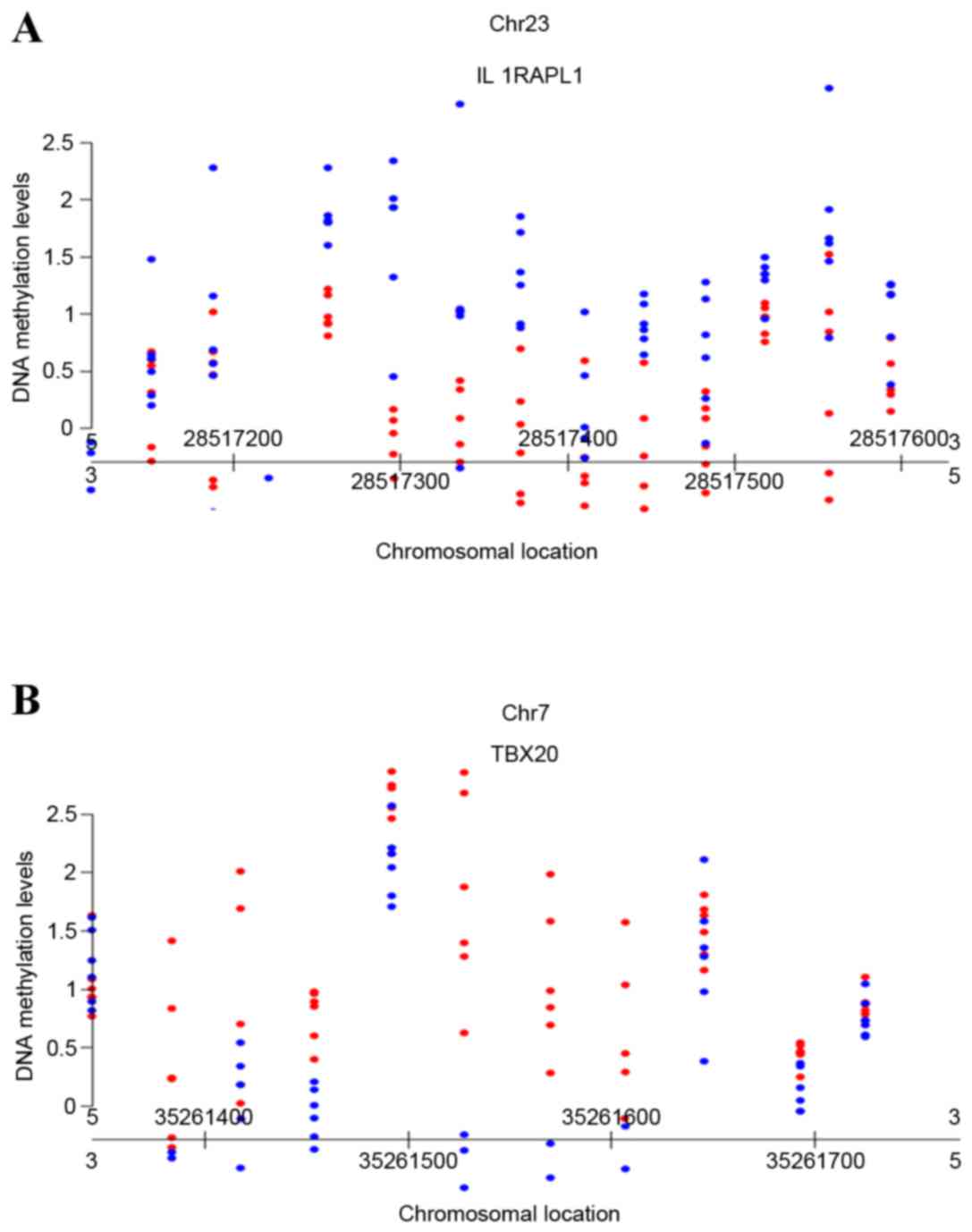
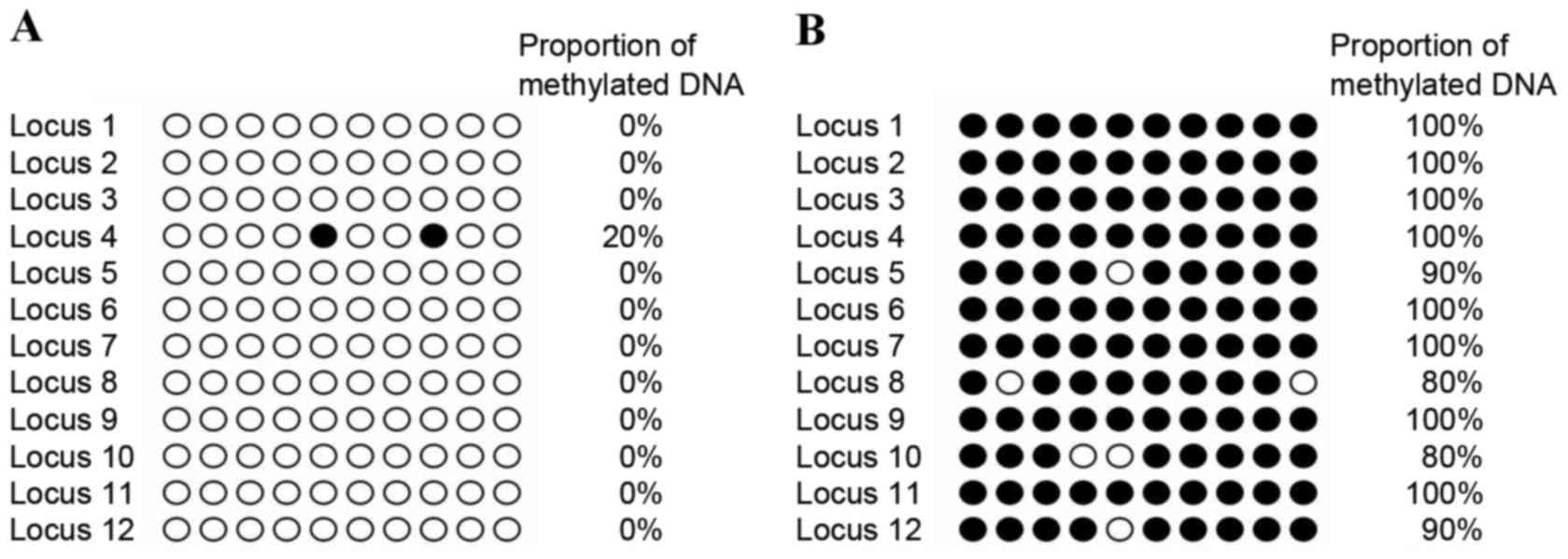
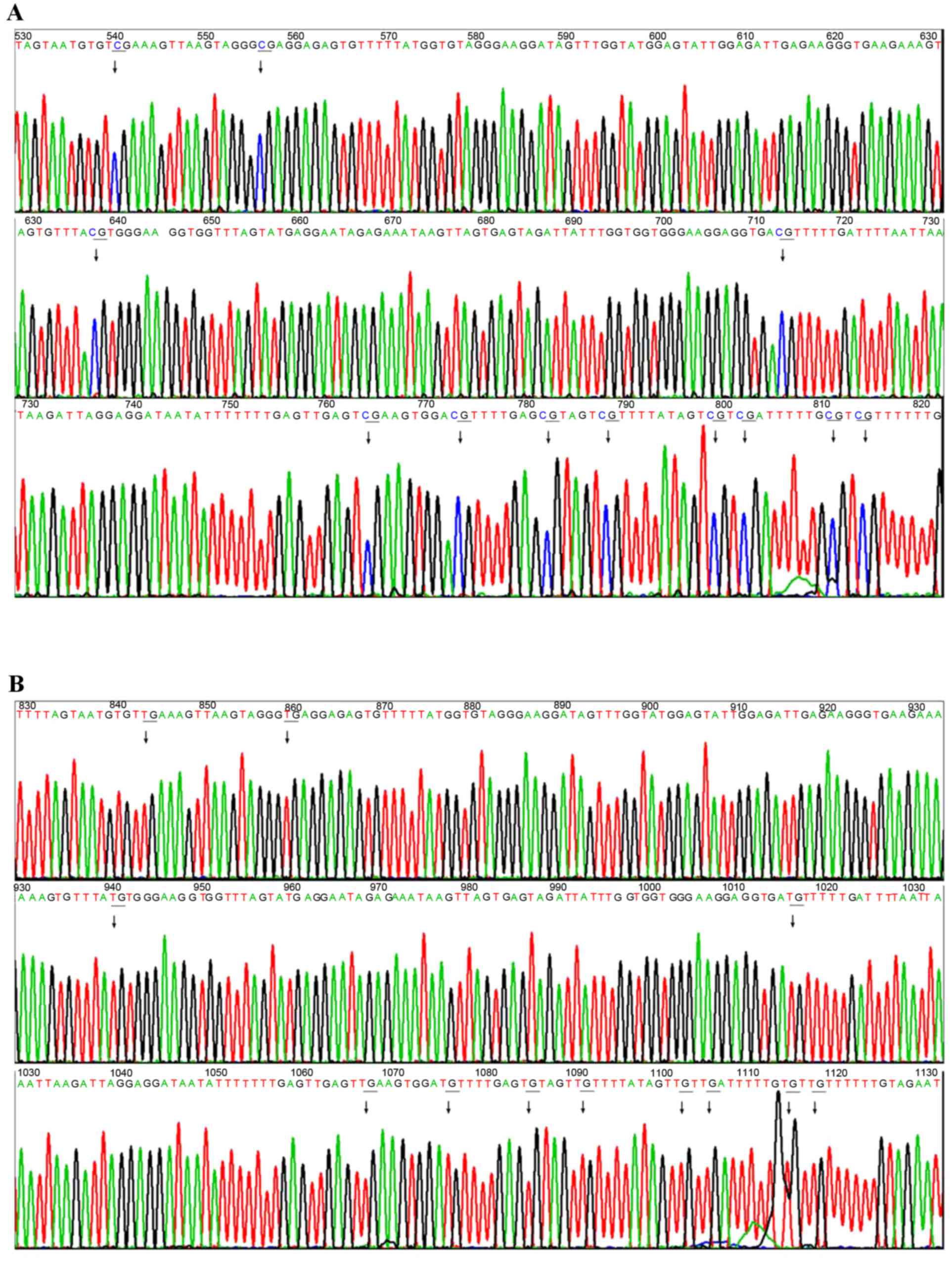
|
1
|
Xiang Y, Zhang J, Li Q, Zhou X, Wang T, Xu
M, Xia S, Xing Q, Wang L, He L and Zhao X: DNA methylome profiling
of maternal peripheral blood and placentas reveal potential fetal
DNA markers for non-invasive prenatal testing. Mol Hum Reprod.
20:875–884. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lapaire O, Holzgreve W, Oosterwijk JC,
Brinkhaus R and Bianchi DW: Georg Schmorl on trophoblasts in the
maternal circulation. Placenta. 28:1–5. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lo YM, Corbetta N, Chamberlain PF, Rai V,
Sargent IL, Redman CW and Wainscoat JS: Presence of fetal DNA in
maternal plasma and serum. Lancet. 350:485–487. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lo YM, Hjelm NM, Fidler C, Sargent IL,
Murphy MF, Chamberlain PF, Poon PM, Redman CW and Wainscoat JS:
Prenatal diagnosis of fetal RhD status by molecular analysis of
maternal plasma. N Engl J Med. 339:1734–1738. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lun FM, Chiu RW, Chan KC, Leung TY, Lau TK
and Lo YM: Microfluidics digital PCR reveals a higher than expected
fraction of fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Clin Chem. 54:1664–1672.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Costa JM, Benachi A, Gautier E, Jouannic
JM, Ernault P and Dumez Y: First-trimester fetal sex determination
in maternal serum using real-time PCR. Prenat Diagn. 21:1070–1074.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Khorshid HR Khorram, Zargari M, Sadeghi
MR, Edallatkhah H, Shahhosseiny MH and Kamali K: Early fetal gender
determination using real-time PCR analysis of cell-free fetal DNA
during 6th-10th weeks of gestation. Acta Med Iran. 51:209–214.
