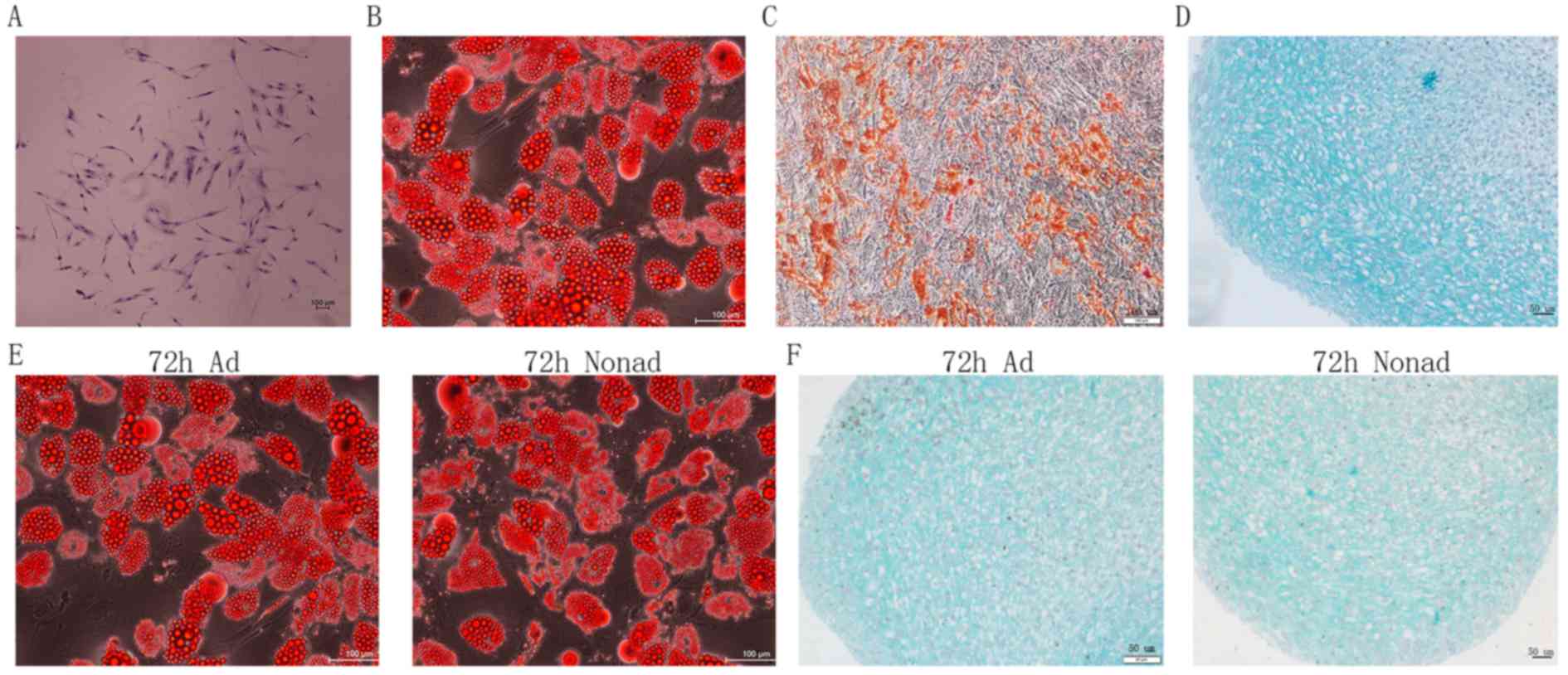
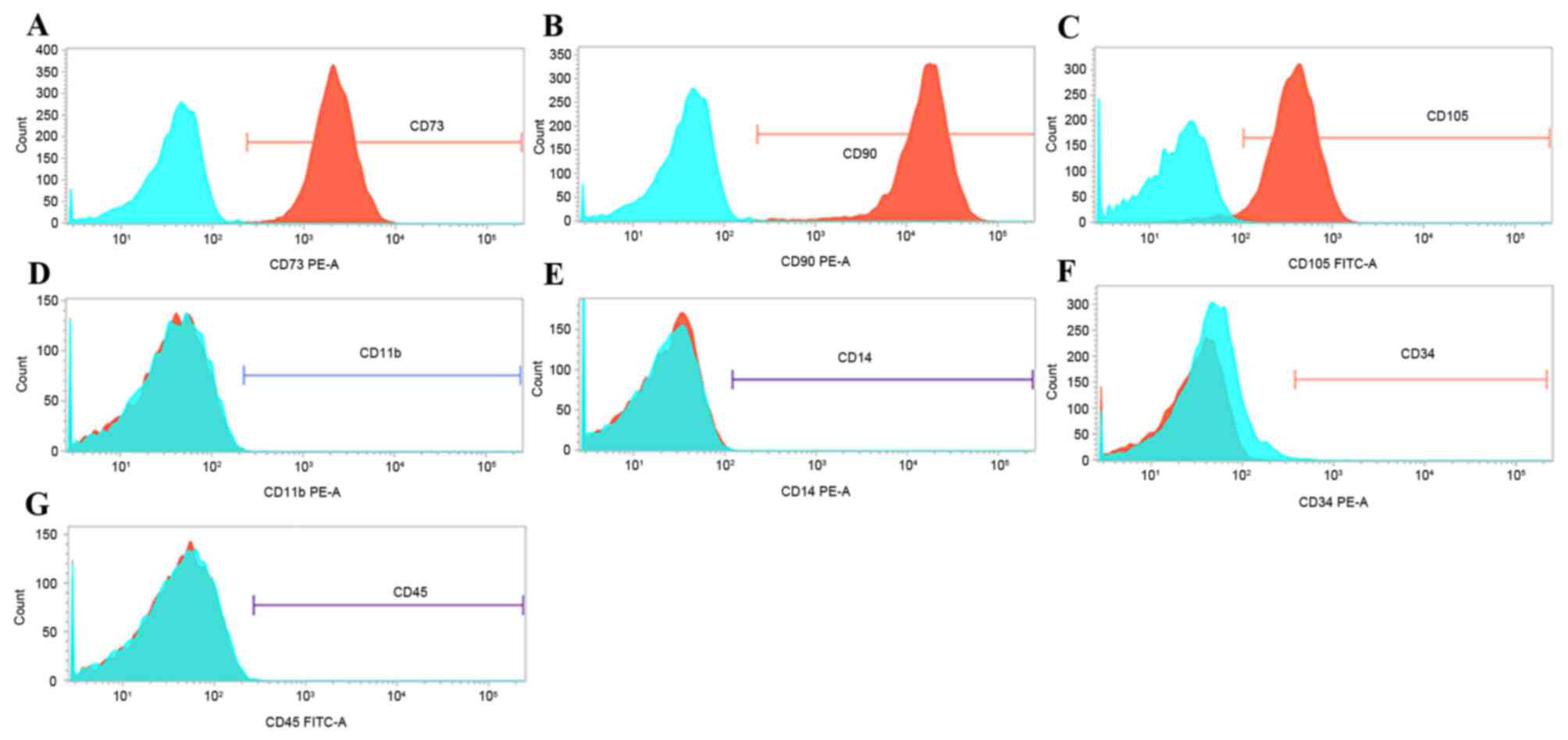
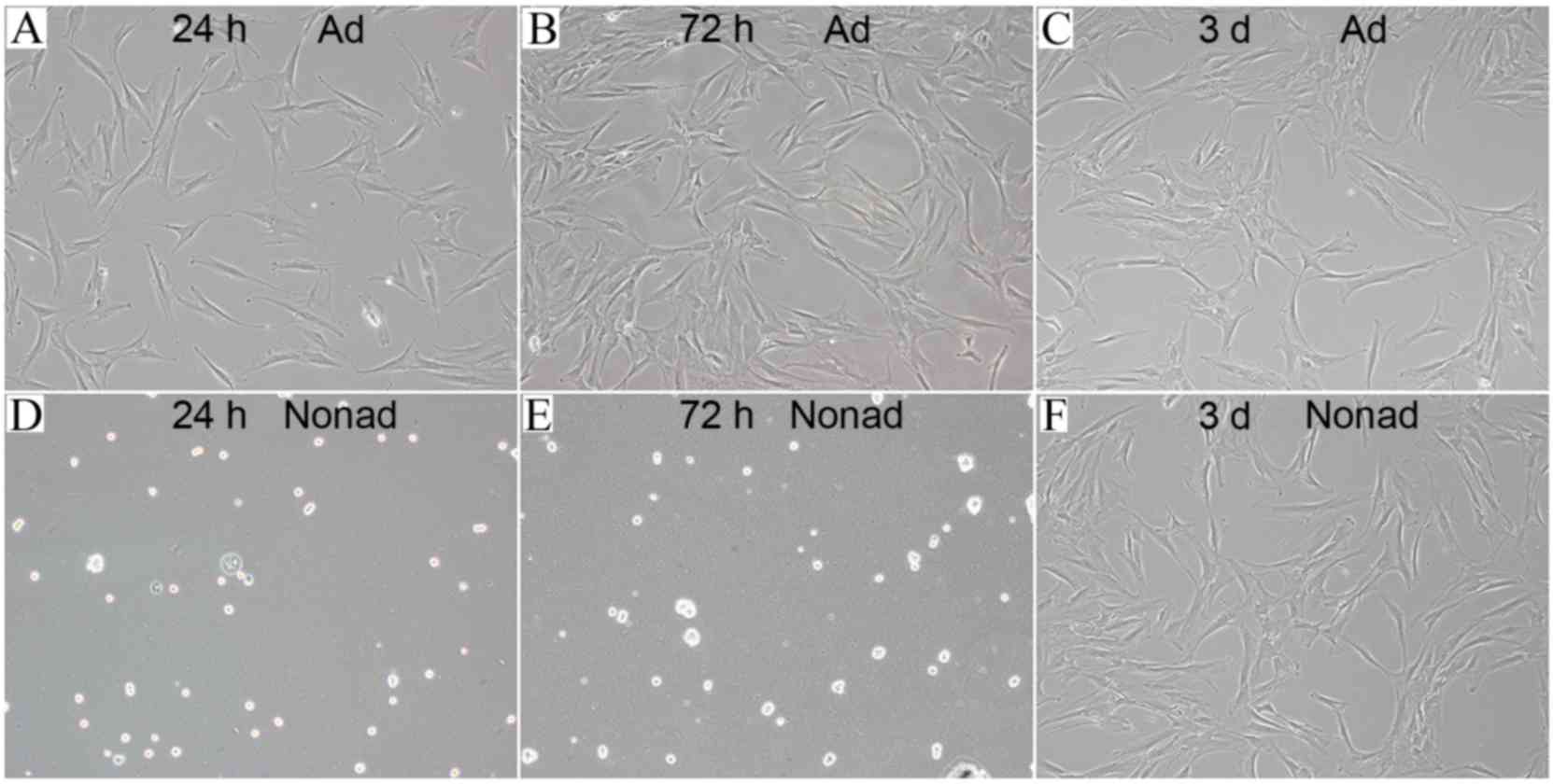
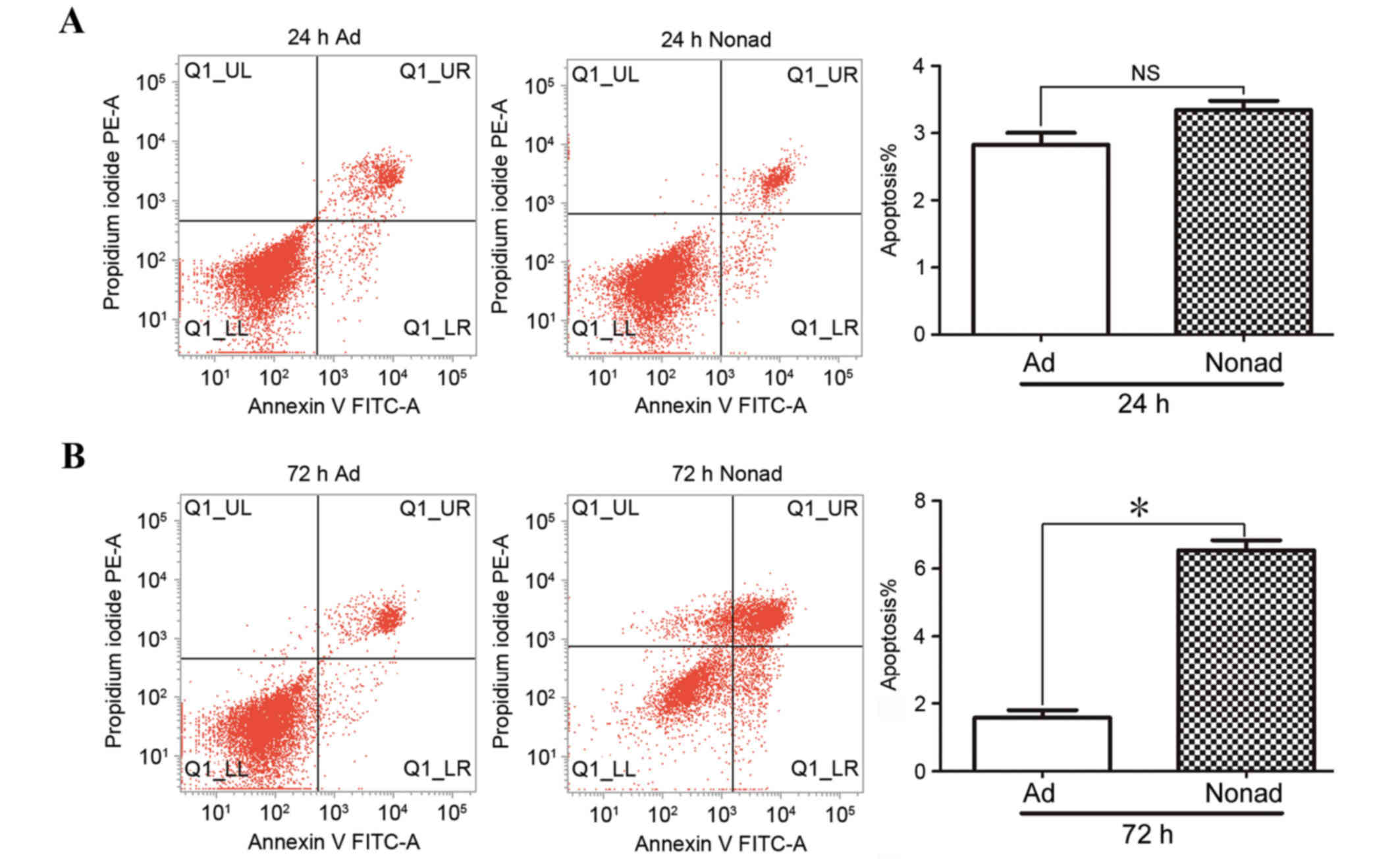
|
1
|
Satija NK, Singh VK, Verma YK, Gupta P,
Sharma S, Afrin F, Sharma M, Sharma P, Tripathi RP and Gurudutta
GU: Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: A new paradigm in
regenerative medicine. J Cell Mol Med. 13:4385–4402. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Novotny NM, Ray R, Markel TA, Crisostomo
PR, Wang M, Wang Y and Meldrum DR: Stem cell therapy in myocardial
repair and remodeling. J Am Coll Surg. 207:423–434. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deuse T, Peter C, Fedak PW, Doyle T,
Reichenspurner H, Zimmermann WH, Eschenhagen T, Stein W, Wu JC,
Robbins RC and Schrepfer S: Hepatocyte growth factor or vascular
endothelial growth factor gene transfer maximizes mesenchymal stem
cell-based myocardial salvage after acute myocardial infarction.
Circulation. 120(11 Suppl): S247–S254. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rabani V, Shahsavani M, Gharavi M, Piryaei
A, Azhdari Z and Baharvand H: Mesenchymal stem cell infusion
therapy in a carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis model
affects matrix metalloproteinase expression. Cell Biol Int.
