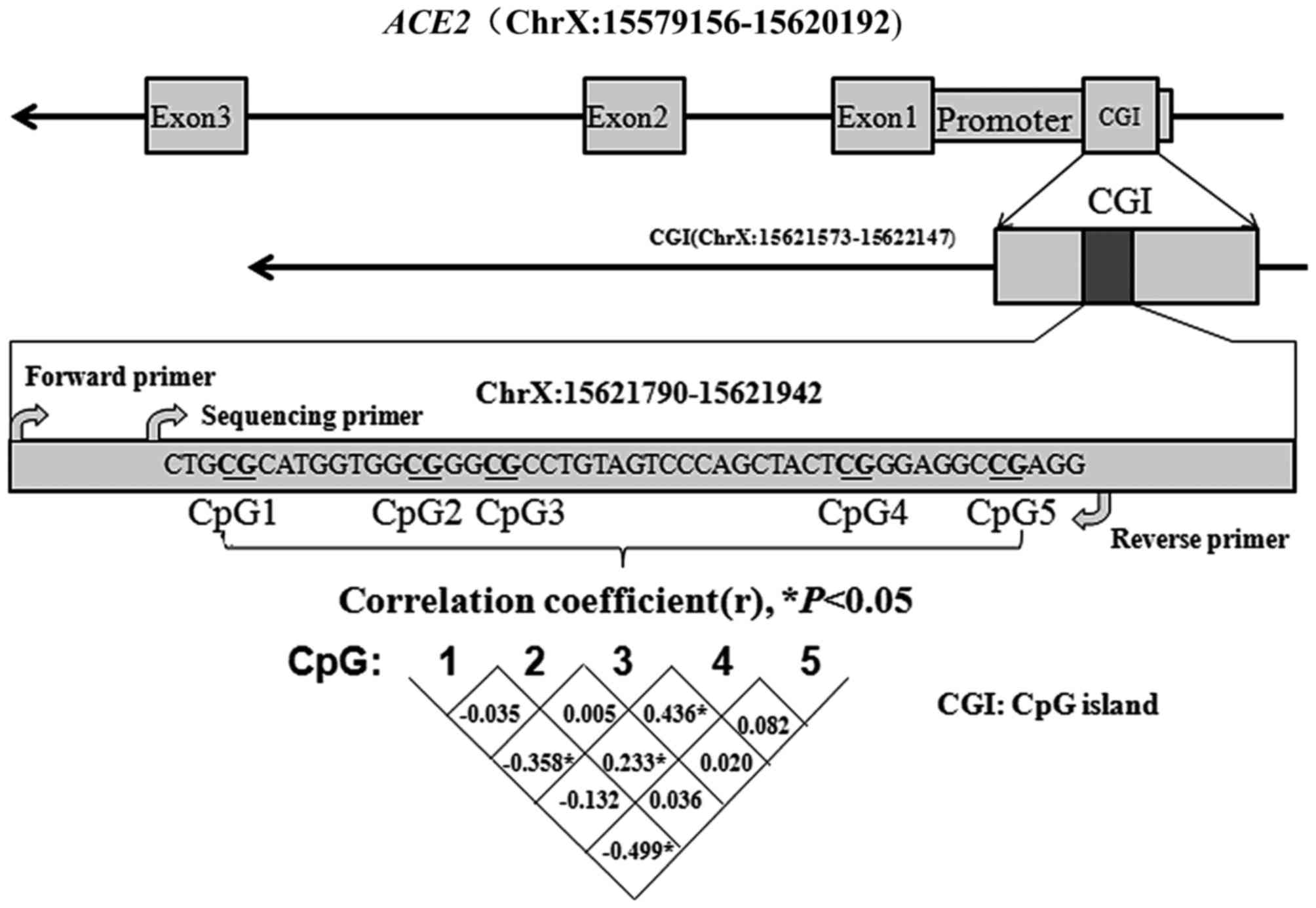
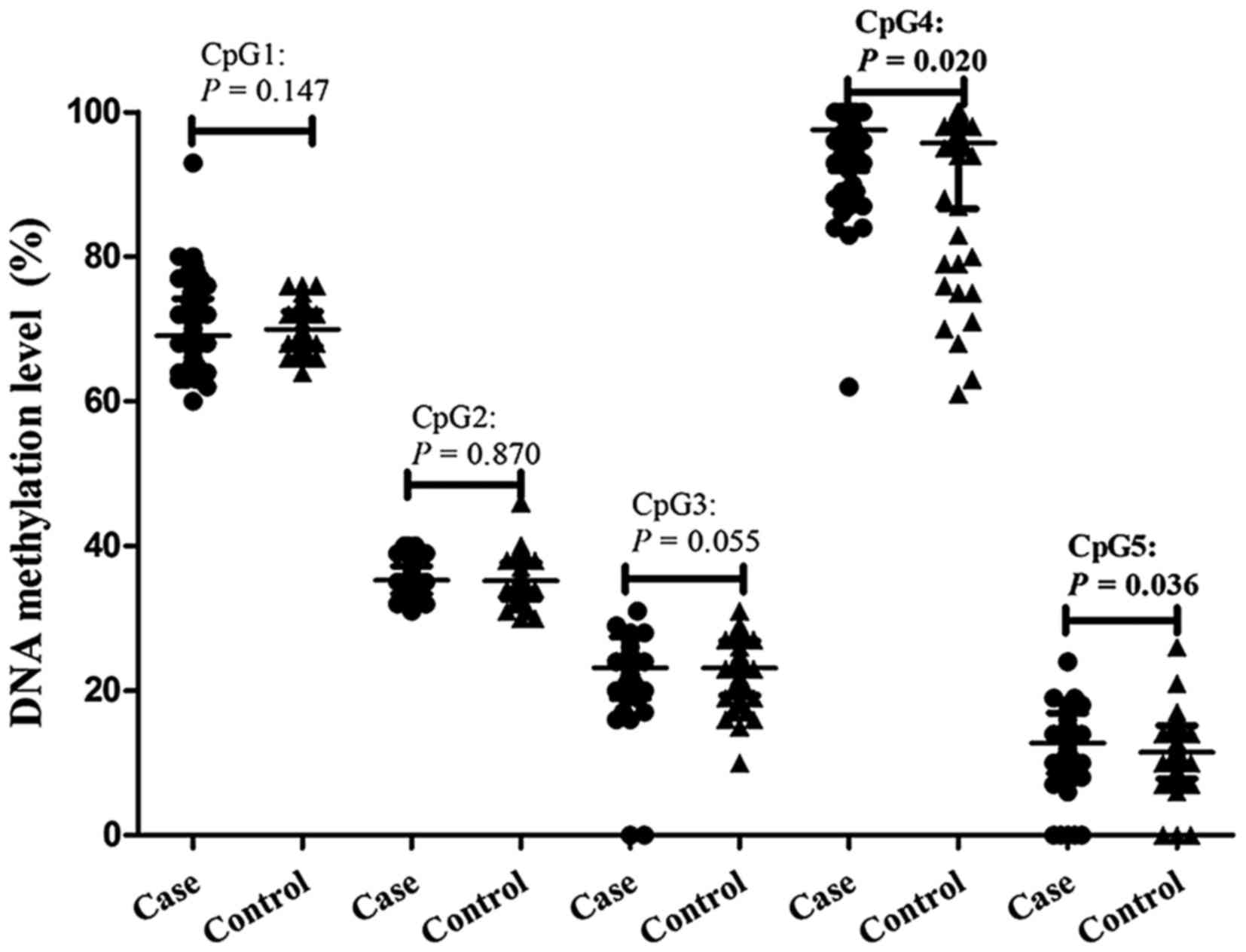
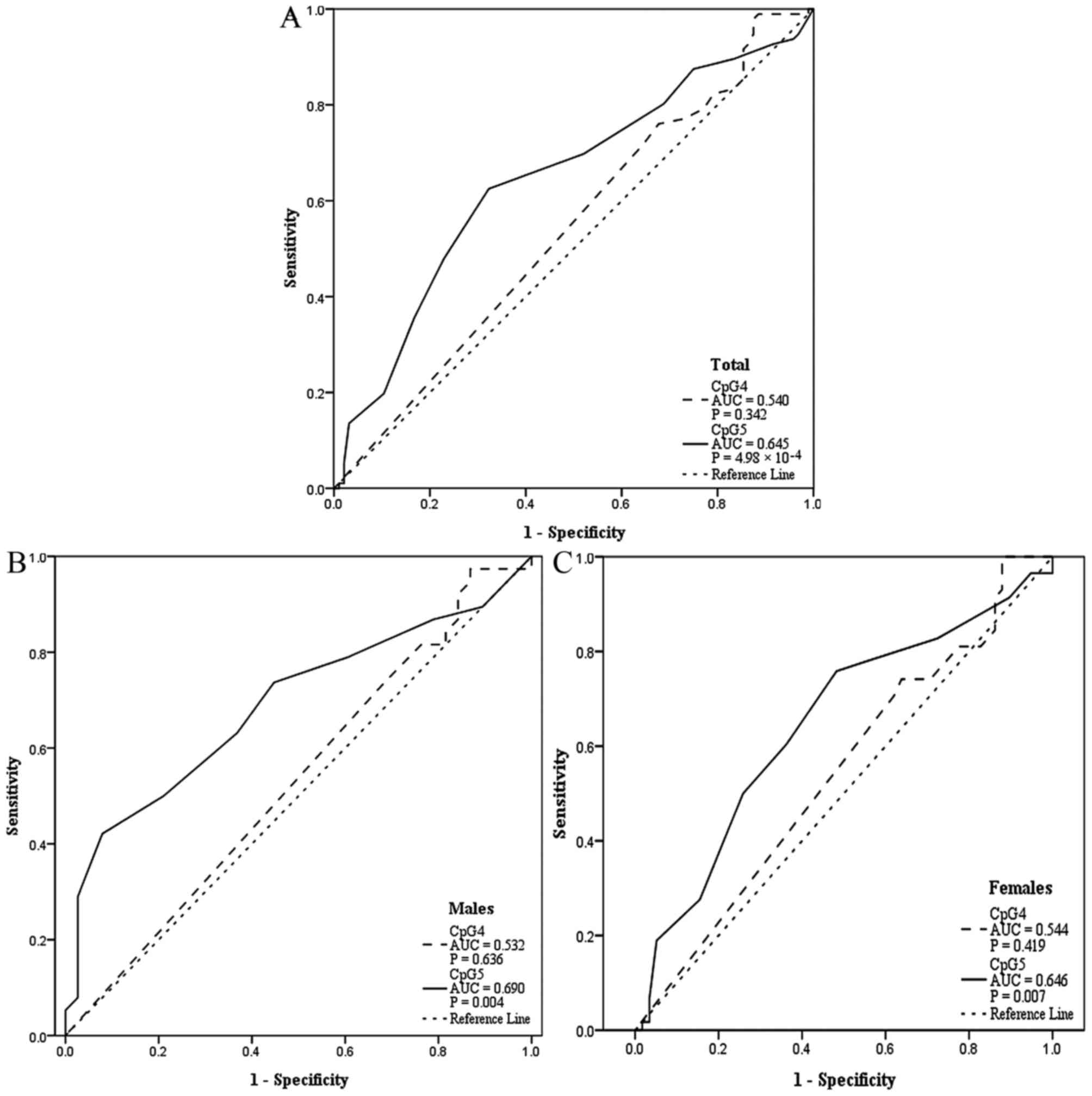
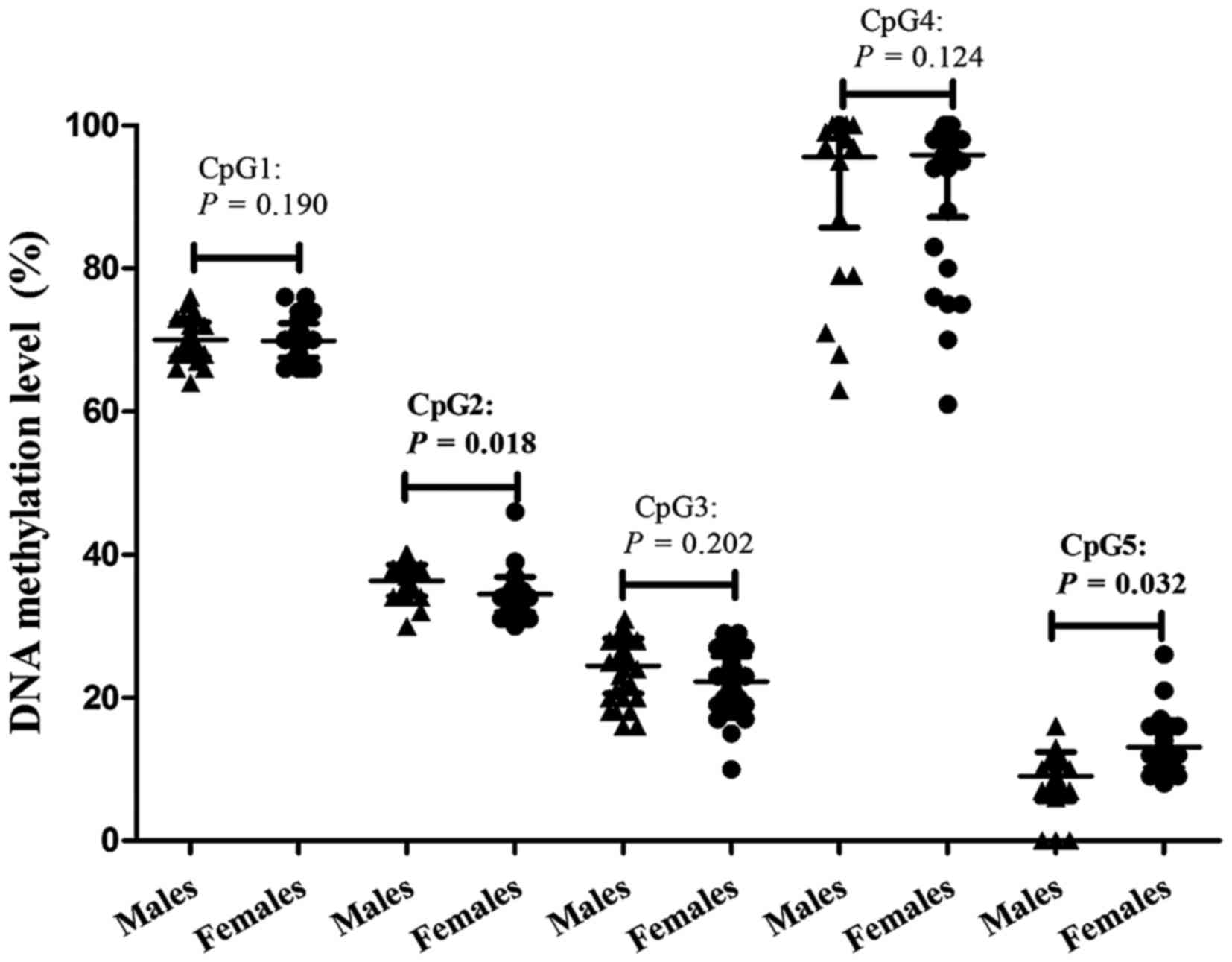
|
1
|
Li D, Lv J, Liu F, Liu P, Yang X, Feng Y,
Chen G and Hao M: Hypertension burden and control in mainland
China: Analysis of nationwide data 2003–2012. Int J Cardiol.
184:637–644. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner
P, Whelton PK and He J: Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of
worldwide data. Lancet. 365:217–223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pausova Z, Tremblay J and Hamet P:
Gene-environment interactions in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep.
