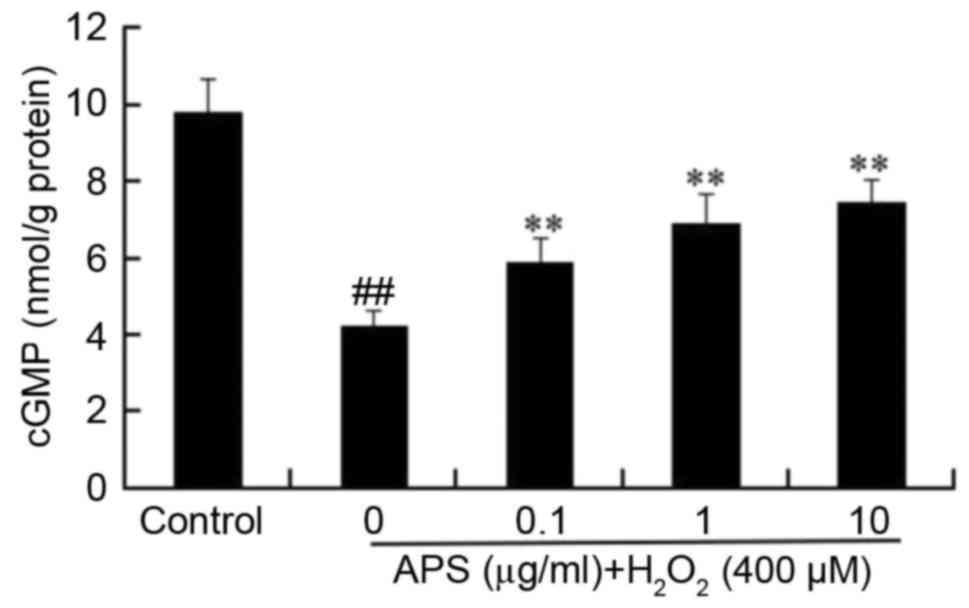
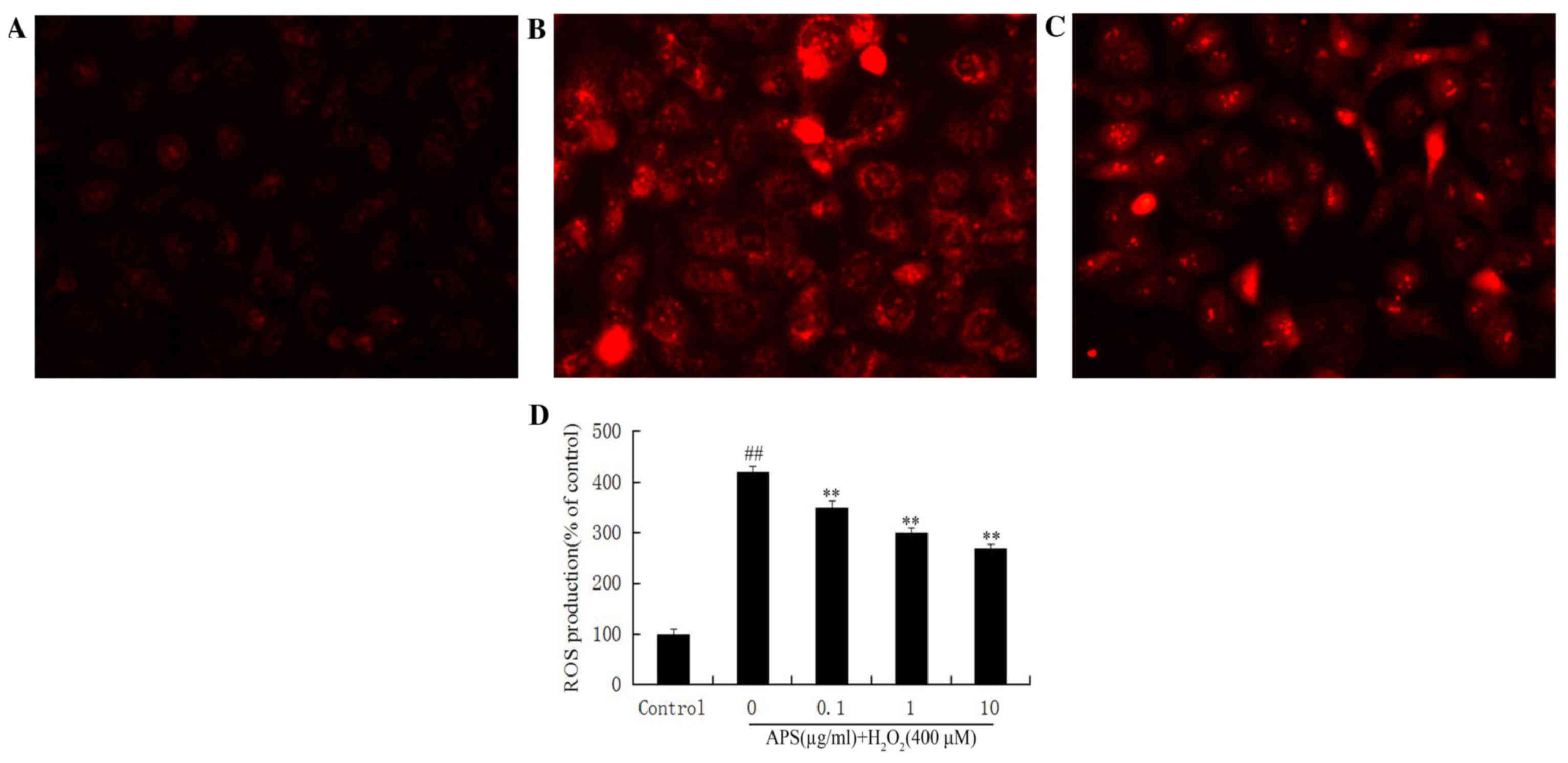
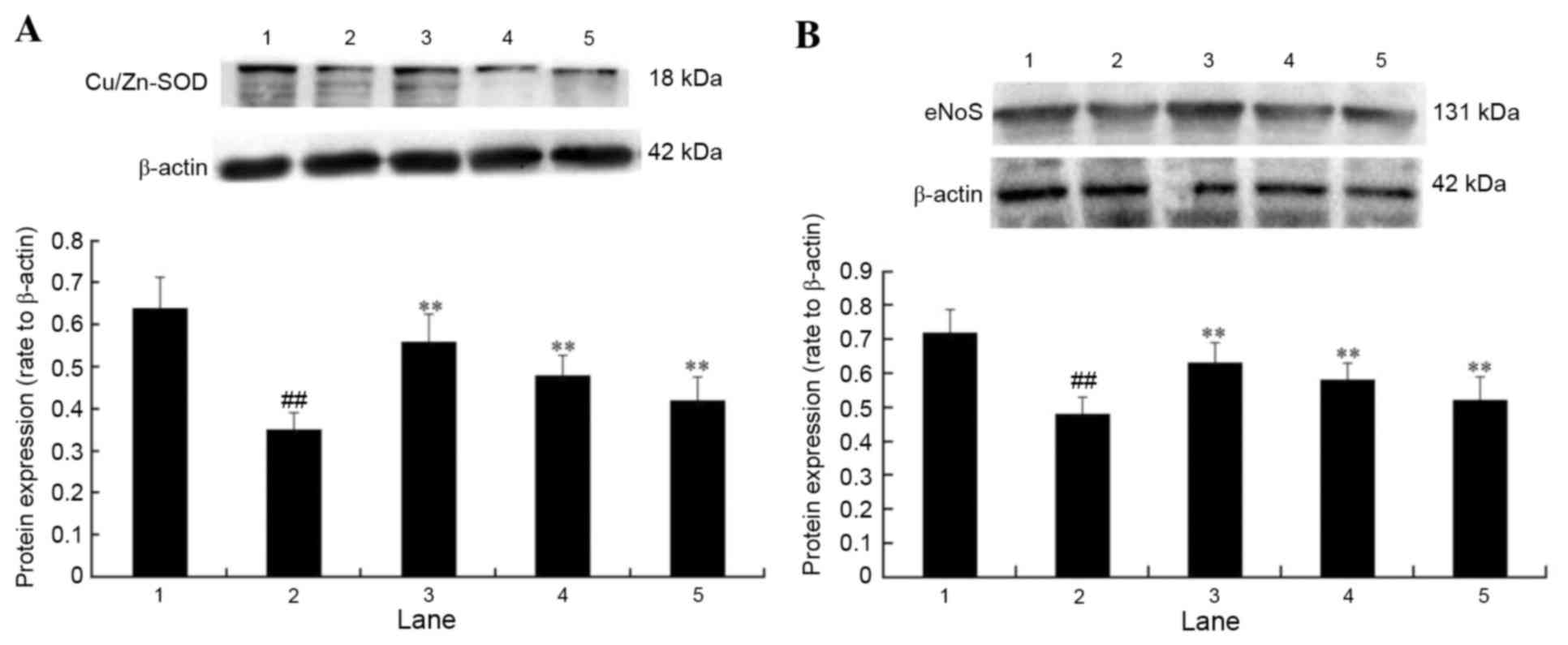
|
1
|
Karsan A and Harlan JM: Modulation of
endothelial cell apoptosis: Mechanisms and pathophysiological
roles. J Atheroscler Thromb. 3:75–80. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Harrison D, Griendling KK, Landmesser U,
Hornig B and Drexler H: Role of oxidative stress in
atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 91:7A–11A. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Szymanski MK, Buikema JH, Van Veldhuisen
DJ, Koster J, van der Velden J, Hamdani N, Hillege JL and
Schoemaker RG: Increased cardiovascular risk in rats with primary
renal dysfunction; mediating role for vascular endothelial
function. Basic Res Cardiol. 107:2422012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Li JM and Shah AM: Endothelial cell
superoxide generation: Regulation and relevance for cardiovascular
pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
287:R1014–R1030. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Loscalzo J: Nitric oxide insufficiency,
platelet activation, and arterial thrombosis. Circ Res. 88:756–762.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Birukov KG: Cyclic stretch, reactive
oxygen species, and vascular remodeling. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:1651–1667. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Urso C and Caimi G: Oxidative stress and
