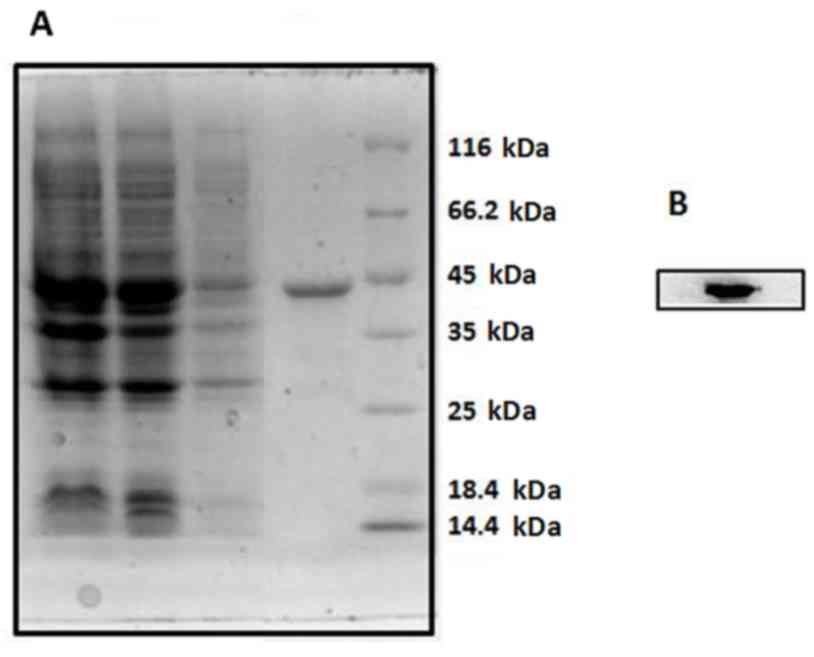
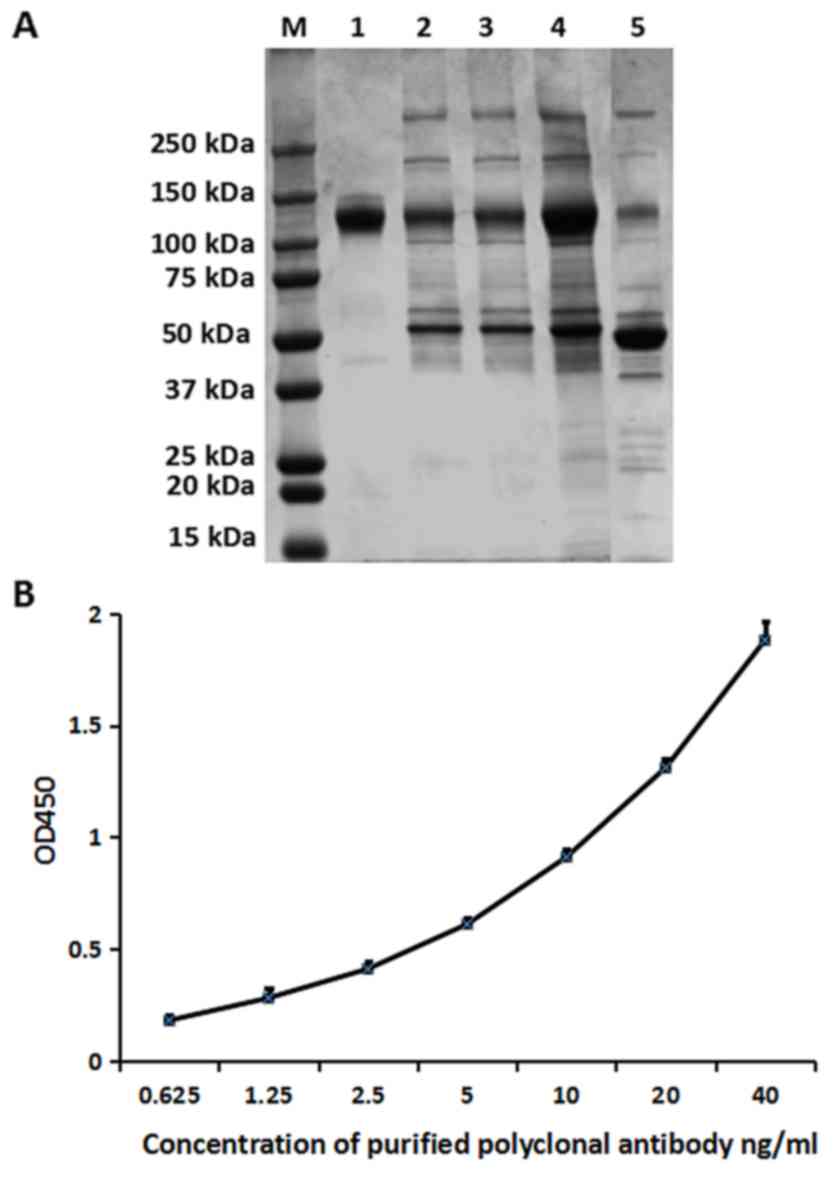
|
1
|
Biswas C: Tumor cell stimulation of
collagenase production by fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
109:1026–1034. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ellis SM, Nabeshima K and Biswas C:
Monoclonal antibody preparation and purification of a tumor cell
collagenase-stimulatory factor. Cancer Res. 49:3385–3391. 1989.
