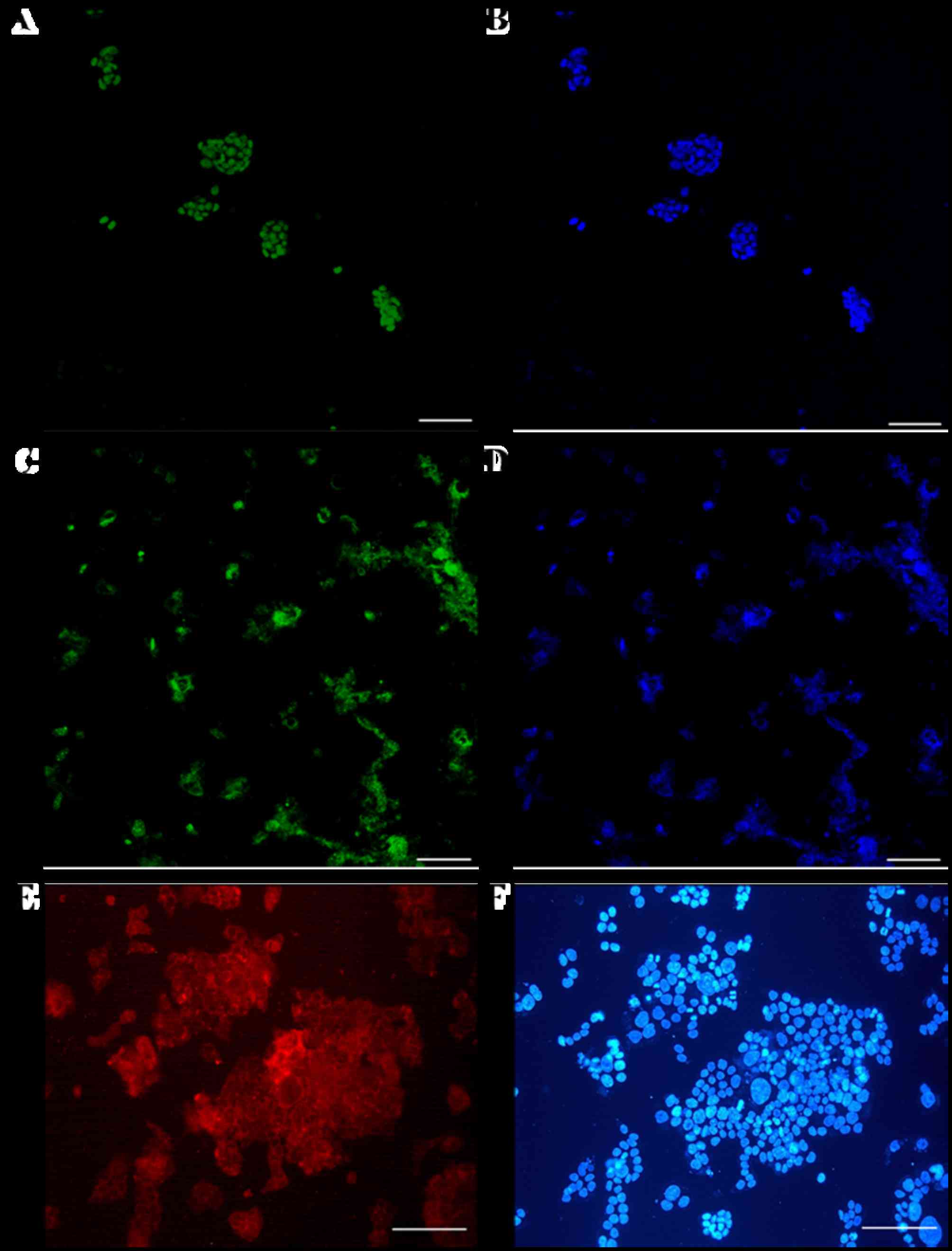
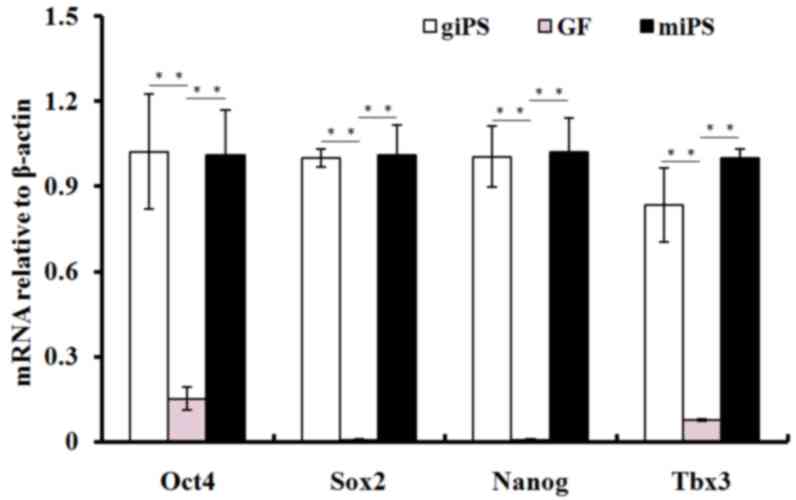
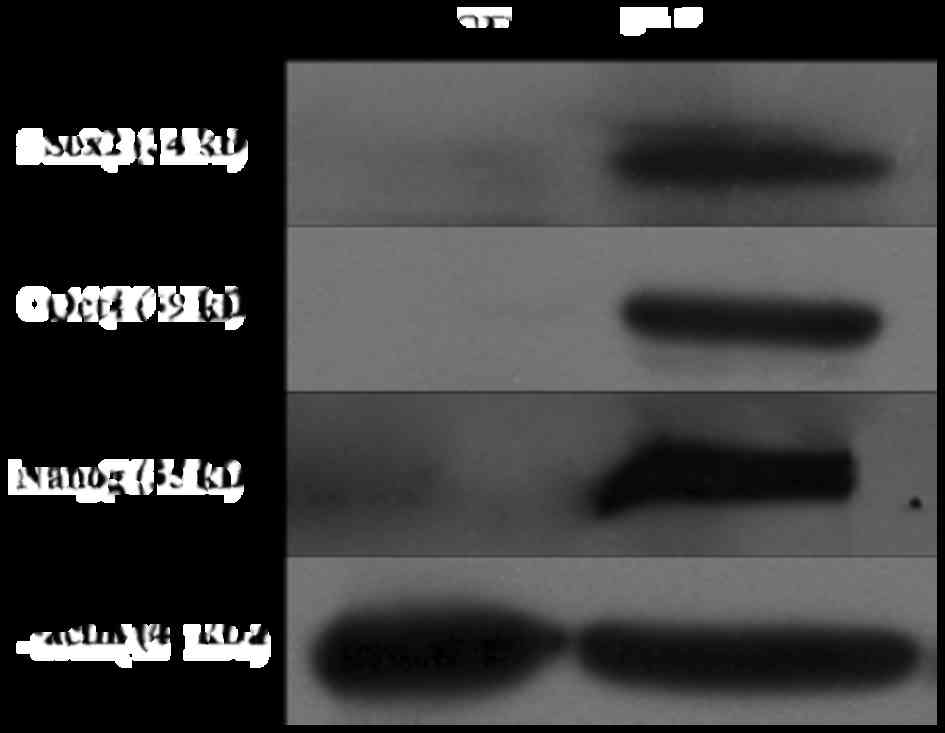
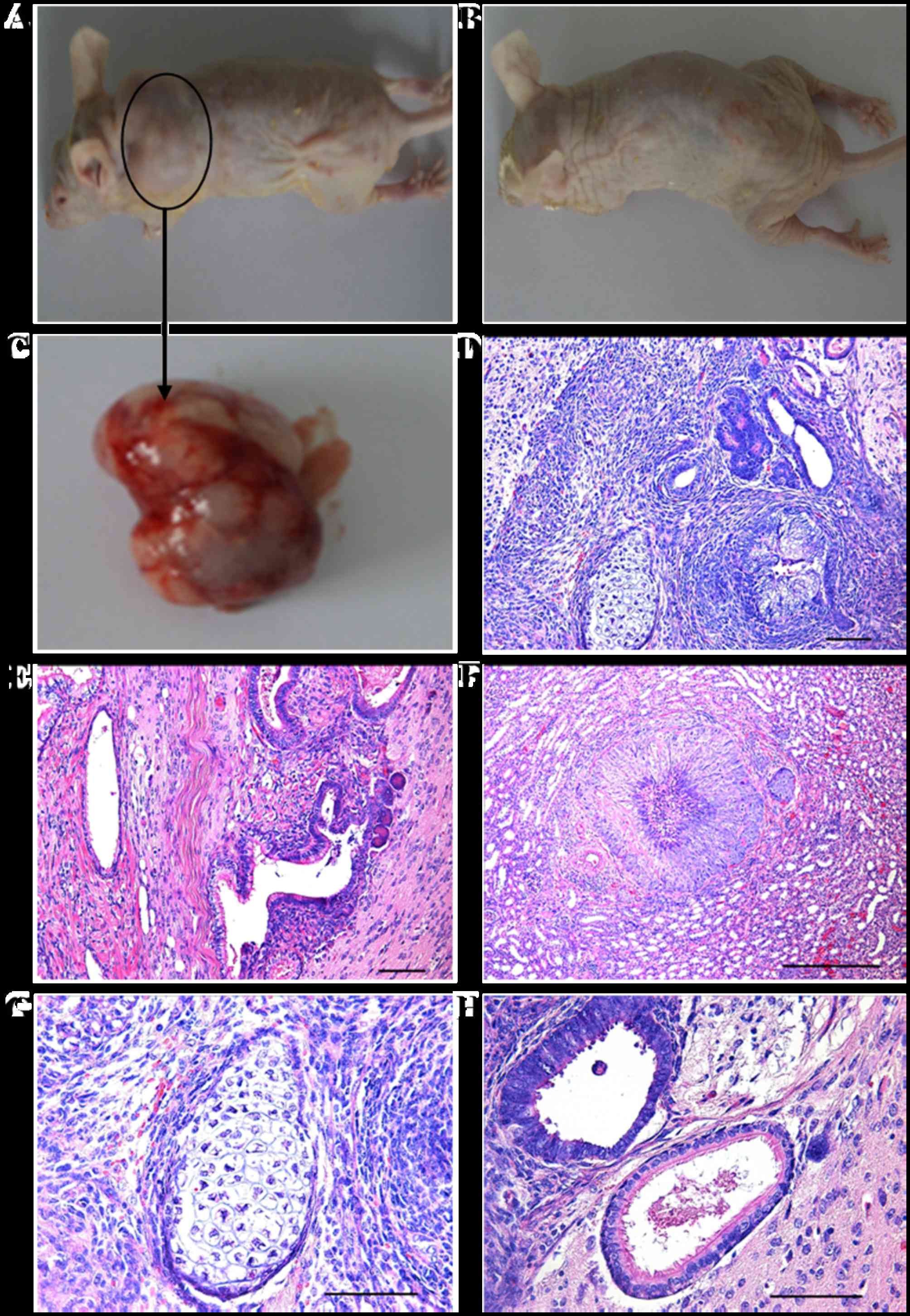
|
1
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu H, Zhu F, Yong J, Zhang P, Hou P, Li
H, Jiang W, Cai J, Liu M, Cui K, et al: Generation of induced
pluripotent stem cells from adult rhesus monkey fibroblasts. Cell
stem cell. 3:587–590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liao J, Cui C, Chen S, Ren J, Chen J, Gao
Y, Li H, Jia N, Cheng L, Xiao H and Xiao L: Generation of induced
pluripotent stem cell lines from adult rat cells. Cell stem cell.
4:11–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ezashi T, Telugu BP, Alexenko AP, Sachdev
S, Sinha S and Roberts RM: Derivation of induced pluripotent stem
cells from pig somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:pp.
