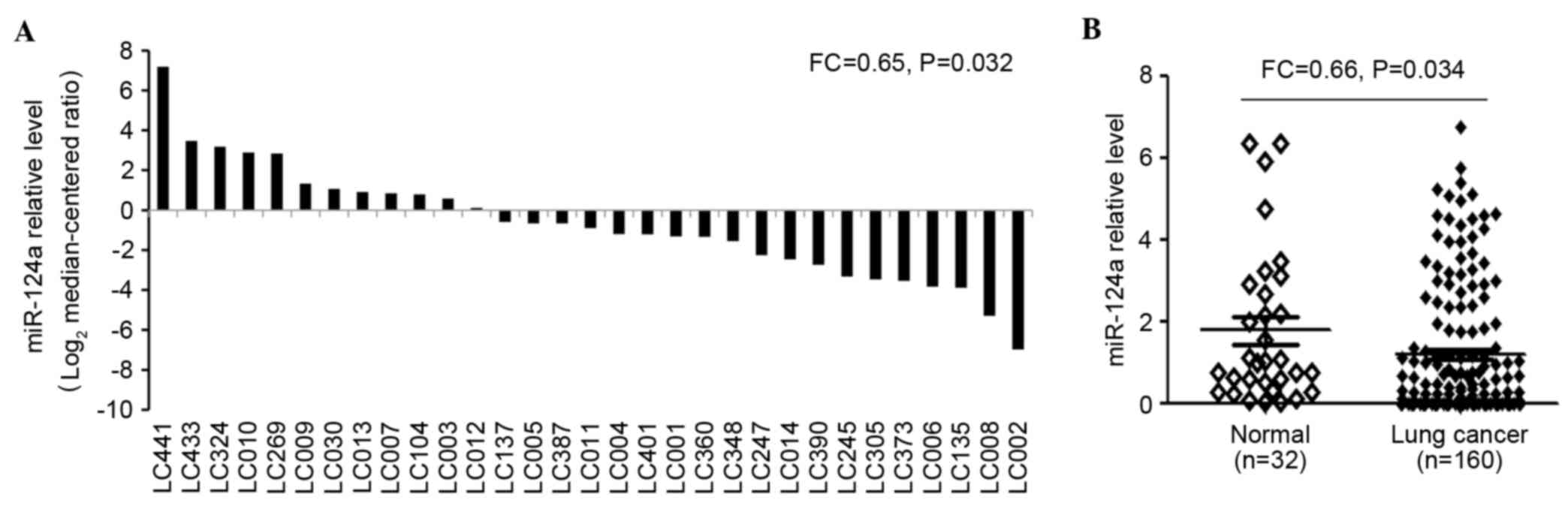
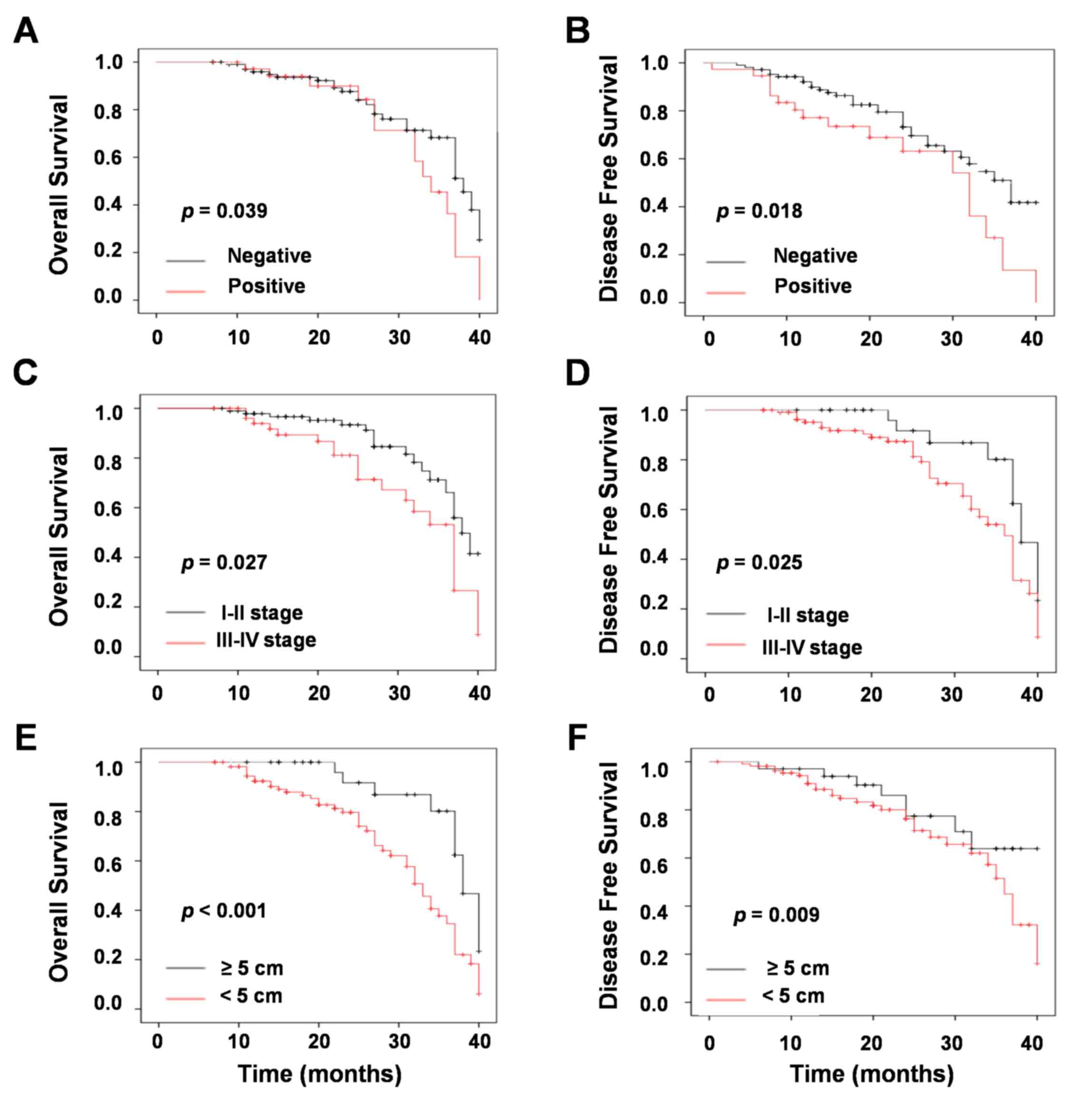
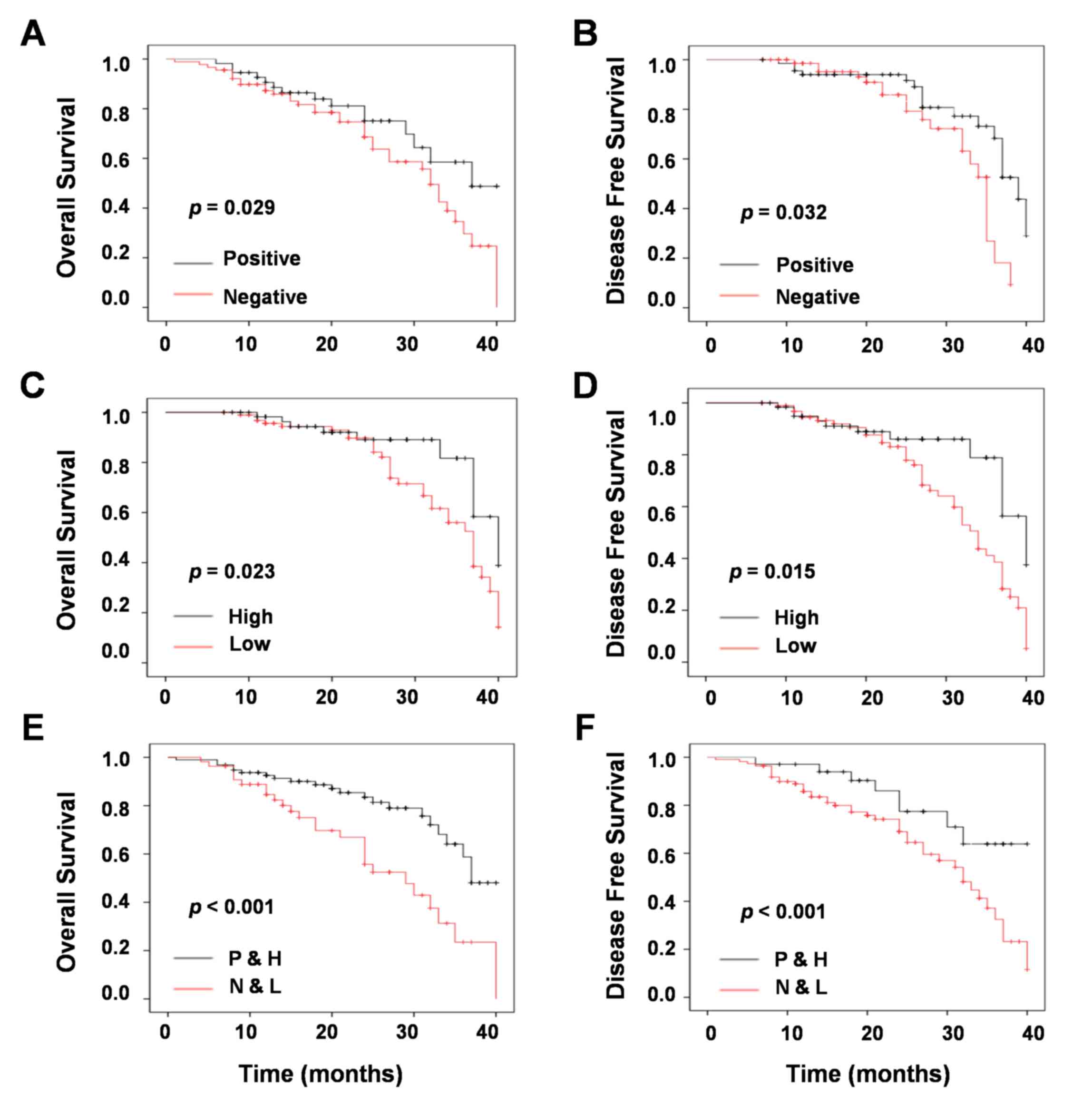
|
1
|
Hamamoto J, Soejima K, Yoda S, Naoki K,
Nakayama S, Satomi R, Terai H, Ikemura S, Sato T, Yasuda H, et al:
Identification of microRNAs differentially expressed between lung
squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
8:456–462. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meng W, Ye Z, Cui R, Perry J,
Dedousi-Huebner V, Huebner A, Wang Y, Li B, Volinia S, Nakanishi H,
et al: MicroRNA-31 predicts the presence of lymph node metastases
and survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
19:5423–5433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tiseo M, Bordi P, Bortesi B, Boni L, Boni
C, Baldini E, Grossi F, Recchia F, Zanelli F, Fontanini G, et al:
ERCC1/BRCA1 expression and gene polymorphisms as prognostic and
predictive factors in advanced NSCLC treated with or without
cisplatin. Br J Cancer. 108:1695–1703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Markou A, Sourvinou I, Vorkas PA, Yousef
GM and Lianidou E: Clinical evaluation of microRNA expression
profiling in non small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 81:388–396.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mitra R, Edmonds MD, Sun J, Zhao M, Yu H,
Eischen CM and Zhao Z: Reproducible combinatorial regulatory
networks elucidate novel oncogenic microRNAs in non-small cell lung
cancer. RNA. 20:1356–1368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xie J, Yu F, Li D, Zhu X, Zhang X and Lv
Z: MicroRNA-218 regulates cisplatin (DPP) chemosensitivity in
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting RUNX2. Tumour Biol.
