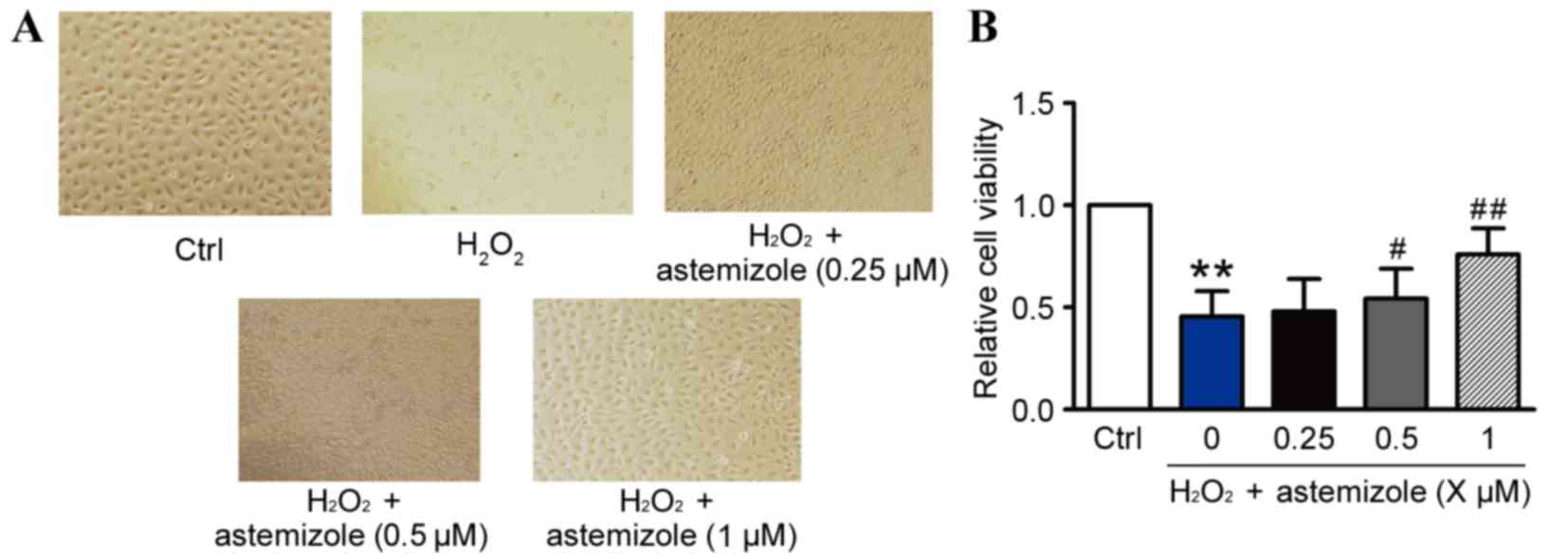
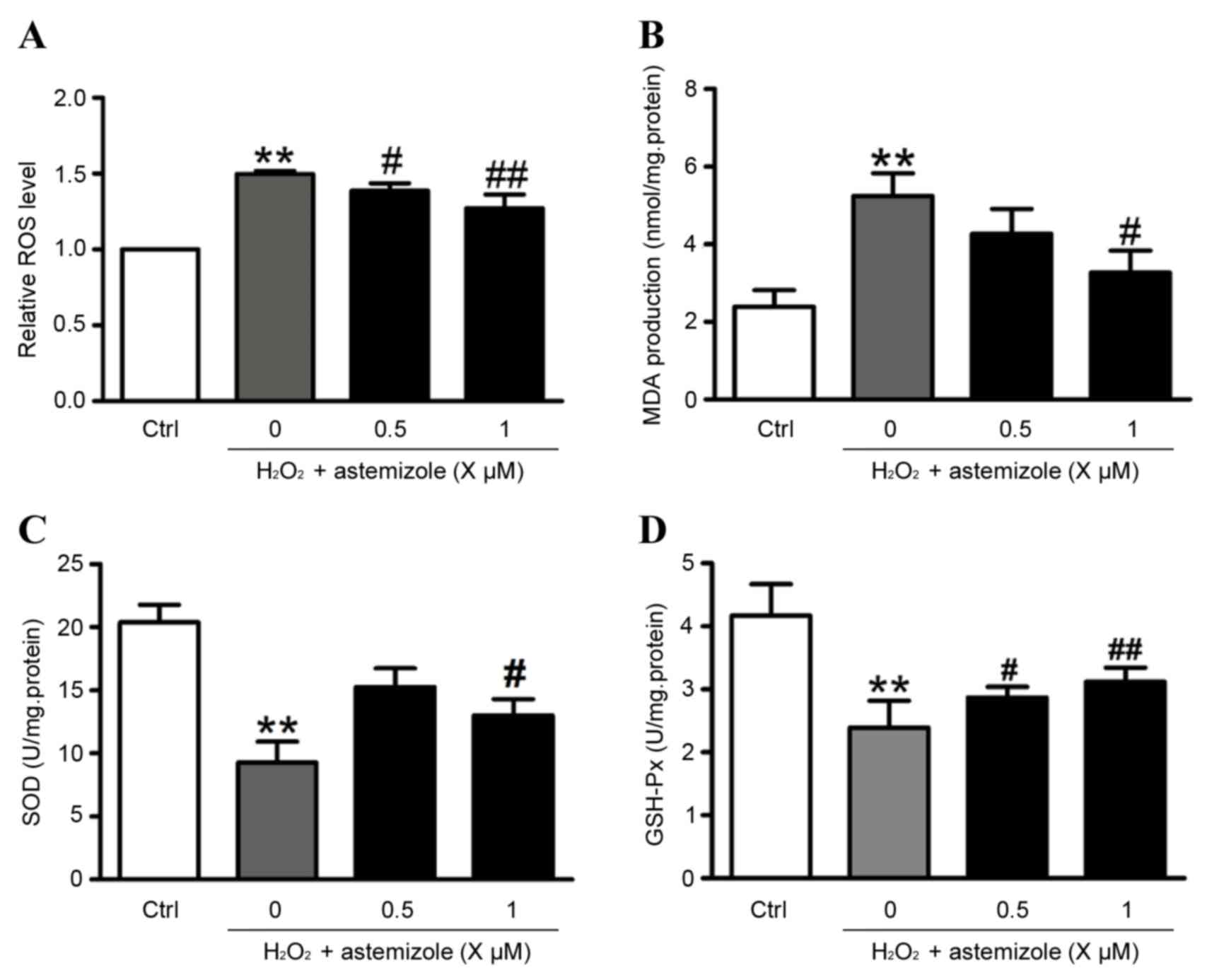
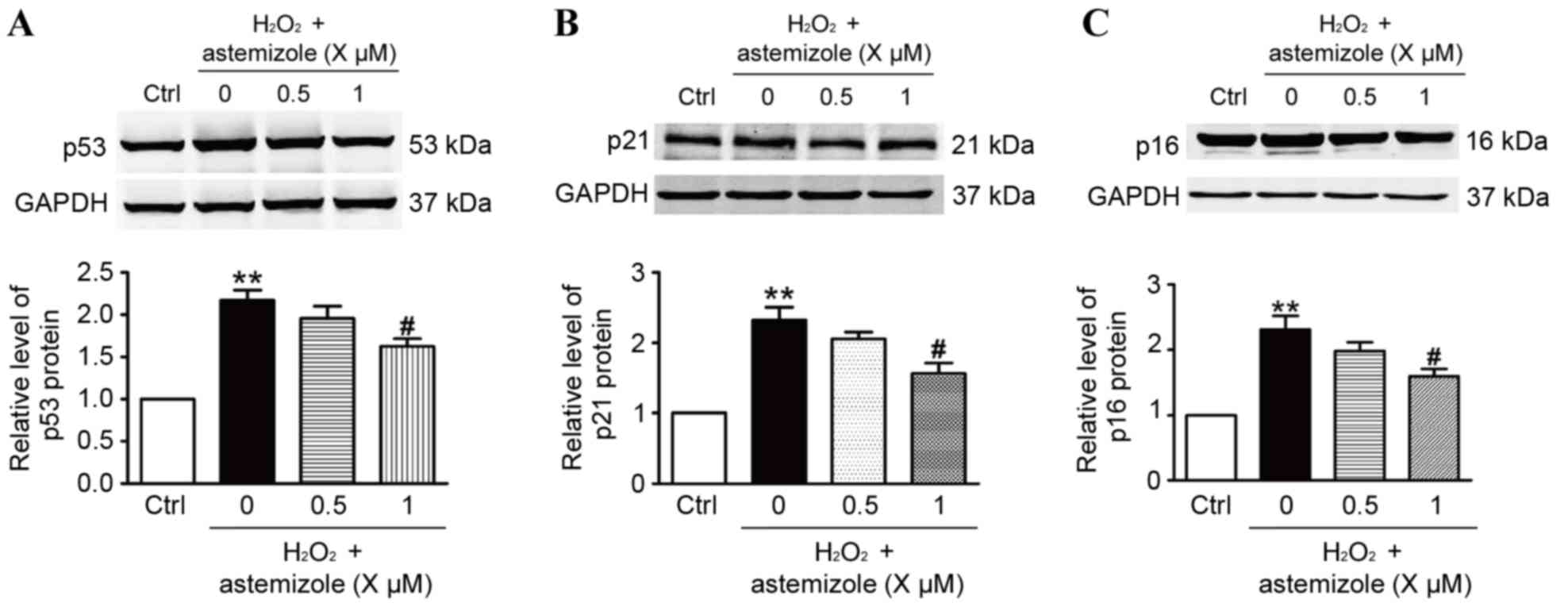
|
1
|
Garcia-Quiroz J, Garcia-Becerra R, Barrera
D, Santos N, Avila E, Ordaz-Rosado D, Rivas-Suárez M, Halhali A,
Rodríguez P, Gamboa-Domínguez A, et al: Astemizole synergizes
calcitriol antiproliferative activity by inhibiting CYP24A1 and
upregulating VDR: A novel approach for breast cancer therapy. PLoS
One. 7:e450632012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Garcia-Quiroz J and Camacho J: Astemizole:
An old anti-histamine as a new promising anti-cancer drug.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:307–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Garcia-Quiroz J, Garcia-Becerra R,
Santos-Martinez N, Barrera D, Ordaz-Rosado D, Avila E, Halhali A,
Villanueva O, Ibarra-Sánchez MJ, Esparza-López J, et al: In vivo
