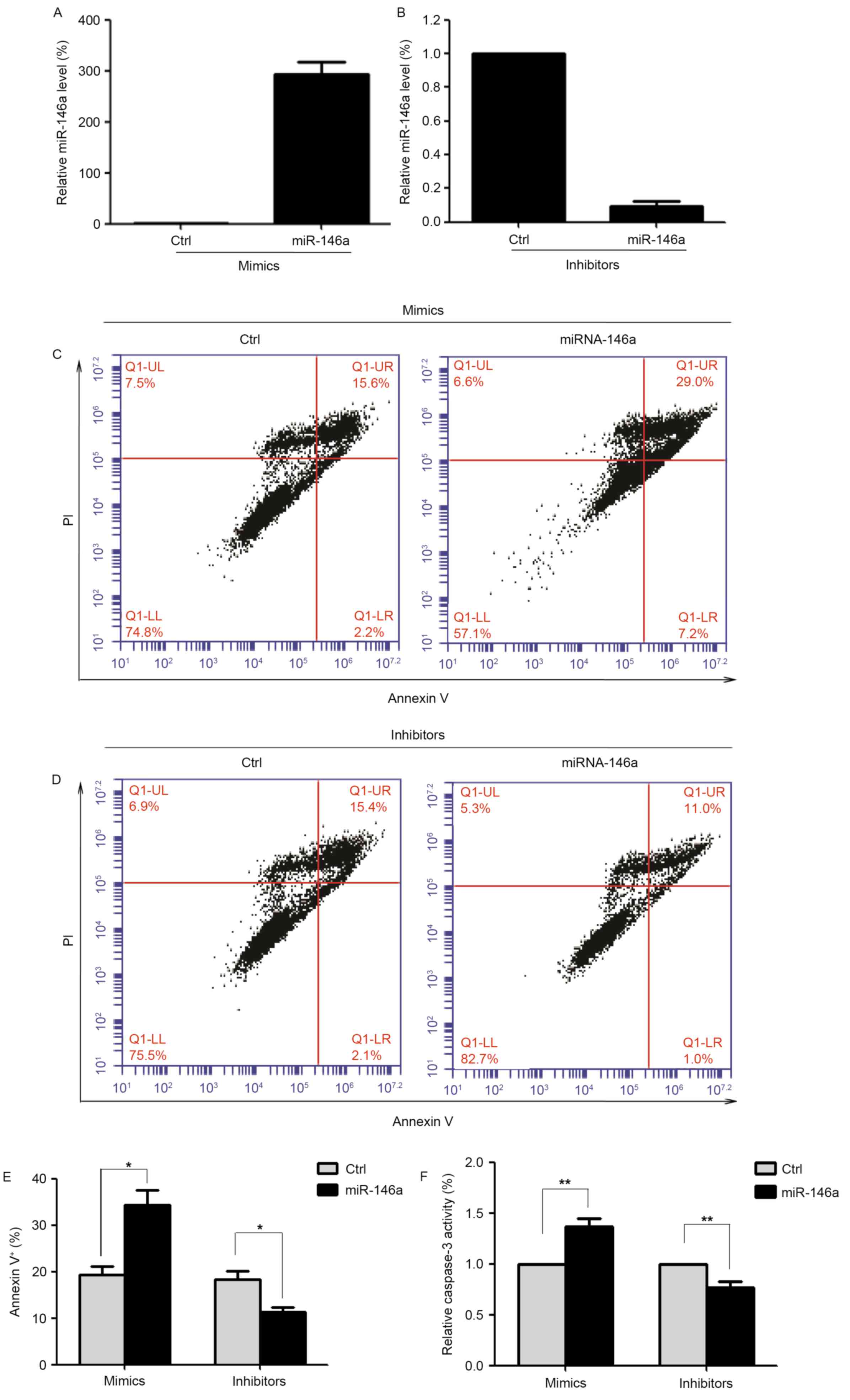
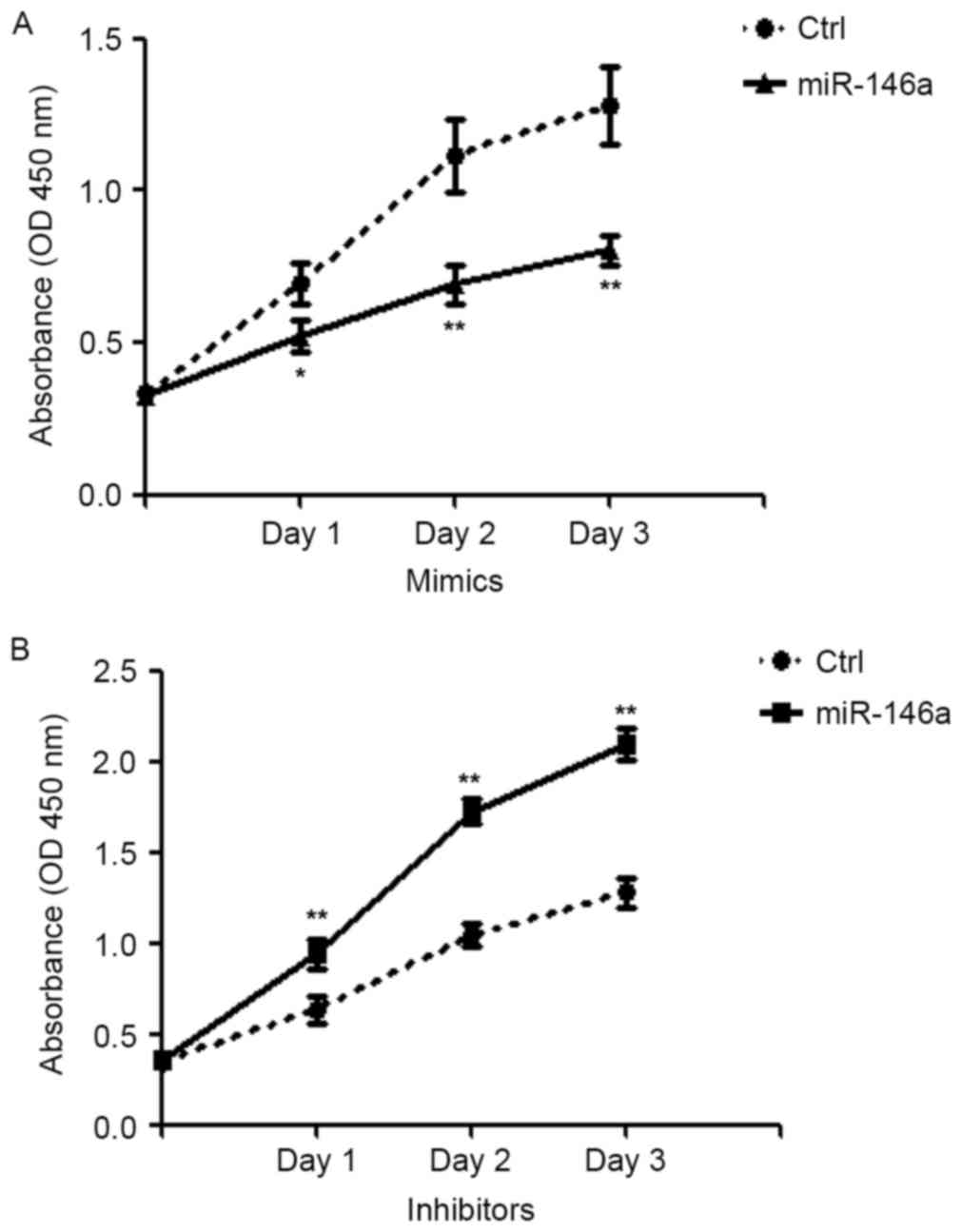
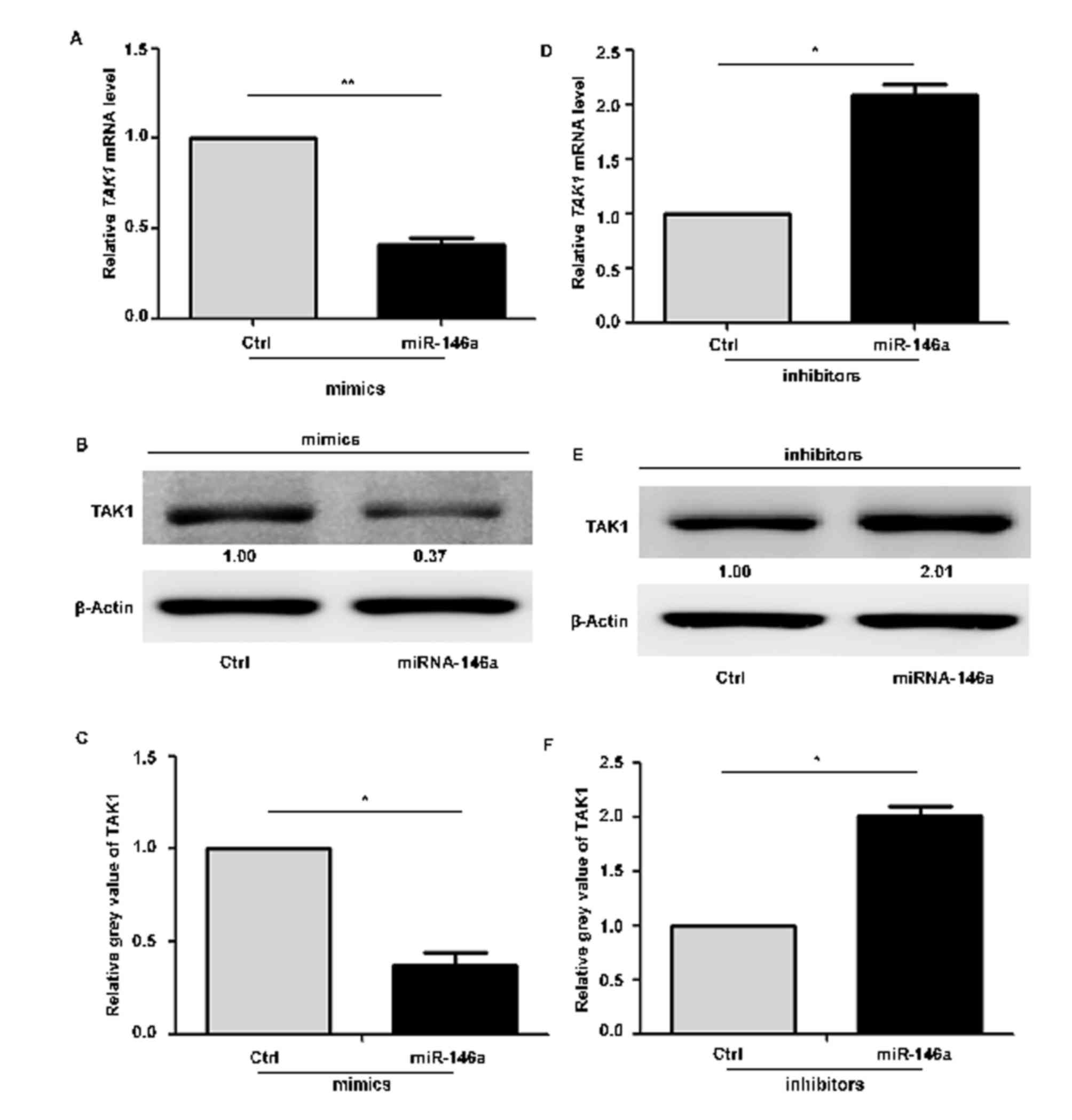
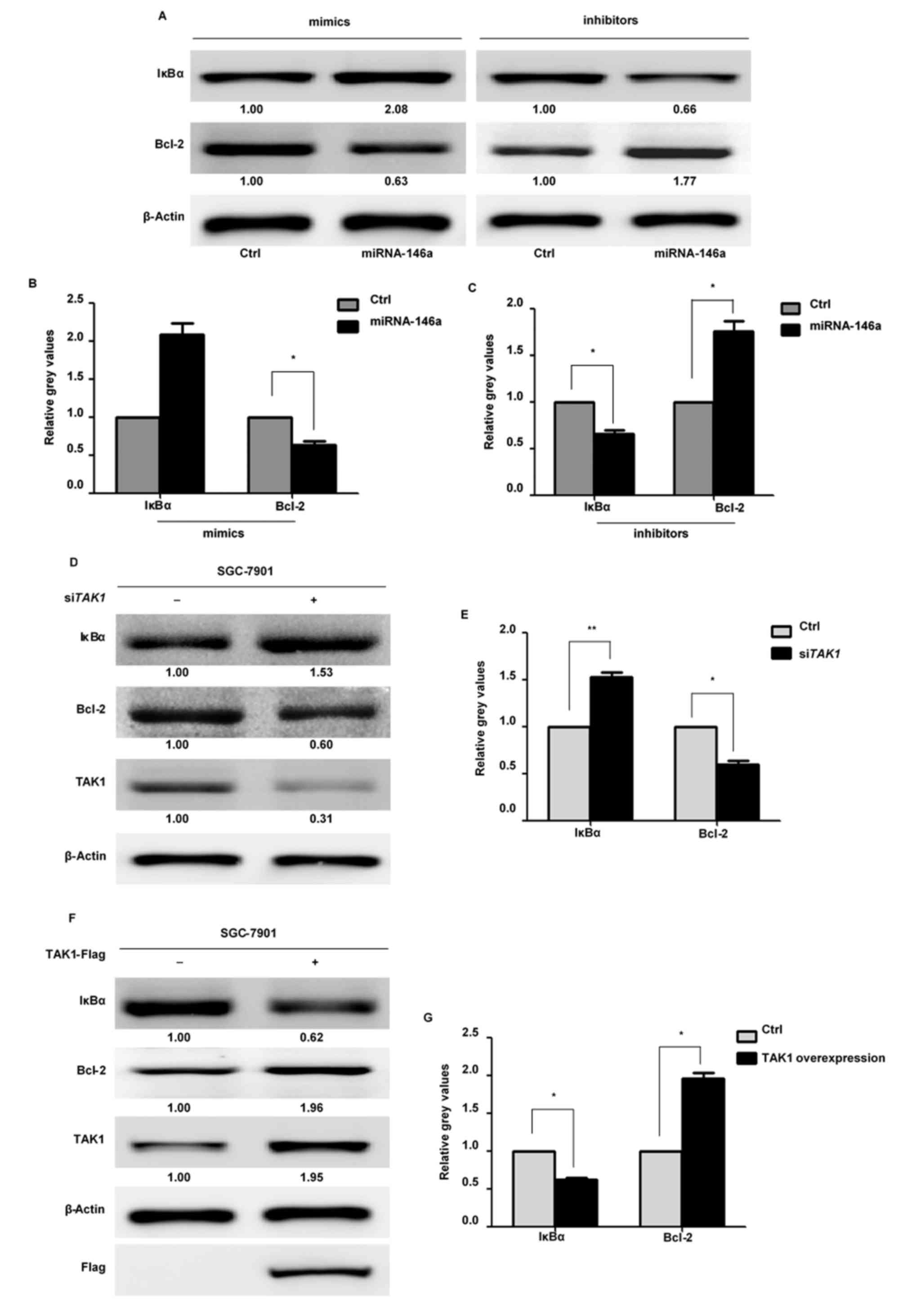
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H,
Zou X and He J: Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010.
Chin J Cancer Res. 26:48–58. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schickel R, Park SM, Murmann AE and Peter
ME: miR-200c regulates induction of apoptosis through CD95 by
targeting FAP-1. Mol Cell. 38:908–915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yanaka Y, Muramatsu T, Uetake H, Kozaki K
and Inazawa J: miR-544a induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through the activation of WNT signaling pathway in gastric cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 36:1363–1371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu X, Ge X, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Chang J, Wu
Z, Tang W, Gan L, Sun M and Li J: MicroRNA-940 promotes tumor cell
invasion and metastasis by downregulating ZNF24 in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:25418–25428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao Q, Cao Z, Tu C, Zhao Y, Liu H and
Zhang S: MicroRNA-146a acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric
cancer by targeting WASF2. Cancer Lett. 335:219–224. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park H, Huang X, Lu C, Cairo MS and Zhou
X: MicroRNA-146a and microRNA-146b regulate human dendritic cell
apoptosis and cytokine production by targeting TRAF6 and IRAK1
proteins. J Biol Chem. 290:2831–2841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hou Z, Yin H, Chen C, Dai X, Li X, Liu B
and Fang X: microRNA-146a targets the L1 cell adhesion molecule and
suppresses the metastatic potential of gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep.
