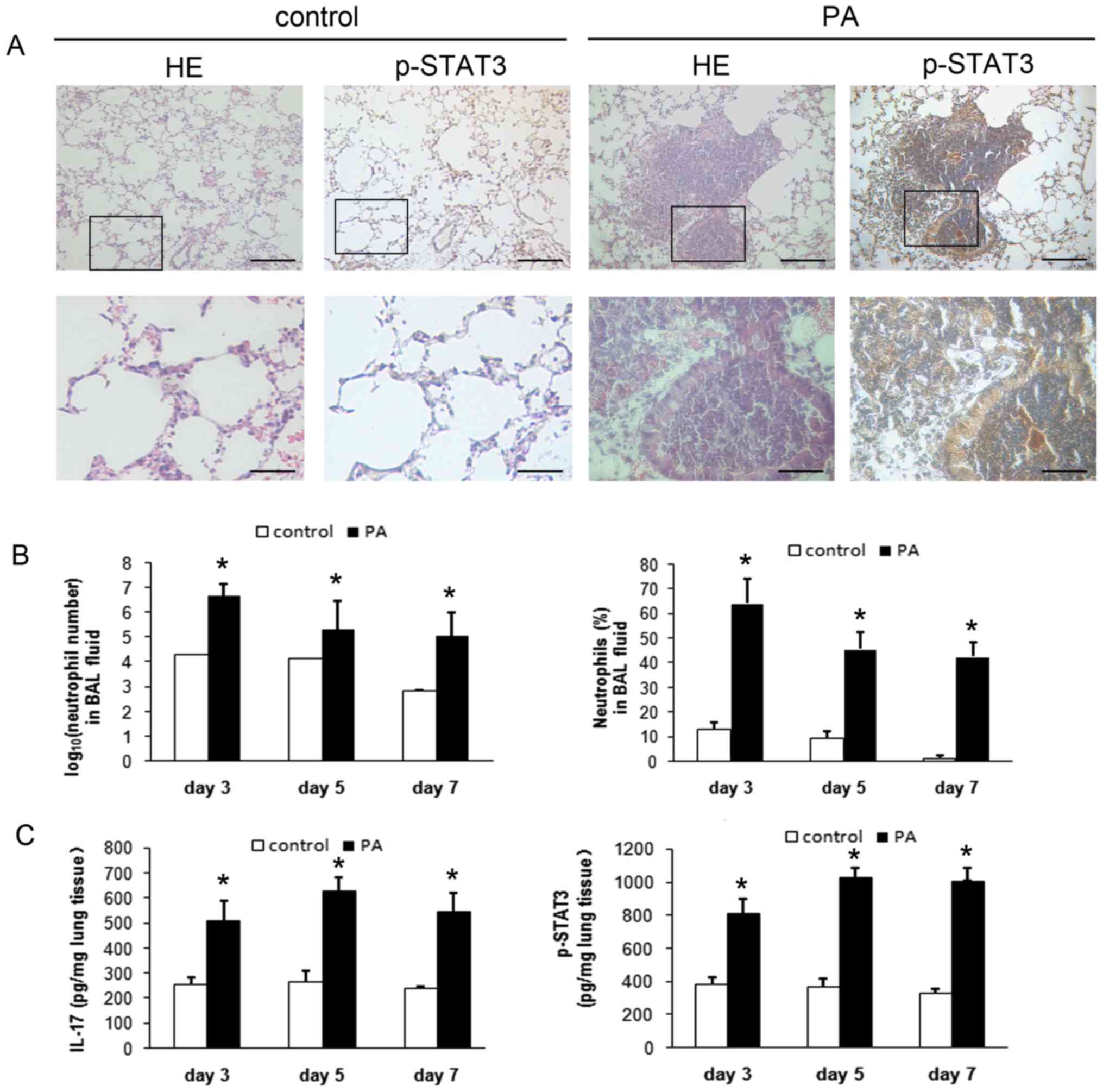
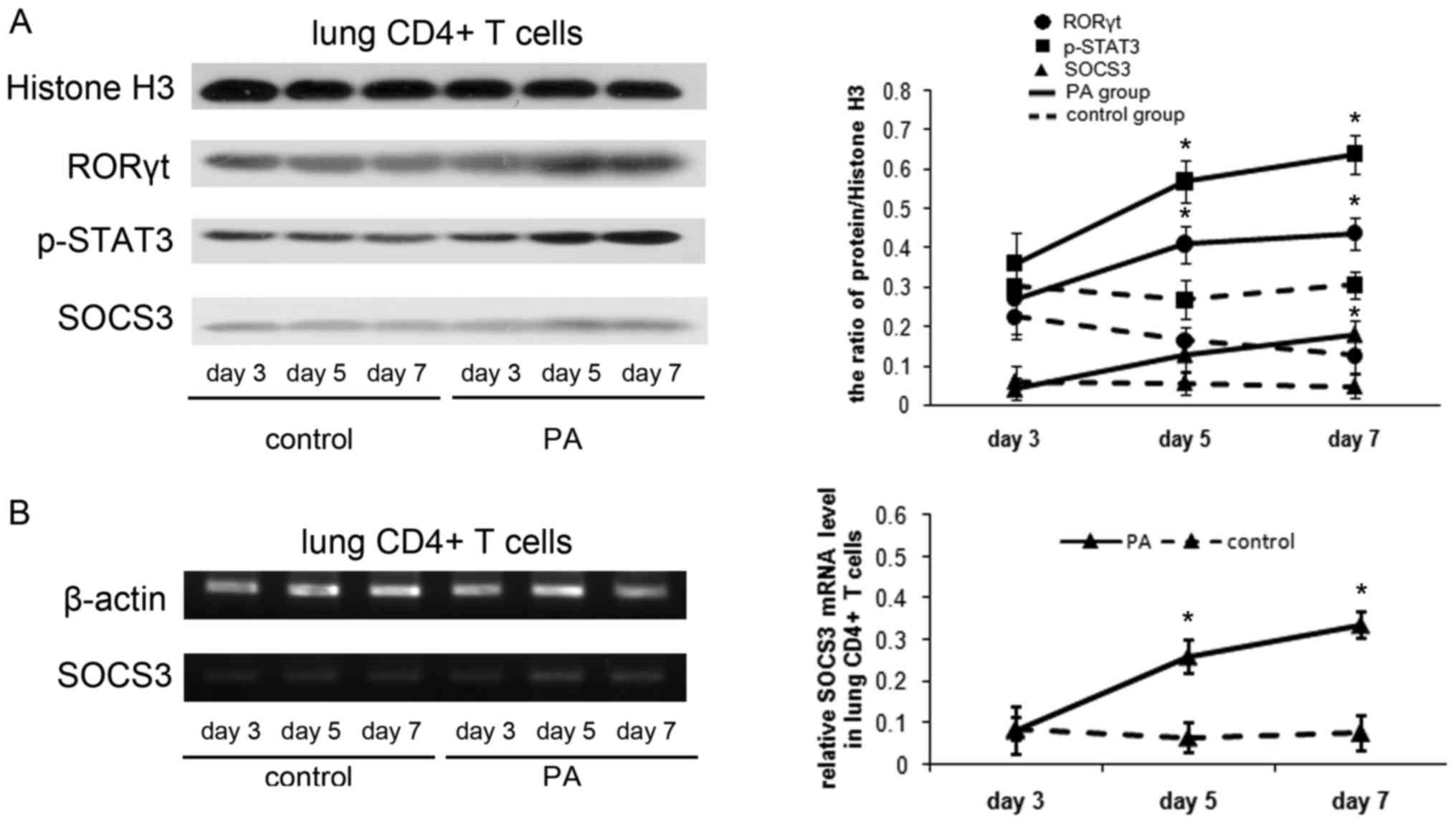
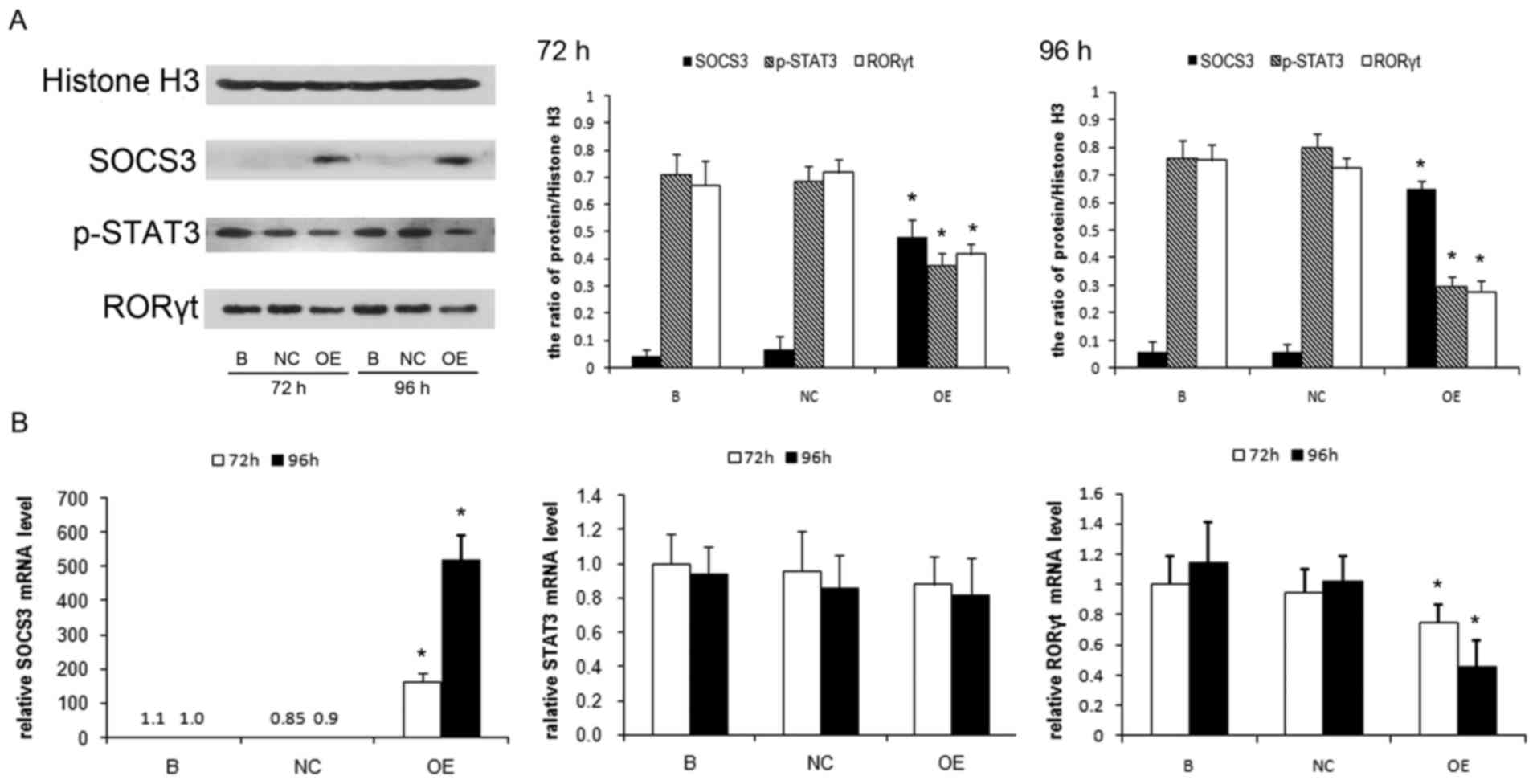
|
1
|
Rada B: Interactions between neutrophils
and pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. Pathogens. 6:pii:
E10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McAllister F, Henry A, Kreindler JL, Dubin
PJ, Ulrich L, Steele C, Finder JD, Pilewski JM, Carreno BM, Goldman
SJ, et al: Role of IL-17A, IL-17F, and the IL-17 receptor in
regulating growth-related oncogene-alpha and granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor in bronchial epithelium: Implications for
airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis. J Immunol. 175:404–412.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tiringer K, Treis A, Fucik P, Gona M,
Gruber S, Renner S, Dehlink E, Nachbaur E, Horak F, Jaksch P, et
al: A Th17- and Th2-skewed cytokine profile in cystic fibrosis