37:1197–1204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou YL, Xu YJ and Qiao CW: MiR-34c-3p
suppresses the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) by inhibiting PAC1/MAPK pathway. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6312–6322. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Agirre X, Vilas-Zornoza A, Jiménez-Velasco
A, Martin-Subero JI, Cordeu L, Gárate L, San José-Eneriz E,
Abizanda G, Rodríguez-Otero P, Fortes P, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of the tumor suppressor microRNA Hsa-miR-124a regulates
CDK6 expression and confers a poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Cancer Res. 69:4443–4453. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pierson J, Hostager B, Fan R and Vibhakar
R: Regulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 by microRNA 124 in
medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol. 90:1–7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao G, Liu L, Zhao T, Jin S, Jiang S, Cao
S, Han J, Xin Y, Dong Q, Liu X and Cui J: Upregulation of miR-24
promotes cell proliferation by targeting NAIF1 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:3693–3701. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arora S, Ranade AR, Tran NL, Nasser S,
Sridhar S, Korn RL, Ross JT, Dhruv H, Foss KM, Sibenaller Z, et al:
MicroRNA-328 is associated with (non-small) cell lung cancer
(NSCLC) brain metastasis and mediates NSCLC migration. Int J
Cancer. 129:2621–2631. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu F, Wang X, Li J, Gu K, Lv L, Zhang S,
Che D, Cao J, Jin S and Yu Y: miR-34c-3p functions as a tumour
suppressor by inhibiting eIF4E expression in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cell Prolif. 48:582–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu SH, Zhang CL, Dong FS and Zhang YM:
miR-99a suppresses the metastasis of human non-small cell lung
cancer cells by targeting AKT1 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
116:268–276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ruike Y, Ichimura A, Tsuchiya S, Shimizu
K, Kunimoto R, Okuno Y and Tsujimoto G: Global correlation analysis
for micro-RNA and mRNA expression profiles in human cell lines. J
Hum Genet. 53:515–523. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Keller A, Leidinger P, Vogel B, Backes C,
ElSharawy A, Galata V, Mueller SC, Marquart S, Schrauder MG, Strick
R, et al: miRNAs can be generally associated with human pathologies
as exemplified for miR-144. BMC Med. 12:2242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Robles AI, Arai E, Mathé EA, Okayama H,
Schetter AJ, Brown D, Petersen D, Bowman ED, Noro R, Welsh JA, et
al: An integrated prognostic classifier for stage I lung
adenocarcinoma based on mRNA, microRNA, and DNA methylation
biomarkers. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1037–1048. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Keller A, Leidinger P, Borries A,
Wendschlag A, Wucherpfennig F, Scheffler M, Huwer H, Lenhof HP and
Meese E: miRNAs in lung cancer-studying complex fingerprints in
patient's blood cells by microarray experiments. BMC Cancer.
9:3532009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer
staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Acunzo M, Visone R, Romano G, Veronese A,
Lovat F, Palmieri D, Bottoni A, Garofalo M, Gasparini P, Condorelli
G, et al: miR-130a targets MET and induces TRAIL-sensitivity in
NSCLC by downregulating miR-221 and 222. Oncogene. 31:634–642.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garofalo M, Romano G, Di Leva G, Nuovo G,
Jeon YJ, Ngankeu A, Sun J, Lovat F, Alder H, Condorelli G, et al:
EGFR and MET receptor tyrosine kinase-altered microRNA expression
induces tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung cancers. Nat
Med. 18:74–82. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hou LK, Ma YS, Han Y, Lu GX, Luo P, Chang
ZY, Xie RT, Yang HQ, Chai L, Cai MX, et al: Association of
microRNA-33a molecular signature with non-small cell lung cancer
diagnosis and prognosis after chemotherapy. PLoS One.
12:e01704312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Faversani A, Amatori S, Augello C, Colombo
F, Porretti L, Fanelli M, Ferrero S, Palleschi A, Pelicci PG,
Belloni E, et al: miR-494-3p is a novel tumor driver of lung
carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 8:7231–7247. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou Q, Long L, Zhou T, Tian J and Zhou B:
Demethylation of MicroRNA-124a genes attenuated proliferation of
rheumatoid arthritis derived fibroblast-like synoviocytes and
synthesis of tumor necrosis factor-α. PLoS One. 11:e01642072016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ben Gacem R, Ben Abdelkrim O, Ziadi S, Ben
Dhiab M and Trimeche M: Methylation of miR-124a-1, miR-124a-2, and
miR-124a-3 genes correlates with aggressive and advanced breast
cancer disease. Tumour Biol. 35:4047–4056. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liang YJ, Wang QY, Zhou CX, Yin QQ, He M,
Yu XT, Cao DX, Chen GQ, He JR and Zhao Q: MiR-124 targets Slug to
regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:713–722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tivnan A, Zhao J, Johns TG, Day BW,
Stringer BW, Boyd AW, Tiwari S, Giles KM, Teo C and McDonald KL:
The tumor suppressor microRNA, miR-124a, is regulated by epigenetic
silencing and by the transcriptional factor, REST in glioblastoma.
