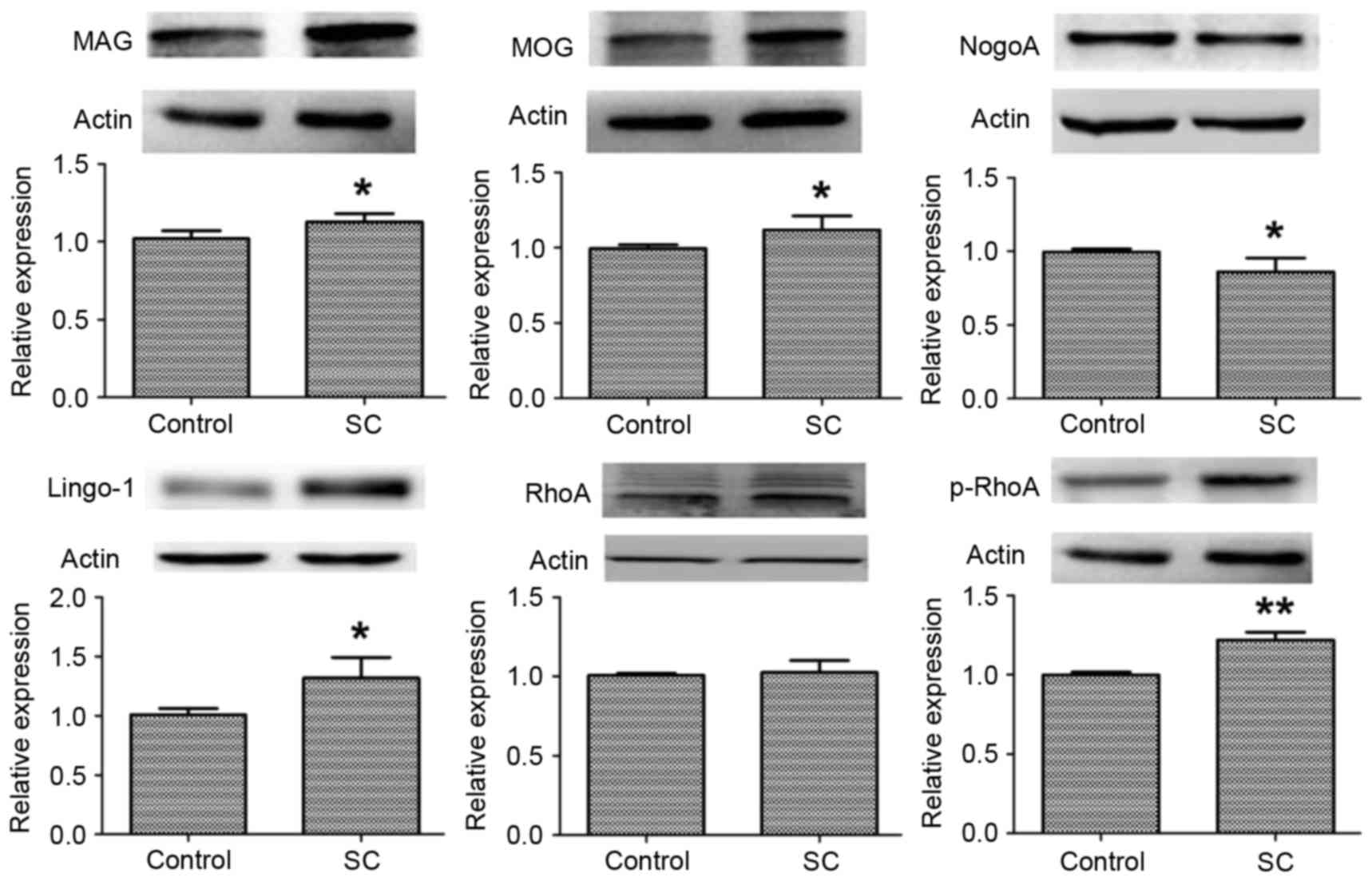
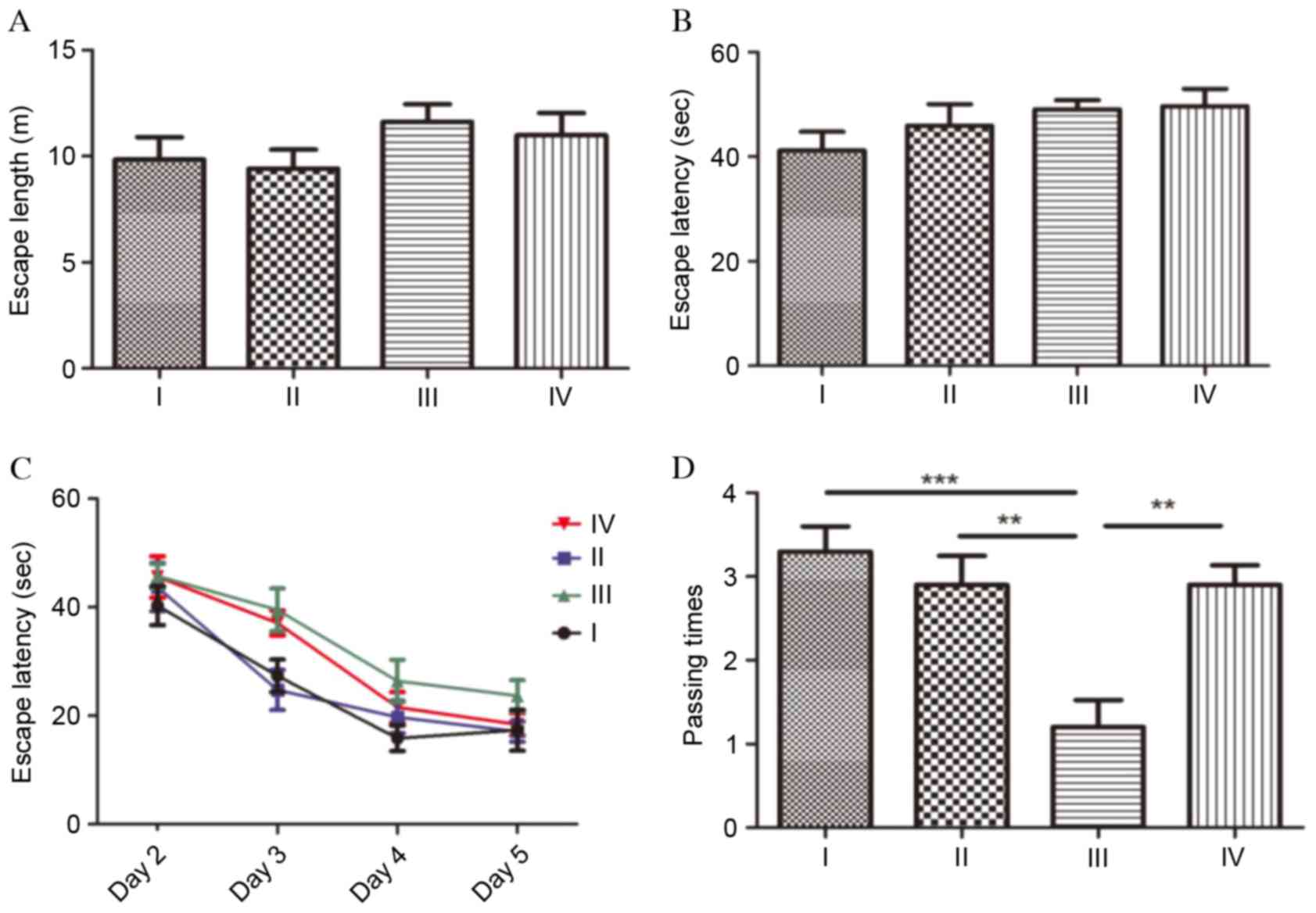
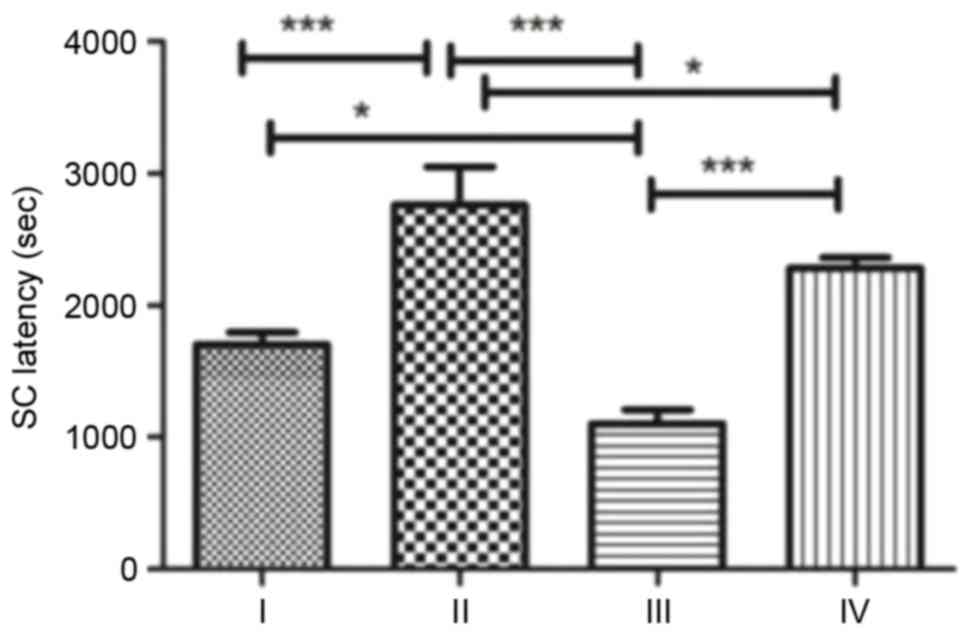
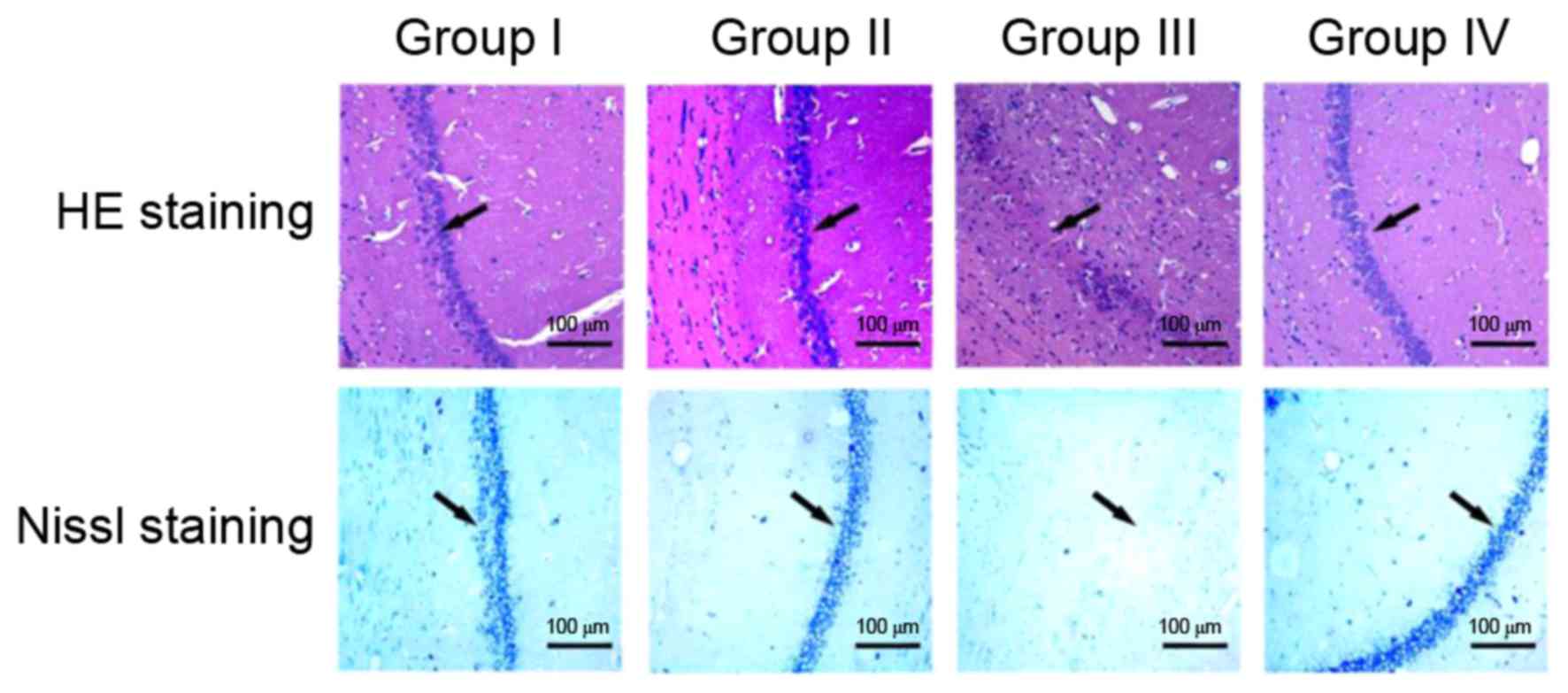
|
1
|
Sadarangani M, Seaton C, Scott JA, Ogutu
B, Edwards T, Prins A, Gatakaa H, Idro R, Berkley JA, Peshu N, et
al: Incidence and outcome of convulsive status epilepticus in
Kenyan children: A cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 7:145–150. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Appleton R, Martl T and Phillips B: Drug
management for acute tonic-clonic convulsions including convulsive
status epilepticus in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev:
CD001905. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee JK, Geoffroy CG, Chan AF, Tolentino
KE, Crawford MJ, Leal MA, Kang B and Zheng B: Assessing spinal axon
regeneration and sprouting in Nogo-, MAG-, and OMgp-deficient mice.
Neuron. 66:663–670. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mi S, Lee X, Shao Z, Thill G, Ji B, Relton