lungs represents a potential risk factor for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 187:621–629. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dubin PJ and Kolls JK: IL-23 mediates
inflammatory responses to mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung
infection in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
292:L519–L528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Egwuagu CE: STAT3 in CD4+ T helper cell
differentiation and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 47:149–156.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ivanov II, Zhou L and Littman DR:
Transcriptional regulation of Th17 cell differentiation. Semin
Immunol. 19:409–417. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harris TJ, Grosso JF, Yen HR, Xin H,
Kortylewski M, Albesiano E, Hipkiss EL, Getnet D, Goldberg MV,
Maris CH, et al: Cutting edge: An in vivo requirement for STAT3
signaling in TH17 development and TH17-dependent autoimmunity. J
Immunol. 179:4313–4317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan K, Huang C, Fox J, Gaid M, Weaver A,
Li G, Singh BB, Gao H and Wu M: Elevated inflammatory response in
caveolin-1-deficient mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection is
mediated by STAT3 protein and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB). J
Biol Chem. 286:21814–21825. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoshimura A, Naka T and Kubo M: SOCS
proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat Rev
Immunol. 7:454–465. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Z, Laurence A, Kanno Y,
Pacher-Zavisin M, Zhu BM, Tato C, Yoshimura A, Hennighausen L and
O'Shea JJ: Selective regulatory function of Socs3 in the formation
of IL-17-secreting T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:8137–8142.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baker BJ, Akhtar LN and Benveniste EN:
SOCS1 and SOCS3 in the control of CNS immunity. Trends Immunol.