|
|
3
|
Polette M, Gilles C, Marchand V, Lorenzato
M, Toole B, Tournier JM, Zucker S and Birembaut P: Tumor
collagenase stimulatory factor (TCSF) expression and localization
in human lung and breast cancers. J Histochem Cytochem. 45:703–709.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tang J, Wu YM, Zhao P, Yang XM, Jiang JL
and Chen ZN: Overexpression of HAb18G/CD147 promotes invasion and
metastasis via alpha3beta1 integrin mediated FAK-paxillin and
FAK-PI3K-Ca2+ pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:2933–2942. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu Y, Zhou X and Zheng PS: Involvement of
CD147 isoform-4 in the proliferation of SiHa cells: A possible
molecular mechanism of cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 26:717–724.
2011.
|
|
6
|
Chen ZN, Yang Z and Mi L: Analysis on the
structure and function of hepatoma transfer-associated factor
HAb18G (in Chinese). J Mol Cell Immunol. 15:341999.
|
|
7
|
Jiang JL, Zhou Q, Yu MK, Ho LS, Chen ZN
and Chan HC: The involvement of HAb18G/CD147 in regulation of
store-operated calcium entry and metastasis of human hepatoma
cells. J Biol Chem. 276:46870–46877. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Haug C, Lenz C, Diaz F and Bachem MG:
Oxidized low-density lipoproteins stimulate extracellular matrix
metalloproteinase Inducer (EMMPRIN) release by coronary smooth
muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:1823–1829. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Egawa N, Koshikawa N, Tomari T, Nabeshima
K, Isobe T and Seiki M: Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase
(MT1-MMP/MMP-14) cleaves and releases a 22-kDa extracellular matrix
metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) fragment from tumor cells. J
Biol Chem. 281:37576–37585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tang Y, Kesavan P, Nakada MT and Yan L:
Tumor-stroma interaction: Positive feedback regulation of
extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) expression
and matrix metalloproteinase-dependent generation of soluble
EMMPRIN. Mol Cancer Res. 2:73–80. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Taylor PM, Woodfield RJ, Hodgkin MN,
Pettitt TR, Martin A, Kerr DJ and Wakelam MJ: Breast cancer
cell-derived EMMPRIN stimulates fibroblast MMP2 release through a
phospholipase A(2) and 5-lipoxygenase catalyzed pathway. Oncogene.
21:5765–5772. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yanaba K, Asano Y, Tada Y, Sugaya M,
Kadono T, Hamaguchi Y and Sato S: Increased serum soluble CD147
levels in patients with systemic sclerosis: Association with
scleroderma renal crisis. Clin Rheumatol. 31:835–839. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu J, Hao ZW, Zhao YX, Yang XM, Tang H,
Zhang X, Song F, Sun XX, Wang B, Nan G, et al: Full-length soluble
CD147 promotes MMP-2 expression and is a potential serological
marker in detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med.
12:1902014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Hornbeck PV: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assays. Curr Protoc Immunol. 110:1–23. 2015.
|
|
15
|
Moonsom S, Tayapiwatana C, Wongkham S,
Kongtawelert P and Kasinrerk W: A competitive ELISA for quantifying
serum CD147: Reduction of soluble CD147 levels in cancer patient
sera. Hybridoma (Larchmt). 29:45–52. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ku XM, Liao CG, Li Y, Yang XM, Yang B, Yao
XY, Wang L, Kong LM, Zhao P and Chen ZN: Epitope mapping of series
of monoclonal antibodies against the hepatocellular
carcinoma-associated antigen HAb18G/CD147. Scand J Immunol.
65:435–443. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nelson PN, Westwood OM, Jefferis R,
Goodall M and Hay FC: Characterisation of anti-IgG monoclonal
antibody A57H by epitope mapping. Biochem Soc Trans. 25:373S1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lipman NS, Jackson LR, Trudel LJ and
Weis-Garcia F: Monoclonal versus polyclonal antibodies:
Distinguishing characteristics, applications, and information
resources. ILAR J. 46:258–268. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lane D: Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual.
Cold Spring Harbor Press; Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: pp. 288–312.
1998
|
|
20
|
Andrew SM and Titus JA: Purification of
immunoglobulin G. Curr Protoc Immunol: Chapter. 2:Unit 2.72001.
|
|
21
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen ZN and Liu YF: Monoclonal antibody
HAb18 to human hepatoma. J Monocl Antibod. 3:15–17. 1990.(In
Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Howard GC and Bethell DR: Basic methods in
antibody production and characterization. CRC Press Ltd; Boca
Raton, Florida: pp. 1–49. 2000, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Verdoliva A, Basile G and Fassina G:
Affinity purification of immunoglobulins from chicken egg yolk
using a new synthetic ligand. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl.
749:233–242. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hage DS: Survey of recent advances in
analytical applications of immunoaffinity chromatography. J
Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 715:3–28. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hage DS and Phillips TM: Immunoaffinity
chromatographyTaylor & Francis, Handbook of Affinity
Chromatography. New York: 62006
|