10993–10998. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shimada H, Nakada A, Hashimoto Y, Shigeno
K, Shionoya Y and Nakamura T: Generation of canine induced
pluripotent stem cells by retroviral transduction and chemical
inhibitors. Mol Reprod Dev. 77:22010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Mishra A, Tardif SD and
Hornsby PJ: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from
newborn marmoset skin fibroblasts. Stem Cell Res. 4:180–188. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu Y, Mishra A, Qiu Z, Farnsworth S,
Tardif SD and Hornsby PJ: Nonhuman primate induced pluripotent stem
cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Int:. 2012:7671952012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu J, Balehosur D, Murray B, Kelly JM,
Sumer H and Verma PJ: Generation and characterization of
reprogrammed sheep induced pluripotent stem cells. Theriogenology.
77:338–346.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bao L, He L, Chen J, Wu Z, Liao J, Rao L,
Ren J, Li H, Zhu H, Qian L, et al: Reprogramming of ovine adult
fibroblasts to pluripotency via drug-inducible expression of
defined factors. Cell Res. 21:600–608. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han X, Han J, Ding F, Cao S, Lim SS, Dai
Y, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Lim B and Li N: Generation of induced
pluripotent stem cells from bovine embryonic fibroblast cells. Cell
Res. 21:1509–1512. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deng Y, Liu Q, Luo C, Chen S, Li X, Wang
C, Liu Z, Lei X, Zhang H, Sun H, et al: Generation of induced
pluripotent stem cells from buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) fetal
fibroblasts with buffalo defined factors. Stem Cells Dev.