30:392–400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruwanpura SM, McLeod L, Brooks GD,
Bozinovski S, Vlahos R, Longano A, Bardin PG, Anderson GP and
Jenkins BJ: IL-6/Stat3-driven pulmonary inflammation, but not
emphysema, is dependent on interleukin-17A in mice. Respirology.
19:419–427. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cacalano NA, Sanden D and Johnston JA:
Tyrosine- phosphorylated SOCS-3 inhibits STAT activation but binds
to p120 RasGAP and activates Ras. Nat Cell Biol. 3:460–465. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sasaki A, Yasukawa H, Suzuki A, Kamizono
S, Syoda T, Kinjyo I, Sasaki M, Johnston JA and Yoshimura A:
Cytokine-inducible SH2 protein-3 (CIS3/SOCS3) inhibits Janus
tyrosine kinase by binding through the N-terminal kinase inhibitory
region as well as SH2 domain. Genes Cells. 4:339–351. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki A, Hanada T, Mitsuyama K, Yoshida
T, Kamizono S, Hoshino T, Kubo M, Yamashita A, Okabe M, Takeda K,
et al: CIS3/SOCS3/SSI3 plays a negative regulatory role in STAT3
activation and intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 193:471–481.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shouda T, Yoshida T, Hanada T, Wakioka T,
Oishi M, Miyoshi K, Komiya S, Kosai K, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, et
al: Induction of the cytokine signal regulator SOCS3/CIS3 as a
therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory arthritis. J Clin
Invest. 108:1781–1788. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang XO, Panopoulos AD, Nurieva R, Chang
SH, Wang D, Watowich SS and Dong C: STAT3 regulates
cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J Biol
Chem. 282:9358–9363. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou L, Ivanov I, Spolski R, Min R,
Shenderov K, Egawa T, Levy DE, Leonard WJ and Littman DR: IL-6
programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential
engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat Immunol. 8:967–974.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aggarwal S, Ghilardi N, Xie MH, de Sauvage
FJ and Gurney AL: Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell
activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17.
J Biol Chem. 278:1910–1914. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM,
Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA and
Cua DJ: IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces
autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 201:233–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ,
Locksley RM and Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an
inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of
IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 24:179–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Floss DM, Mrotzek S, Klöcker T, Schröder
J, Grötzinger J, Rose-John S and Scheller J: Identification of
canonical tyrosine-dependent and non-canonical tyrosine-independent
STAT3 activation sites in the intracellular domain of the
interleukin 23 receptor. J Biol Chem. 288:19386–19400. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dubin PJ and Kolls JK: IL-23 mediates
inflammatory responses to mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung
infection in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
292:L519–L528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Keijsers RR, Joosten I, van Erp PE, Koenen
HJ and van de Kerkhof PC: Cellular sources of IL-17 in psoriasis: A
paradigm shift? Exp Dermatol. 23:799–803. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bayes HK, Bicknell S, MacGregor G and
Evans TJ: T helper cell subsets specific for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
in healthy individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis. PLoS One.
9:e902632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chan YR, Chen K, Duncan SR, Lathrop KL,
Latoche JD, Logar AJ, Pociask DA, Wahlberg BJ, Ray P, Ray A, et al:
Patients with cystic fibrosis have inducible IL-17+IL-22+ memory
cells in lung draining lymph nodes. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
131:1117–1129, e1-e5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|