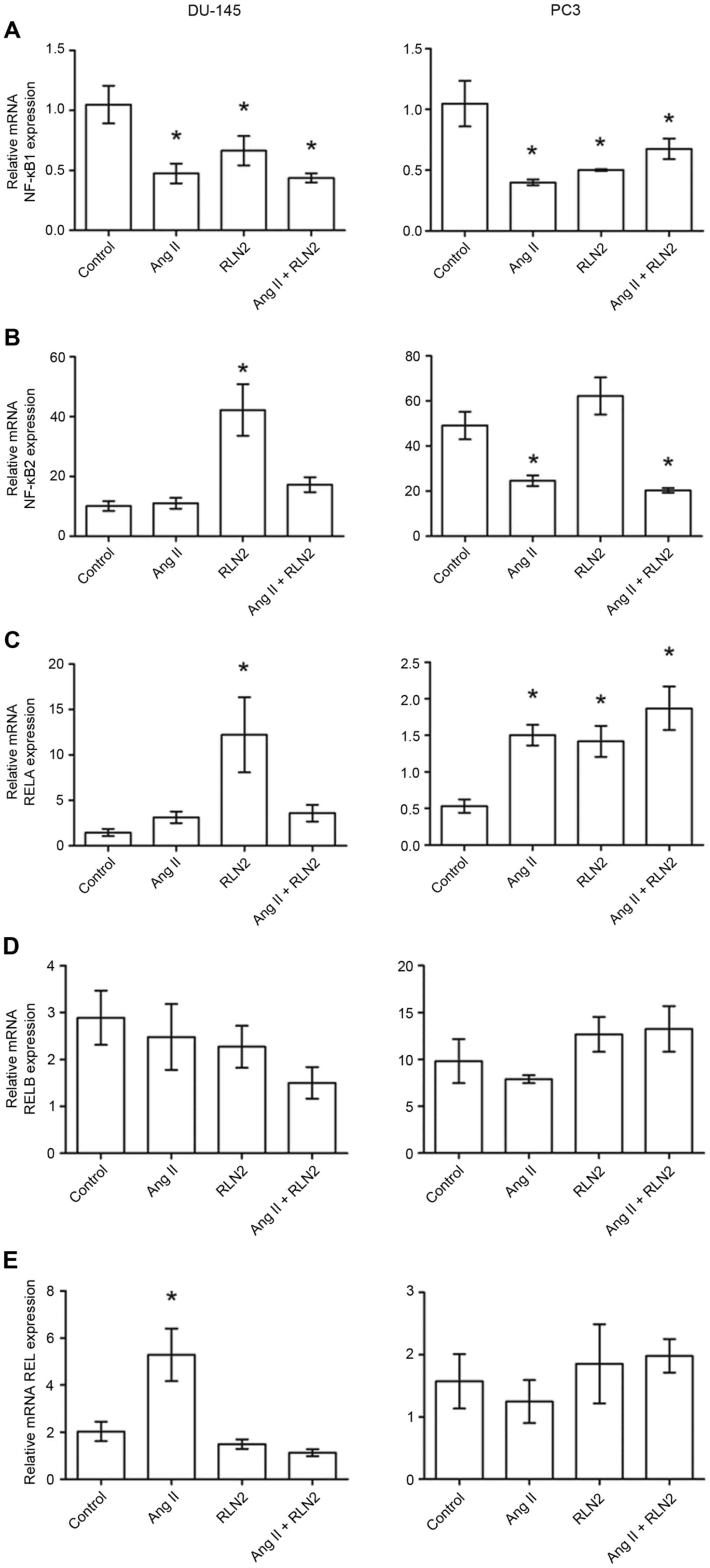
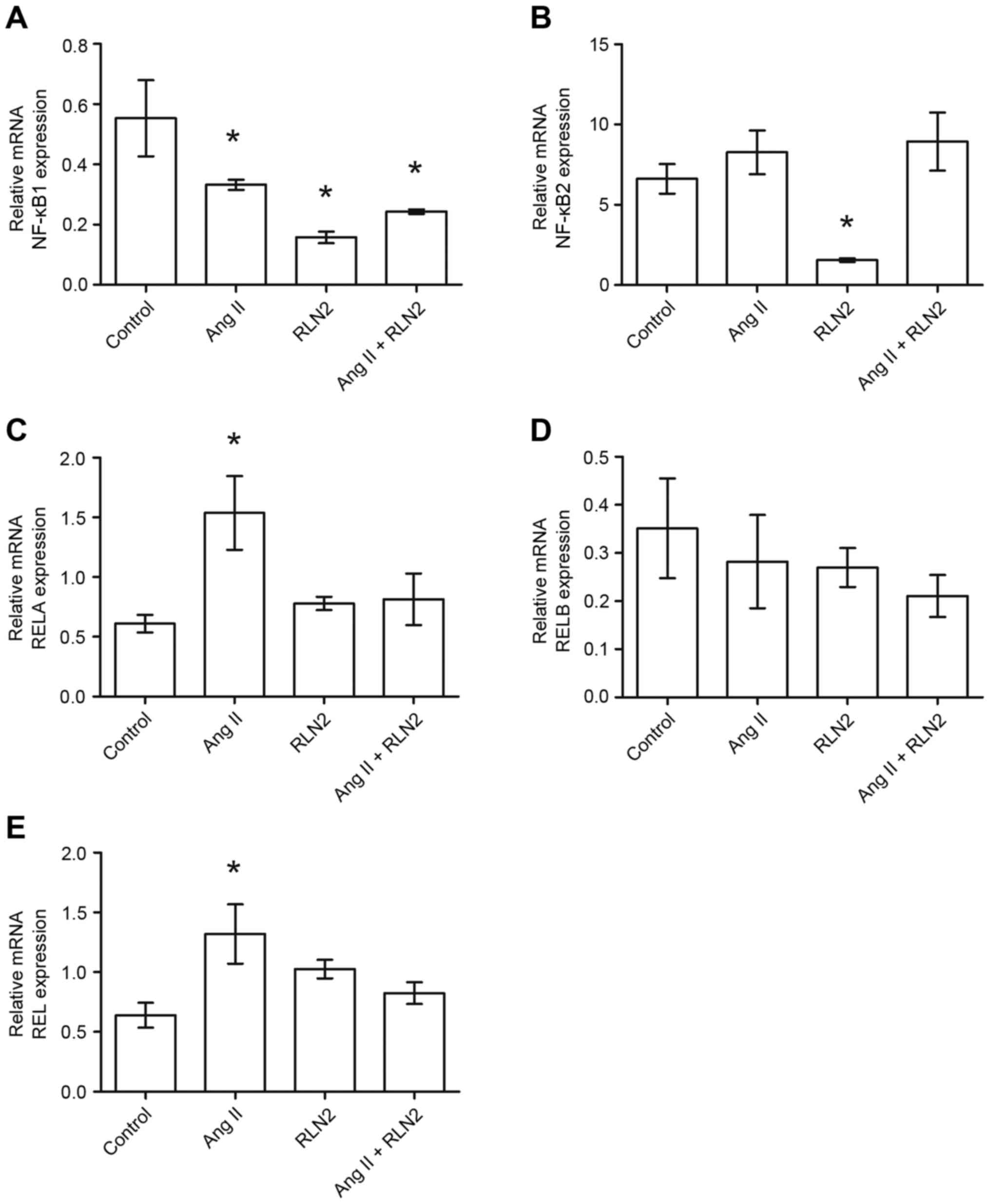
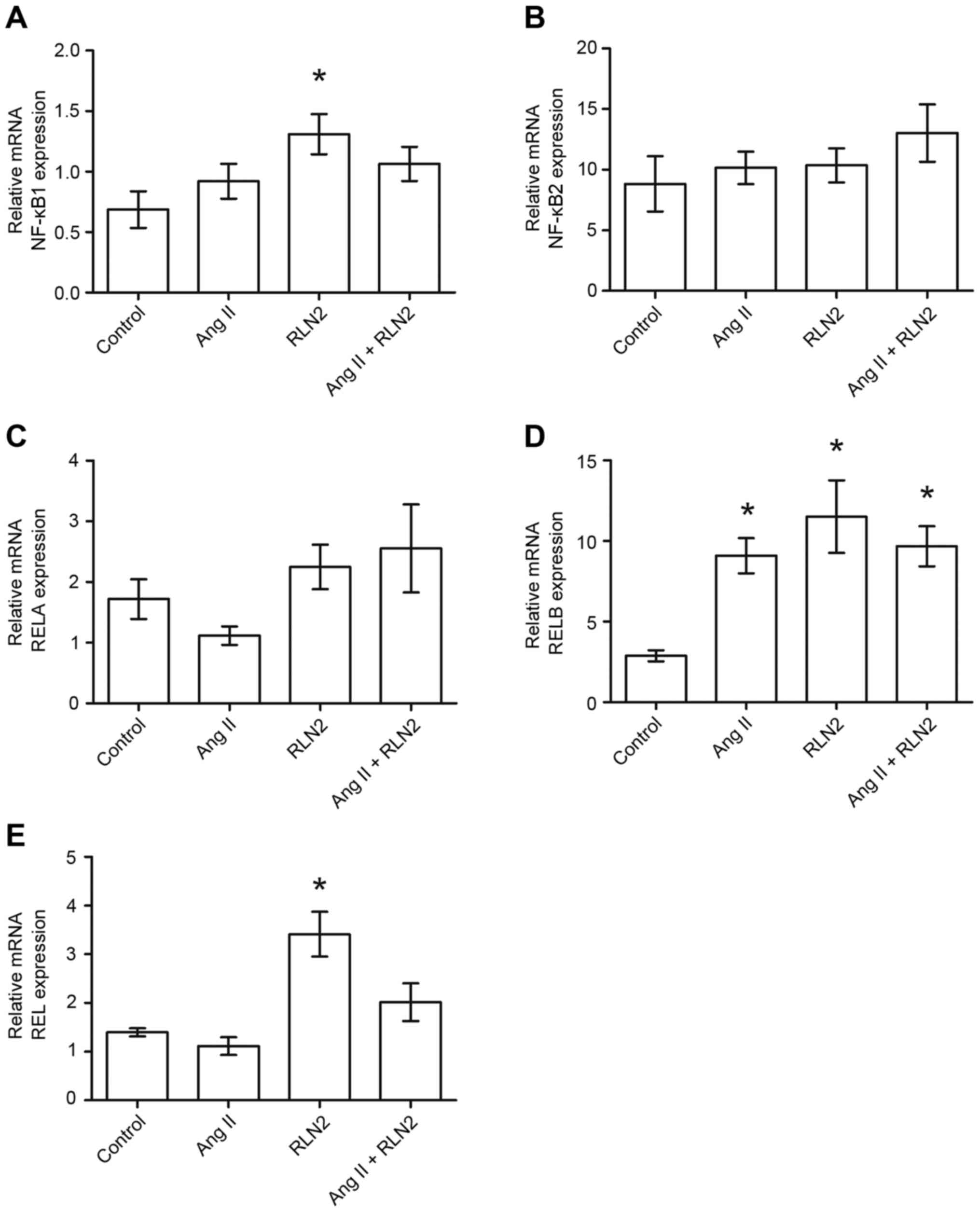
|
1
|
Domińska K: Relaxin 2-a pregnancy hormone
involved in the process of carcinogenesis. Ginekol Pol. 84:126–130.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Domińska K and Lachowicz-Ochedalska A: The
involvement of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in
cancerogenesis. Postepy Biochem. 54:294–300. 2008.(In Polish).