J, Levesque M, Allaire N, Perrin S, Sands B, et al: LINGO-1 is a
component of the Nogo-66 receptor/p75 signaling complex. Nat
Neurosci. 7:221–228. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo L: Actin cytoskeleton regulation in
neuronal morphogenesis and structural plasticity. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 18:601–635. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stankiewicz TR and Linseman DA: Rho family
GTPases: Key players in neuronal development, neuronal survival,
and neurodegeneration. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:3142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fujita Y and Yamashita T: Axon growth
inhibition by RhoA/ROCK in the central nervous system. Front
Neurosci. 8:3382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roloff F, Scheiblich H, Dewitz C,
Dempewolf S, Stern M and Bicker G: Enhanced neurite outgrowth of
human model (NT2) neurons by small-molecule inhibitors of Rho/ROCK
signaling. PLoS One. 10:e01185362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kitaoka Y, Kitaoka Y, Kumai T, Lam TT,
Kuribayashi K, Isenoumi K, Munemasa Y, Motoki M, Kobayashi S and
Ueno S: Involvement of RhoA and possible neuroprotective effect of
fasudil, a Rho kinase inhibitor, in NMDA-induced neurotoxicity in
the rat retina. Brain Res. 1018:111–118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishiguro M, Kawasaki K, Suzuki Y, Ishizuka
F, Mishiro K, Egashira Y, Ikegaki I, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M,
Yoshimura S, et al: A Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, fasudil,
prevents matrix metalloproteinase-9-related hemorrhagic
transformation in mice treated with tissue plasminogen activator.
Neuroscience. 220:302–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saito A, Inoue M, Kon H, Imaruoka S,
Basaki K, Midorikawa H, Sasaki T and Nishijima M: Effectiveness of
intraarterial administration of fasudil hydrochloride for
preventing symptomatic vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Acta Neurochir Suppl. 120:297–301. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iwabuchi S, Hayashi M, Yokouchi T, Sato K,
Nakayama H, Harashina J, Iwama J, Ishii M, Hiramoto Y, Hirai N, et
al: Prophylactic intra-arterial administration of fasudil
hydrochloride for vasospasm following subarachnoid haemorrhage.
Acta Neurochir Suppl. 120:167–169. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu YH, Zhao Y, Huang FZ, Chen YH, Wang
HX, Bonney E and Liu BQ: Combination of early constraint-induced
movement therapy and fasudil enhances motor recovery after ischemic
stroke in rats. Int J Neurosci. 126:168–173. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Inan S and Büyükafşar K: Antiepileptic
effects of two Rho-kinase inhibitors, Y-27632 and fasudil, in mice.