21:2485–2494. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagy K, Sung HK, Zhang P, Laflamme S,
Vincent P, Agha-Mohammadi S, Woltjen K, Monetti C, Michael IP,
Smith LC and Nagy A: Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived
from equine fibroblasts. Stem Cell Rev. 7:693–702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mo X, Li N and Wu S: Generation and
characterization of bat-induced pluripotent stem cells.
Theriogenology. 82:283–293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carey BW, Markoulaki S, Hanna J, Saha K,
Gao Q, Mitalipova M and Jaenisch R: Reprogramming of murine and
human somatic cells using a single polycistronic vector. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:pp. 157–162. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta UD and Katoch VM: Animal models of
tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 85:277–293. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Collins FM: Tuberculosis: The return of an
old enemy. Crit Rev Microbiol. 19:1–16. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mehrabani D, Mahboobi R, Dianatpour M,
Zare S, Tamadon A and Hosseini SE: Establishment, culture, and
characterization of Guinea pig fetal fibroblast cell. Vet Med Int.
2014:5103282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu Y, Melton DW, Zhang Y and Hornsby PJ:
Improved coinfection with amphotropic pseudotyped retroviral
vectors. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009:9010792009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morita S, Kojima T and Kitamura T: Plat-E:
An efficient and stable system for transient packaging of
retroviruses. Gene Ther. 7:1063–1066. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Shu J, He C, Li M, Wang Y, Ou W and
He Y: ROCK inhibitor Y27632 promotes proliferation and diminishes
apoptosis of marmoset induced pluripotent stem cells by suppressing
expression and activity of caspase 3. Theriogenology. 85:302–314.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hentze H, Soong PL, Wang ST, Phillips BW,
Putti TC and Dunn NR: Teratoma formation by human embryonic stem
cells: Evaluation of essential parameters for future safety
studies. Stem Cell Res. 2:198–210. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Prokhorova TA, Harkness LM, Frandsen U,
Ditzel N, Schrøder HD, Burns JS and Kassem M: Teratoma formation by
human embryonic stem cells is site dependent and enhanced by the
presence of Matrigel. Stem Cells Dev. 18:47–54. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huangfu D, Osafune K, Maehr R, Guo W,
Eijkelenboom A, Chen S, Muhlestein W and Melton DA: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from primary human fibroblasts with only
Oct4 and Sox2. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1269–1275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Okita K, Nakagawa M, Hyenjong H, Ichisaka
T and Yamanaka S: Generation of mouse induced pluripotent stem
cells without viral vectors. Science. 322:949–953. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hasegawa K, Fujioka T, Nakamura Y,
Nakatsuji N and Suemori H: A method for the selection of human
embryonic stem cell sublines with high replating efficiency after
single-cell dissociation. Stem Cells. 24:2649–2660. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Esteban MA, Wang T, Qin B, Yang J, Qin D,
Cai J, Li W, Weng Z, Chen J, Ni S, et al: Vitamin C enhances the
generation of mouse and human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell
Stem Cell. 6:71–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K,
Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Okita K, Mochiduki Y, Takizawa N
and Yamanaka S: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells
without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol.
26:101–106. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Soldner F, Hockemeyer D, Beard C, Gao Q,
Bell GW, Cook EG, Hargus G, Blak A, Cooper O, Mitalipova M, et al:
Parkinson's disease patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells
free of viral reprogramming factors. Cell. 136:964–977. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang CW, Lai YS, Pawlik KM, Liu K, Sun
CW, Li C, Schoeb TR and Townes TM: Polycistronic lentiviral vector
for ‘hit and run’ reprogramming of adult skin fibroblasts to
induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 27:1042–1049. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou H, Wu S, Joo JY, Zhu S, Han DW, Lin
T, Trauger S, Bien G, Yao S, Zhu Y, et al: Generation of induced
pluripotent stem cells using recombinant proteins. Cell Stem Cell.
4:381–384. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim D, Kim CH, Moon JI, Chung YG, Chang
MY, Han BS, Ko S, Yang E, Cha KY, Lanza R and Kim KS: Generation of
human induced pluripotent stem cells by direct delivery of
reprogramming proteins. Cell Stem Cell. 4:472–476. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|