|
|
3
|
Wegman-Ostrosky T, Soto-Reyes E,
Vidal-Millán S and Sánchez-Corona J: The renin-angiotensin system
meets the hallmarks of cancer. J Renin angiotensin Aldosterone
Syst. 16:227–233. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nair VB, Samuel CS, Separovic F, Hossain
MA and Wade JD: Human relaxin-2: Historical perspectives and role
in cancer biology. Amino Acids. 43:1131–1140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Domińska K, Ochędalski T, Kowalska K,
Matysiak-Burzyńska ZE, Płuciennik E and Piastowska-Ciesielska AW: A
common effect of angiotensin II and relaxin 2 on the PNT1A normal
prostate epithelial cell line. J Physiol Biochem. 72:381–392. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Domińska K, Ochędalski T, Kowalska K,
Matysiak-Burzyńska ZE, Płuciennik E and Piastowska-Ciesielska AW:
Interaction between angiotensin II and relaxin 2 in the progress of
growth and spread of prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
48:2619–2628. 2016.
|
|
7
|
Jin R, Sterling JA, Edwards JR, DeGraff
DJ, Lee C, Park SI and Matusik RJ: Activation of NF-kappa B
signaling promotes growth of prostate cancer cells in bone. PLoS
One. 8:e609832013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Nguyen DP, Li J, Yadav SS and Tewari AK:
Recent insights into NF-κB signalling pathways and the link between
inflammation and prostate cancer. BJU Int. 114:168–176. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Luo JL, Kamata H and Karin M: IKK/NF-κB
signaling: Balancing life and death-a new approach to cancer
therapy. J Clin Invest. 115:2625–2632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Wu X, Gong S, Roy-Burman P, Lee P and
Culig Z: Current mouse and cell models in prostate cancer research.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:R155–R170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Avancès C, Georget V, Térouanne B, Orio F,
Cussenot O, Mottet N, Costa P and Sultan C: Human prostatic cell
line PNT1A, a useful tool for studying androgen receptor
transcriptional activity and its differential subnuclear
localization in the presence of androgens and antiandrogens. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 184:13–24. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dominska K, Piastowska-Ciesielska AW,
Pluciennik E, Lachowicz-Ochedalska A and Ochedalski T: A comparison
of the effects of angiotensin IV on androgen-dependent and
androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines. J Renin
angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 14:74–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression soft-ware tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Gasparian AV, Yao YJ, Kowalczyk D, Lyakh
LA, Karseladze A, Slaga TJ and Budunova IV: The role of IKK in
constitutive activation of NF-kappa B transcription factor in
prostate carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci. 115:141–151. 2002.
|
|
16
|
Suh J, Payvandi F, Edelstein LC, Amenta
PS, Zong WX, Gélinas C and Rabson AB: Mechanisms of constitutive
NF-kappa B activation in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate.
52:183–200. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Alimirah F, Chen J, Basrawala Z, Xin H and
Choubey D: DU-145 and PC-3 human prostate cancer cell lines express
androgen receptor: Implications for the androgen receptor functions
and regulation. FEBS Lett. 580:2294–2300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bidaux G, Roudbaraki M, Merle C, Crépin A,
Delcourt P, Slomianny C, Thebault S, Bonnal JL, Benahmed M, Cabon
F, et al: Evidence for specific TRPM8 expression in human prostate
secretory epithelial cells: Functional androgen receptor
requirement. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12:367–382. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu Y, Josson S, Fang F, Oberley TD, St
Clair DK, Wan XS, Sun Y, Bakthavatchalu V, Muthuswamy A and St
Clair WH: RelB enhances prostate cancer growth: Implications for
the role of the nuclear factor-kappaB alternative pathway in
tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 69:3267–3271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Setlur SR, Royce TE, Sboner A, Mosquera
JM, Demichelis F, Hofer MD, Mertz KD, Gerstein M and Rubin MA:
Integrative microarray analysis of pathways dysregulated in
metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:10296–10303. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Altuwaijri S, Lin HK, Chuang KH, Lin WJ,
Yeh S, Hanchett LA, Rahman MM, Kang HY, Tsai MY, Zhang Y, et al:
Interruption of nuclear factor kappaB signaling by the androgen
receptor facilitates 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbolacetate-induced
apoptosis in androgen-sensitive prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Cancer
Res. 63:7106–7112. 2003.