34:601–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Burlacu A: Tracking the mesenchymal stem
cell fate after transplantation into the infarcted myocardium. Curr
Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:284–291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei H, Li Z, Hu S, Chen X and Cong X:
Apoptosis of mesenchymal stem cells induced by hydrogen peroxide
concerns both endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial death
pathway through regulation of caspases, p38 and JNK. J Cell
Biochem. 111:967–978. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Potier E, Ferreira E, Meunier A, Sedel L,
Logeart-Avramoglou D and Petite H: Prolonged hypoxia concomitant
with serum deprivation induces massive human mesenchymal stem cell
death. Tissue Eng. 13:1325–1331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vunjak-Novakovic G and Scadden DT:
Biomimetic platforms for human stem cell research. Cell Stem Cell.
8:252–261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng B, Deng W, Xiao P, Zeng K, Zhang S,
Zhang H, Deng DY and Yang Y: Nonadherent culture method
downregulates stem cell antigen-1 expression in mouse bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 10:31–36. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qian H, Le Blanc K and Sigvardsson M:
Primary mesenchymal stem and progenitor cells from bone marrow lack
expression of CD44 protein. J Biol Chem. 287:25795–25807. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH image to imageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop Dj and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International society for cellular
therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sheikh AY, Huber BC, Narsinh KH, Spin JM,
van der Bogt K, de Almeida PE, Ransohoff KJ, Kraft DL, Fajardo G,
Ardigo D, et al: In vivo functional and transcriptional profiling
of bone marrow stem cells after transplantation into ischemic
myocardium. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:92–102. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baksh D, Davies JE and Zandstra PW: Adult
human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells are capable
of adhesion-independent survival and expansion. Exp Hematol.
31:723–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baksh D, Zandstra PW and Davies JE: A
non-contact suspension culture approach to the culture of
osteogenic cells derived from a CD49elow subpopulation of human
bone marrow-derived cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 98:1195–1208. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parrish AB, Freel CD and Kornbluth S:
Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:pii: a0086722013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Berghe T Vanden, Van Loo G, Saelens X, Van
Gurp M, Brouckaert G, Kalai M, Declercq W and Vandenabeele P:
Differential signaling to apoptotic and necrotic cell death by
Fas-associated death domain protein FADD. J Biol Chem.
279:7925–7933. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rowinsky EK: Targeted induction of
apoptosis in cancer management: The emerging role of tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor activating
agents. J Clin Oncol. 23:9394–9407. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Philchenkov A, Zavelevich M, Kroczak TJ
and Los M: Caspases and cancer: Mechanisms of inactivation and new
treatment modalities. Exp Oncol. 26:82–97. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Deschepper M, Oudina K, David B, Myrtil V,
Collet C, Bensidhoum M, Logeart-Avramoglou D and Petite H: Survival
and function of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) depend on glucose to
overcome exposure to long-term, severe and continuous hypoxia. J
Cell Mol Med. 15:1505–1514. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|