dual targeting of the oncogenic Ether-à-go-go-1 potassium channel
by calcitriol and astemizole results in enhanced antineoplastic
effects in breast tumors. BMC Cancer. 14:7452014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Sanderson JT: The steroid hormone
biosynthesis pathway as a target for endocrine-disrupting
chemicals. Toxicol Sci. 94:3–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fischer MJ, Paulussen JJ, Kok-Van Esterik
JA, Van der Heijden VS, De Mol NJ and Janssen LH: Effects of the
anti-allergics astemizole and norastemizole on Fc epsilon RI
receptor-mediated signal transduction processes. Eur J Pharmacol.
322:97–105. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nishimoto M, Hashimoto H, Ohmura T, Ikeda
Y, Watanabe S, Ohashi K, Umemura K and Nakashima M: Effects of
astemizole on ventricular activation delay and RT intervals in a
canine myocardial infarction model. Biol Pharm Bull. 20:1020–1023.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Romero L, Trenor B, Yang PC, Saiz J and
Clancy CE: In silico screening of the impact of hERG channel
kinetic abnormalities on channel block and susceptibility to
acquired long QT syndrome. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 87:271–282. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Cai H: Hydrogen peroxide regulation of
endothelial function: Origins, mechanisms, and consequences.
Cardiovasc Res. 68:26–36. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu L, Gu L, Ma Q, Zhu D and Huang X:
Resveratrol attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
17:88–94. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Ross R: The pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 362:801–809.
