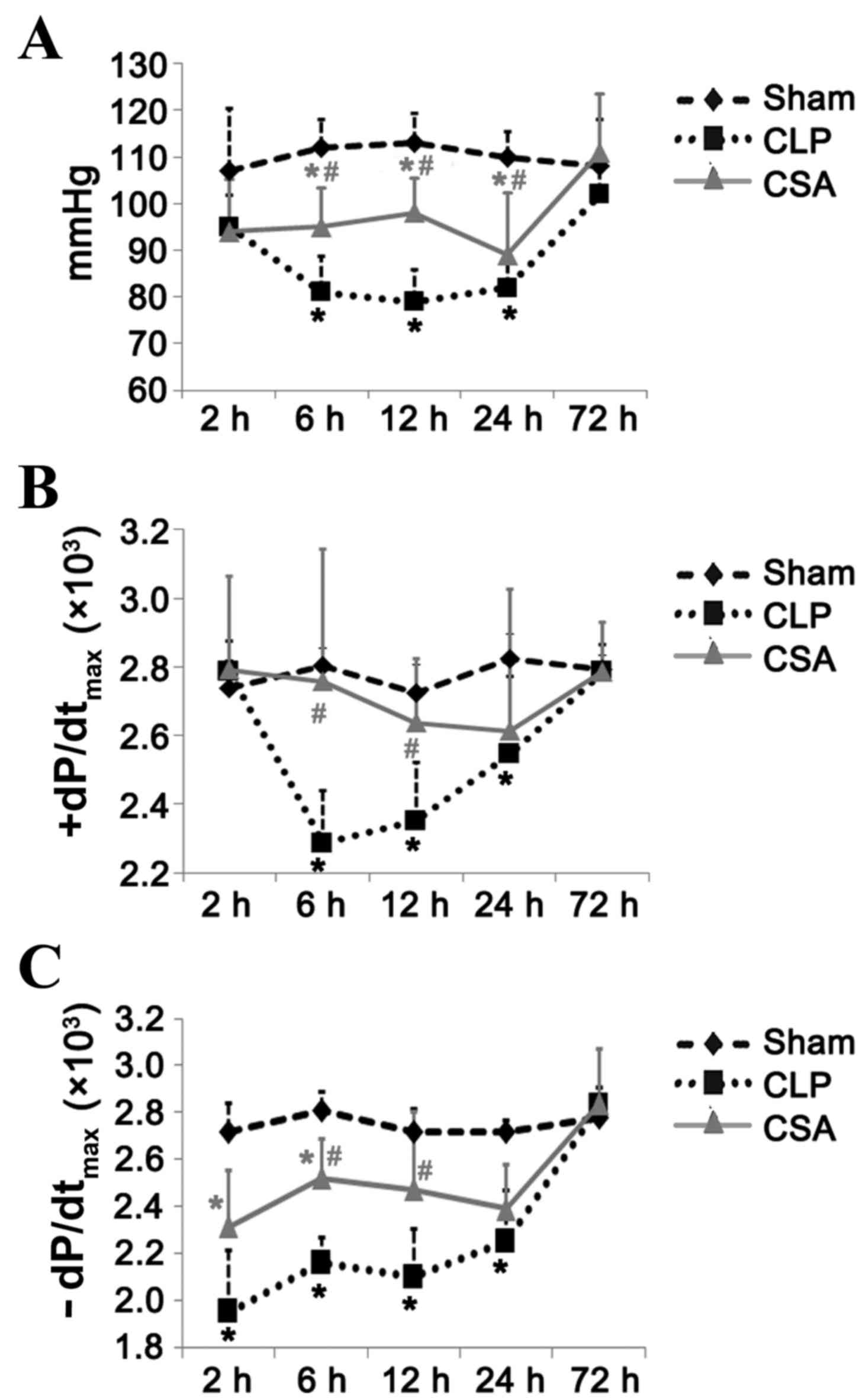
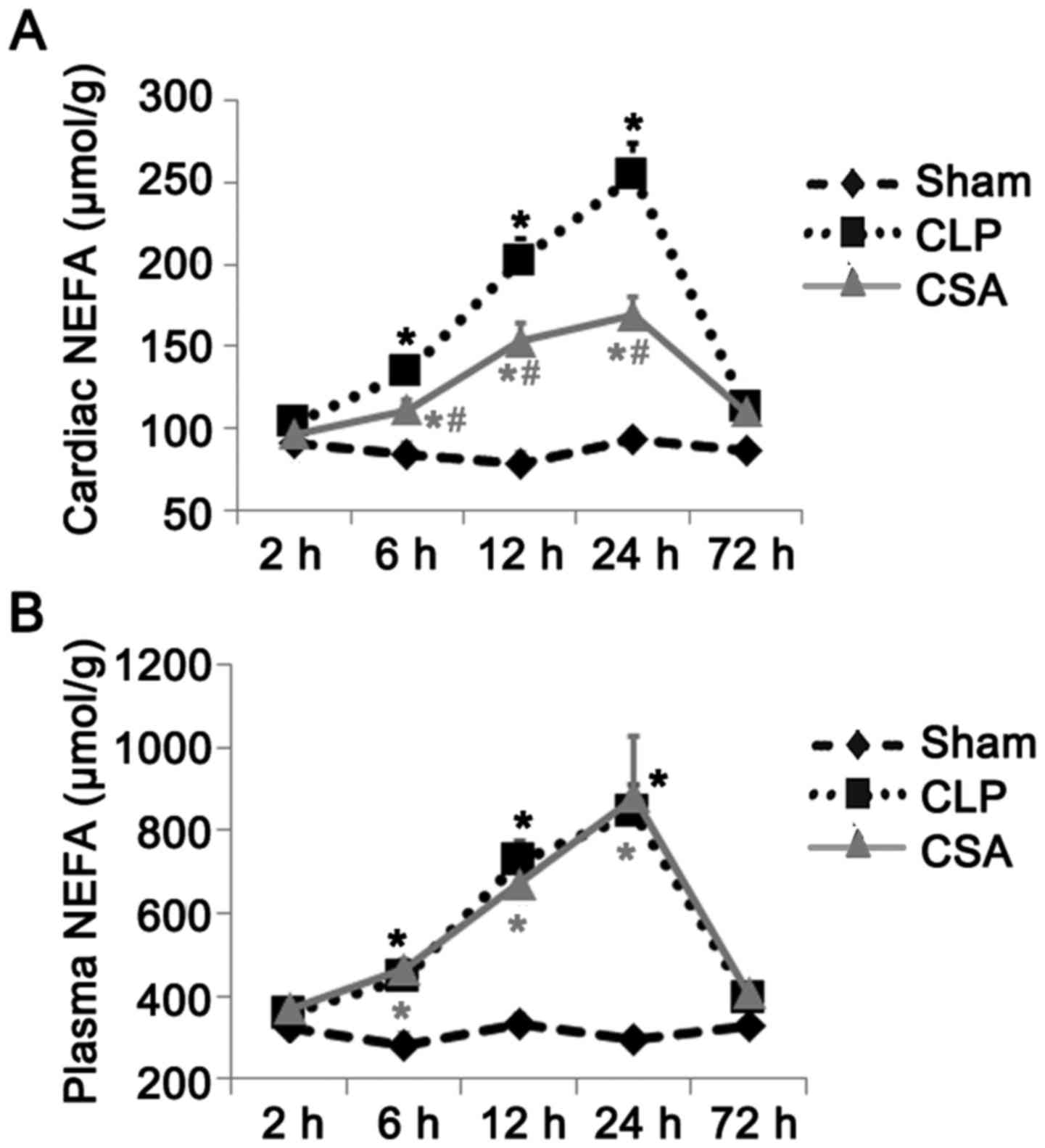
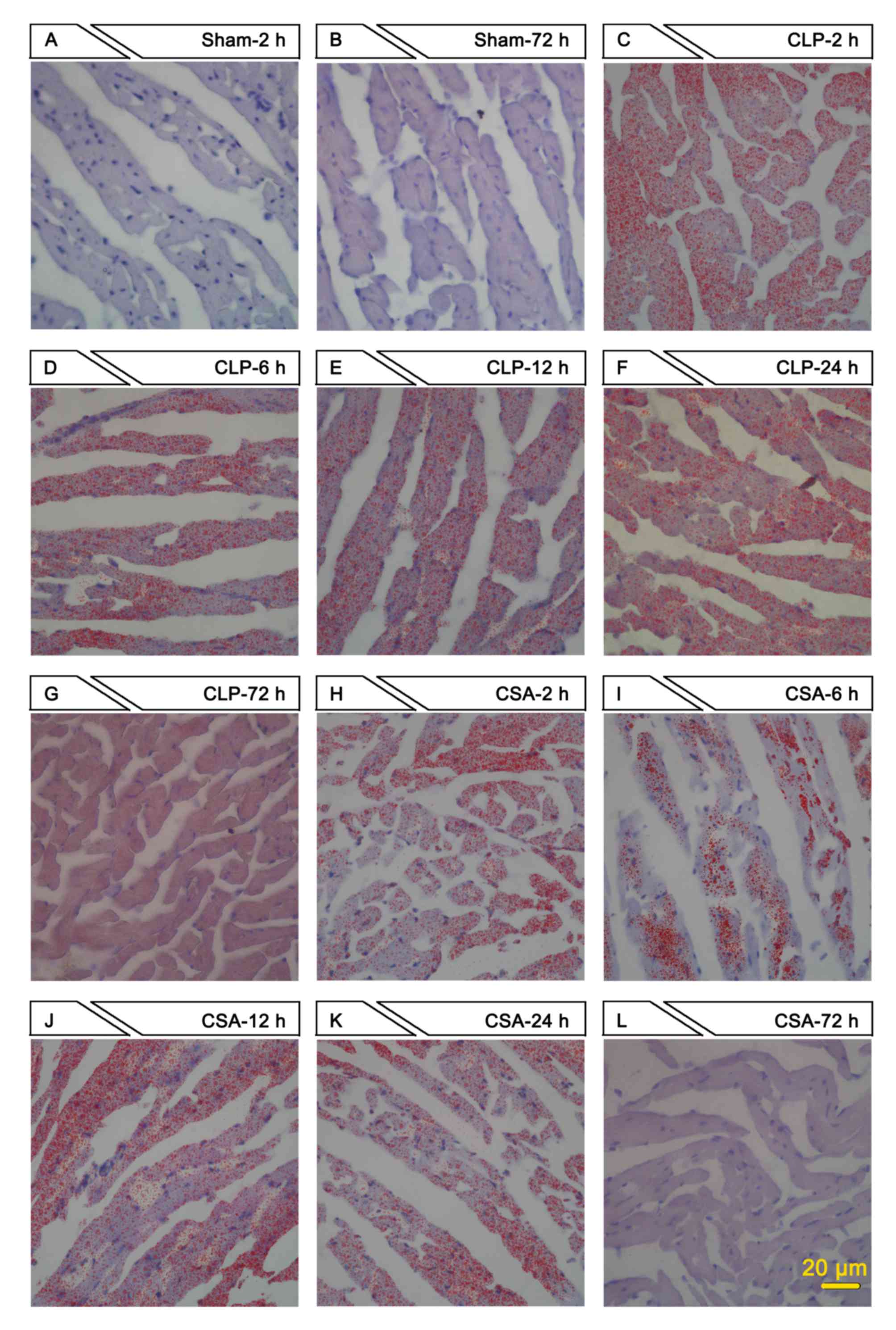
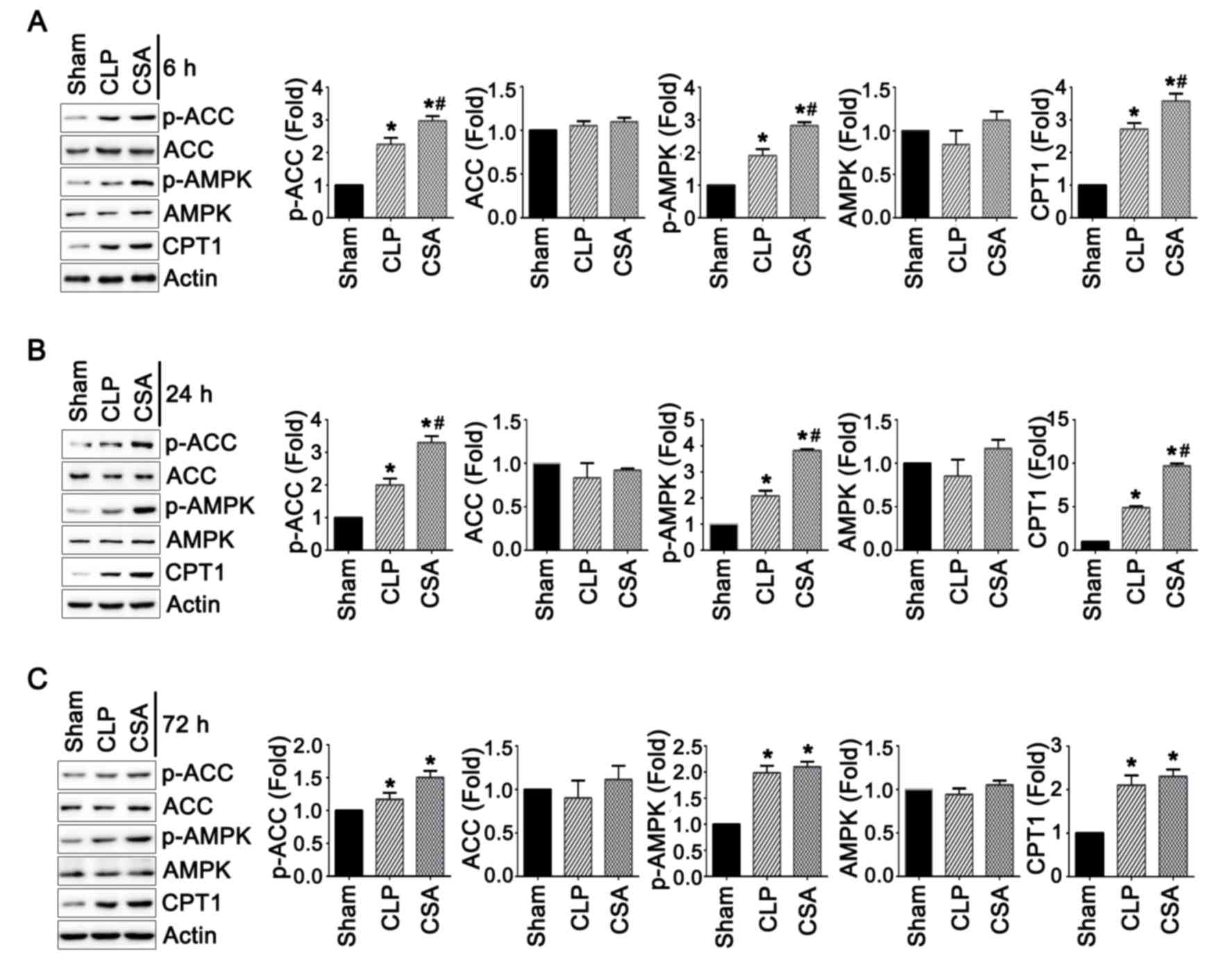
|
1
|
Iskander KN, Osuchowski MF,
Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Kurosawa S, Stepien D, Valentine C and Remick
DG: Sepsis: Multiple abnormalities, heterogeneous responses, and
evolving understanding. Physiol Rev. 93:1247–1288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Park HG, Yi H, Kim SH, Yu HS, Ahn YM, Lee
YH, Roh MS and Kim YS: The effect of cyclosporine A on the
phosphorylation of the AMPK pathway in the rat hippocampus. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 35:1933–1937. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parrillo JE: The cardiovascular
pathophysiology of sepsis. Annu Rev Med. 40:469–485. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
dos Santos CC, Gattas DJ, Tsoporis JN,
Smeding L, Kabir G, Masoom H, Akram A, Plotz F, Slutsky AS, Husain
M, et al: Sepsis-induced myocardial depression is associated with
transcriptional changes in energy metabolism and contractile
related genes: A physiological and gene expression-based approach.
