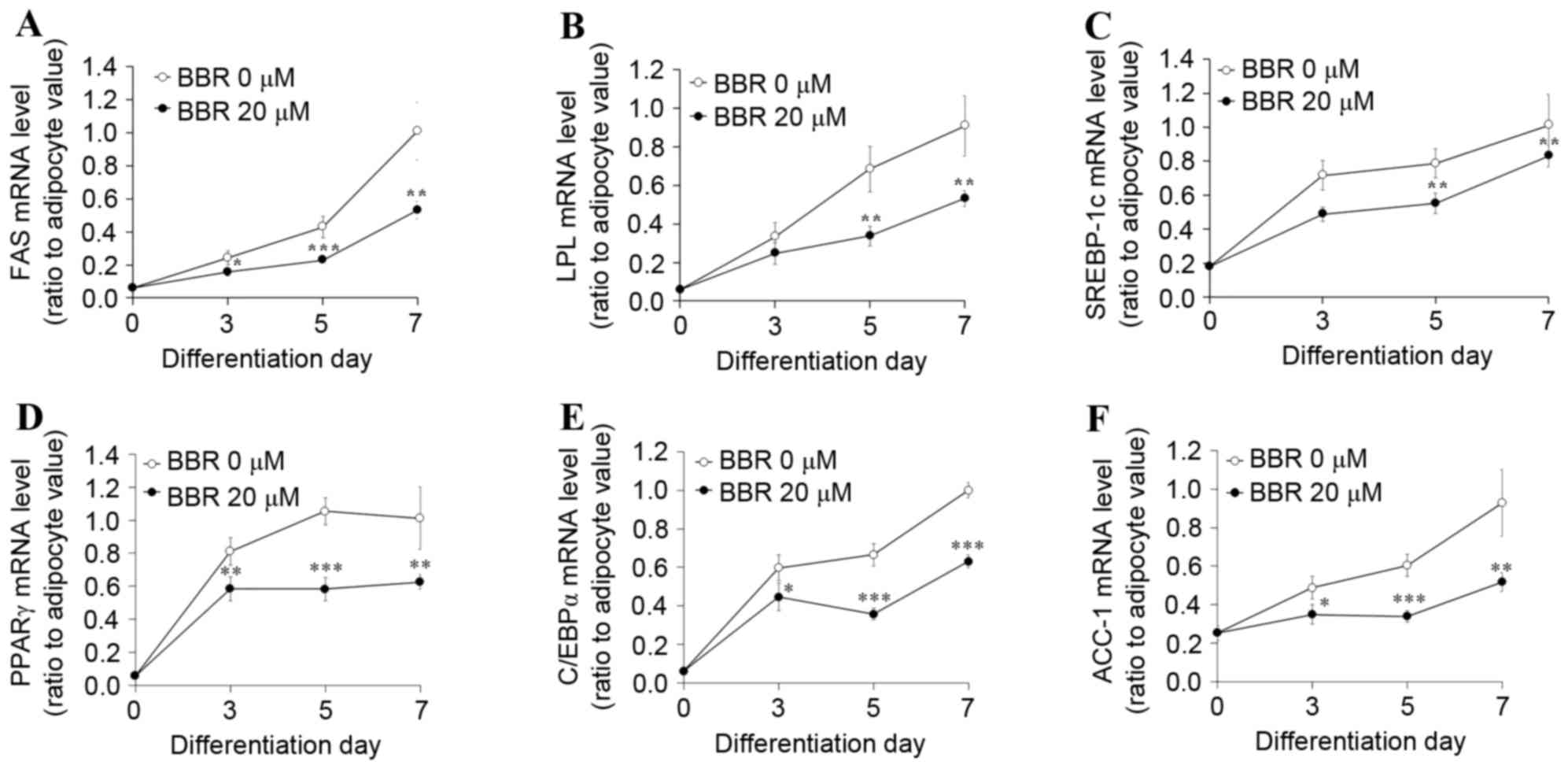
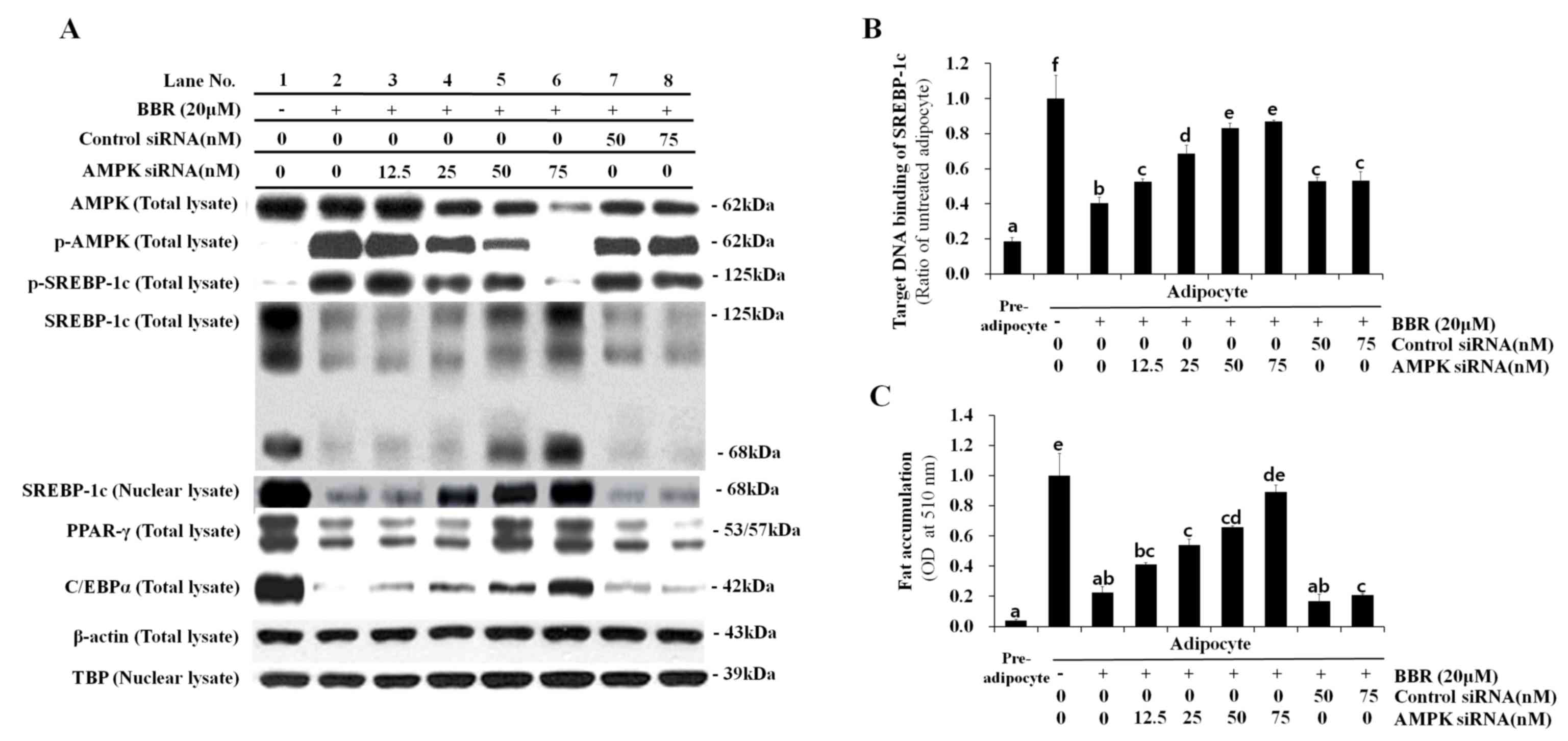
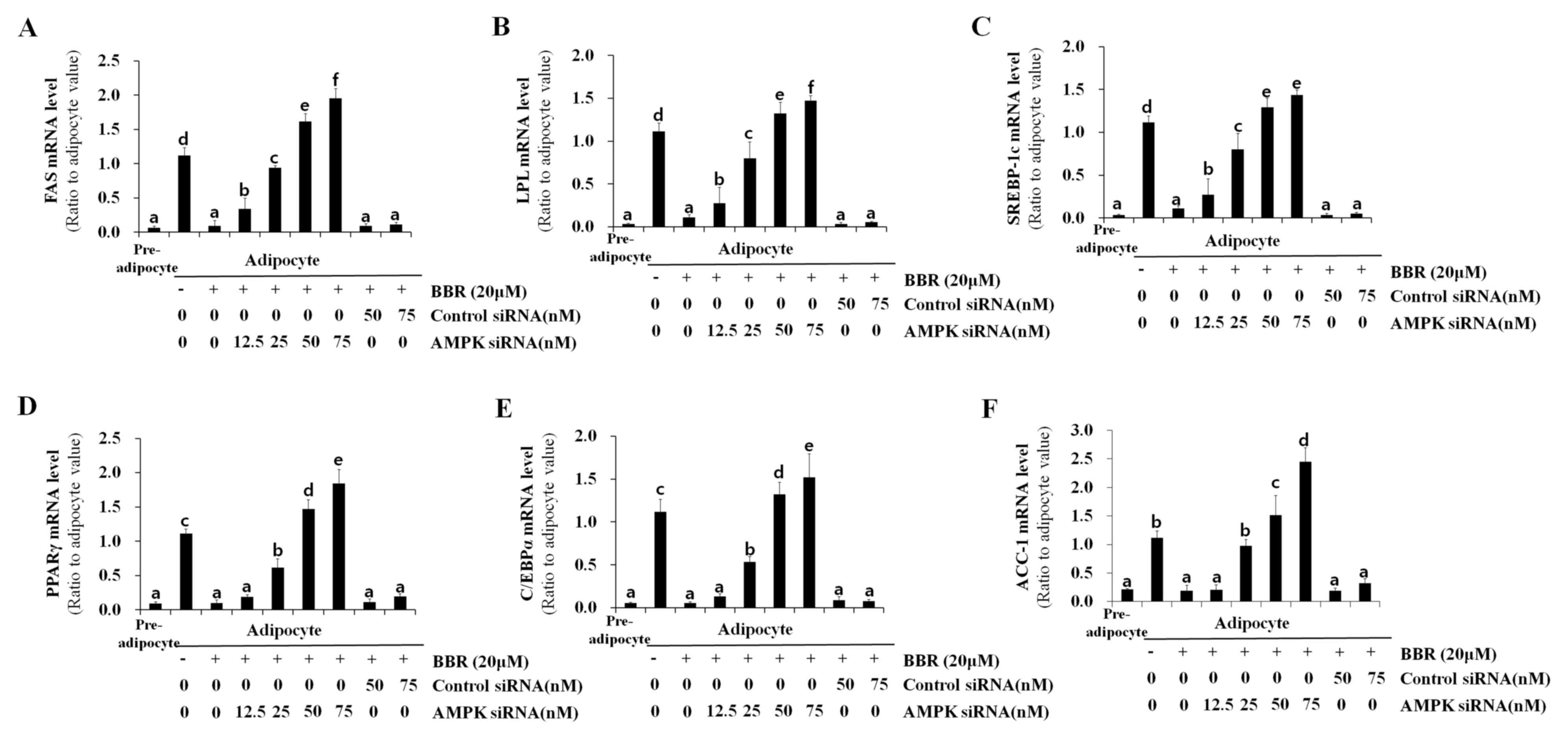
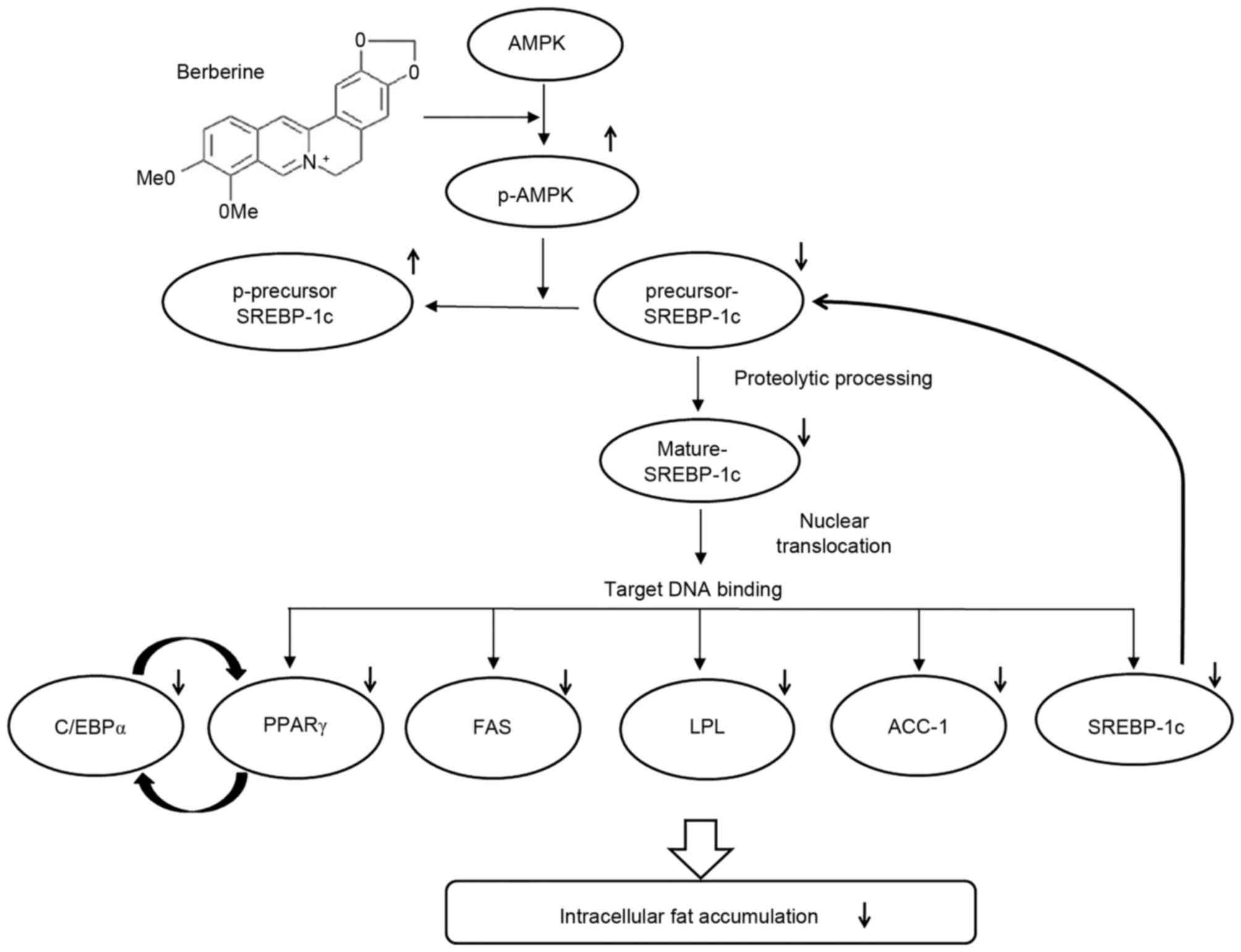
|
1
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Daval M, Diot-Dupuy F, Bazin R, Hainault
I, Viollet B, Vaulont S, Hajduch E, Ferré P and Foufelle F:
Anti-lipolytic action of AMP-activated protein kinase in rodent
adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 280:25250–25257. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gowans GJ, Hawley SA, Ross FA and Hardie
DG: AMP is a true physiological regulator of AMP-activated protein
kinase by both allosteric activation and enhancing net
phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 18:556–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Vuddanda PR, Chakraborty S and Singh S:
Berberine: A potential phytochemical with multispectrum therapeutic
activities. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19:1297–1307. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, Yoon MJ, Cho HJ,
Shen Y, Ye JM, Lee CH, Oh WK, Kim CT, et al: Berberine, a natural
plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with
beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant
states. Diabetes. 55:2256–2264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Turner N, Li JY, Gosby A, To SW, Cheng Z,
Miyoshi H, Taketo MM, Cooney GJ, Kraegen EW, James DE, et al:
Berberine and its more biologically available derivative,
dihydroberberine, inhibit mitochondrial respiratory complex I: A
mechanism for the action of berberine to activate AMP-activated
protein kinase and improve insulin action. Diabetes. 57:1414–1418.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jeon TI and Osborne TF: SREBPs: Metabolic
integrators in physiology and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
23:65–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li GS, Liu XH, Zhu H, Huang L, Liu YL, Ma
CM and Qin C: Berberine-improved visceral white adipose tissue
insulin resistance associated with altered sterol regulatory
element-binding proteins, liver × receptors and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors transcriptional programs in
diabetic hamsters. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:644–654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hu Y, Kutscher E and Davies GE: Berberine
inhibits SREBP-1-related clozapine and risperidone induced
adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Phytother Res. 24:1831–1838. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Huang C, Zhang Y, Gong Z, Sheng X, Li Z,
Zhang W and Qin Y: Berberine inhibits 3T3-L1 adipocyte
differentiation through the PPARgamma pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 348:571–578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gustafson B and Smith U: Cytokines promote
Wnt signaling and inflammation and impair the normal
differentiation and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J
Biol Chem. 281:9507–9516. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li J, Zhang D, Ward KM, Prendergast GC and
Ayene IS: Hydroxyethyl disulfide as an efficient metabolic assay
for cell viability in vitro. Toxicology in Vitro. 26:603–612. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Lee H, Bae S and Yoon Y: The
anti-adipogenic effects of (−)epigallocatechin gallate are
dependent on the WNT/β-catenin pathway. J Nutr Biochem.
24:1232–1240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X,
Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY, et al: AMPK
phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic
steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant
mice. Cell Metab. 13:376–388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Yoshikawa T,
Yahagi N, Hasty AH, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Shionoiri F, Iizuka Y,
