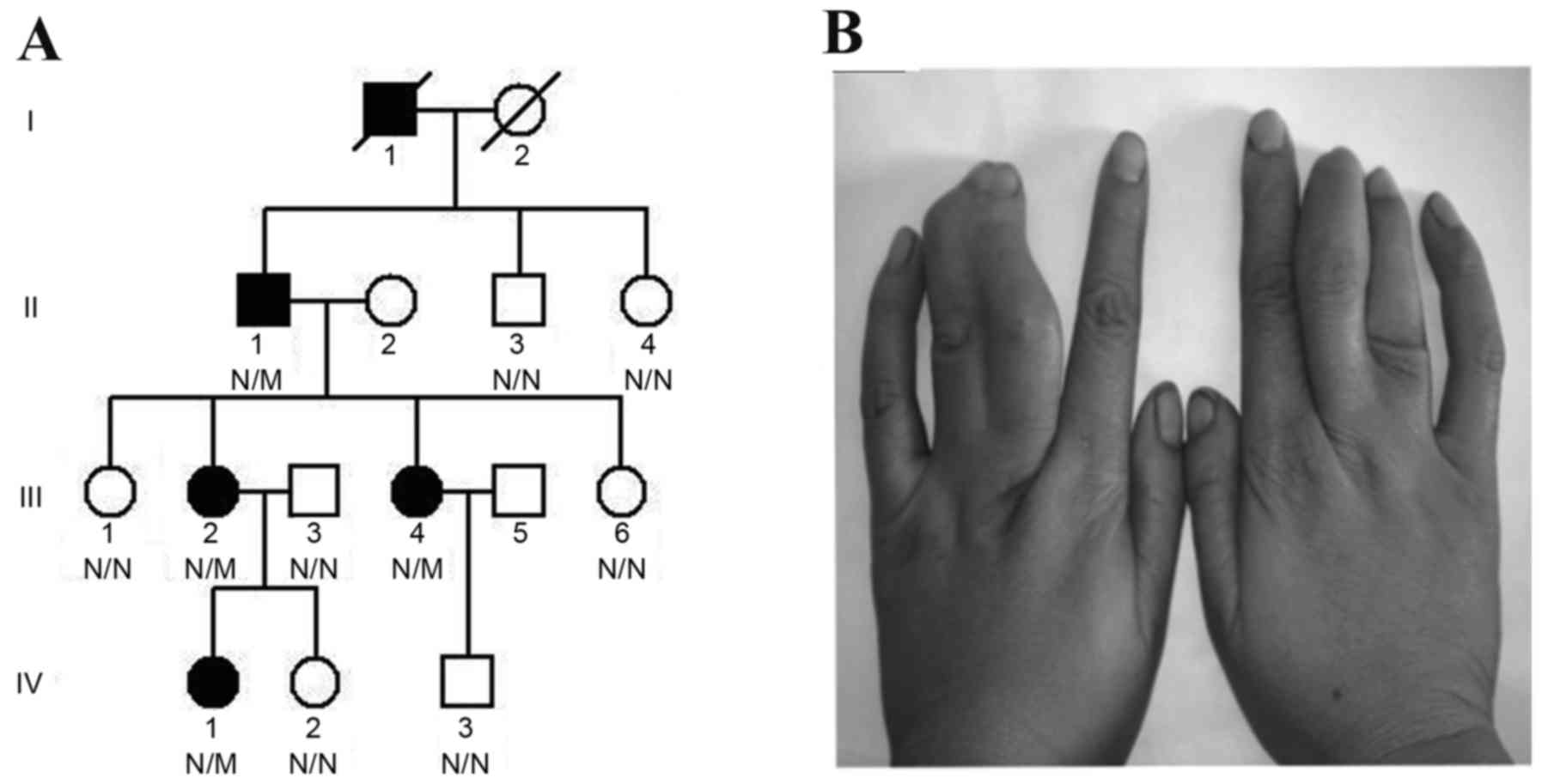
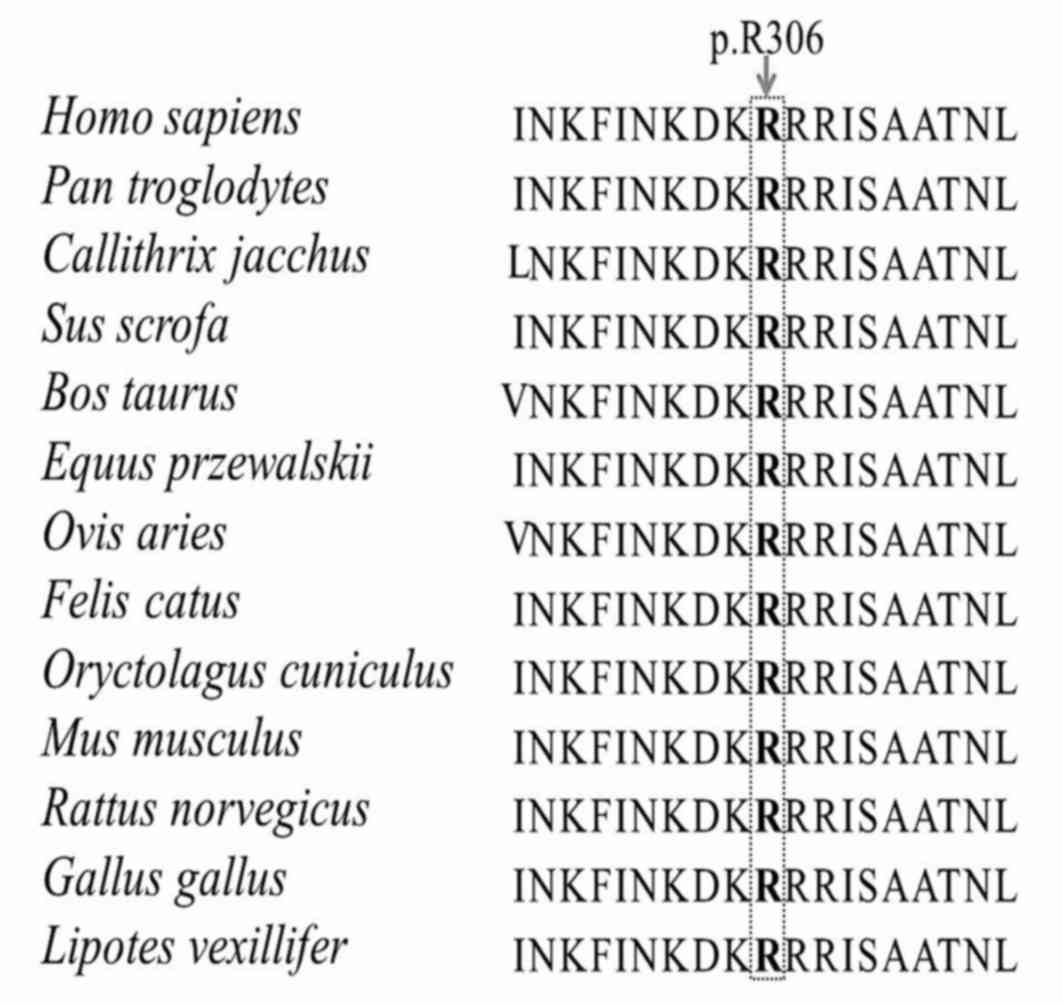
|
1
|
Malik S: Syndactyly: Phenotypes, genetics
and current classification. Eur J Hum Genet. 20:817–824. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malik S, Schott J, Ali SW, Oeffner F,
Amin-ud-Din M, Ahmad W, Grzeschik KH and Koch MC: Evidence for
clinical and genetic heterogeneity of syndactyly type I: The
phenotype of second and third toe syndactyly maps to chromosome
3p21.31. Eur J Hum Genet. 13:1268–1274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jordan D, Hindocha S, Dhital M, Saleh M
and Khan W: The epidemiology, genetics and future management of
syndactyly. Open Orthop J. 6:14–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sobreira NL, Cernach MC, Brunoni D and
Perez AB: Complex toe syndactyly with characteristic facial
phenotype: A new syndrome? Am J Med Genet A. 146A:1725–1728. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujii S, Yabe K, Kimura Y, Ito Y, Rokukawa
M, Furukawa M, Ito K, Matsuura M and Kiguchi M: Syndactyly lethal:
New mutation with multiple malformations occurring in Sprague
Dawley rats. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 49:262–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jamsheer A, Zemojtel T, Kolanczyk M,
Stricker S, Hecht J, Krawitz P, Doelken SC, Glazar R, Socha M and
Mundlos S: Whole exome sequencing identifies FGF16 nonsense
mutations as the cause of X-linked recessive metacarpal 4/5 fusion.