endothelial dysfunction. Minerva Med. 102:59–77. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Lu X, Dang CQ, Guo X, Molloi S, Wassall
CD, Kemple MD and Kassab GS: Elevated oxidative stress and
endothelial dysfunction in right coronary artery of right
ventricular hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol (1985). 110:1674–1681.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Lee YJ, Kang IJ, Bünger R and Kang YH:
Mechanisms of pyruvate inhibition of oxidant-induced apoptosis in
human endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 66:91–101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Maio R, Perticone M, Sciacqua A, Tassone
EJ, Naccarato P, Bagnato C, Iannopollo G, Sesti G and Perticone F:
Oxidative stress impairs endothelial function in nondipper
hypertensive patients. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:85–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nohl H, Kozlov AV, Gille L and Staniek K:
Cell respiration and formation of reactive oxygen species: Facts
and artefacts. Biochem Soc Trans. 31:1308–1311. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang B, Oo TN and Rizzo V: Lipid rafts
mediate H2O2 prosurvival effects in cultured endothelial cells.
FASEB J. 20:1501–1503. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang YK, Hong YJ, Wei M, Wu Y, Huang ZQ,
Chen RZ and Chen HZ: Curculigoside attenuates human umbilical vein
endothelial cell injury induced by H2O2. J Ethnopharmacol.
132:233–239. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu J, Chen HB, Guo BL, Zhao ZZ, Liang ZT
and Yi T: Study of the relationship between genetics and geography
in determining the quality of Astragali Radix. Biol Pharm Bull.
34:1404–1412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang J, Wang HX, Zhang YJ, Lu ML, Zhang J,
Li ST, Zhang SP and Li G: Astragaloside IV attenuates inflammatory
cytokines by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in
isoproterenol-induced myocardial hypertrophy. J Ethnopharmacol.
150:1062–1070. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang D, Hu Y, Sun J, Kong X, Zhang B and
Liu J: Comparative study on adjuvanticity of compound Chinese
herbal medicinal ingredients. Vaccine. 23:3704–3708. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huang WM, Liang YQ, Tang LJ, Ding Y and
Wang XH: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Astragalus
polysaccharide on EA.hy926 cells. Exp Ther Med. 6:199–203.
2013.
|
|
18
|
Lu J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhang L, Li
Z, Liu W, Ouyang J, Han S and He X: Astragalus polysaccharide
induces anti-inflammatory effects dependent on AMPK activity in
palmitate-treated RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:1463–1470.