Br J Pharmacol. 155:44–51. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Davies S, Reddy H, Caivano M and Cohen P:
Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein
kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 351:95–105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen S, Luo M, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, He M, Cai
W and Liu A: Fasudil stimulates neurite outgrowth and promotes
differentiation in C17.2 neural stem cells by modulating notch
signalling but not autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:531–541.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Coque E, Raoul C and Bowerman M: ROCK
inhibition as a therapy for spinal muscular atrophy: Understanding
the repercussions on multiple cellular targets. Front Neurosci.
8:2712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th.
Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011
|
|
19
|
Lively S and Brown IR: Analysis of the
extracellular matrix protein SC1 during reactive gliosis in the rat
lithium-pilocarpine seizure model. Brain Res. 1163:1–9. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Racine RJ: Modification of seizure
activity by electrical stimulation: II. Motor seizure.
Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 32:281–294. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong Z, Bai Y, Wu X, Li H, Gong B, Howland
JG, Huang Y, He W, Li T and Wang YT: Hippocampal long-term
depression mediates spatial reversal learning in the Morris water
maze. Neuropharmacology. 64:65–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyoshi E, Wietzikoski EC, Bortolanza M,
Boschen SL, Canteras NS, Izquierdo I and Da Cunha C: Both the
dorsal hippocampus and the dorsolateral striatum are needed for rat
navigation in the Morris water maze. Behav Brain Res. 226:171–178.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
D'Agostino DP, Pilla R, Held HE, Landon
CS, Puchowicz M, Brunengraber H, Ari C, Arnold P and Dean JB:
Therapeutic ketosis with ketone ester delays central nervous system
oxygen toxicity seizures in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 304:R829–R836. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chapman CD, Frey WH II, Craft S, Danielyan
L, Hallschmid M, Schiöth HB and Benedict C: Intranasal treatment of
central nervous system dysfunction in humans. Pharm Res.
30:2475–2484. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Browning RA, Wang C, Nelson DK and Jobe
PC: Effect of precollicular transection on audiogenic seizures in
genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Exp Neurol. 155:295–301. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tamura B, Almeida D, Felizardo R, Olanda
G, Bocca L, Pinhal N, Alves-de-Moraes L, Covolan L, Cãmara N and
Longo BM: Convulsive seizure protection after hippocampal
transplantation of mesenchymal cells from adipose tissue in mice. J
Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:22014.
|
|
27
|
Scharfman HE: Epileptogenesis in the
parahippocampal region. Parallels with the dentate gyrus. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 911:305–327. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nishio Y, Koda M, Kitajo K, Seto M, Hata
K, Taniguchi J, Moriya H, Fujitani M, Kubo T and Yamashita T:
Delayed treatment with Rho-kinase in-hibior dose not enhance axonal
regeneration or functional recovery after spinal cord injury in
rats. Exp Neurol. 200:392–397. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lingor P, Teusch N, Schwarz K, Mueller R,
Mack H, Bähr M and Mueller BK: Inhibition of Rho kinase (ROCK)
increases neurite outgrowth on chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan in
vitro and axonal regeneration in the adult optic nerve in vivo. J
Neurochem. 103:181–189. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Howland JG, Cazakoff BN and Zhang Y:
Altered object-in-place recognition memory, prepulse inhibition,
and locomotor activity in the offspring of rats exposed to a viral
mimetic during pregnancy. Neuroscience. 201:184–198. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang R, Xue G, Wang S, Zhang L, Shi C and
Xie X: Novel object recognition as a facile behavior test for
evaluating drug effects in AβPP/PS1 Alzheimer's disease mouse
model. J Alzheimers Dis. 31:801–812. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vorhees CV and Williams MT: Morris water
maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of
learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 1:848–858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Khazipov R, Khalilov I, Tyzio R, Morozova
E, Ben-Ari Y and Holmes GL: Developmental changes in GABAergic
actions and seizure susceptibility in the rat hippocampus. Eur J
Neurosci. 19:590–600. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moshé SL, Albala BJ, Ackermann RF and
Engel J Jr: Increased seizure susceptibility of the immature brain.
Brain Res. 283:81–85. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|