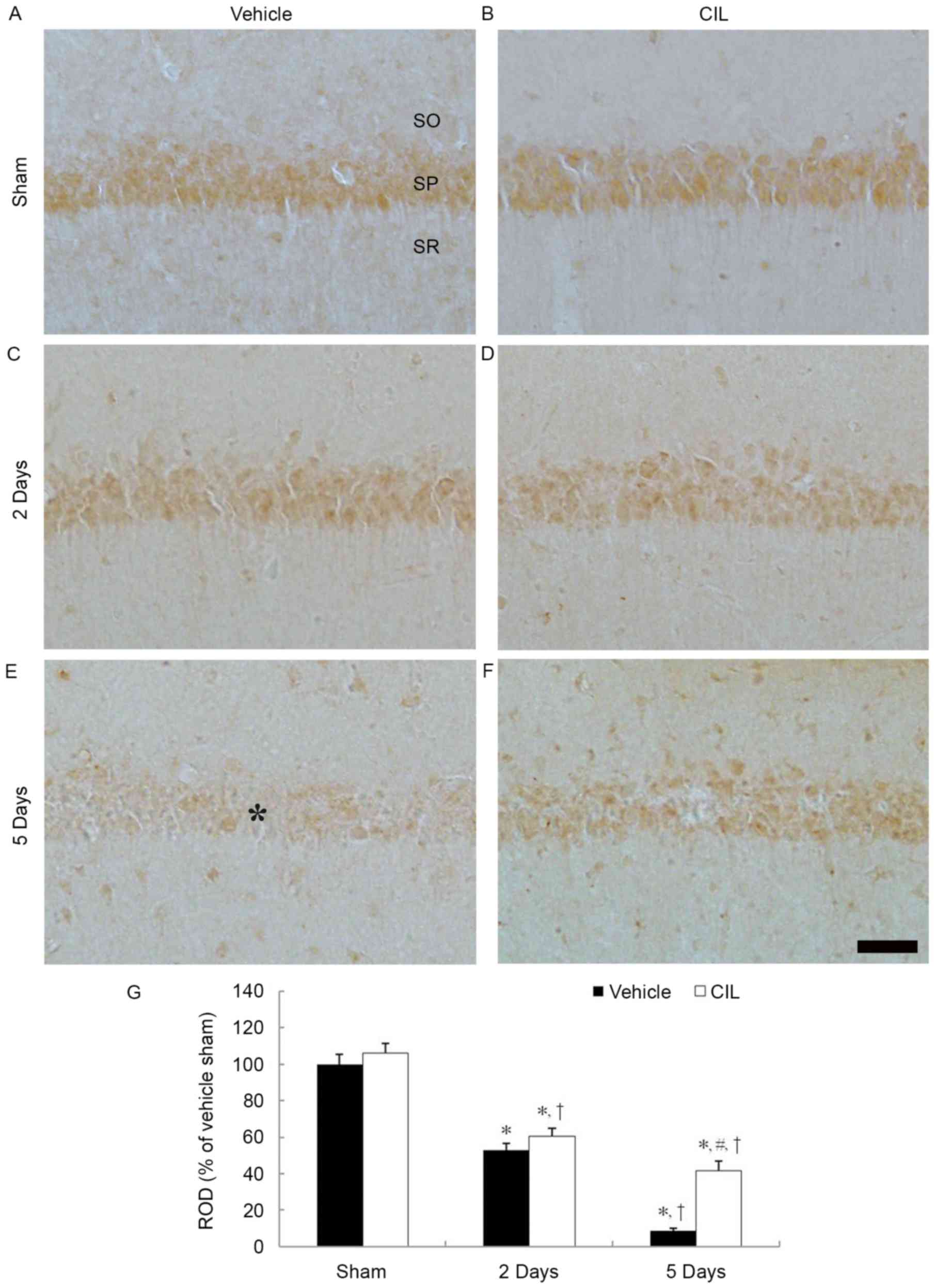
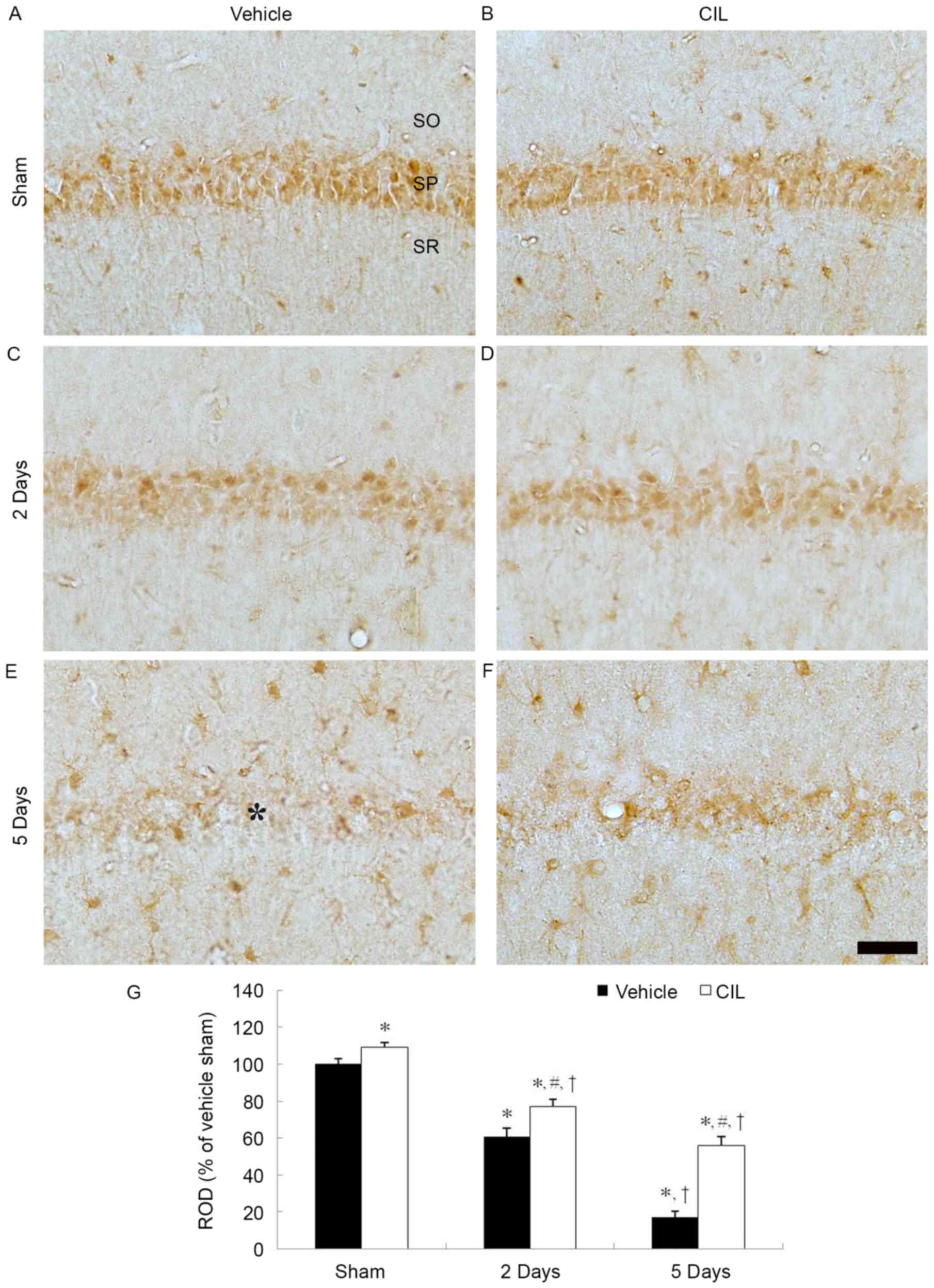
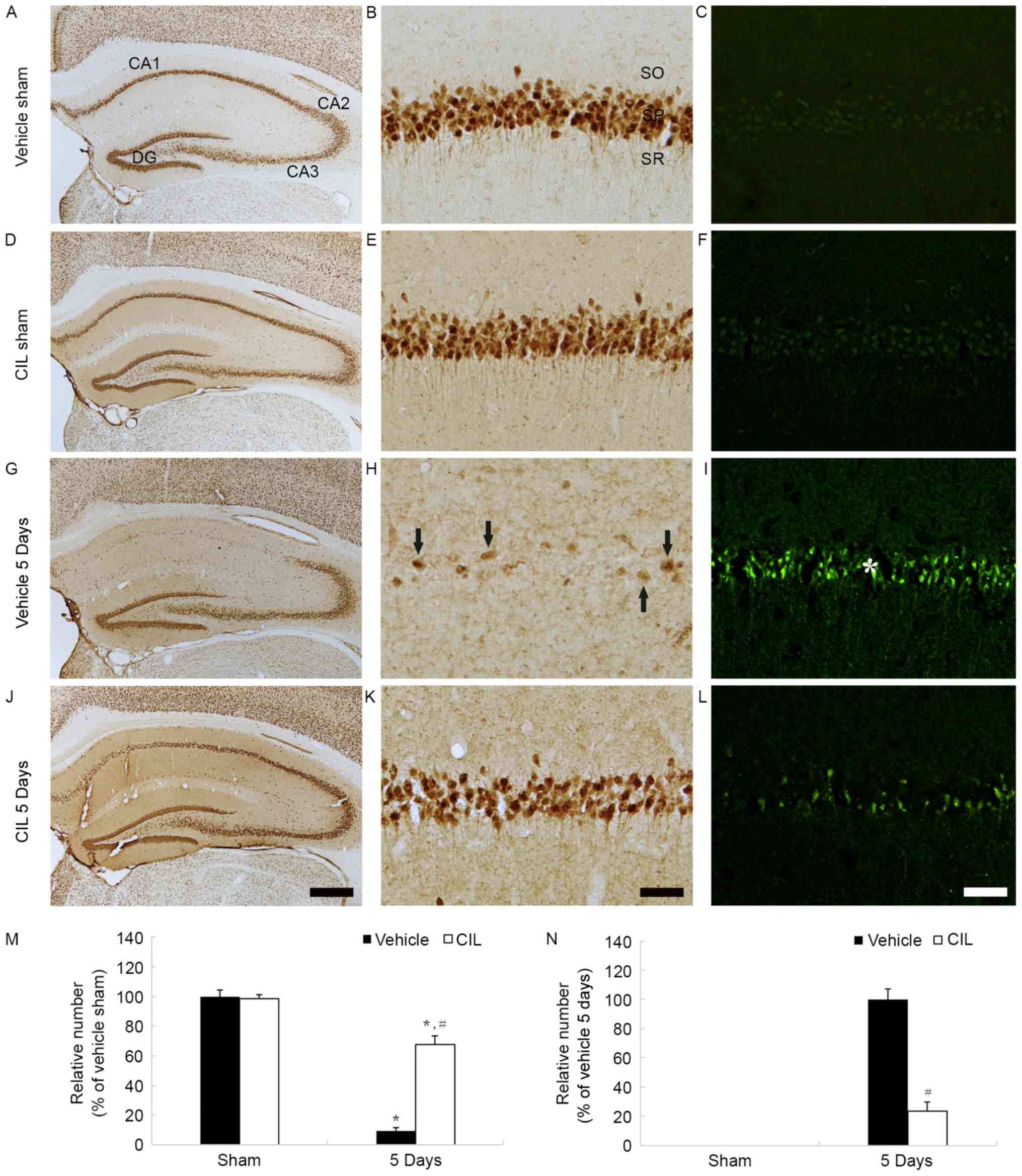
|
1
|
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Adams RJ,
Berry JD, Brown TM, Carnethon MR, Dai S, de Simone G, Ford ES, et
al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2011 update: A report from
the American heart association. Circulation. 123:e18–e209. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liang G, Shi B, Luo W and Yang J: The
protective effect of caffeic acid on global cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Behav Brain Funct. 11:182015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
White BC, Grossman LI and Krause GS: Brain
injury by global ischemia and reperfusion: A theoretical
perspective on membrane damage and repair. Neurology. 43:1656–1665.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Butler TL, Kassed CA, Sanberg PR, Willing
AE and Pennypacker KR: Neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampus and
striatum after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Brain Res.
929:252–260. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Crain BJ, Westerkam WD, Harrison AH and
Nadler JV: Selective neuronal death after transient forebrain
ischemia in the Mongolian gerbil: A silver impregnation study.
Neuroscience. 27:387–402. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kirino T: Delayed neuronal death.
Neuropathology. 20:(Suppl). 95–97. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lewén A, Matz P and Chan PH: Free radical
pathways in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. 17:871–890. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JC and Won MH: Neuroprotection of
antioxidant enzymes against transient global cerebral ischemia in
gerbils. Anat Cell Biol. 47:149–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park JH, Park OK, Yan B, Ahn JH, Kim IH,
Lee JC, Kwon SH, Yoo KY, Lee CH, Hwang IK, et al: Neuroprotection
via maintenance or increase of antioxidants and neurotrophic
factors in ischemic gerbil hippocampus treated with tanshinone I.
