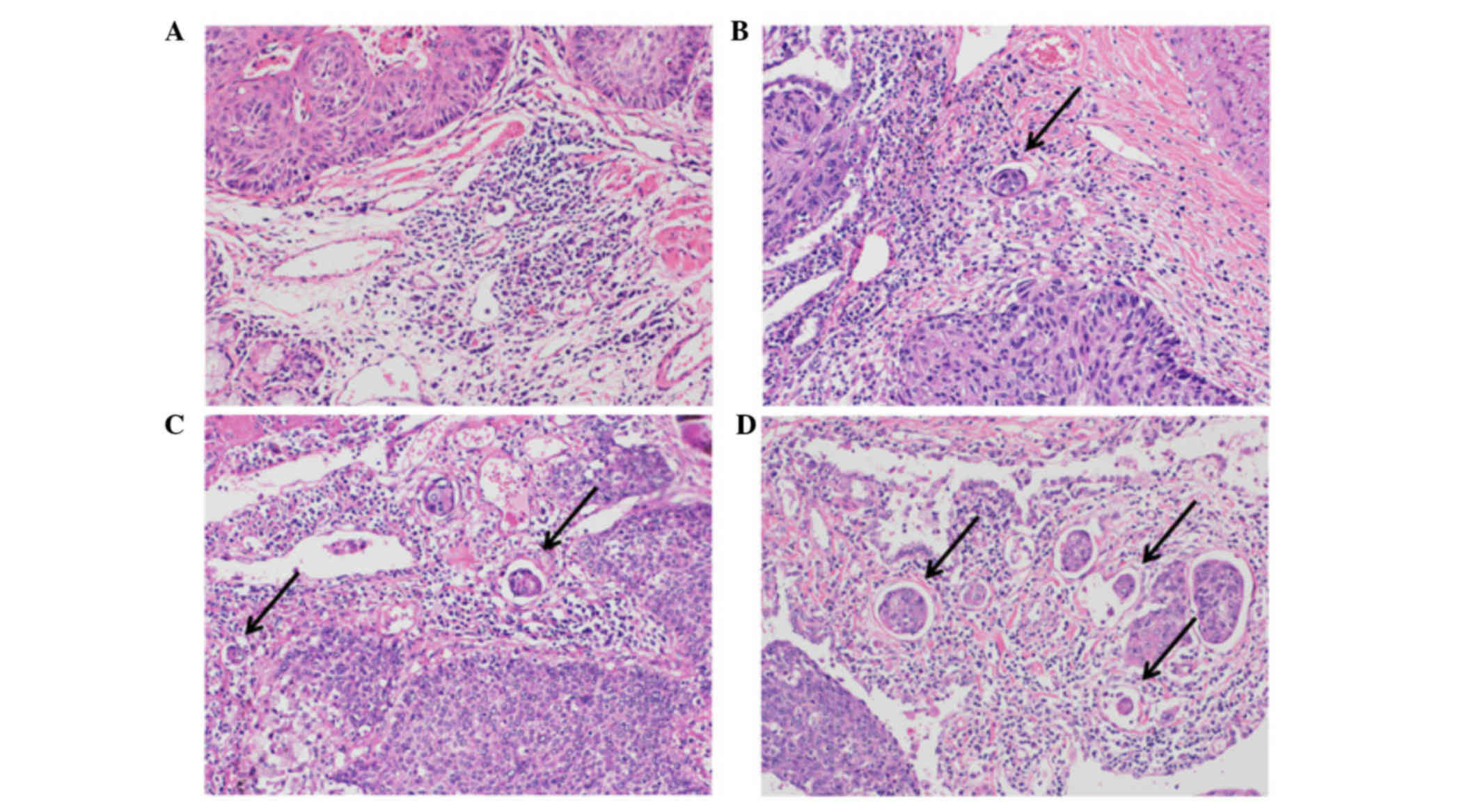
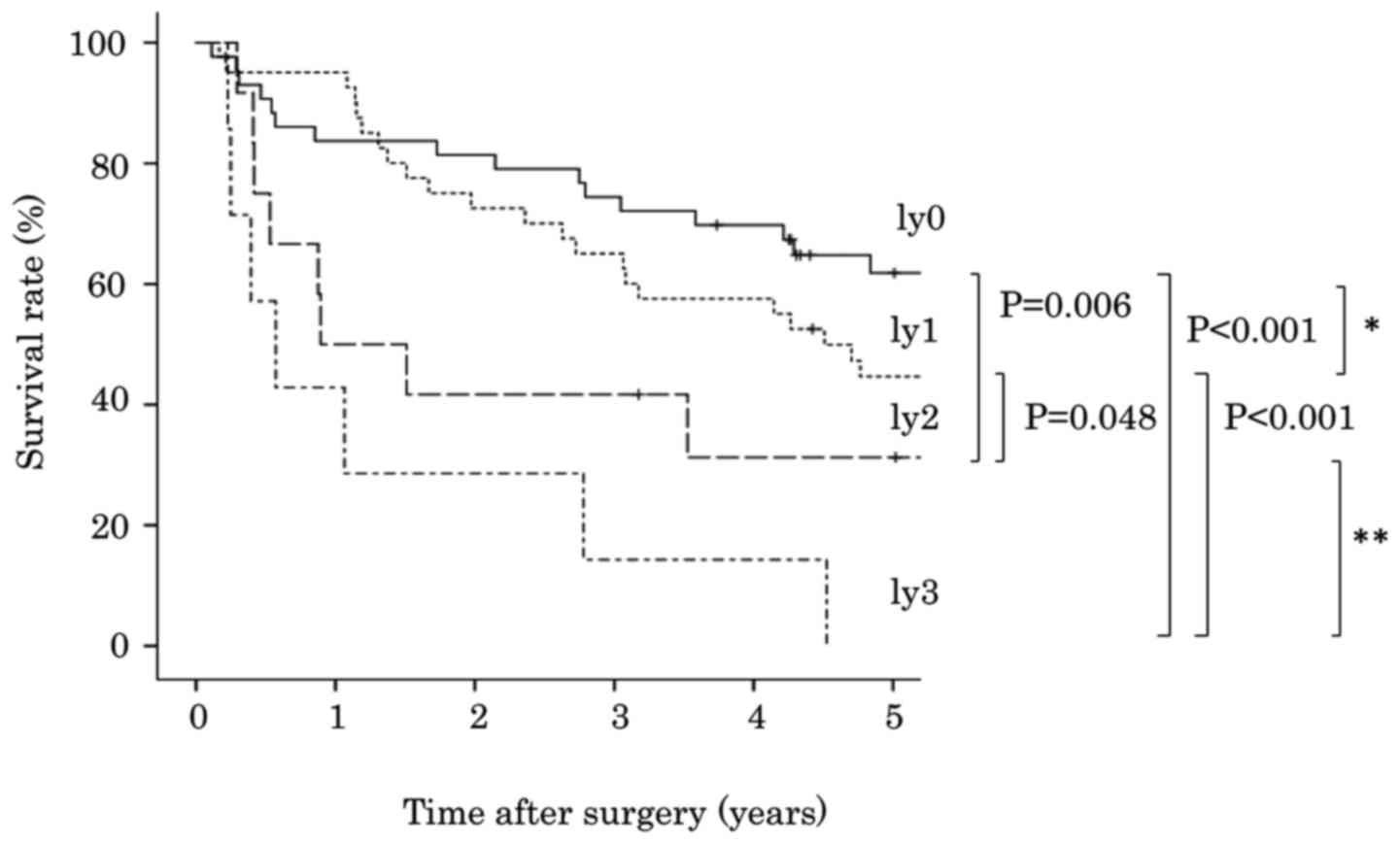
|
1
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux
DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V and Sobin L:
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions: The
IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of
the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the
TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chung CK, Zaino R, Stryker JA, O'Neill M
Jr and DeMuth WE Jr: Carcinoma of the lung: Evaluation of
histological grade and factors influencing prognosis. Ann Thorac
Surg. 33:599–604. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gajra A, Newman N, Gamble GP, Abraham NZ,
Kohman LJ and Graziano SL: Impact of tumor size on survival in
stage IA non-small cell lung cancer: A case for subdividing stage
IA disease. Lung Cancer. 42:51–57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ito E, Ozawa S, Kijima H, Kazuno A, Nishi
T, Chino O, Shimada H, Tanaka M, Inoue S, Inokuchi S and Makuuchi
H: New invasive patterns as a prognostic factor for superficial
esophageal cancer. J Gastroenterol. 47:1279–1289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okada K, Kijima H, Imaizumi T, Hirabayashi
K, Matsuyama M, Yazawa N, Dowaki S, Tobita K, Ohtani Y, Tanaka M,
et al: Clinical significance of wall invasion pattern of
subserosa-invasive gallbladder carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 28:1531–1536.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Masuda R, Kijima H, Imamura N, Aruga N,
Nakamura Y, Masuda D, Takeichi H, Kato N, Nakagawa T, Tanaka M, et
al: Tumor budding is a significant indicator of a poor prognosis in
lung squamous cell carcinoma patients. Mol Med Rep. 6:937–943.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yokota T, Kunii Y, Teshima S, Yamada Y,
Saito T, Takahashi M, Kikuchi S and Yamauchi H: Significant
prognostic factors in patients with early gastric cancer. Int Surg.
