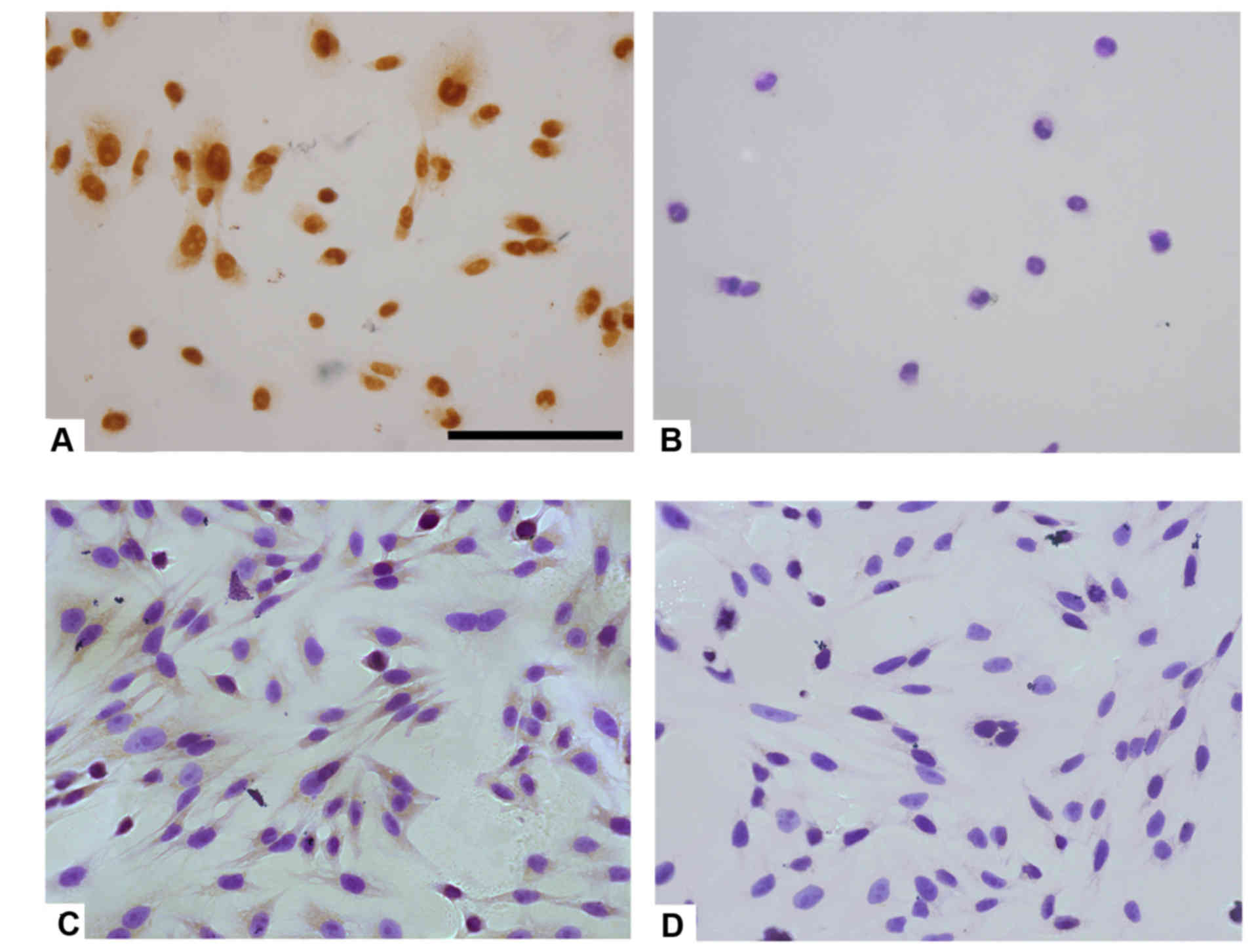
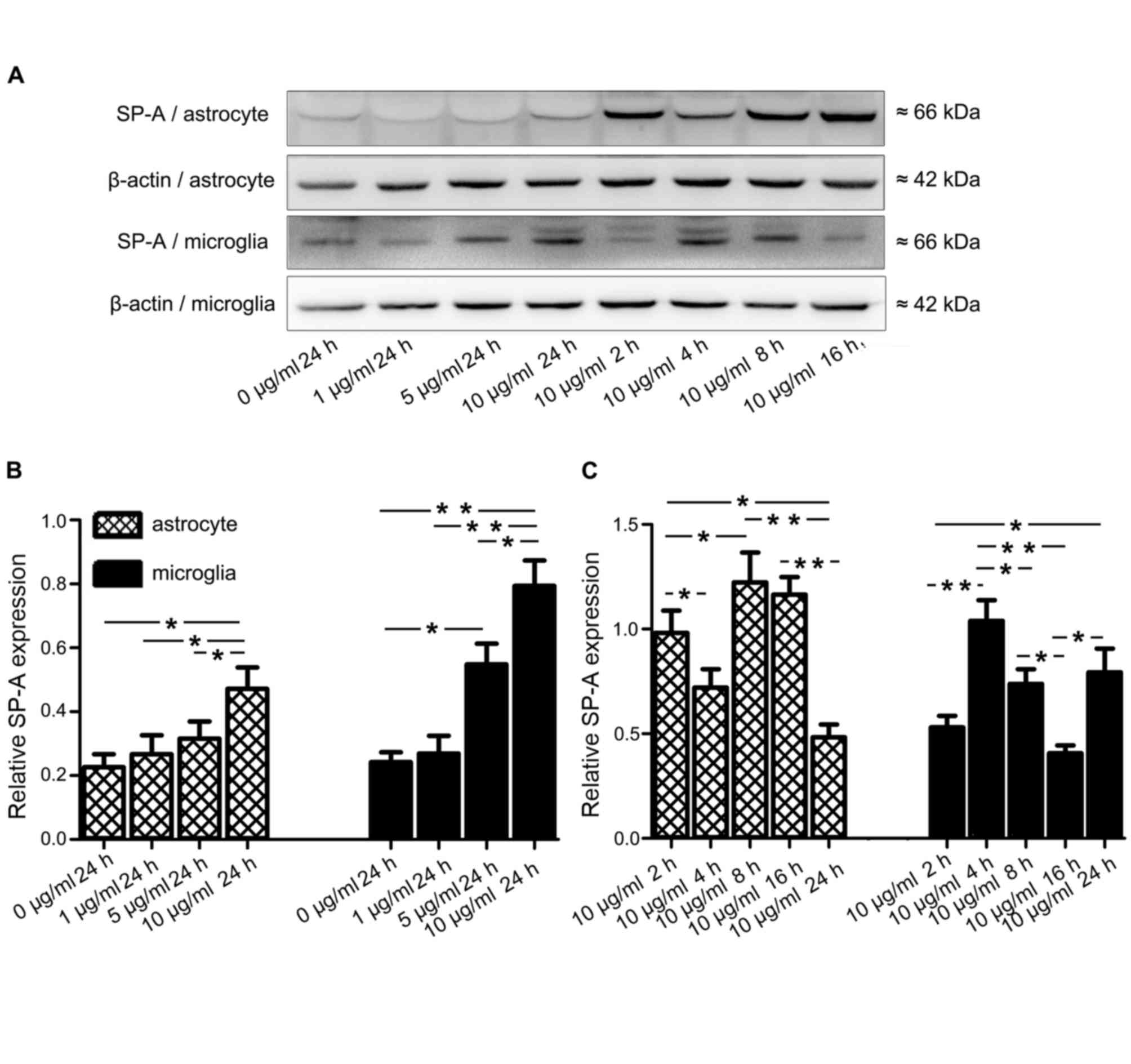
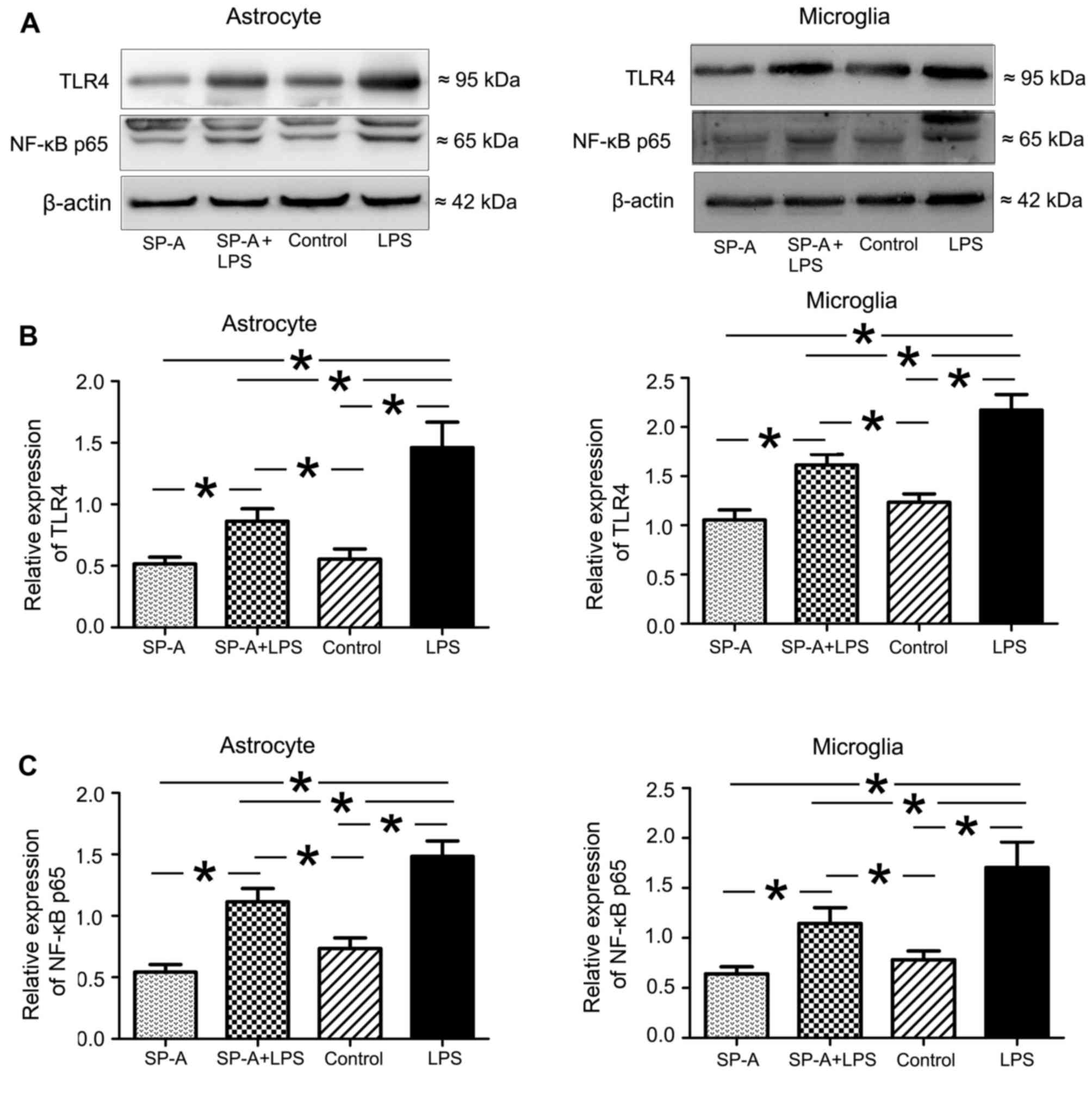
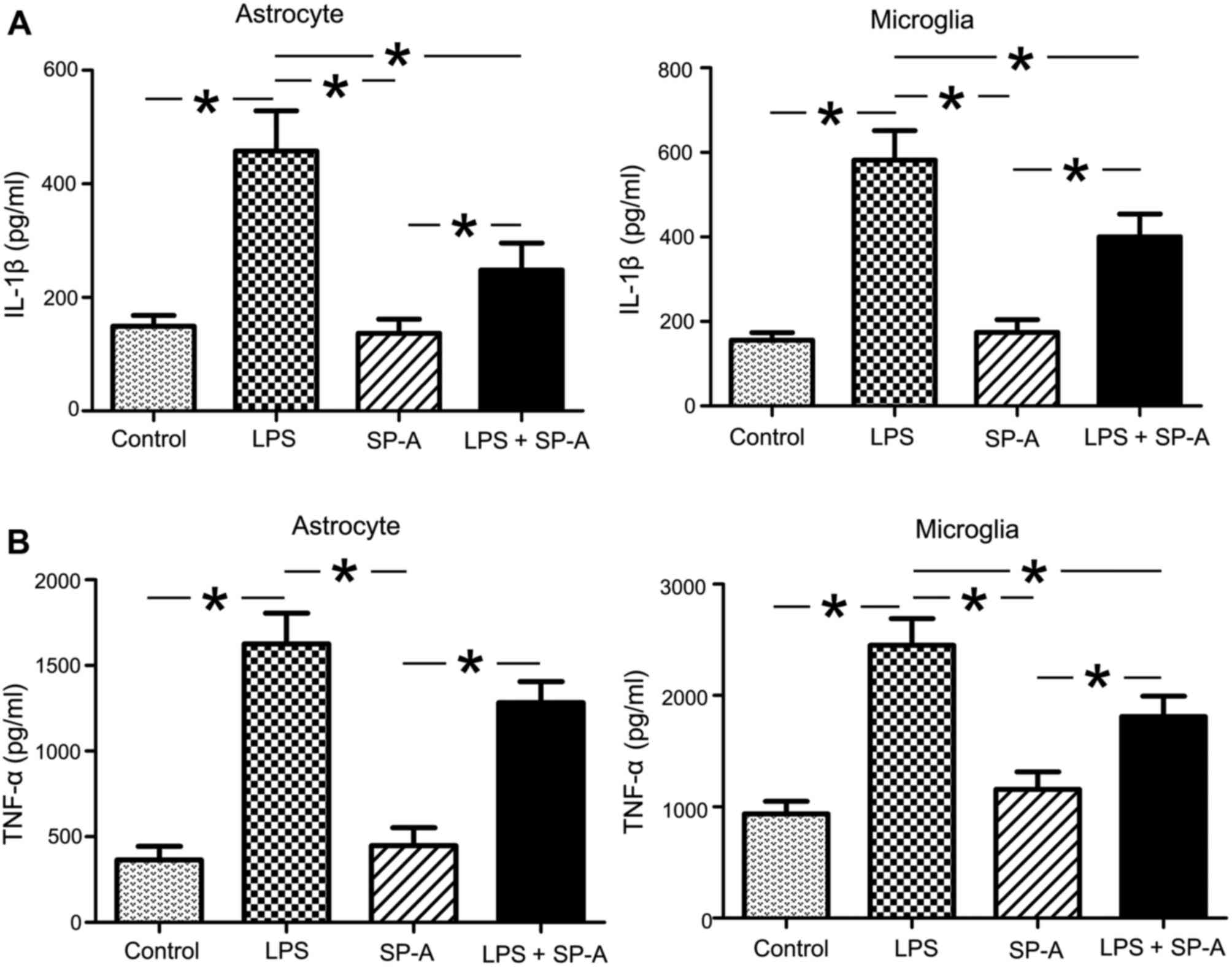
|
1
|
Wright JR: Immunoregulatory functions of
surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:58–68. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chroneos ZC, Midde K, Sever-Chroneos Z and
Jagannath C: Pulmonary surfactant and tuberculosis. Tuberculosis
(Edinb). 89 Suppl 1:S10–S14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kishore U, Greenhough TJ, Waters P, Shrive
AK, Ghai R, Kamran MF, Bernal AL, Reid KB, Madan T and Chakraborty
T: Surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D: Structure, function and
receptors. Mol Immunol. 43:1293–1315. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schaub B, Westlake RM, He H, Arestides R,
Haley KJ, Campo M, Velasco G, Bellou A, Hawgood S, Poulain FR, et
al: Surfactant protein D deficiency influences allergic immune
responses. Clin Exp Allergy. 34:1819–1826. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hartshorn KL, Crouch E, White MR,
Colamussi ML, Kakkanatt A, Tauber B, Shepherd V and Sastry KN:
Pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D enhance neutrophil uptake of
bacteria. Am J Physiol. 274:L958–L969. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chuang CY, Chen TL and Chen RM: Molecular
mechanisms of lipopolysaccharide-caused induction of surfactant
protein-A gene expression in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells.
Toxicol Lett. 191:132–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan HT, Gowan S, Kelly FJ and Bingle CD:
Cloning of guinea pig surfactant protein A defines a distinct
cellular distribution pattern within the lung. Am J Physiol.