Crit Care Med. 38:894–902. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Remick DG: Pathophysiology of sepsis. Am J
Pathol. 170:1435–1444. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bueno OF, Van Rooij E, Molkentin JD,
Doevendans PA and De Windt LJ: Calcineurin and hypertrophic heart
disease: Novel insights and remaining questions. Cardiovasc Res.
53:806–821. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Molkentin JD, Lu JR, Antos CL, Markham B,
Richardson J, Robbins J, Grant SR and Olson EN: A
calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac
hypertrophy. Cell. 93:215–228. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Berry JM, Le V, Rotter D, Battiprolu PK,
Grinsfelder B, Tannous P, Burchfield JS, Czubryt M, Backs J, Olson
EN, et al: Reversibility of adverse, calcineurin-dependent cardiac
remodeling. Circ Res. 109:407–417. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sussman MA, Lim HW, Gude N, Taigen T,
Olson EN, Robbins J, Colbert MC, Gualberto A, Wieczorek DF and
Molkentin JD: Prevention of cardiac hypertrophy in mice by
calcineurin inhibition. Science. 281:1690–1693. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki J, Bayna E, Li HL, Molle ED and Lew
WY: Lipopolysaccharide activates calcineurin in ventricular
myocytes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:491–499. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Larche J, Lancel S, Hassoun SM, Favory R,
Decoster B, Marchetti P, Chopin C and Neviere R: Inhibition of
mitochondrial permeability transition prevents sepsis-induced
myocardial dysfunction and mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol.
48:377–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rudiger A and Singer M: Mechanisms of
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 35:1599–1608.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iwamura H, Sato M and Wakitani K:
Comparative study of glucocorticoids, cyclosporine A, and JTE-607
[(−)-Ethyl-N[3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxy-4-[2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]benzoyl]-L-phenylalaninate
dihydrochloride] in a mouse septic shock model. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 311:1256–1263. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Joshi MS, Julian MW, Huff JE, Bauer JA,
Xia Y and Crouser ED: Calcineurin regulates myocardial function
during acute endotoxemia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 173:999–1007.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fauvel H, Marchetti P, Obert G, Joulain O,
Chopin C, Formstecher P and Nevière R: Protective effects of
cyclosporin A from endotoxin-induced myocardial dysfunction and
apoptosis in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 165:449–455. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zu L, He J, Jiang H, Xu C, Pu S and Xu G:
Bacterial endotoxin stimulates adipose lipolysis via toll-like
receptor 4 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. J
Biol Chem. 284:5915–5926. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heidrich F, Schotola H, Popov AF, Sohns C,
Schuenemann J, Friedrich M, Coskun KO, von Lewinski D, Hinz J,
Bauer M, et al: AMPK-activated protein kinase and its role in
energy metabolism of the heart. Curr Cardiol Rev. 6:337–342. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fillmore N and Lopaschuk GD: Targeting
mitochondrial oxidative metabolism as an approach to treat heart
failure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:857–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kiuchi S, Matsuo N, Takeyama N and Tanaka
T: Accelerated hepatic lipid synthesis in fasted septic rats. Eur
Surg Res. 25:146–154. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Borradaile NM, Han X, Harp JD, Gale SE,
Ory DS and Schaffer JE: Disruption of endoplasmic reticulum
structure and integrity in lipotoxic cell death. J Lipid Res.