Ohashi K, et al: Promoter analysis of the mouse sterol regulatory
element-binding protein-1c gene. J Biol Chem. 275:31078–31085.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fajas L, Schoonjans K, Gelman L, Kim JB,
Najib J, Martin G, Fruchart JC, Briggs M, Spiegelman BM and Auwerx
J: Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
expression by adipocyte differentiation and determination factor
1/sterol regulatory element binding protein 1: Implications for
adipocyte differentiation and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol.
19:5495–5503. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Schoonjans K, Gelman L, Haby C, Briggs M
and Auwerx J: Induction of LPL gene expression by sterols is
mediated by a sterol regulatory element and is independent of the
presence of multiple E boxes. J Mol Biol. 304:323–334. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Barber MC, Vallance AJ, Kennedy HT and
Travers MT: Induction of transcripts derived from promoter III of
the acetyl-CoA carboxylase-alpha gene in mammary gland is
associated with recruitment of SREBP-1 to a region of the proximal
promoter defined by a DNase I hypersensitive site. Biochem J.
375:489–501. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Griffin MJ and Sul HS: Insulin regulation
of fatty acid synthase gene transcription: Roles of USF and
SREBP-1c. IUBMB Life. 56:595–600. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bene H, Lasky D and Ntambi JM: Cloning and
characterization of the human stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene
promoter: Transcriptional activation by sterol regulatory element
binding protein and repression by polyunsaturated fatty acids and
cholesterol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 284:1194–1198. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Sato R, Brown MS, Hua X and
Goldstein JL: SREBP-1, a membrane-bound transcription factor
released by sterol-regulated proteolysis. Cell. 77:53–62. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Eberle D, Hegarty B, Bossard P, Ferré P
and Foufelle F: SREBP transcription factors: Master regulators of
lipid homeostasis. Biochimie. 86:839–848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao QH, Wang SG, Liu SX, Li JP, Zhang YX,
Sun ZY, Fan QM and Tian JW: PPARγ forms a bridge between DNA
methylation and histone acetylation at the C/EBPα gene promoter to
regulate the balance between osteogenesis and adipogenesis of bone
marrow stromal cells. FEBS J. 280:5801–5814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|