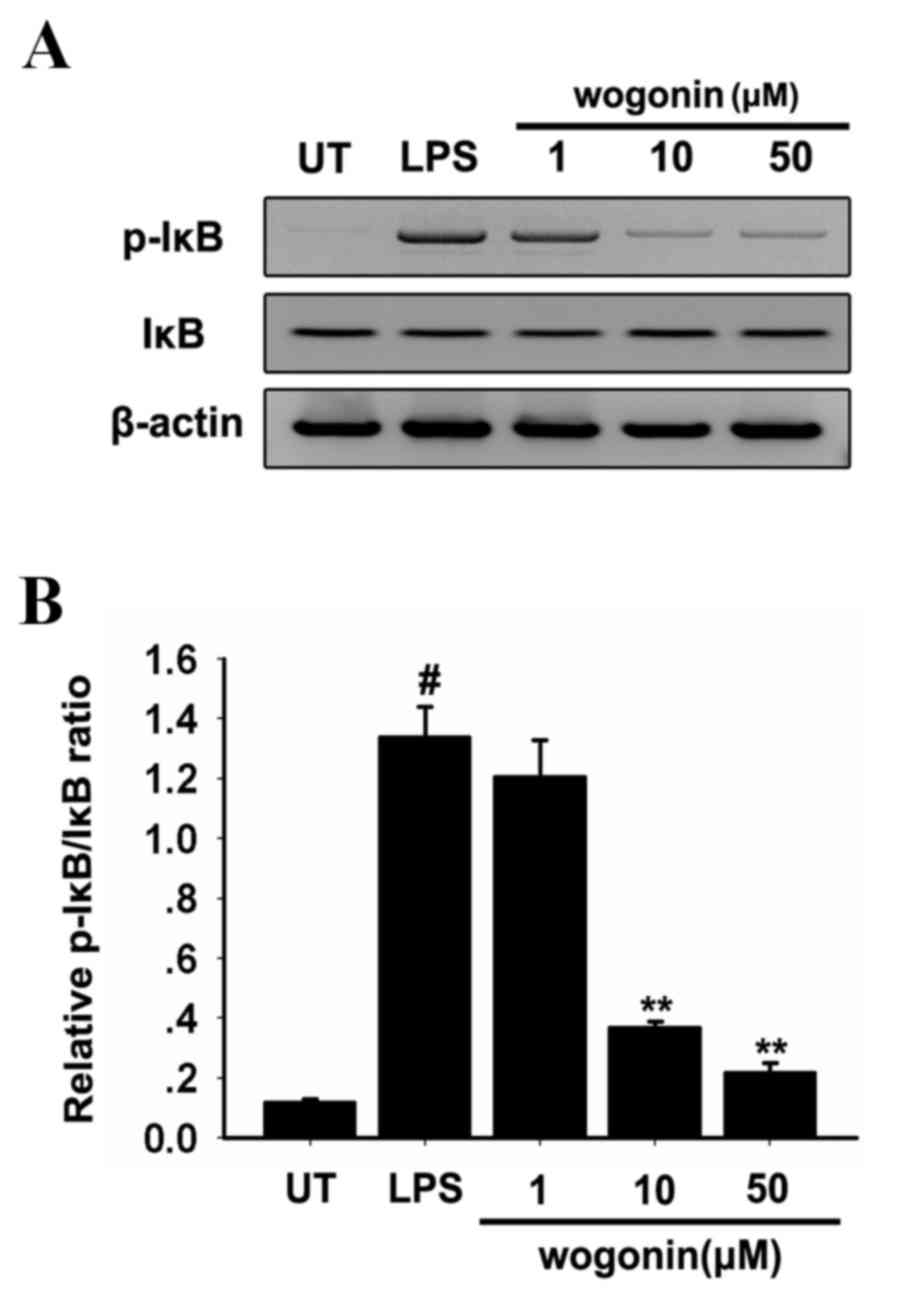
|
1
|
Lu L, Hackett SF, Mincey A, Lai H and
Campochiaro PA: Effects of different types of oxidative stress in
RPE cells. J Cell Physiol. 206:119–125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ding X, Patel M and Chan CC: Molecular
pathology of age-related macular degeneration. Prog Retin Eye Res.
28:1–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Anderson DH, Mullins RF, Hageman GS and
Johnson LV: A role for local inflammation in the formation of
drusen in the aging eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 134:411–431. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Salminen A, Kauppinen A, Hyttinen JM,
Toropainen E and Kaarniranta K: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in
age-related macular degeneration: Trigger for neovascularization.
