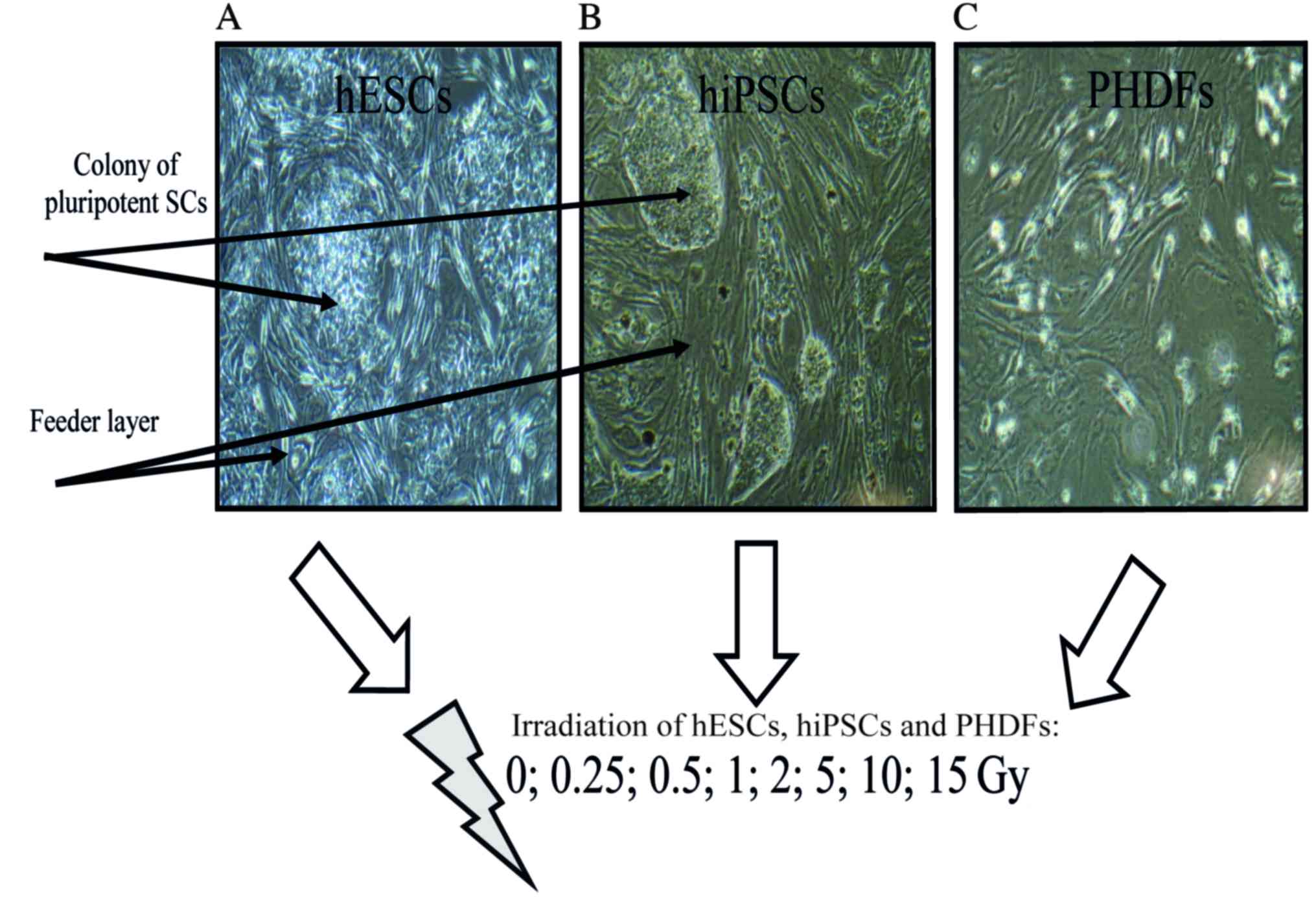
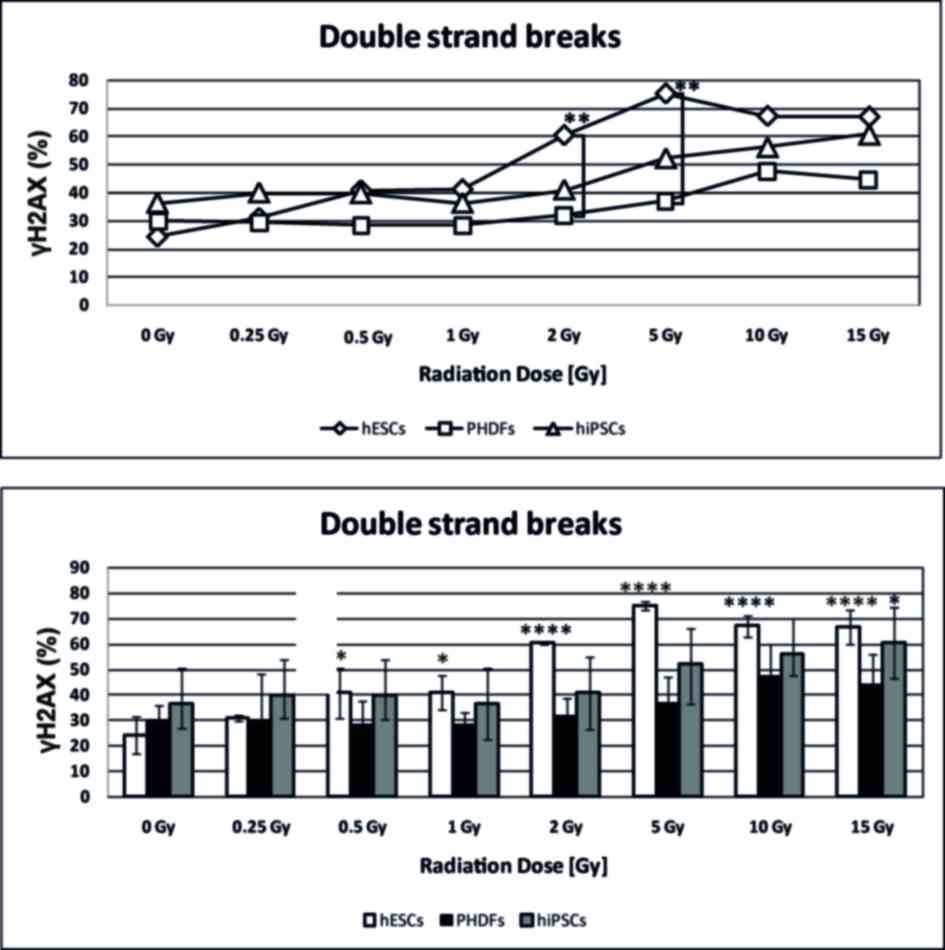
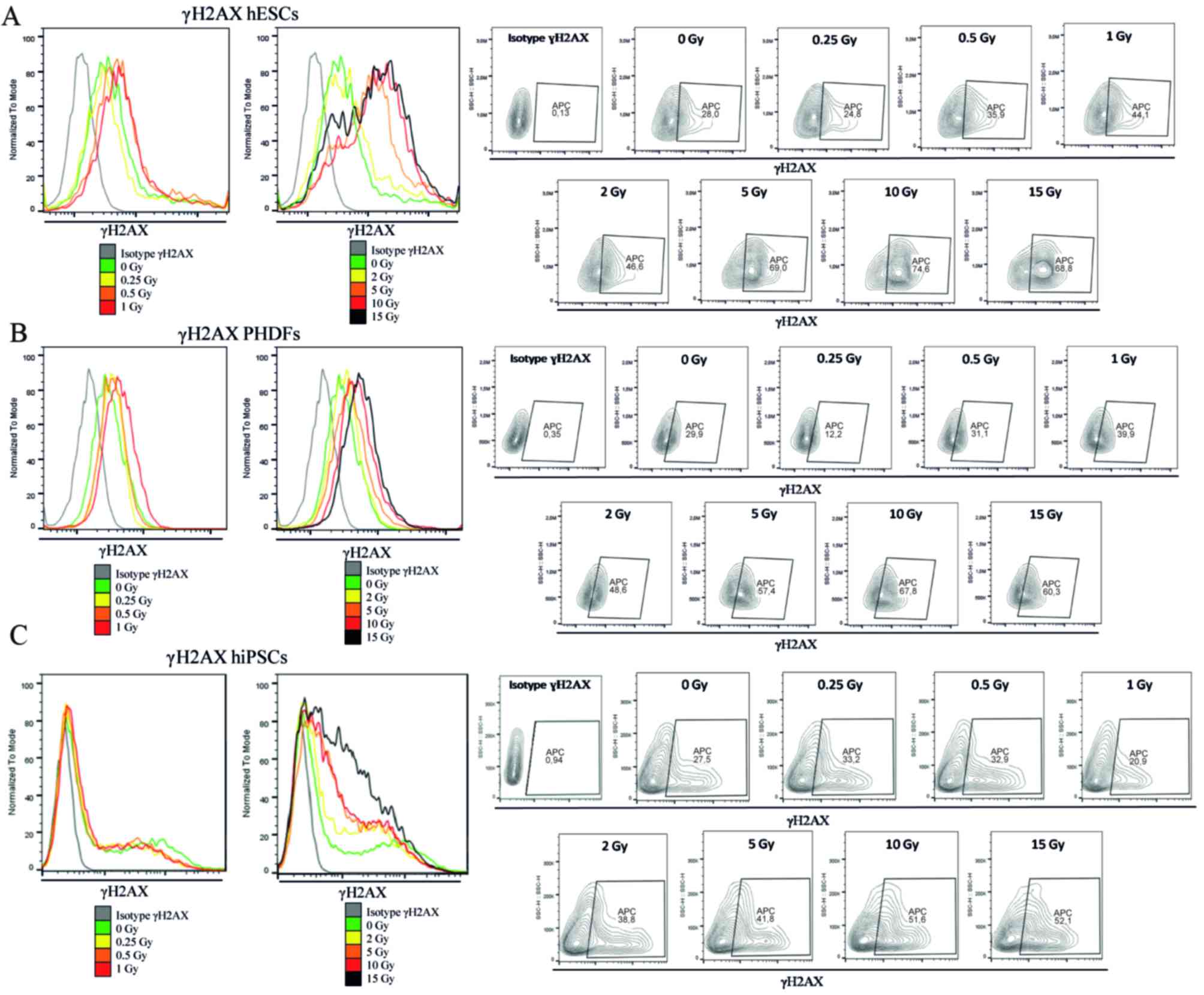
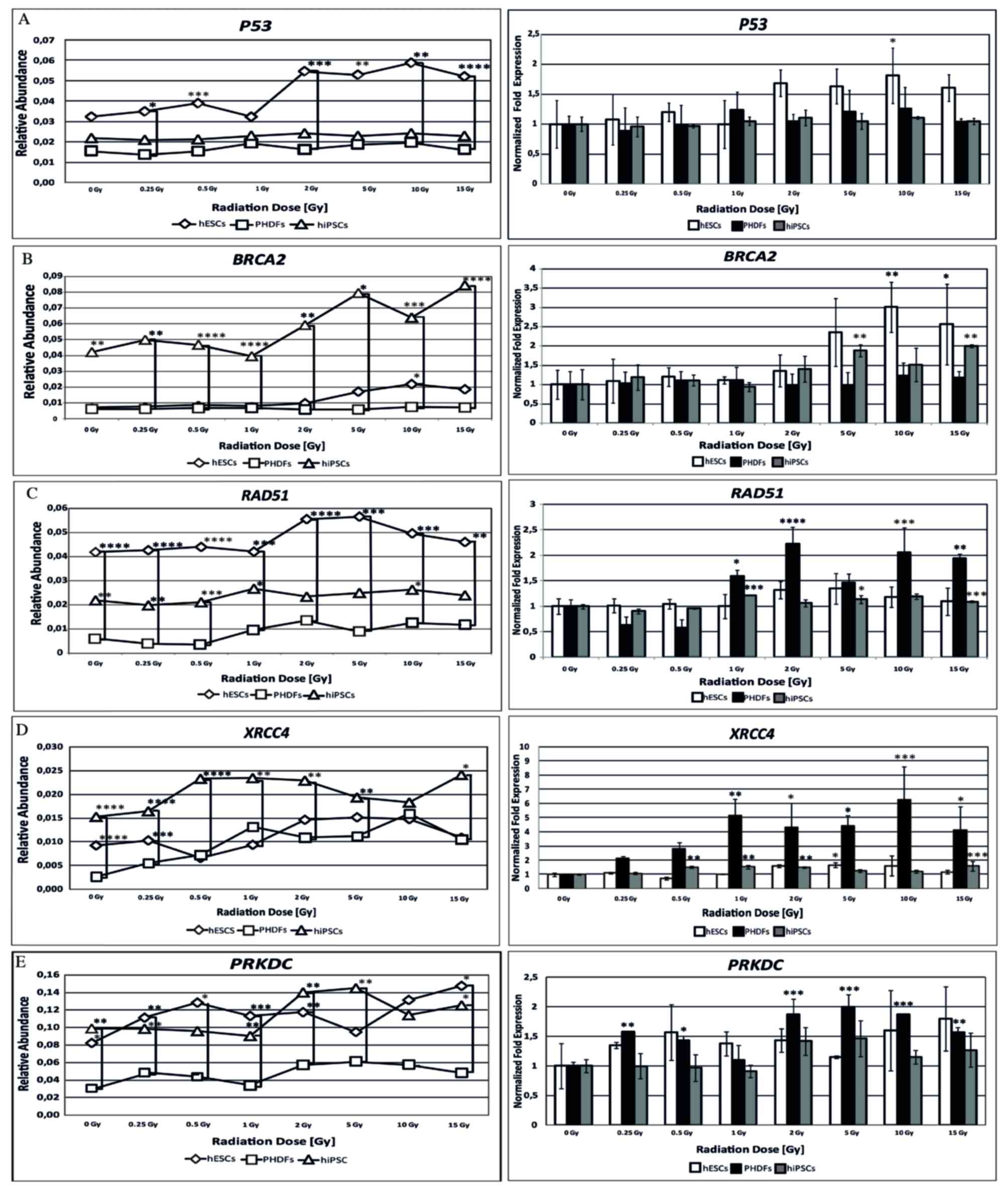
|
1
|
Suchorska WM, Lach MS, Richter M,
Kaczmarczyk J and Trzeciak T: Bioimaging: An useful tool to monitor
differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into chondrocytes.
Ann Biomed Eng. 44:1845–1859. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Augustyniak E, Trzeciak T, Richter M,
Kaczmarczyk J and Suchorska W: The role of growth factors in stem
cell-directed chondrogenesis: A real hope for damaged cartilage
regeneration. Int Orthop. 39:995–1003. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen MF, Lin CT, Chen WC, Yang CT, Chen
CC, Liao SK, Liu JM, Lu CH and Lee KD: The sensitivity of human