Chin Med J (Engl). 127:3396–3405. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chan PH: Reactive oxygen radicals in
signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 21:2–14. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Delanty N and Dichter MA: Antioxidant
therapy in neurologic disease. Arch Neurol. 57:1265–1270. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pastore A, Petrillo S, Piermarini E and
Piemonte F: Systemic redox biomarkers in neurodegenerative
diseases. Curr Drug Metab. 16:46–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duan X, Wang W, Liu X, Yan H, Dai R and
Lin Q: Neuroprotective effect of ethyl acetate extract from
gastrodia elata against transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats
induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Tradit Chin Med.
35:671–678. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Surapaneni S, Prakash T, Ansari M,
Manjunath P, Kotresha D and Goli D: Study on cerebroprotective
actions of Clerodendron glandulosumleaves extract against
long term bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 80:87–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng W, Li J, You T and Hu C:
Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of the extracts
from the inflorescence of Chrysanthemum indicum Linné. J
Ethnopharmacol. 101:334–337. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee DY, Choi G, Yoon T, Cheon MS, Choo BK
and Kim HK: Anti-inflammatory activity of Chrysanthemum
indicum extract in acute and chronic cutaneous inflammation. J
Ethnopharmacol. 123:149–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shunying Z, Yang Y, Huaidong Y, Yue Y and
Guolin Z: Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the
essential oils of Chrysanthemum indicum. J Ethnopharmacol.
96:151–158. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang C, Qin MJ, Shu P, Hong JL, Lu L and
He DX: Chemical variations of the essential oils in flower heads of
Chrysanthemum indicum L. From China. Chem Biodivers.
7:2951–2962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheon MS, Yoon T, Lee DY, Choi G, Moon BC,
Lee AY, Choo BK and Kim HK: Chrysanthemum indicum Linné
extract inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing NF-kappaB
and MAPKs activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7
macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 122:473–477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dekanski D, Selaković V, Piperski V,
Radulović Z, Korenić A and Radenović L: Protective effect of olive
leaf extract on hippocampal injury induced by transient global
cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in Mongolian gerbils.
Phytomedicine. 18:1137–1143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rocher MN, Carré D, Spinnewyn B, Schulz J,
Delaflotte S, Pignol B, Chabrier PE and Auguet M: Long-term
treatment with standardized Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761)
attenuates cognitive deficits and hippocampal neuron loss in a
gerbil model of vascular dementia. Fitoterapia. 82:1075–1080. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoo KY, Kim IH, Cho JH, Ahn JH, Park JH,
Lee JC, Tae HJ, Kim DW, Kim JD, Hong S, et al: Neuroprotection of
Chrysanthemum indicum Linne against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury by anti-inflammatory effect in gerbils.
Neural Regen Res. 11:270–277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim IH, Yan BC, Park JH, Yeun GH, Yim Y,
Ahn JH, Lee JC, Hwang IK, Cho JH, Kim YM, et al: Neuroprotection of
a novel synthetic caffeic acid-syringic acid hybrid compound
against experimentally induced transient cerebral ischemic damage.
Planta Med. 79:313–321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim DW, Lee JC, Cho JH, Park JH, Ahn JH,
Chen BH, Shin BN, Tae HJ, Seo JY, Cho JH, et al: Neuroprotection of
ischemic preconditioning is mediated by anti-inflammatory, not
pro-inflammatory, cytokines in the gerbil hippocampus induced by a
subsequent lethal transient cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Res.
40:1984–1995. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N
and León OS: Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces measures of
oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils.
Neurosci Res. 47:245–253. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee JC, Kim IH, Cho GS, Park JH, Ahn JH,
Yan BC, Kwon HM, Kim YM, Cheon SH, Cho JH, et al: Ischemic
preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against transient cerebral
ischemic damage via attenuating ubiquitin aggregation. J Neurol
Sci. 336:74–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Petito CK, Olarte JP, Roberts B, Nowak TS
Jr and Pulsinelli WA: Selective glial vulnerability following
transient global ischemia in rat brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
57:231–238. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugawara T, Fujimura M, Morita-Fujimura Y,
Kawase M and Chan PH: Mitochondrial release of cytochrome c
corresponds to the selective vulnerability of hippocampal CA1
neurons in rats after transient global cerebral ischemia. J
Neurosci. 19:RC391999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang QG, Wang R, Han D, Dong Y and Brann
DW: Role of Rac1 GTPase in JNK signaling and delayed neuronal cell
death following global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1265:138–147.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Levine S and Sohn D: Cerebral ischemia in
infant and adult gerbils. Relation to incomplete circle of Willis.