2013.
|
|
19
|
Shao BM, Xu W, Dai H, Tu P, Li Z and Gao
XM: A study on the immune receptors for polysaccharides from the
roots of Astragalus membranaceus, a Chinese medicinal herb. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 320:1103–1111. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Luan A, Tang F, Yang Y, Lu M, Wang H and
Zhang Y: Astragalus polysaccharide attenuates isoproterenol-induced
cardiac hypertrophy by regulating TNF-α/PGC-1α signaling mediated
energy biosynthesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 39:1081–1090. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dai H, Jia G, Liu X, Liu Z and Wang H:
Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits isoprenaline-induced cardiac
hypertrophy via suppressing Ca2+-mediated calcineurin/NFATc3 and
CaMKII signaling cascades. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 38:263–271.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li ZL, Liu JC, Hu J, Li XQ, Wang SW, Yi DH
and Zhao MG: Protective effects of hyperoside against human
umbilical vein endothelial cell damage induced by hydrogen
peroxide. J Ethnopharmacol. 139:388–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gong G, Qin Y, Huang W, Zhou S, Yang X and
Li D: Rutin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis through
regulating reactive oxygen species mediated mitochondrial
dysfunction pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur
J Pharmacol. 628:27–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ishikawa K, Takenaga K, Akimoto M,
Koshikawa N, Yamaguchi A, Imanishi H, Nakada K, Honma Y and Hayashi
J: ROS-generating mitochondrial DNA mutations can regulate tumor
cell metastasis. Science. 320:661–664. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gonda K, Tsuchiya H, Sakabe T, Akechi Y,
Ikeda R, Nishio R, Terabayashi K, Ishii K, Matsumi Y, Ashla AA, et
al: Synthetic retinoid CD437 induces mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 370:629–633. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Han YS and Lee CS: Antidepressants reveal
differential effect against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium toxicity in
differentiated PC12 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 604:36–44. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Calderone A, Thaik CM, Takahashi N, Chang
DL and Colucci WS: Nitric oxide, atrial natriuretic peptide, and
cyclic GMP inhibit the growth-promoting effects of norepinephrine
in cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 101:812–818.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Bleske BE, Hwang HS, Zineh I, Ghannam MG
and Boluyt MO: Evaluation of immunomodulatory biomarkers in a
pressure overload model of heart failure. Pharmacotherapy.
27:504–509. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cai H and Harrison DG: Endothelial
dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The role of oxidant stress.
Circ Res. 87:840–844. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Vita JA and Keaney JF Jr: Endothelial
function: A barometer for cardiovascular risk? Circulation.
106:640–642. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Poulikakos D, Ross L, Recio-Mayoral A,
Cole D, Andoh J, Chitalia N, Sharma R, Kaski J Carlos and Banerjee
D: Left ventricular hypertrophy and endothelial dysfunction in
chronic kidney disease. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 15:56–61.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang BQ, Hu SJ, Qiu LH, Zhu JH, Xie XJ,
Sun J, Zhu ZH, Xia Q and Bian K: Effects of Astragalus membranaceus
and its main components on the acute phase endothelial dysfunction
induced by homocysteine. Vascul Pharmacol. 46:278–285. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang M, Qian XH, Zhao DH and Fu SZ:
Effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on the erythroid lineage and
microarray analysis in K562 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 127:242–250.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lu L, Wang DT, Shi Y, Yin Y, Wei LB, Zou
YC, Huang B, Zhao Y, Wang M, Wan H, et al: Astragalus
polysaccharide improves muscle atrophy from dexamethasone- and
peroxide-induced injury in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol. 61:7–16.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dimmeler S and Zeiher AM: Nitric oxide-an
endothelial cell survival factor. Cell Death Differ. 6:964–968.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Nightingale AK, Sverdlov AL, Rajendran S,
Mishra K, Heresztyn T, Ngo DT and Horowitz JD: Lack of association
between aortic sclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy in
elderly subjects. Int J Cardiol. 150:33–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Clapp BR, Hingorani AD, Kharbanda RK,
Mohamed-Ali V, Stephens JW, Vallance P and MacAllister RJ:
Inflammation-induced endothelial dysfunction involves reduced
nitric oxide bioavailability and increased oxidant stress.
Cardiovasc Res. 64:172–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zorov DB, Filburn CR, Klotz LO, Zweier JL
and Sollott SJ: Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced ROS release:
A new phenomenon accompanying induction of the mitochondrial
permeability transition in cardiac myocytes. J Exp Med.
192:1001–1014. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Touyz RM and Schiffrin EL: Reactive oxygen
species in vascular biology: Implications in hypertension.
Histochem Cell Biol. 122:339–352. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cai H: Hydrogen peroxide regulation of
endothelial function: Origins, mechanisms and consequences.
Cardiovasc Res. 68:26–36. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu YM, Jiang B, Bao YM and An LJ:
Protocatechuic acid inhibits apoptosis by mitochondrial dysfunction
in rotenone-induced PC12 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 22:430–437. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|