J Med Genet. 50:579–584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou X, Zheng C, He B, Zhu Z, Li P, He X,
Zhu S, Yang C, Lao Z, Zhu Q and Liu X: A novel mutation outside
homeodomain of HOXD13 causes synpolydactyly in a Chinese family.
Bone. 57:237–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao X, Sun M, Zhao J, Leyva JA, Zhu H,
Yang W, Zeng X, Ao Y, Liu Q, Liu G, et al: Mutations in HOXD13
underlie syndactyly type V and a novel brachydactyly-syndactyly
syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 80:361–371. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng H and Tan T: Advances in the
molecular genetics of non-syndromic syndactyly. Curr Genomics.
16:183–193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo Y, Yuan L, Yi J, Xiao J, Xu H, Lv H,
Xiong W, Zheng W, Guan L, Zhang J, et al: Identification of a GJA3
mutation in a Chinese family with congenital nuclear cataract using
exome sequencing. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 50:253–258.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang JL, Cao L, Li XH, Hu ZM, Li JD, Zhang
JG, Liang Y San-A, Li N, Chen SQ, et al: Identification of PRRT2 as
the causative gene of paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesias. Brain.
134:3490–3498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Shi Y, Li Y, Zhang D, Zhang H, Li Y, Lu F,
Liu X, He F, Gong B, Cai L, et al: Exome sequencing identifies
ZNF644 mutations in high myopia. PLoS Genet. 7:e10020842011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li R, Li Y, Kristiansen K and Wang J:
SOAP: Short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics.
24:713–714. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu J and Ng PC: SIFT Indel: Predictions
for the functional effects of amino acid insertions/deletions in
proteins. PLoS One. 8:e779402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Adzhubei I, Jordan DM and Sunyaev SR:
Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using
PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet Chapter. 7:Unit 7.20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lei J, Deng X, Zhang J, Su L, Xu H, Liang
H, Huang X, Song Z and Deng H: Mutation screening of the HDC gene
in Chinese Han patients with Tourette syndrome. Am J Med Genet B
Neuropsychiatr Genet. 159B:72–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan L, Song Z, Xu H, Gu S, Zhu A, Gong L,
Zhao Y and Deng H: EIF4G1 Ala502Val and Arg1205His variants in
Chinese patients with Parkinson disease. Neurosci Lett. 543:69–71.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo Y, Yuan J, Liang H, Xiao J, Xu H, Yuan
L, Gao K, Wu B, Tang Y, Li X and Deng H: Identification of a novel
COL4A5 mutation in a Chinese family with X-linked Alport syndrome
using exome sequencing. Mol Biol Rep. 41:3631–3635. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brison N, Tylzanowski P and Debeer P: Limb
skeletal malformations-what the HOX is going on? Eur J Med Genet.
55:1–7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dai L, Liu D, Song M, Xu X, Xiong G, Yang
K, Zhang K, Meng H, Guo H and Bai Y: Mutations in the homeodomain
of HOXD13 cause syndactyly type 1-c in two Chinese families. PLoS
One. 9:e961922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cooper DN and Youssoufian H: The CpG
dinucleotide and human genetic disease. Hum Genet. 78:151–155.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kurban M, Wajid M, Petukhova L, Shimomura
Y and Christiano AM: A nonsense mutation in the HOXD13 gene
underlies synpolydactyly with incomplete penetrance. J Hum Genet.
56:701–706. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Akarsu AN, Stoilov I, Yilmaz E, Sayli BS
and Sarfarazi M: Genomic structure of HOXD13 gene: A nine
polyalanine duplication causes synpolydactyly in two unrelated
families. Hum Mol Genet. 5:945–952. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jamsheer A, Sowinska A, Kaczmarek L and
Latos-Bielenska A: Isolated brachydactyly type E caused by a HOXD13
nonsense mutation: A case report. BMC Med Genet. 13:42012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bruneau S, Johnson KR, Yamamoto M, Kuroiwa
A and Duboule D: The mouse Hoxd13(spdh) mutation, a polyalanine
expansion similar to human type II synpolydactyly (SPD), disrupts
the function but not the expression of other Hoxd genes. Dev Biol.
237:345–353. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zakany J and Duboule D: Synpolydactyly in
mice with a targeted deficiency in the HoxD complex. Nature.
384:69–71. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dollé P, Dierich A, LeMeur M, Schimmang T,
Schuhbaur B, Chambon P and Duboule D: Disruption of the Hoxd-13
gene induces localized heterochrony leading to mice with neotenic
limbs. Cell. 75:431–441. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|