Mol Med. 16:535–542. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nowak JZ: Age-related macular degeneration
(AMD): Pathogenesis and therapy. Pharmacol Rep. 58:353–363.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen C, Cano M, Wang JJ, Li J, Huang C, Yu
Q, Herbert TP, Handa JT and Zhang SX: Role of unfolded protein
response dysregulation in oxidative injury of retinal pigment
epithelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:2091–2106. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kucuksayan E, Konuk EK, Demir N, Mutus B
and Aslan M: Neutral sphingomyelinase inhibition decreases ER
stress-mediated apoptosis and inducible nitric oxide synthase in
retinal pigment epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 72:113–123.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Strauss O: The retinal pigment epithelium
in visual function. Physiol Rev. 85:845–881. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoshikawa T, Ogata N, Izuta H, Shimazawa
M, Hara H and Takahashi K: Increased expression of tight junctions
in ARPE-19 cells under endoplasmic reticulum stress. Curr Eye Res.
36:1153–1163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Du M, Wu M, Fu D, Chen J, Wilson K and
Lyons TJ: Effects of modified LDL and HDL on retinal pigment
epithelial cells: A role in diabetic retinopathy? Diabetologia.
56:2318–2328. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yeh CH, Yang ML, Lee CY, Li YC, Chen CJ
and Kuan YH: Wogonin attenuates endotoxin-induced prostaglandin E2
and nitric oxide production via Src-ERK1/2-NFκB pathway in BV-2
microglial cells. Environ Toxicol. 29:1162–1170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gibbons HM and Dragunow M: Microglia
induce neural cell death via a proximity-dependent mechanism
involving nitric oxide. Brain Res. 1084:1–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu H, Gao F, Shu G, Xia G, Shao Z, Lu H
and Cheng K: Wogonin inhibits the proliferation of myelodysplastic
syndrome cells through the induction of cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:7285–7292. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Piao HZ, Choi IY, Park JS, Kim HS, Cheong
JH, Son KH, Jeon SJ, Ko KH and Kim WK: Wogonin inhibits microglial
cell migration via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B activity.
Int Immunopharmacol. 8:1658–1662. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin CM, Chen YH, Ong JR, Ma HP, Shyu KG
and Bai KJ: Functional role of wogonin in anti-angiogenesis. Am J
Chin Med. 40:415–427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chi YS, Lim H, Park H and Kim HP: Effects
of wogonin, a plant flavone from Scutellaria radix, on skin
inflammation: In vivo regulation of inflammation-associated gene
expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1271–1278. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin CM, Chang H, Chen YH, Li SY, Wu IH and
Chiu JH: Protective role of wogonin against
lipopolysaccharide-induced angiogenesis via VEGFR-2, not VEGFR-1.
Int Immunopharmacol. 6:1690–1698. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burke JM: Epithelial phenotype and the RPE
Is the answer blowing in the Wnt? Prog Retin Eye Res. 27:579–595.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen S, Xiong J, Zhan Y, Liu W and Wang X:
Wogonin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses in rat dorsal
root ganglion neurons via inhibiting TLR4-MyD88-TAK1-mediated NF-κB
and MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:523–531. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen F, Wu R, Zhu Z, Yin W, Xiong M, Sun
J, Ni M, Cai G and Zhang X: Wogonin protects rat dorsal root
ganglion neurons against tunicamycin-induced ER stress through the
PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 signaling pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 55:995–1005.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu S, Zhao X, Zhao Q, Zheng Q, Fang Z,
Yang X, Wang H, Liu P and Xu H: Wogonin prevents rat dorsal root
ganglion neurons death via inhibiting tunicamycin-induced ER stress
in vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:389–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Xia T and Yu X: Wogonin suppresses
inflammatory response and maintains intestinal barrier function via
TLR4-MyD88-TAK1-mediated NF-κB pathway in vitro. Inflamm Res.
64:423–431. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shen W, Gao Y, Lu B, Zhang Q, Hu Y and
Chen Y: Negatively regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling via PPARα in
endotoxin-induced uveitis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1842:1109–1120.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paeng SH, Park WS, Jung WK, Lee DS, Kim
GY, Choi YH, Seo SK, Jang WH, Choi JS, Lee YM, et al: YCG063
inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa LPS-induced inflammation in human
retinal pigment epithelial cells through the TLR2-mediated
AKT/NF-κB pathway and ROS-independent pathways. Int J Mol Med.
36:808–816. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mateos MV, Kamerbeek CB, Giusto NM and
Salvador GA: The phospholipase D pathway mediates the inflammatory
response of the retinal pigment epithelium. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 55:119–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Breccia M and Alimena G: NF-κB as a
potential therapeutic target in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute
myeloid leukemia. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1157–1176. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He X, Wei Z, Zhou E, Chen L, Kou J, Wang J
and Yang Z: Baicalein attenuates inflammatory responses by
suppressing TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in
LPS-induced mastitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:470–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wardill HR, Van Sebille YZ, Mander KA,
Gibson RJ, Logan RM, Bowen JM and Sonis ST: Toll-like receptor 4
signaling: A common biological mechanism of regimen-related
toxicities: An emerging hypothesis for neuropathy and
gastrointestinal toxicity. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:122–128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|