mesenchymal stem cells to ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 66:244–253. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jin YW, Na YJ, Lee YJ, An S, Lee JE, Jung
M, Kim H, Nam SY, Kim CS, Yang KH, et al: Comprehensive analysis of
time- and dose-dependent patterns of gene expression in a human
mesenchymal stem cell line exposed to low-dose ionizing radiation.
Oncol Rep. 19:135–144. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zaman MH: The role of engineering
aproaches in analysis cancer invasion and metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 13:596–603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
De Magalhães JP: How ageing processess
influence cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:357–365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sokolov MV and Neumann RD: Human embryonic
stem cell responses to ionizing radiation exposures: Current state
of knowledge and future challenges. Stem Cells Int.
2012:5791042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suchorska WM, Augustyniak E and Łukjanow
M: Genetic stability of pluripotent stem cells during anti-cancer
therapies. Exp Ther Med. 11:695–702. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soldner F, Hockemeyer D, Beard C, Gao Q,
Bell GW, Cook EG, Hargus G, Blak A, Cooper O and Mitalipova M:
Parkinson's disease patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells
free of viral reprogramming factor. Cell. 136:964–977. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fung H and Weinstock DM: Repair at single
targeted DNA double-strand breaks in pluripotent and differentiated
human cells. PLoS One. 6:e205142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rocha CR, Lerner LK and Okamoto OK: The
role of DNA repair in the pluripotency and differentiation of human
stem cells. Mutat Res. 752:25–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Long XH, Zhao ZQ, He XP, Wang HP, Xu QZ,
An J, Bai B, Sui JL and Zhou PK: Dose-dependent expression changes
of early response genes to ionizing radiation in human
lymphoblastoid cells. Int J Mol Med. 19:607–615. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wróblewska J: A new method to generate
human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) and the role of the
protein KAP1 in epigenetic regulation of self-renewal. Doctoral
dissertation. http://www.wbc.poznan.pl/Content/373798/index.pdf2015.
|
|
14
|
Banáth JP, MacPhail SH and Olive PL:
Radiation sensitivity, H2AX phosphorylation and kinetics of repair
of DNA strand breaks in irradiated cervical cancer cell lines.