2013.
|
|
8
|
Rijnders RJ, van der Schoot CE, Bossers B,
de Vroede MA and Christiaens GC: Fetal sex determination from
maternal plasma in pregnancies at risk for congenital adrenal
hyperplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 98:374–378. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chiu RW, Chan KC, Gao Y, Lau VY, Zheng W,
Leung TY, Foo CH, Xie B, Tsui NB, Lun FM, et al: Noninvasive
prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy by massively
parallel genomic sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:pp. 20458–20463. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Porreco RP, Garite TJ, Maurel K, Marusiak
B; Obstetrix Collaborative Research Network, ; Ehrich M, van den
Boom D, Deciu C and Bombard A: Noninvasive prenatal screening for
fetal trisomies 21, 18, 13 and the common sex chromosome
aneuploidies from maternal blood using massively parallel genomic
sequencing of DNA. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 211:365.e1–e12. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Norton ME, Rose NC and Benn P: Noninvasive
prenatal testing for fetal aneuploidy: Clinical assessment and a
plea for restraint. Obstet Gynecol. 121:847–850. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lun FM, Tsui NB, Chan KC, Leung TY, Lau
TK, Charoenkwan P, Chow KC, Lo WY, Wanapirak C, Sanguansermsri T,
et al: Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of monogenic diseases by
digital size selection and relative mutation dosage on DNA in
maternal plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp. 19920–19925. 2008;
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Lam KW, Jiang P, Liao GJ, Chan KC, Leung
TY, Chiu RW and Lo YM: Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of monogenic
diseases by targeted massively parallel sequencing of maternal
plasma: Application to β-thalassemia. Clin Chem. 58:1467–1475.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Papageorgiou EA and Patsalis PC:
Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of aneuploidies: New technologies
and clinical applications. Genome Med. 4:462012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Lim JH, Lee da E, Park SY, Kim DJ, Ahn HK,
Han YJ, Kim MY and Ryu HM: Disease specific characteristics of
fetal epigenetic markers for non-invasive prenatal testing of
trisomy 21. BMC Med Genomics. 7:12014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Lee DE, Kim SY, Lim JH, Park SY and Ryu
HM: Non-invasive prenatal testing of trisomy 18 by an epigenetic
marker in first trimester maternal plasma. PLoS One. 8:e781362013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Tong YK, Jin S, Chiu RW, Ding C, Chan KC,
Leung TY, Yu L, Lau TK and Lo YM: Noninvasive prenatal detection of
trisomy 21 by an epigenetic-genetic chromosome-dosage approach.
Clin Chem. 56:90–98. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Papageorgiou EA, Koumbaris G, Kypri E,
Hadjidaniel M and Patsalis PC: The epigenome view: An effort
towards non-invasive prenatal diagnosis. Genes (Basel). 5:310–329.
2014.
|
|
19
|
Bianchi DW: Circulating fetal DNA: Its
origin and diagnostic potential-a review. Placenta. 25 Suppl
A:S93–S101. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alberry M, Maddocks D, Jones M, Hadi M
Abdel, Abdel-Fattah S, Avent N and Soothill PW: Free fetal DNA in
maternal plasma in anembryonic pregnancies: Confirmation that the
origin is the trophoblast. Prenat Diagn. 27:415–418. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Keller EF: From gene action to reactive
genomes. J Physiol. 592:2423–2429. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Shenderov BA and Midtvedt T: Epigenomic
programing: A future way to health? Microb Ecol Health Dis.
25:2014.
|
|
23
|
Yao HW and Li J: Epigenetic modifications
in fibrotic diseases: Implications for pathogenesis and
pharmacological targets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 352:2–13. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Geiman TM and Muegge K: DNA methylation in
early development. Mol Reprod Dev. 77:105–113. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Patil V, Ward RL and Hesson LB: The
evidence for functional non-CpG methylation in mammalian cells.