Arch Pathol. 87:315–317. 1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Martínez NS, Machado JM, Pérez-Saad H,
Coro-Antich RM, Berlanga-Acosta JA, Salgueiro SR, Illera GG, Alba
JS and del Barco DG: Global brain ischemia in Mongolian gerbils:
Assessing the level of anastomosis in the cerebral circle of
Willis. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 72:377–384. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim IH, Yoo KY, Park JH, Yan BC, Ahn JH,
Lee JC, Kwon HM, Kim JD, Kim YM, You SG, et al: Comparison of
neuroprotective effects of extract and fractions from Agarum
clathratum against experimentally induced transient cerebral
ischemic damage. Pharm Biol. 52:335–343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park JH, Shin BN, Chen BH, Kim IH, Ahn JH,
Cho JH, Tae HJ, Lee JC, Lee CH, Kim YM, et al: Neuroprotection and
reduced gliosis by atomoxetine pretreatment in a gerbil model of
transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurol Sci. 359:373–380. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Numagami Y, Sato S and Ohnishi ST:
Attenuation of rat ischemic brain damage by aged garlic extracts: A
possible protecting mechanism as antioxidants. Neurochem Int.
29:135–143. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tu Q, Wang R, Ding B, Zhong W and Cao H:
Protective and antioxidant effect of Danshen polysaccharides on
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Biol Macromol.
60:268–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chan PH: Oxygen radicals in focal cerebral
ischemia. Brain Pathol. 4:59–65. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodrigo R, Fernández-Gajardo R, Gutiérrez
R, Matamala JM, Carrasco R, Miranda-Merchak A and Feuerhake W:
Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: Novel
therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
12:698–714. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mantha AK, Sarkar B and Tell G: A short
review on the implications of base excision repair pathway for
neurons: Relevance to neurodegenerative diseases. Mitochondrion.
16:38–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sugawara T and Chan PH: Reactive oxygen
radicals and pathogenesis of neuronal death after cerebral
ischemia. Antioxid Redox Signal. 5:597–607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park JH, Cho JH, Kim IH, Ahn JH, Lee JC,
Chen BH, Shin BN, Tae HJ, Yoo KY, Hong S, et al: Oenanthe
Javanica extract protects against experimentally induced
ischemic neuronal damage via its antioxidant effects. Chin Med J
(Engl). 128:2932–2937. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim TW, Kim YJ, Park SR, Seo CS, Ha H,
Shin HK and Jung JY: Chrysanthemum indicum attenuates
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity both in vivo and in vitro. Nat
Prod Commun. 10:397–402. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Murakami K, Kondo T, Epstein CJ and Chan
PH: Overexpression of CuZn-superoxide dismutase reduces hippocampal
injury after global ischemia in transgenic mice. Stroke.
28:1797–1804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chan PH, Kawase M, Murakami K, Chen SF, Li
Y, Calagui B, Reola L, Carlson E and Epstein CJ: Overexpression of
SOD1 in transgenic rats protects vulnerable neurons against
ischemic damage after global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J
Neurosci. 18:8292–8299. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kondo T, Reaume AG, Huang TT, Carlson E,
Murakami K, Chen SF, Hoffman EK, Scott RW, Epstein CJ and Chan PH:
Reduction of CuZn-superoxide dismutase activity exacerbates
neuronal cell injury and edema formation after transient focal
cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 17:4180–4189. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Murakami K, Kondo T, Kawase M, Li Y, Sato
S, Chen SF and Chan PH: Mitochondrial susceptibility to oxidative
stress exacerbates cerebral infarction that follows permanent focal
cerebral ischemia in mutant mice with manganese superoxide
dismutase deficiency. J Neurosci. 18:205–213. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kim DW, Kim DS, Kim MJ, Kwon SW, Ahn EH,
Jeong HJ, Sohn EJ, Dutta S, Lim SS, Cho SW, et al: Imipramine
enhances neuroprotective effect of PEP-1-Catalase against ischemic
neuronal damage. BMB Rep. 44:647–652. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim JE, Jun S, Song M, Kim JH and Song YJ:
The extract of Chrysanthemum indicum Linne inhibits EBV
LMP1-induced NF-κB activation and the viability of EBV-transformed
lymphoblastoid cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1524–1528. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim IS, Ko HM, Koppula S, Kim BW and Choi
DK: Protective effect of Chrysanthemum indicum Linne against
1-methyl-4-phenylpridinium ion and lipopolysaccharide-induced
cytotoxicity in cellular model of Parkinson's disease. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:963–973. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|