6:501–506. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garcia AI, Buisson M, Bertrand P, Rimokh
R, Rouleau E, Lopez BS, Lidereau R, Mikaélian I and Mazoyer S:
Down-regulation of BRCA1 expression by miR-146a and miR-146b-5p in
triple negative sporadic breast cancers. EMBO Mol Med. 3:279–290.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu R, Liu C, Chen D, Yang WH, Liu X, Liu
CG, Dugas CM, Tang F, Zheng P, Liu Y and Wang L: FOXP3 controls an
miR-146/NF-κB negative feedback loop that inhibits apoptosis in
breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 75:1703–1713. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stuckrath I, Rack B, Janni W, Jäger B,
Pantel K and Schwarzenbach H: Aberrant plasma levels of circulating
miR-16, miR-107, miR-130a and miR-146a are associated with lymph
node metastasis and receptor status of breast cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 6:13387–13401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS,
Meyers C and Zheng ZM: Aberrant expression of oncogenic and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for
cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pacifico F, Crescenzi E, Mellone S,
Iannetti A, Porrino N, Liguoro D, Moscato F, Grieco M, Formisano S
and Leonardi A: Nuclear factor-{kappa}B contributes to anaplastic
thyroid carcinomas through up-regulation of miR-146a. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 95:1421–1430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kogo R, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Komune S and
Mori M: Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:4277–4284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Perkins ND: Integrating cell-signalling
pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:49–62. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Espinosa L, Margalef P and Bigas A:
Non-conventional functions for NF-kappaB members: The dark side of
NF-κB. Oncogene. 34:2279–2287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh A, Sweeney MF, Yu M, Burger A,
Greninger P, Benes C, Haber DA and Settleman J: TAK1 inhibition
promotes apoptosis in KRAS-dependent colon cancers. Cell.
148:639–650. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mihaly SR, Ninomiya-Tsuji J and Morioka S:
TAK1 control of cell death. Cell Death Differ. 21:1667–1676. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Zhao L, Shi B, Ma S, Xu Z, Ge Y, Liu
Y, Zheng D and Shi J: Functions of miR-146a and miR-222 in
Tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer. Sci Rep.
5:186482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun Q, Zhao X, Liu X, Wang Y, Huang J,
Jiang B, Chen Q and Yu J: miR-146a functions as a tumor suppressor
in prostate cancer by targeting Rac1. Prostate. 74:1613–1621. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hou Z, Xie L, Yu L, Qian X and Liu B:
MicroRNA-146a is down-regulated in gastric cancer and regulates
cell proliferation and apoptosis. Med Oncol. 29:886–892. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Crone SG, Jacobsen A, Federspiel B,
Bardram L, Krogh A, Lund AH and Friis-Hansen L: microRNA-146a
inhibits G protein-coupled receptor-mediated activation of NF-κB by
targeting CARD10 and COPS8 in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer.
11:712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Avci CB, Harman E, Dodurga Y, Susluer SY
and Gunduz C: Therapeutic potential of an anti-diabetic drug,
metformin: Alteration of miRNA expression in prostate cancer cells.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:765–768. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ma H, Gao L, Li S, Qin J, Chen L, Liu X,
Xu P, Wang F, Xiao H, Zhou S, et al: CCR7 enhances TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is associated with lymph node
metastasis and poor overall survival in gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
6:24348–24360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS and Ghosh S:
Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol. 12:695–708.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen G, Umelo IA, Lv S, Teugels E, Fostier
K, Kronenberger P, Dewaele A, Sadones J, Geers C and De Greve J:
miR-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e603172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hou DX, Luo D, Tanigawa S, Hashimoto F,
Uto T, Masuzaki S, Fujii M and Sakata Y: Prodelphinidin B-4
3′-O-gallate, a tea polyphenol, is involved in the inhibition of
COX-2 and iNOS via the downregulation of TAK1-NF-kappaB pathway.
Biochem Pharmacol. 74:742–751. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|