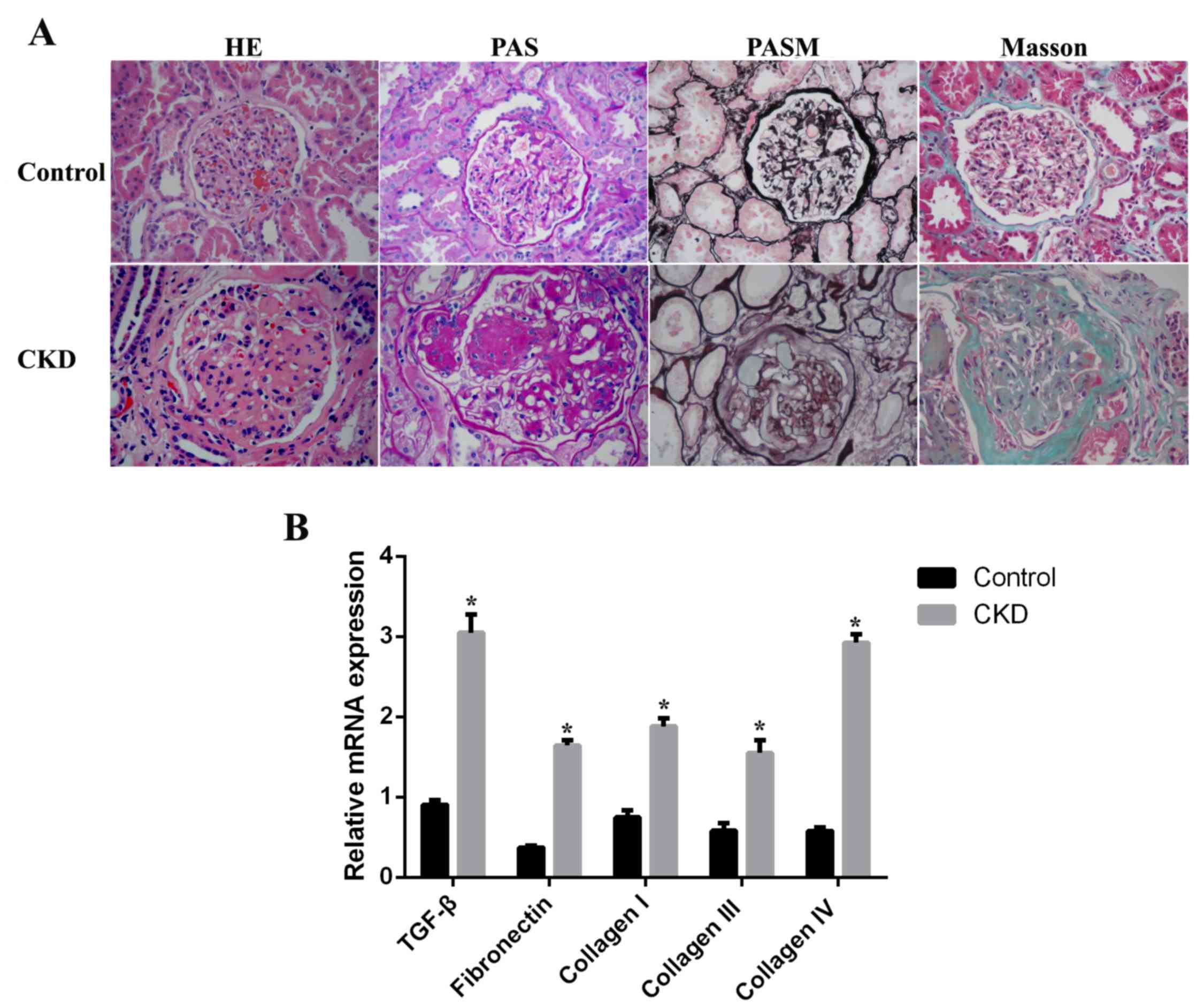
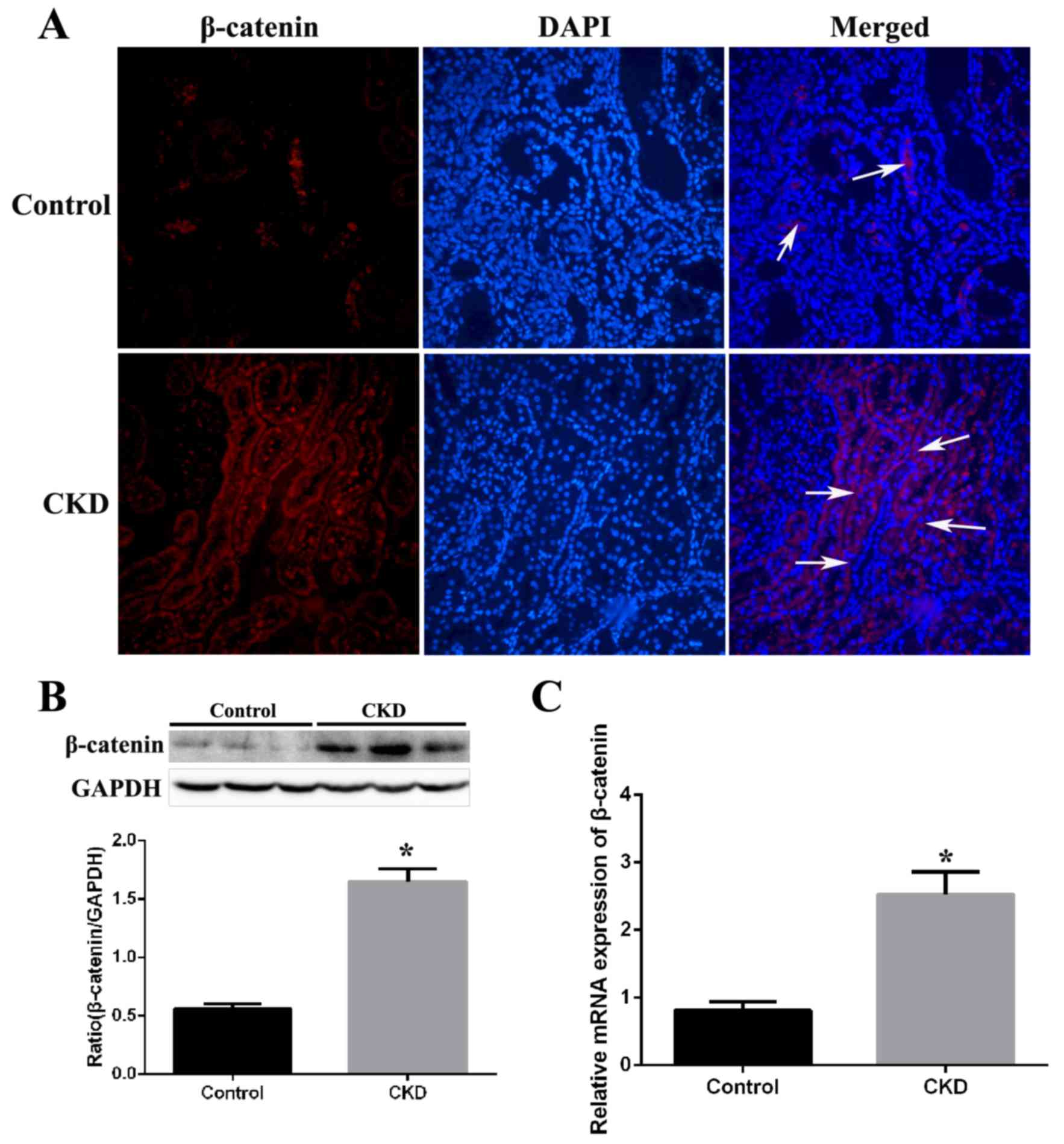
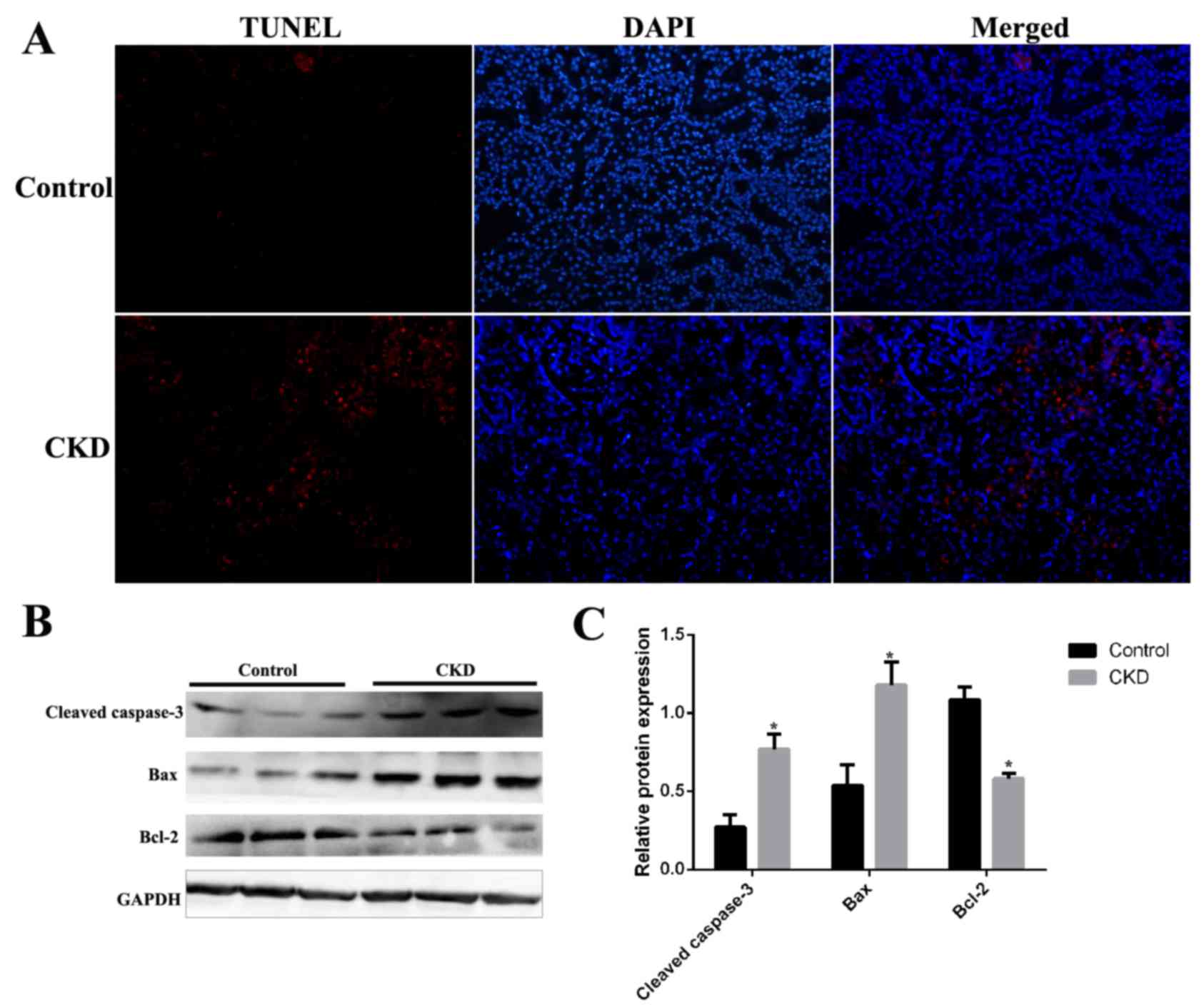
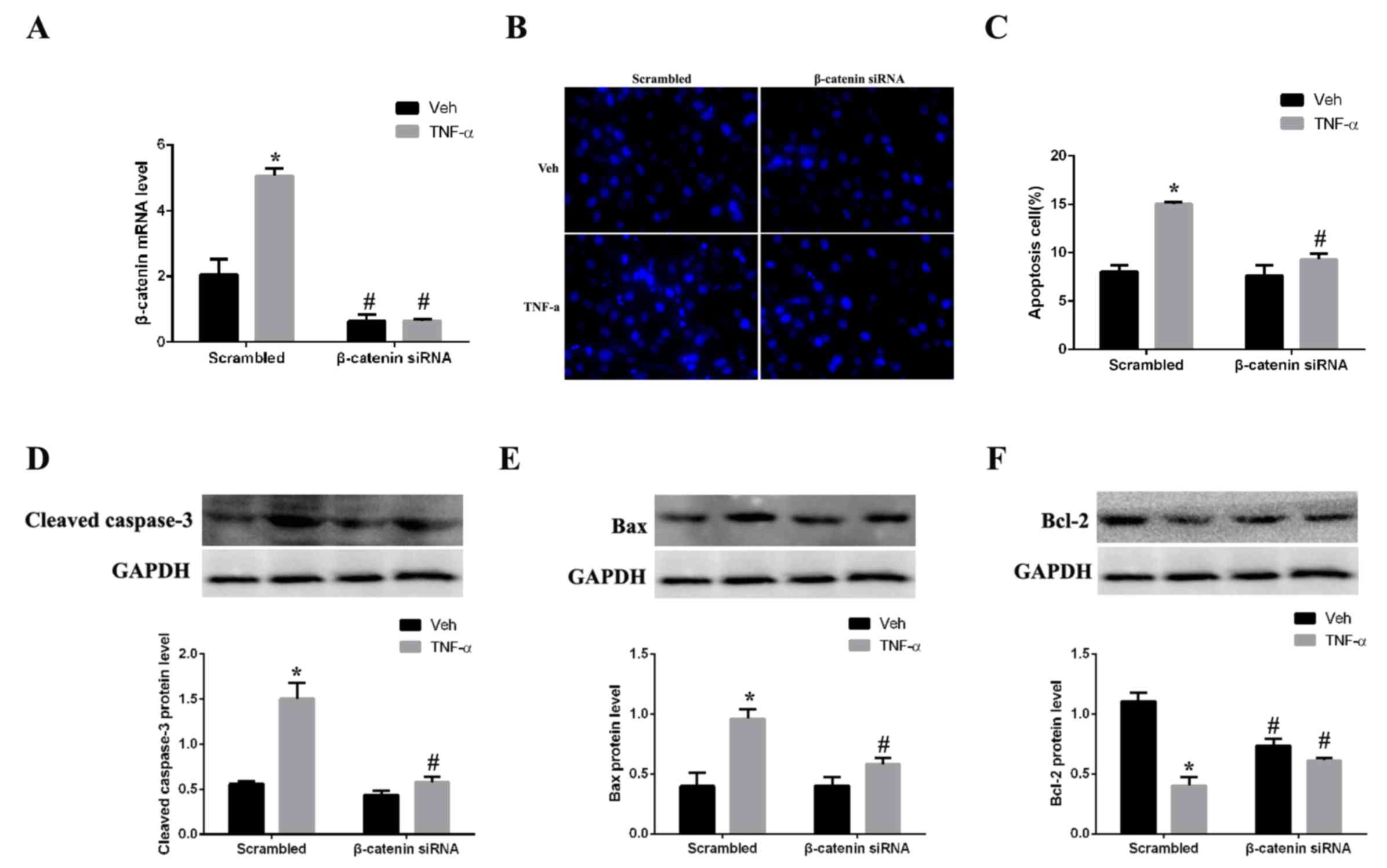
|
1
|
Kazancioğlu R: Risk factors for chronic
kidney disease: An update. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 3:368–371.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Falke LL, Gholizadeh S, Goldschmeding R,
Kok RJ and Nguyen TQ: Diverse origins of the
myofibroblast-implications for kidney fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol.