1:42–50. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu X, Chang YP, Yan D, Weder A, Cooper R,
Luke A, Kan D and Chakravarti A: Associations between hypertension
and genes in the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension.
41:1027–1034. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K,
Gosselin M, Stagliano N, Donovan M, Woolf B, Robison K, Jeyaseelan
R, et al: A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related
carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9.
Circ Res. 87:E1–E9. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E,
Christie G and Turner AJ: A human homolog of angiotensin-converting
enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a
captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem.
275:33238–33243. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tallant EA and Clark MA: Molecular
mechanisms of inhibition of vascular growth by angiotensin-(1–7).
Hypertension. 42:574–579. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yagil Y and Yagil C: Hypothesis: ACE2
modulates blood pressure in the mammalian organism. Hypertension.
41:871–873. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu N, Yang Y, Wang Y, Liu Y, Fu G, Chen D,
Dai H, Fan X, Hui R and Zheng Y: ACE2 gene polymorphism and
essential hypertension: An updated meta-analysis involving 11,051
subjects. Mol Biol Rep. 39:6581–6589. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Patel SK, Wai B, Ord M, MacIsaac RJ, Grant
S, Velkoska E, Panagiotopoulos S, Jerums G, Srivastava PM and
Burrell LM: Association of ACE2 genetic variants with blood
pressure, left ventricular mass, and cardiac function in Caucasians
with type 2 diabetes. Am J Hypertens. 25:216–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Razin A, Webb C, Szyf M, Yisraeli J,
Rosenthal A, Naveh-Many T, Sciaky-Gallili N and Cedar H: Variations
in DNA methylation during mouse cell differentiation in vivo and in
vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 81:pp. 2275–2279. 1984; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deaton AM and Bird A: CpG islands and the
regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 25:1010–1022. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bogdarina I, Welham S, King PJ, Burns SP
and Clark AJ: Epigenetic modification of the renin-angiotensin
system in the fetal programming of hypertension. Circ Res.
100:520–526. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rangel M, dos Santos JC, Ortiz PH, Hirata
M, Jasiulionis MG, Araujo RC, Ierardi DF and Mdo C Franco:
Modification of epigenetic patterns in low birth weight children:
Importance of hypomethylation of the ACE gene promoter. PLoS One.
9:e1061382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang F, Demura M, Cheng Y, Zhu A,
Karashima S, Yoneda T, Demura Y, Maeda Y, Namiki M, Ono K, et al:
Dynamic CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-associated changes of DNA
methylation in the angiotensinogen gene. Hypertension. 63:281–288.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fan R, Mao S, Zhong F, Gong M, Yin F, Hao
L and Zhang L: Association of AGTR1 promoter methylation levels
with essential hypertension risk: A matched case-control study.
Cytogenet Genome Res. 147:95–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang LN, Liu PP, Wang L, Yuan F, Xu L,
Xin Y, Fei LJ, Zhong QL, Huang Y, Xu L, et al: Lower ADD1 gene
promoter DNA methylation increases the risk of essential
hypertension. PLoS One. 8:e634552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fan R, Wang WJ, Zhong QL, Duan SW, Xu XT,
Hao LM, Zhao J and Zhang LN: Aberrant methylation of the GCK gene
body is associated with the risk of essential hypertension. Mol Med
Rep. 12:2390–2394. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
European Society of Hypertension-European
Society of Cardiology Guidelines Committee, . 2003 European Society
of Hypertension-European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the
management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 21:1011–1053.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Perloff D, Grim C, Flack J, Frohlich ED,
Hill M, McDonald M and Morgenstern BZ: Human blood pressure
determination by sphygmomanometry. Circulation. 88:2460–2470. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bassil CF, Huang Z and Murphy SK:
Bisulfite pyrosequencing. Methods Mol Biol. 1049:95–107. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li LC and Dahiya R: MethPrimer: Designing
primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics. 18:1427–1431. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mikeska T, Felsberg J, Hewitt CA and
Dobrovic A: Analysing DNA methylation using bisulphite
pyrosequencing. Methods Mol Biol. 791:33–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lou XY, Chen GB, Yan L, Ma JZ, Zhu J,
Elston RC and Li MD: A generalized combinatorial approach for
detecting gene-by-gene and gene-by-environment interactions with
application to nicotine dependence. Am J Hum Genet. 80:1125–1137.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pei F, Wang X, Yue R, Chen C, Huang J,
Huang J, Li X and Zeng C: Differential expression and DNA
methylation of angiotensin type 1A receptors in vascular tissues
during genetic hypertension development. Mol Cell Biochem. 402:1–8.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang D, Zheng D, Wang L, Huang Y, Liu H,
Xu L, Liao Q, Liu P, Shi X, Wang Z, et al: Elevated PLA2G7 gene
promoter methylation as a gender-specific marker of aging increases
the risk of coronary heart disease in females. PLoS One.