85:286–290. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Harpole DH Jr, JE II Herndon, Young WG Jr,
Wolfe WG and Sabiston DC Jr: Stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer. A
multivariate analysis of treatment methods and patterns of
recurrence. Cancer. 76:787–796. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ichinose Y, Yano T, Asoh H, Yokoyama H,
Yoshino I and Katsuda Y: Prognostic factors obtained by a
pathologic examination in completely resected non-small-cell lung
cancer. An analysis in each pathologic stage. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 110:601–605. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Duarte IG, Bufkin BL, Pennington MF, Gal
AA, Cohen C, Kosinski AS, Mansour KA and Miller JI: Angiogenesis as
a predictor of survival after surgical resection for stage I
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 115:652–659.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Crabbe MM, Patrissi GA and Fontenelle LJ:
Minimal resection for bronchogenic carcinoma. An update. Chest.
99:1421–1424. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martini N, Rusch VW, Bains MS, Kris MG,
Downey RJ, Flehinger BJ and Ginsberg RJ: Factors influencing
ten-year survival in resected stages I to IIIa non-small cell lung
cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 117:32–38. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hylkema MN, Sterk PJ, deBoer WI and Postma
DS: Tobacco use in relation to COPD and asthma. Eur Respir J.
29:438–445. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gratziou Ch, Florou A, Ischaki E,
Eleftheriou K, Sachlas A, Bersimis S and Zakynthinos S: Smoking
cessation effectiveness in smokers with COPD and asthma under real
life conditions. Respir Med. 108:577–583. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association, .
Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edition.
Gastric Cancer. 14:101–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Maehara Y, Oshiro T, Adachi Y, Ohno S,
Akazawa K and Sugimachi K: Growth pattern and prognosis of gastric
cancer invading the subserosa. J Surg Oncol. 55:203–208. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haraguchi M, Yamamoto M, Saito A, Kakeji
Y, Orita H, Korenaga D and Sugimachi K: Prognostic value of depth
and pattern of stomach wall invasion in patients with an advanced
gastric carcinoma. Semin Surg Oncol. 10:125–129. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dembitzer FR, Flores RM, Parides MK and
Beasley MB: Impact of histological subtyping on outcome in lobar vs
sublobar resections for lung cancer: A pilot study. Chest.
146:175–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koike T, Koike T, Yoshiya K, Tsuchida M
and Toyabe S: Risk factor analysis of locoregional recurrence after
sublobar resection in patients with clinical stage IA non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 146:372–378. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rossi A, Ricciardi S, Maione P, de Marinis
F and Gridelli C: Pemetrexed in the treatment of advanced
non-squamous lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 66:141–149. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reck M, von Pawel J, Zatloukal P, Ramlau
R, Gorbounova V, Hirsh V, Leighl N, Mezger J, Archer V, Moore N and
Manegold C: Phase III trial of cisplatin plus gemcitabine with
either placebo or bevacizumab as first-line therapy for nonsquamous
non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAil. J Clin Oncol. 27:1227–1234.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rosell R, Perez-Roca L, Sanchez JJ, Cobo
M, Moran T, Chaib I, Provencio M, Domine M, Sala MA, Jimenez U, et
al: Customized treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer based on
EGFR mutations and BRCA1 mRNA expression. PLoS One. 4:e51332009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hong J, Kyung SY, Lee SP, Park JW, Jung
SH, Lee JI, Park SH, Sym SJ, Park J, Cho EK, et al: Pemetrexed
versus gefitinib versus erlotinib in previously treated patients
with non-small cell lung cancer. Korean J Intern Med. 25:294–300.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and
Wittekind C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 7th edition.
Wiley; Oxford: 2009
|
|
26
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Müller-Hermelin HK
and Harris CC: World Health Organization Classification of Tumors.
Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and
Heart. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
27
|
Beattie G, Bannon F and McGuigan J: Lung
cancer resection rates have increased significantly in females
during a 15-year period. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 38:484–490. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martin-Ucar AE, Waller DA, Atkins JL,
Swinson D, O'Byrne KJ and Peake MD: The beneficial effects of
specialist thoracic surgery on the resection rate for
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 46:227–232. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Masuda R, Kijima H, Imamura N, Aruga N,
Nakazato K, Oiwa K, Nakano T, Watanabe H, Ikoma Y, Tanaka M, et al:
Laminin-5γ2 chain expression is associated with tumor cell
invasiveness and prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed
Res. 33:309–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Okada K, Kijima H, Imaizumi T, Hirabayashi
K, Matsuyama M, Yazawa N, Oida Y, Dowaki S, Tobita K, Ohtani Y, et
al: Stromal laminin-5gamma2 chain expression is associated with the
wall-invasion pattern of gallbladder adenocarcinoma. Biomed Res.
30:53–62. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|