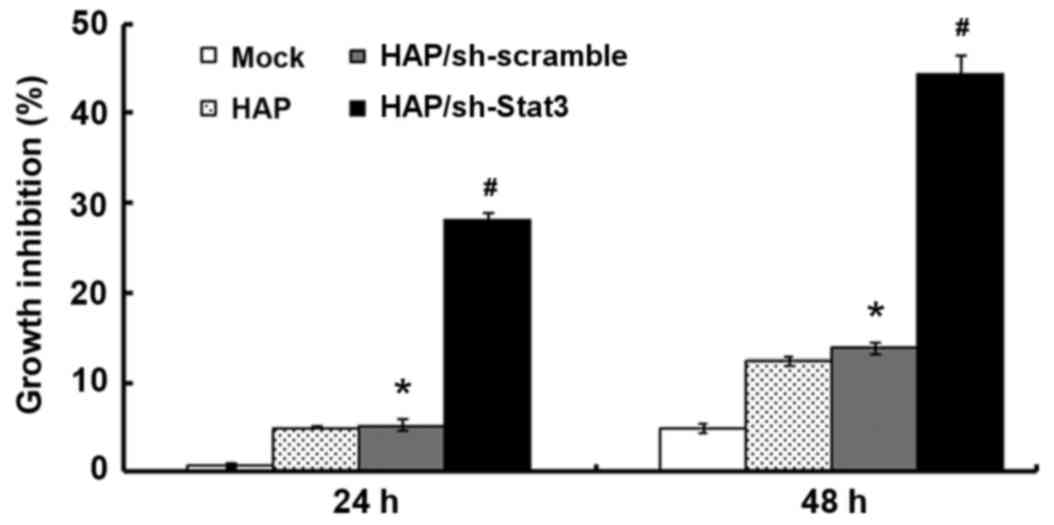
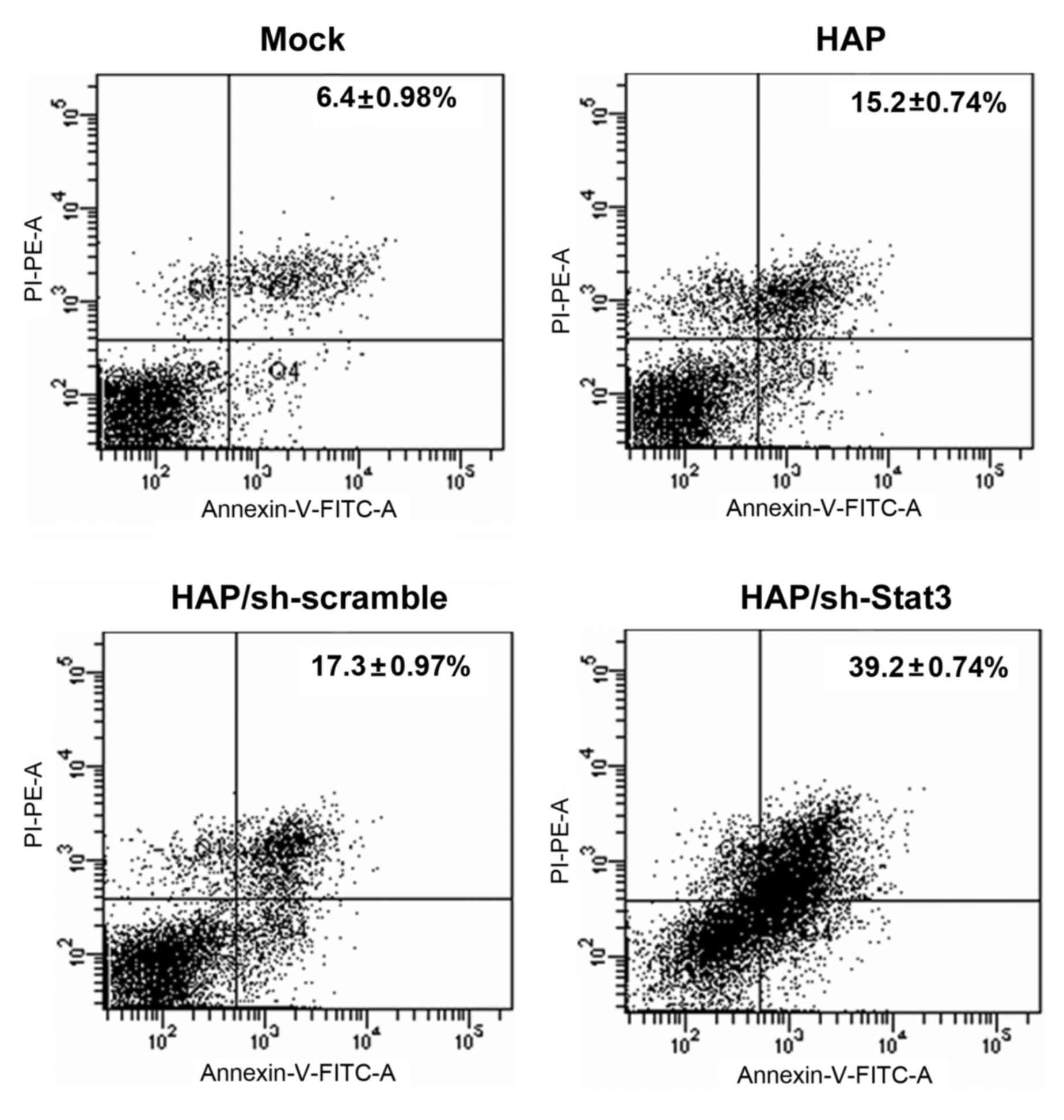
|
1
|
Do TN, Lee WH, Loo CY, Zavgorodniy AV and
Rohanizadeh R: Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as vectors for gene
delivery. Ther Deliv. 3:623–632. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bose S and Tarafder S: Calcium phosphate
ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue
engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 8:1401–1421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Olton D, Li J, Wilson ME, Rogers T, Close
J, Huang L, Kumta PN and Sfeir C: Nanostructured calcium phosphates
(NanoCaPs) for non-viral gene delivery: Influence of the synthesis
parameters on transfection efficiency. Biomaterials. 28:1267–1279.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ginebra MP, Canal C, Espanol M, Pastorino
D and Montufar EB: Calcium phosphate cements as drug delivery
materials. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 64:1090–1110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Loo SC, Moore T, Banik B and Alexis F:
Biomedical applications of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 11:333–342. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, McCrate JM, Lee JC and Li H: The
role of surface charge on the uptake and biocompatibility of
hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with osteoblast cells. Nanotechnology.
22:1057082011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zakaria SM, Zein Sharif SH, Othman MR,
Yang F and Jansen JA: Nanophase hydroxyapatite as a biomaterial in
advanced hard tissue engineering: A review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
19:431–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan K, Cheang P, Ho IA, Lam PY and Hui KM:
Nanosized bioceramic particles could function as efficient gene
delivery vehicles with target specificity for the spleen. Gene
Ther. 14:828–835. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun H, Jiang M and Zhu SH: In vitro and in
vivo studies on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a novel vector for
inner ear gene therapy. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 43:51–57. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu X, Ding D, Jiang H, Xing X, Huang S,
Liu H, Chen Z and Sun H: Transfection using hydroxyapatite
nanoparticles in the inner ear via an intact round window membrane
in chinchilla. J Nanopart Res. 14:7082012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yan-Zhong Z, Yan-Yan H, Jun Z, Shai-Hong
Z, Zhi-You L and Ke-Chao Z: Characteristics of functionalized
nano-hydroxyapatite and internalization by human epithelial cell.