11:233–244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guo Y, Xiao L, Sun L and Liu F:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: A promising new target for fibrosis
diseases. Physiol Res. 61:337–346. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sutariya B, Jhonsa D and M N Saraf: TGF-β:
The connecting link between nephropathy and fibrosis.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 38:39–49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wynn TA: Common and unique mechanisms
regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. J Clin
Invest. 117:524–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kriz W, Kaissling B and Le Hir M:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in kidney fibrosis: Fact or
fantasy? J Clin Invest. 121:468–474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eger A, Stockinger A, Park J, Langkopf E,
Mikula M, Gotzmann J, Mikulits W, Beug H and Foisner R:
Beta-catenin and TGFbeta signalling cooperate to maintain a
mesenchymal phenotype after FosER-induced epithelial to mesenchymal
transition. Oncogene. 23:2672–2680. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sato M: Upregulation of the
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway induced by transforming growth factor-beta
in hypertrophic scars and keloids. Acta Derm Venereol. 86:300–307.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng JH, She H, Han YP, Wang J, Xiong S,
Asahina K and Tsukamoto H: Wnt antagonism inhibits hepatic stellate
cell activation and liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 294:G39–G49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei J, Melichian D, Komura K, Hinchcliff
M, Lam AP, Lafyatis R, Gottardi CJ, MacDougald OA and Varga J:
Canonical Wnt signaling induces skin fibrosis and subcutaneous
lipoatrophy: A novel mouse model for scleroderma? Arthritis Rheum.