1993. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pandian RP, Kutala VK, Liaugminas A,
Parinandi NL and Kuppusamy P: Lipopolysaccharide-induced
alterations in oxygen consumption and radical generation in
endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 278:119–127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fasanaro P, Magenta A, Zaccagnini G,
Cicchillitti L, Fucile S, Eusebi F, Biglioli P, Capogrossi MC and
Martelli F: Cyclin D1 degradation enhances endothelial cell
survival upon oxidative stress. FASEB J. 20:1242–1244. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xu HB and Huang ZQ: Icariin enhances
endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression on human endothelial
cells in vitro. Vascul Pharmacol. 47:18–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kamata H and Hirata H: Redox regulation of
cellular signalling. Cell Signal. 11:1–14. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Falone S, Marchesi N, Osera C, Fassina L,
Comincini S, Amadio M and Pascale A: Pulsed electromagnetic field
(PEMF) prevents pro-oxidant effects of H2O2
in SK-N-BE(2) human neuroblastoma cells. Int J Radiat Biol.
92:281–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Venditti P, Costagliola IR and Di Meo S:
H2O2 production and response to stress
conditions by mitochondrial fractions from rat liver. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 34:115–125. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xia Z, Liu M, Wu Y, Sharma V, Luo T,
Ouyang J and McNeill JH: N-acetylcysteine attenuates
TNF-alpha-induced human vascular endothelial cell apoptosis and
restores eNOS expression. Eur J Pharmacol. 550:134–142. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ormenisan C, Kubik M, Legrand S, Kraemer
D, Smotherman C and Masood S: The potential of ki67 and p53
assessment in development of individualized targeted therapy in
breast cancer patients. Pathologica. 107:177–180. 2015.
|
|
19
|
Zhang M, Liu D, Li S, Chang L, Zhang Y,
Liu R, Sun F, Duan W, Du W, Wu Y, et al: Bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cell transplantation retards the natural senescence of rat
hearts. Stem Cells Transl Med. 4:494–502. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Oka T, Morita H and Komuro I: Novel
molecular mechanisms and regeneration therapy for heart failure. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 92:46–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pietrzkowicz M and Grzelewska-Rzymowska I:
The effect of new H1-receptor antagonists on cardiovascular system.
Pol Merkur Lekarski. 5:360–362. 1998.(In Polish).
|
|
22
|
Griendling KK and FitzGerald GA: Oxidative
stress and cardiovascular injury: Part II: Animal and human
studies. Circulation. 108:2034–2040. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Griendling KK and FitzGerald GA: Oxidative
stress and cardiovascular injury: Part I: Basic mechanisms and in
vivo monitoring of ROS. Circulation. 108:1912–1916. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Giustarini D, Dalle-Donne I, Tsikas D and
Rossi R: Oxidative stress and human diseases: Origin, link,
measurement, mechanisms, and biomarkers. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.
46:241–281. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang YK and Huang ZQ: Protective effects
of icariin on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced
by H2O2 in vitro. Pharmacol Res. 52:174–182.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ray PD, Huang BW and Tsuji Y: Reactive
oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular
signaling. Cell Signal. 24:981–990. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Tseng CY, Wang JS, Chang YJ, Chang JF and
Chao MW: Exposure to high-dose diesel exhaust particles induces
intracellular oxidative stress and causes endothelial apoptosis in
cultured in vitro capillary tube cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol.
15:345–354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xu LL, Liu ML, Wang JL, Yu M and Chen JX:
Saligenin cyclic-o-tolyl phosphate (SCOTP) induces autophagy of rat
spermatogonial stem cells. Reprod Toxicol. 60:62–68. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Song YM, Lee WK, Lee YH, Kang ES, Cha BS
and Lee BW: Metformin restores parkin-mediated mitophagy,
suppressed by cytosolic p53. Int J Mol Sci. 17:pii: E1222016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sato C, Iso Y, Mizukami T, Otabe K, Sasai
M, Kurata M, Sanbe T, Sekiya I, Miyazaki A and Suzuki H: Fibroblast
growth factor-23 induces cellular senescence in human mesenchymal
stem cells from skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
470:657–662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Vaikundamoorthy R, Sundaramoorthy R,
Krishnamoorthy V, Vilwanathan R and Rajendran R: Marine steroid
derived from Acropora formosa enhances mitochondrial-mediated
apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
37:10517–10531. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lee EH, Oh JH, Park HJ, Kim DG, Lee JH,
Kim CY, Kwon MS and Yoon S: Simultaneous gene expression signature
of heart and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in
astemizole-treated rats. Arch Toxicol. 84:609–618. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|