Nanoscale Res Lett. 6:6002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang ZW, Guo BF, Li Y, Li XJ, Li X, Zhao
LJ, Gao LF, Yu H, Zhao XJ, Zhang L and Yang BX: Plasmid-based Stat3
siRNA delivered by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles suppresses mouse
prostate tumour growth in vivo. Asian J Androl. 13:481–486. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gao L, Zhang L, Hu J, Li F, Shao Y, Zhao
D, Kalvakolanu DV, Kopecko DJ, Zhao X and Xu DQ: Down-regulation of
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expression using
vector-based small interfering RNAs suppresses growth of human
prostate tumor in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6333–6341. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamada M, Ueno T, Tsukimura N, Ikeda T,
Nakagawa K, Hori N, Suzuki T and Ogawa T: Bone integration
capability of nanopolymorphic crystalline hydroxyapatite coated on
titanium implants. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:859–873. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fernandez JM, Molinuevo MS, Cortizo MS and
Cortizo AM: Development of an osteoconductive
PCL-PDIPF-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold for bone tissue
engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 5:e126–e135. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ye F, Guo H, Zhang H and He X: Polymeric
micelle-templated synthesis of hydroxyapatite hollow nanoparticles
for a drug delivery system. Acta Biomater. 6:2212–2218. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu H, Xi P, Xie G, Chen F, Li Z, Bai D
and Zeng Z: Biocompatible hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a redox
luminescence switch. J Biol Inorg Chem. 16:1135–1140. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barghi L, Asgari D, Barar J, Nakhlband A
and Valizadeh H: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro
anti-tumoral evaluation of Erlotinib-PCEC nanoparticles. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 15:10281–10287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu J, Xu P, Li Z, Huang J and Yang Z:
Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by hydroxyapatite
nanoparticles in C6 cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 100:738–745. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Gao L, Li Y, Lin G, Shao Y, Ji K,
Yu H, Hu J, Kalvakolanu DV, Kopecko DJ, et al: Effects of
plasmid-based Stat3-specific short hairpin RNA and GRIM-19 on PC-3M
tumor cell growth. Clin Cancer Res. 14:559–568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barton BE, Karras JG, Murphy TF, Barton A
and Huang HF: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
(STAT3) activation in prostate cancer: Direct STAT3 inhibition
induces apoptosis in prostate cancer lines. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:11–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Da Silveira RA, Hermes CL, Almeida TC,
Bochi GV, De Bona KS, Moretto MB and Moresco RN: Ischemia-modified
albumin and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with prostate
cancer. Clin Lab. 60:1703–1708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dumache R, Puiu M, Motoc M, Vernic C and
Dumitrascu V: Prostate cancer molecular detection in plasma samples
by glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) methylation analysis. Clin
Lab. 60:847–852. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aneknan P, Kukongviriyapan V, Prawan A,
Kongpetch S, Sripa B and Senggunprai L: Luteolin arrests cell
cycling, induces apoptosis and inhibits the JAK/STAT3 pathway in
human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:5071–5076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Siveen KS, Sikka S, Surana R, Dai X, Zhang
J, Kumar AP, Tan BK, Sethi G and Bishayee A: Targeting the STAT3
signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural
inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:136–154. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han Z, Wang X, Ma L, Chen L, Xiao M, Huang
L, Cao Y, Bai J, Ma D, Zhou J and Hong Z: Inhibition of STAT3
signaling targets both tumor-initiating and differentiated cell
populations in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 5:8416–8428. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim WJ and Kim SW: Efficient siRNA
delivery with non-viral polymeric vehicles. Pharm Res. 26:657–666.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu SH, Huang BY, Zhou KC, Huang SP, Liu
F, Li YM, Xue ZG and Long ZG: Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a
novel gene carrier. J Nanopart Res. 6:307–311. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lim SL, Park SY, Kang S, Park D, Kim SH,
Um JY, Jang HJ, Lee JH, Jeong CH, Jang JH, et al: Morusin induces
cell death through inactivating STAT3 signaling in prostate cancer
cells. Am J Cancer Res. 5:289–299. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou Y, Tian L, Zhang YC, Guo BF and Zhou
QW: Apoptotic effects of psiRNA-STAT3 on 4T1 breast cancer cells in
vitro. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:6977–6982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Z and Han ZC: STAT3: A critical
transcription activator in angiogenesis. Med Res Rev. 28:185–200.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|