Cancer Res. 64:7144–7149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
An J, Huang YC, Xu QZ, Zhou LJ, Shang ZF,
Huang B, Wang Y, Liu XD, Wu DC and Zhou PK: DNA-PKcs plays a
dominant role in the regulation of H2AX phosphorylation in response
to DNA damage and cell cycle progression. BMC Mol Biol. 11:182010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scarpanto E, Castagna S, Aliotta R, Azzarà
A, Ghetti F, Filomeni E, Giovannini C, Pirillo C, Testi S, Lombardi
S and Tomei A: Kinetics of nuclear phosphorylation (γ-H2AX) in
human lymphocytes treated in vitro with UVB, bleomycin and
mitomycin C. Mutagenesis. 28:465–473. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mah LJ, Vasireddy RS, Tang MM, Georgiadis
GT, El-Osta A and Karagiannis TC: Quantification of gammaH2AX foci
in response to ionising radiation. J Vis Exp. pii:19572010.
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)). Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiong J, Todorova D, Su NY, Kim J, Lee PJ,
Shen Z, Briggs SP and Xu Y: Stemness factor Sall4 is required for
DNA damage response in embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biol.
208:513–520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koledova Z, Kafkova LR, Krämer A and
Divoky V: DNA damage-induced degradation of Cdc25A does not lead to
inhibition of Cdk2 activity in mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem
Cells. 28:450–461. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Banáth JP, Bañuelos CA, Klokov D, MacPhail
SM, Lansdorp PM and Olive PL: Explanation for excessive DNA
single-strand breaks and endogenous repair foci in pluripotent
mouse embryonic stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 315:1505–1520. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sokolov MV, Panyutin IV, Onyshchenko MI,
Panyutin IG and Neumann RD: Expression of pluripotency-associated
genes in the surviving fraction of cultured human embryonic stem
cells is not significantly affected by ionizing radiation. Gene.
455:8–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Momčilovic O, Choi S, Varum S, Bakkenist
C, Schatten G and Navara C: Ionizing radiation induces ataxia
telangiectasia mutated-dependent checkpoint signaling and G(2) but
not G(1) cell cycle arrest in pluripotent human embryonic stem
cells. Stem Cells. 27:1822–1835. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Filion TM, Qiao M, Ghule PN, Mandeville M,
van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Lian JB, Altieri DC and Stein GS: Survival
responses of human embryonic stem cells to DNA damage. J Cell
Physiol. 220:586–592. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Neganova I, Vilella F, Atkinson SP, Lloret
M, Passos JF, von Zglinicki T, O'Connor JE, Burks D, Jones R,
Armstrong L and Lako M: An important role for CDK2 in G1 to S
checkpoint activation and DNA damage response in human embryonic
stem cells. Stem Cells. 29:651–659. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hayashi N, Monzen S, Ito K, Fujioka T,
Nakamura Y and Kashiwakura I: Effects of ionizing radiation on
proliferation and differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem
cells. J Radiat Res. 53:195–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nagaria PK, Robert C, Park TS, Huo JS,
Zambidis ET and Rassool FV: High-fidelity reprogrammed human IPSCs
have a high efficacy of DNA repair and resemble hESCs in their MYC
transcriptional signature. Stem Cell Int. 2016:38262492016.
|
|
28
|
Han MK, Song EK, Guo Y, Ou X, Mantel C and
Broxmeyer HE: SIRT1 regulates apoptosis and Nanog expression in
mouse embryonic stem cells by controlling p53 subcellular
localization. Cell Stem Cell. 2:241–251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chuykin IA, Lianguzova MS, Pospelova TV
and Pospelov VA: Activation of DNA damage response signaling in
mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Cycle. 7:2922–2928. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee KH, Li M, Michalowski AM, Zhang X,
Liao H, Chen L, Xu Y, Wu X and Huang J: A genomwide study
identifies the Wnt signaling pathway as a major target of p53 in
murine embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:69–74.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abdelalim EM and Tooyama I: Knockdown of
p53 suppressess Nanog expression in embryonic stem cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 443:652–657. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Solozobova V, Rolletschek A and Blattner
C: Nuclear accumulation and activation of p53 in embryonic stem
cells after DNA damage. BMC Cell Biol. 10:462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dolezalova D, Mraz M, Barta T, Plevova K,
Vinarsky V, Holubcova Z, Jaros J, Dvorak P, Pospisilova S and Hampl
A: MicroRNAs regulate p21(Waf1/Cip1) protein expression and the DNA
damage response in human ebryonic stem cells. Stem Cells.