63:1707–1717. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou T, He X, Cheng R, Zhang B, Zhang RR,
Chen Y, Takahashi Y, Murray AR, Lee K, Gao G and Ma JX: Implication
of dysregulation of the canonical wingless-type MMTV integration
site (WNT) pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia.
55:255–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He W, Dai C, Li Y, Zeng G, Monga SP and
Liu Y: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes renal interstitial
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:765–776. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hao S, He W, Li Y, Ding H, Hou Y, Nie J,
Hou FF, Kahn M and Liu Y: Targeted inhibition of β-catenin/CBP
signaling ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 22:1642–1653. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Akhmetshina A, Palumbo K, Dees C, Bergmann
C, Venalis P, Zerr P, Horn A, Kireva T, Beyer C, Zwerina J, et al:
Activation of canonical Wnt signalling is required for
TGF-β-mediated fibrosis. Nat Commun. 3:7352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Samant RS, Li
Y, Conner M, Hidalgo B, Alvarez RD, Landen CN, Straughn JM and
Buchsbaum DJ: Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway by niclosamide: A
therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 134:112–120.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Zhu H, Sun Z, Xiang Z, Ge Y, Ni C,
Luo Z, Qian W and Han X: Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
promotes epithelial differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and
repairs bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
307:C234–C244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanjore H, Degryse AL, Crossno PF, Xu XC,
McConaha ME, Jones BR, Polosukhin VV, Bryant AJ, Cheng DS, Newcomb
DC, et al: β-Catenin in the alveolar epithelium protects from lung
fibrosis after intratracheal bleomycin. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
187:630–639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang DT, Huang RH, Cheng X, Zhang ZH, Yang
YJ and Lin X: Tanshinone IIA attenuates renal fibrosis and
inflammation via altering expression of TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB
signaling pathway in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Int Immunopharmacol.
26:4–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Verma UN, Surabhi RM, Schmaltieg A,
Becerra C and Gaynor RB: Small interfering RNAs directed against
β-catenin inhibit the in vitro and in vivo growth of colon cancer
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1291–1300. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan RJ, Zhou D, Zhou L and Liu Y:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int Suppl
(2011). 4:84–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou D, Tan RJ, Fu H and Liu Y:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in kidney injury and repair: A double-edged
sword. Lab Invest. 96:156–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peng J and Dong Z: Role changes of
β-catenin in kidney injury and repair. Kidney Int. 82:509–511.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Kiss LP, Monga SP,
Holzman LB and Liu Y: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte
dysfunction and albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1997–2008. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
von Toerne C, Schmidt C, Adams J, Kiss E,
Bedke J, Porubsky S, Gretz N, Lindenmeyer MT, Cohen CD, Gröne HJ
and Nelson PJ: Wnt pathway regulation in chronic renal allograft
damage. Am J Transplant. 9:2223–2239. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao L, Zhou D, Tan RJ, Fu H, Zhou L, Hou
FF and Liu Y: Sustained activation of Wnt/β-Catenin signaling
drives AKI to CKD progression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:1724–1740.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lin CL, Cheng H, Tung CW, Huang WJ, Chang
PJ, Yang JT and Wang JY: Simvastatin reverses high glucose-induced
apoptosis of mesangial cells via modulation of Wnt Signaling
pathway. Am J Nephrol. 28:290–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haramis AP, Begthel H, van den Born M, Van
Es J, Jonkheer S, Offerhaus GJ and Clevers H: De novo crypt
formation and juvenile polyposis on BMP inhibition in mouse
intestine. Science. 30:1684–1686. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Polakis P: The many ways of Wnt in cancer.
CurrOpin Genet Dev. 17:45–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhou L, Li Y, Zhou D, Tan RJ and Liu Y:
Loss of Klotho contributes to kidney injury by derepression of
Wnt/β-Catenin signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:771–785. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|