Tumour Biol. 35:1459–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu SH, Jiang XJ, Xiao GL, Liu DY and Yuan
XR: miR-124a restoration inhibits glioma cell proliferation and
invasion by suppressing IQGAP1 and β-catenin. Oncol Rep.
32:2104–2110. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Deng G, Kakar S and Kim YS: MicroRNA-124a
and microRNA-34b/c are frequently methylated in all histological
types of colorectal cancer and polyps, and in the adjacent normal
mucosa. Oncol Lett. 2:175–180. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ueda Y, Ando T, Nanjo S, Ushijima T and
Sugiyama T: DNA methylation of microRNA-124a is a potential risk
marker of colitis-associated cancer in patients with ulcerative
colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 59:2444–2451. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, He D, Dong XD, Dong F, Wang J,
Wang L, Tang J, Hu DN, Yan D and Tu L: MicroRNA-124a is
epigenetically regulated and acts as a tumor suppressor by
controlling multiple targets in uveal melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 54:2248–2256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He T, Feng G, Chen H, Wang L and Wang Y:
Identification of host encoded microRNAs interacting with novel
swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus and swine influenza virus.
Bioinformation. 4:112–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim YH, Lee WK, Lee EB, Son JW, Kim DS and
Park JY: Combined effect of metastasis-related MicroRNA, miR-34 and
miR-124 family, methylation on prognosis of non-small-cell lung
cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 18:e13–e20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li X, Yu Z, Li Y, Liu S, Gao C, Hou X, Yao
R and Cui L: The tumor suppressor miR-124 inhibits cell
proliferation by targeting STAT3 and functions as a prognostic
marker for postoperative NSCLC patients. Int J Oncol. 46:798–808.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Paz-Ares L, de Marinis F, Dediu M, Thomas
M, Pujol JL, Bidoli P, Molinier O, Sahoo TP, Laack E, Reck M, et
al: Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed plus best supportive care
versus placebo plus best supportive care after induction therapy
with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced non-squamous
non-small-cell lung cancer (PARAMOUNT): A double-blind, phase 3,
randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:247–255. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee SH, Jung SH, Kim TM, Rhee JK, Park HC,
Kim MS, Kim SS, An CH, Lee SH and Chung YJ: Whole-exome sequencing
identified mutational profiles of high-grade colon adenomas.
Oncotarget. 8:6579–6588. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Perez-Carbonell L, Sinicrope FA, Alberts
SR, Oberg AL, Balaguer F, Castells A, Boland CR and Goel A:
MiR-320e is a novel prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Br J
Cancer. 113:83–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Franchina T, Amodeo V, Bronte G, Savio G,
Ricciardi GR, Picciotto M, Russo A, Giordano A and Adamo V:
Circulating miR-22, miR-24 and miR-34a as novel predictive
biomarkers to pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. J Cell Physiol. 229:97–99. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang F, Lou JF, Cao Y, Shi XH, Wang P, Xu
J, Xie EF, Xu T, Sun RH, Rao JY, et al: miR-638 is a new biomarker
for outcome prediction of non-small cell lung cancer patients
receiving chemotherapy. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tanaka K, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Sugimura
K, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori M and
Doki Y: Circulating miR-200c levels significantly predict response
to chemotherapy and prognosis of patients undergoing neoadjuvant
chemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 20:(Suppl 3).
S607–S615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miyamae M, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D,
Kawaguchi T, Hirajima S, Okajima W, Ohashi T, Imamura T, Konishi H,
Shiozaki A, et al: Plasma microRNA profiles: Identification of
miR-744 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in
pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 113:1467–1476. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Frères P, Josse C, Bovy N, Boukerroucha M,
Struman I, Bours V and Jerusalem G: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
breast cancer patients induces miR-34a and miR-122 expression. J
Cell Physiol. 230:473–481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|