8:e597522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Berletch JB, Yang F, Xu J, Carrel L and
Disteche CM: Genes that escape from X inactivation. Hum Genet.
130:237–245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hellman A and Chess A: Gene body-specific
methylation on the active X chromosome. Science. 315:1141–1143.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carrel L and Willard HF: X-inactivation
profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression
in females. Nature. 434:400–404. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sebag IA, Gillis MA, Calderone A, Kasneci
A, Meilleur M, Haddad R, Noiles W, Patel B and Chalifour LE: Sex
hormone control of left ventricular structure/function: Mechanistic
insights using echocardiography, expression, and DNA methylation
analyses in adult mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H1706–H1715. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Christensen BC, Houseman EA, Marsit CJ,
Zheng S, Wrensch MR, Wiemels JL, Nelson HH, Karagas MR, Padbury JF,
Bueno R, et al: Aging and environmental exposures alter
tissue-specific DNA methylation dependent upon CpG island context.
PLoS Genet. 5:e10006022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Breitling LP, Yang R, Korn B, Burwinkel B
and Brenner H: Tobacco-smoking-related differential DNA
methylation: 27K discovery and replication. Am J Hum Genet.
88:450–457. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Philibert RA, Plume JM, Gibbons FX, Brody
GH and Beach SR: The impact of recent alcohol use on genome wide
DNA methylation signatures. Front Genet. 3:542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ronn T, Volkov P, Davegårdh C, Dayeh T,
Hall E, Olsson AH, Nilsson E, Tornberg A, Nitert M Dekker, Eriksson
KF, et al: A six months exercise intervention influences the
genome-wide DNA methylation pattern in human adipose tissue. PLoS
Genet. 9:e10035722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Alexeeff SE, Baccarelli AA, Halonen J,
Coull BA, Wright RO, Tarantini L, Bollati V, Sparrow D, Vokonas P
and Schwartz J: Association between blood pressure and DNA
methylation of retrotransposons and pro-inflammatory genes. Int J
Epidemiol. 42:270–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ishida K, Kobayashi T, Ito S, Komatsu Y,
Yokoyama T, Okada M, Abe A, Murasawa A and Yoshie H: Interleukin-6
gene promoter methylation in rheumatoid arthritis and chronic
periodontitis. J Periodontol. 83:917–925. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pogribny IP, Pogribna M, Christman JK and
James SJ: Single-site methylation within the p53 promoter region
reduces gene expression in a reporter gene construct: Possible in
vivo relevance during tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 60:588–594.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zou B, Chim CS, Zeng H, Leung SY, Yang Y,
Tu SP, Lin MC, Wang J, He H, Jiang SH, et al: Correlation between
the single-site CpG methylation and expression silencing of the
XAF1 gene in human gastric and colon cancers. Gastroenterology.
131:1835–1843. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fan S and Zhang X: CpG island methylation
pattern in different human tissues and its correlation with gene
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 383:421–425. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mirza S, Sharma G, Parshad R, Srivastava
A, Gupta SD and Ralhan R: Clinical significance of promoter
hypermethylation of ERβ and RARβ2 in tumor and serum DNA in Indian
breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:3107–3115. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|