47:2726–2737. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Son NH, Park TS, Yamashita H, Yokoyama M,
Huggins LA, Okajima K, Homma S, Szabolcs MJ, Huang LS and Goldberg
IJ: Cardiomyocyte expression of PPARgamma leads to cardiac
dysfunction in mice. J Clin Invest. 117:2791–2801. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Torac E, Gaman L and Atanasiu V: The
regulator of calcineurin (RCAN1. an important factor involved in
atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases development. J Med
Life. 7:481–487. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuwabara Y, Horie T, Baba O, Watanabe S,
Nishiga M, Usami S, Izuhara M, Nakao T, Nishino T, Otsu K, et al:
MicroRNA-451 exacerbates lipotoxicity in cardiac myocytes and
high-fat diet-induced cardiac hypertrophy in mice through
suppression of the LKB1/AMPK pathway. Circ Res. 116:279–288. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ahrens T: Hemodynamics in sepsis. AACN Adv
Crit Care. 17:435–445. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Merx MW and Weber C: Sepsis and the heart.
Circulation. 116:793–802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zaky A, Deem S, Bendjelid K and Treggiari
MM: Characterization of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis: An ongoing
challenge. Shock. 41:12–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Molnar AO, Fergusson D, Tsampalieros AK,
Bennett A, Fergusson N, Ramsay T and Knoll GA: Generic
immunosuppression in solid organ transplantation: Systematic review
and meta-analysis. BMJ. 350:h31632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K
and Yasuda T: Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction:
Pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Care. 4:222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stanley WC, Lopaschuk GD, Hall JL and
McCormack JG: Regulation of myocardial carbohydrate metabolism
under normal and ischaemic conditions. Potential for
pharmacological interventions. Cardiovasc Res. 33:243–257. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JF, Stam HC and
Reneman RS: Fatty acid homeostasis in the normoxic and ischemic
heart. Physiol Rev. 72:881–940. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ebong IA, Goff DC Jr, Rodriguez CJ, Chen H
and Bertoni AG: Mechanisms of heart failure in obesity. Obes Res
Clin Pract. 8:e540–e548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Haffar T, Bérubé-Simard FA and Bousette N:
Cardiomyocyte lipotoxicity is mediated by Il-6 and causes
down-regulation of PPARs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 459:54–59.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Srivastava RA, Pinkosky SL, Filippov S,
Hanselman JC, Cramer CT and Newton RS: AMP-activated protein
kinase: An emerging drug target to regulate imbalances in lipid and
carbohydrate metabolism to treat cardio-metabolic diseases. J Lipid
Res. 53:2490–2514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Viollet B and Andreelli F: AMP-activated
protein kinase and metabolic control. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 303–330.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park TS, Hu Y, Noh HL, Drosatos K, Okajima
K, Buchanan J, Tuinei J, Homma S, Jiang XC, Abel ED and Goldberg
IJ: Ceramide is a cardiotoxin in lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. J Lipid
Res. 49:2101–2112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Borradaile NM, Buhman KK, Listenberger LL,
Magee CJ, Morimoto ET, Ory DS and Schaffer JE: A critical role for
eukaryotic elongation factor 1A-1 in lipotoxic cell death. Mol Biol
Cell. 17:770–778. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Song XJ, Yang CY, Liu B, Wei Q, Korkor MT,
Liu JY and Yang P: Atorvastatin inhibits myocardial cell apoptosis
in a rat model with post-myocardial infarction heart failure by
downregulating ER stress response. Int J Med Sci. 8:564–572. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Turner MD: Fatty acyl CoA-mediated
inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1693:1–4. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
He H, Liu X, Lv L, Liang H, Leng B, Zhao
D, Zhang Y, Du Z, Chen X, Li S, et al: Calcineurin suppresses
AMPK-dependent cytoprotective autophagy in cardiomyocytes under
oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 5:e9972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|