30:1362–1372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Solozobova V and Blattner C: Regulation of
p53 in embryonic stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 316:2434–2446. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qin H, Yu T, Qing T, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Cai J,
Li J, Song Z, Qu X, Zhou P, et al: Regulation of apoptosis and
differentiation by p53 in human embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem.
282:5842–5852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wilson KD, Sun H, Huang M, Zhang WY, Lee
AS, Li Z, Wang SX and Wu JC: Effects of ionizing radiation on
self-renewal and pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells. Cancer
Res. 70:5539–5558. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Akdemir KC, Jain AK, Allton K, Aronow B,
Xu X, Cooney AJ, Li W and Barton MC: Genome-wide profiling reveals
stimulus-specific functions of p53 during differentiation and DNA
damage of human embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acid Research.
42:205–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sokolov M and Neumann R: Effects of low
doses of ionizing radiation exposures on stress-responsive gene
expression in human embryonic stem cells. Int J Mol Sci.
15:588–604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sokolov M, Nguyen V and Neumann R:
Comparative analysis of whole-genome gene expression changes in
cultured human embryonic stem cells in response to low, clinical
diagnostic relevant and high doses of ionizing radiation exposure.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:14737–14748. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rasmussen MA, Holst B, Tümer Z, Johnsen
MG, Zhou S, Stummann TC, Hyttel P and Clausen C: Transient p53
suppression increases reprogramming of human fibroblasts without
affecting apoptosis and DNA damage. Stem Cell Reports. 3:404–413.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dannenmann B, Lehle S, Hildebrand DG,
Kübler A, Grondona P, Schmid V, Holzer K, Fröschl M, Essmann F,
Rothfuss O and Schulze-Osthoff K: High glutathione and glutathione
preoxidase-2 levels mediate cell-type-specific DNA damage
protection in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell
Reports. 4:886–898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Momcilovic O, Knobloch L, Fornsaqlio J,
Varum S, Easley C and Schatten G: DNA damage responses in human
induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells. PLoS One.
5:e134102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Griffin C, Waard Hd, Deans B and Thacker
J: The involvement of key DNA repair pathways in the formation of
chromosome rearrangements in embryonic stem cells. DNA Repair
(Amst). 4:1019–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tichy ED, Pillai R, Deng L, Tischfield JA,
Hexley P, Babcock GF and Stambrook PJ: The abundance of Rad51
protein in mouse embryonic stem cells is regulated at multiple
levels. Stem Cell Res. 9:124–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sioftanos G, Ismail A, Föhse L, Shanley S,
Worku M and Short SC: BRCA1 and BRCA2 heterozygosity in embryonic
stem cells reduces radiation-induced Rad51 focus formation but is
not associated with radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Biol.
86:1095–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bañuelos CA, Banáth JP, MacPhail SH, Zhao
J, Eaves CA, O'Connor MD, Lansdorp PM and Olive PL: Mouse but not
human embryonic stem cells are deficient in rejoining of ionizing
radiation- induced DNA double-strand breaks. DNA Repair (Amst).
7:1471–1483. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Maynard S, Swistowska AM, Lee JW, Liu Y,
Liu ST, Da Cruz AB, Rao M, de S, ouza-Pinto NC, Zeng X and Bohr VA:
Human embryonic stem cells have enhanced of multiple forms of DNA
damage. Stem Cells. 26:2266–2274. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Felgentreff K, Du L, Weinacht KG, Dobbs K,
Bartish M, Giliani S, Schlaeger T, DeVine A, Schambach A, Woodbine
LJ, et al: Differential role of nonhomologous end joining factors
in the generation, DNA damage response and myeloid differentiation
of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:8889–8894. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|