273:L900–L906. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rubio S, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, Chailley-Heu
B, Kahn A, Bourbon JR and Ducroc R: Pulmonary surfactant protein A
(SP-A) is expressed by epithelial cells of small and large
intestine. J Biol Chem. 270:12162–12169. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Snyder GD, Oberley-Deegan RE, Goss KL,
Romig-Martin SA, Stoll LL, Snyder JM and Weintraub NL: Surfactant
protein D is expressed and modulates inflammatory responses in
human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 294:H2053–H2059. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schob S, Schicht M, Sel S, Stiller D,
Kekulé AS, Paulsen F, Maronde E and Bräuer L: The detection of
surfactant proteins a, b, c and d in the human brain and their
regulation in cerebral infarction, autoimmune conditions and
infections of the CNS. PLoS One. 8:e744122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quintanilla HD, Liu Y, Fatheree NY, Atkins
CL, Hashmi SS, Floros J, McCormack FX, Rhoads JM and Alcorn JL:
Oral administration of surfactant protein-a reduces pathology in an
experimental model of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr
Gastroenterol Nutr. 60:613–620. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee HM, Kang HJ, Woo JS, Chae SW, Lee SH
and Hwang SJ: Upregulation of surfactant protein a in chronic
rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 116:328–330. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wootten CT, Labadie RF, Chen A and Lane
KF: Differential expression of surfactant protein A in the nasal
mucosa of patients with allergy symptoms. Arch Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 132:1001–1007. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo JM, Wan YS, Liu ZQ, Wang GR, Floros J
and Zhou HH: Regularity of distribution of immunoreactive pulmonary
surfactant protein A in rat tissues. Int J Mol Med. 14:343–351.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Henning LN, Azad AK, Parsa KV, Crowther
JE, Tridandapani S and Schlesinger LS: Pulmonary surfactant protein
a regulates TLR expression and activity in human macrophages. J
Immunol. 180:7847–7858. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duperray A, Barbe D, Raguenez G, Weksler
BB, Romero IA, Couraud PO, Perron H and Marche PN: Inflammatory
response of endothelial cells to an endogenous retrovirus
associated to MS is mediated by TLR4. Int Immunol. 27:545–553.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parajuli B, Sonobe Y, Kawanokuchi J, Doi
Y, Noda M, Takeuchi H, Mizuno T and Suzumura A: GM-CSF increases
LPS-induced production of proinflammatory mediators via
upregulation of TLR4 and CD14 in murine microglia. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:2682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu Y, Li W and Zhou C, Lu F, Gao T, Liu Y,
Cao J, Zhang Y, Zhang Y and Zhou C: Ketamine inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced astrocytes activation by suppressing
TLR4/NF-ĸB pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 30:609–617. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao L, Kan EM, Lu J, Hao A, Dheen ST, Kaur
C and Ling EA: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates microglial activation
and production of inflammatory mediators in neonatal rat brain
following hypoxia: Role of TLR4 in hypoxic microglia. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Blanco AM, Vallés SL, Pascual M and Guerri
C: Involvement of TLR4/type IIL-1 receptor signaling in the
induction of inflammatory mediators and cell death induced by
ethanol in cultured astrocytes. J Immunol. 175:6893–6899. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mohajeri M, Sadeghizadeh M and Javan M:
Pertussis toxin promotes relapsing-remitting experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. J Neuroinflammation.
289:105–110. 2015.
|
|
22
|
Nayak A, Dodagatta-Marri E, Tsolaki AG and
Kishore U: An insight into the diverse roles of surfactant
proteins, SP-A and SP-D in innate and adaptive immunity. Frontiers
in immunology. 3:1312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, Hu F, Wang G, Zhou Q and Ding G:
Lipopolysaccharide- induced expression of surfactant proteins A1
and A2 in human renal tubular epithelial cells. J Inflamm (Lond).
10:22013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Furlan R, Cuomo C and Martino G: Animal
models of multiple sclerosis. Methods Mol Biol. 549:157–173. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Files DK, Jausurawong T, Katrajian R and
Danoff R: Multiple Sclerosis. Primary Care. 42:159–175. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsumoto Y, Ohmori K and Fujiwara M:
Microglial and astroglial reactions to inflammatory lesions of
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the rat central
nervous system. J Neuroimmunol. 37:23–33. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Napoli I and Neumann H: Protective effects
of microglia in multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol. 225:24–28. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lundgaard I, Osório MJ, Kress BT,
Sanggaard S and Nedergaard M: White matter astrocytes in health and
disease. Neuroscience. 276:161–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Awasthi S, Madhusoodhanan R and Wolf R:
Surfactant protein-A and toll-like receptor-4 modulate immune
functions of preterm baboon lung dendritic cell precursor cells.
Cell Immunol. 268:87–96. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bhatti F, Ball G, Hobbs R, Linens A,
Munzar S, Akram R, Barber AJ, Anderson M, Elliott M and Edwards M:
Pulmonary surfactant protein a is expressed in mouse retina by
muller cells and impacts neovascularization in oxygen-induced
retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:232–242. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Agrawal V, Smart K, Jilling T and Hirsch
E: Surfactant Protein (SP)-A suppresses preterm delivery and
inflammation via TLR2. PLoS One. 8:e6399902013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kawai T and Akira S: Pathogen recognition
with Toll-like receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 17:338–344. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Holmskov U, Lawson P, Teisner B, Tornoe I,
Willis AC, Morgan C, Koch C and Reid KB: Isolation and
characterization of a new member of the scavenger receptor
superfamily, glycoprotein-340 (gp-340), as a lung surfactant
protein-D binding molecule. J Biol Chem. 272:13743–13749. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sano H, Sohma H, Muta T, Nomura S, Voelker
DR and Kuroki Y: Pulmonary surfactant protein A modulates the
cellular response to smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides by
interaction with CD14. J Immunol. 163:387–395. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|