|
|
22
|
Lessard L, Bégin LR, Gleave ME, Mes-Masson
AM and Saad F: Nuclear localisation of nuclear factor-kappa B
transcription factors in prostate cancer: An immunohistochemical
study. Br J Cancer. 93:1019–1023. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Josson S, Xu Y, Fang F, Dhar SK, St Clair
DK and St Clair WH: RelB regulates manganese superoxide dismutase
gene and resistance to ionizing radiation of prostate cancer cells.
Oncogene. 25:1554–1559. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Hatano K, Miyamoto Y, Nonomura N and
Kaneda Y: Expression of gangliosides, GD1a, and sialyl
paragloboside is regulated by NF-κB-dependent transcriptional
control of α2,3-sialyltransferase III and VI in human
castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
129:1838–1847. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Yi S, Zhou J, Zhang Y and Guo F:
The NF-κB subunit RelB regulates the migration and invasion
abilities and the radio-sensitivity of prostate cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 49:381–392. 2016.
|
|
26
|
Domingo-Domenech J, Mellado B, Ferrer B,
Truan D, Codony-Servat J, Sauleda S, Alcover J, Campo E, Gascon P,
Rovira A, et al: Activation of nuclearfactor-kappaB in human
prostate carcinogenesis and association to biochemical relapse. Br
J Cancer. 93:1285–1294. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Seo SI, Song SY, Kang MR, Kim MS, Oh JE,
Kim YR, Lee JY, Yoo NJ and Lee SH: Immunohistochemical analysis of
NF-kappaB signaling proteins IKK epsilon, p50/p105, p52/p100 and
RelA in prostate cancers. APMIS. 117:623–628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Palvimo JJ, Reinikainen P, Ikonen T,
Kallio PJ, Moilanen A and Jänne OA: Mutual transcriptional
interference between RelA and androgen receptor. J Biol Chem.
271:24151–24156. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nelius T, Filleur S, Yemelyanov A,
Budunova I, Shroff E, Mirochnik Y, Aurora A, Veliceasa D, Xiao W,
Wang Z and Volpert OV: Androgen receptor targets NFkappaB and TSP1
to suppress prostate tumor growth in vivo. Int J Cancer.
121:999–1008. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Hunter JE, Leslie J and Perkins ND: c-Rel
and its manyroles in cancer: An oldstory with new twists. Br J
Cancer. 114:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Weichert W, Boehm M, Gekeler V, Bahra M,
Langrehr J, Neuhaus P, Denkert C, Imre G, Weller C, Hofmann HP, et
al: Highexpression of RelA/p65 is associated with activation of
nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent signaling in pancreatic cancer and
marks a patient population with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer.
97:523–530. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Sarkar DK, Jana D, Patil PS, Chaudhari KS,
Chattopadhyay BK, Chikkala BR, Mandal S and Chowdhary P: Role of
NF-κB as a prognostic marker in breast cancer: A pilot study in
Indian patients. Indian J Surg Oncol. 4:242–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Mukhopadhyay NK, Ferdinand AS,
Mukhopadhyay L, Cinar B, Lutchman M, Richie JP, Freeman MR and Liu
BC: Unraveling androgen receptor interactomes by an array-based
method: discovery of proto-oncoprotein c-Rel as a negative
regulator of androgen receptor. Exp Cell Res. 312:3782–3795. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|