Epigenetics. 9:823–828. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Kwak W, Kim JN, Kim D, Hong JS, Jeong JH,
Kim H, Cho S and Kim YY: Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles of
small intestine and liver in fast-growing and slow-growing weaning
piglets. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 27:1532–1539. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Ji H, Jiang H, Ma W, Johnson DS, Myers RM
and Wong WH: An integrated software system for analyzing ChIP-chip
and ChIP-seq data. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1293–1300. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Kumaki Y, Oda M and Okano M: QUMA:
Quantification tool for methylation analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
36(Web Server Issue): W170–W175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
R Core Team, . R: A language and
environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing; Vienna, Austria: ISBN: 3-900051-07-02008, http://www.R-project.org/
|
|
30
|
Denadai R, Raposo-Amaral CE, Bertola D,
Kim C, Alonso N, Hart T, Han S, Stelini RF, Buzzo CL, Raposo-Amaral
CA and Hart PS: Identification of 2 novel ANTXR2 mutations in
patients with hyaline fibromatosis syndrome and proposal of a
modified grading system. Am J Med Genet A. 158A:732–742. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lingaiah K, Sosalagere DM, Mysore SR,
Krishnamurthy B, Narayanappa D and Nallur RB: Mutations of TFAP2B
in congenital heart disease patients in Mysore, South India. Indian
J Med Res. 134:621–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Posch MG, Gramlich M, Sunde M, Schmitt KR,
Lee SH, Richter S, Kersten A, Perrot A, Panek AN, Al Khatib IH, et
al: A gain-of-function TBX20 mutation causes congenital atrial
septal defects, patent foramen ovale and cardiac valve defects. J
Med Genet. 47:230–235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Saito A, Kuratomi G, Ito C, Matsuoka H,
Suzuki T, Ozeki Y, Watanabe T, Fujii K, Shimoda K, Fukushima Y, et
al: An association study of the Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 4
gene in schizophrenic patients. Psychiatr Genet. 23:163–173. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Martin E, Palmic N, Sanquer S, Lenoir C,
Hauck F, Mongellaz C, Fabrega S, Nitschké P, Esposti MD,
Schwartzentruber J, et al: CTP synthase 1 deficiency in humans
reveals its central role in lymphocyte proliferation. Nature.
510:288–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Youngs EL, Henkhaus R, Hellings JA and
Butler MG: IL1RAPL1 gene deletion as a cause of X-linked
intellectual disability and dysmorphic features. Eur J Med Genet.
55:32–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Burke JP, O'Connell RM, Lennon G, Doherty
GA, Keegan D, O'Donoghue D, Mulcahy H, Hyland J, Winter DC, Sheahan
K and O'Connell PR: The influence of CTGF single-nucleotide
polymorphisms on outcomes in Crohn's disease. Ann Surg.
258:767–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhao C, Takita J, Tanaka Y, Setou M,
Nakagawa T, Takeda S, Yang HW, Terada S, Nakata T, Takei Y, et al:
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A caused by mutation in a
microtubule motor KIF1Bbeta. Cell. 105:587–597. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schroeder V and Kohler HP: Factor XIII
deficiency: An update. Semin Thromb Hemost. 39:632–641. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dong Z, Yang L and Lai D: KLF5 strengthens
drug resistance of ovarian cancer stem-like cells by regulating
survivin expression. Cell Prolif. 46:425–435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chim SS, Tong YK, Chiu RW, Lau TK, Leung
TN, Chan LY, Oudejans CB, Ding C and Lo YM: Detection of the
placental epigenetic signature of the maspin gene in maternal
plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 14753–14758. 2005;
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Heyn H, Carmona FJ, Gomez A, Ferreira HJ,
Bell JT, Sayols S, Ward K, Stefansson OA, Moran S, Sandoval J, et
al: DNA methylation profiling in breast cancer discordant identical
twins identifies DOK7 as novel epigenetic biomarker.
Carcinogenesis. 34:102–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|