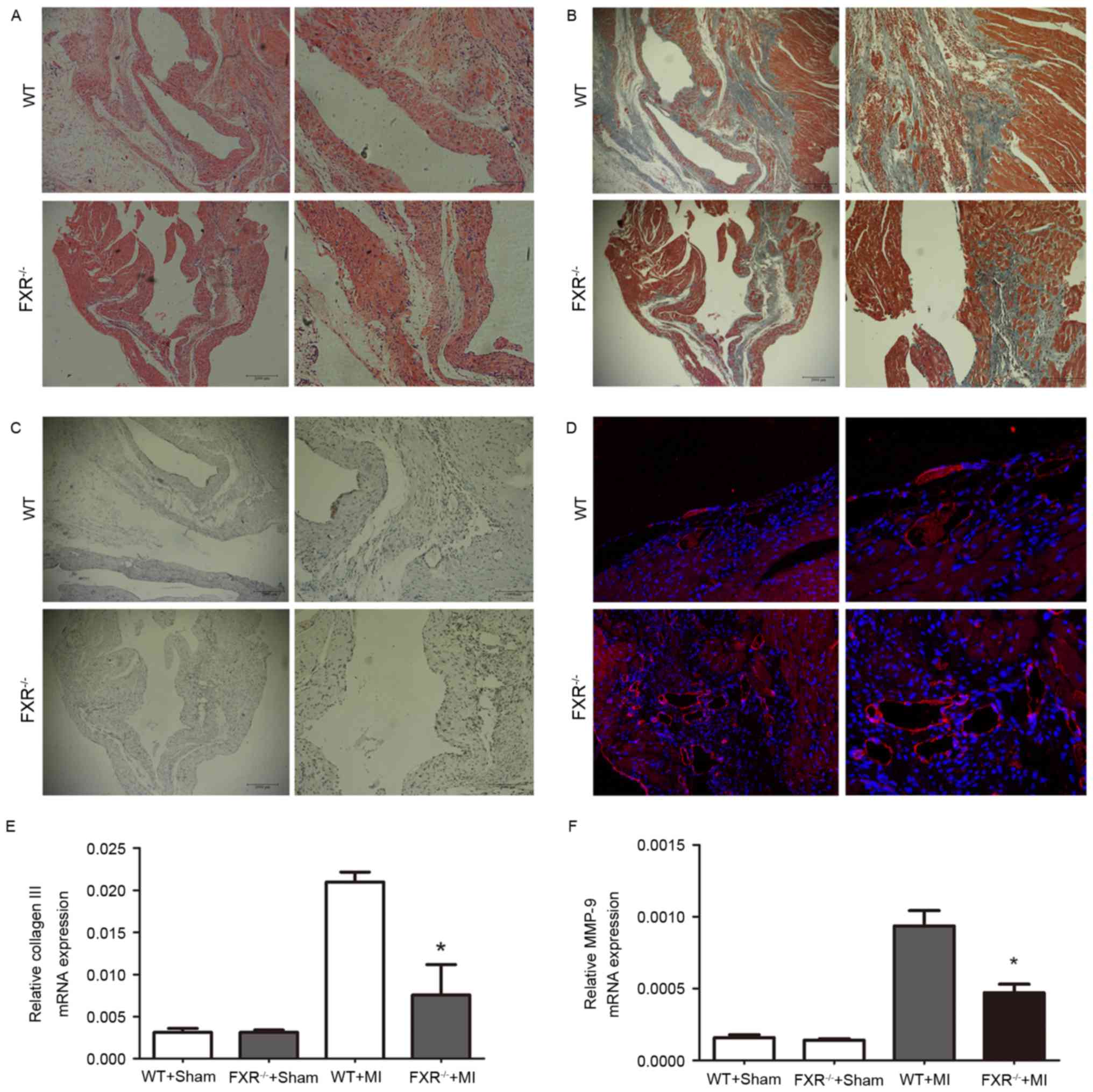
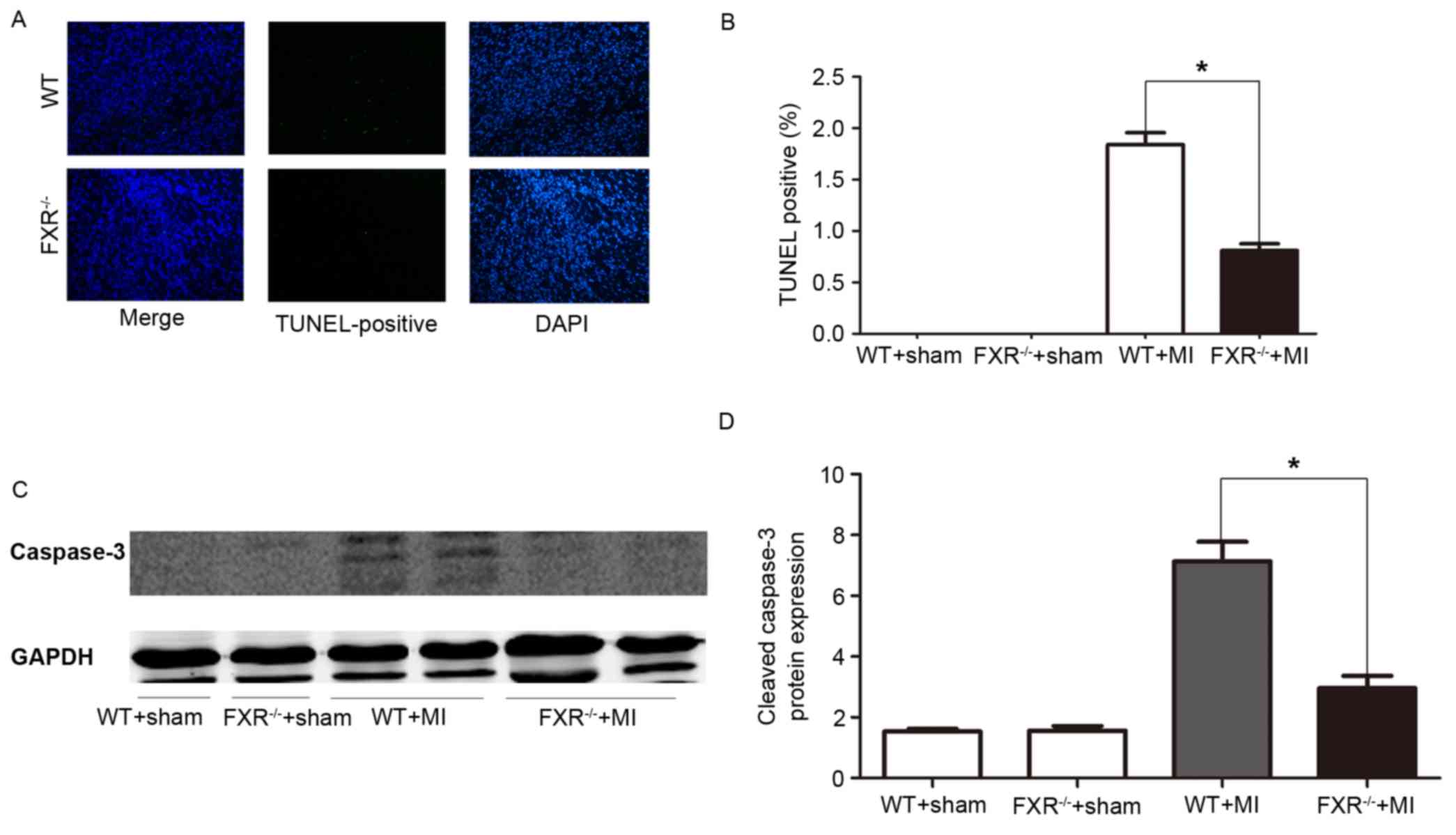
|
1
|
Ma Y, Halade GV, Zhang J, Ramirez TA,
Levin D, Voorhees A, Jin YF, Han HC, Manicone AM and Lindsey ML:
Matrix metalloproteinase-28 deletion exacerbates cardiac
dysfunction and rupture after myocardial infarction in mice by
inhibiting M2 macrophage activation. Circ Res. 112:675–688. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2014 update: A report from the
American Heart Association. Circulation. 129:e28–e292. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krishnamurthy P, Thal M, Verma S, Hoxha E,
Lambers E, Ramirez V, Qin G, Losordo D and Kishore R:
Interleukin-10 deficiency impairs bone marrow-derived endothelial
progenitor cell survival and function in ischemic myocardium. Circ
Res. 109:1280–1289. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu S, Yin R, Ernest R, Li Y, Zhelyabovska
O, Luo J, Yang Y and Yang Q: Liver X receptors are negative
regulators of cardiac hypertrophy via suppressing NF-kappaB
signalling. Cardiovasc Res. 84:119–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kuipers I, Li J, Vreeswijk-Baudoin I,
Koster J, van der Harst P, Silljé HH, Kuipers F, van Veldhuisen DJ,
van Gilst WH and de Boer RA: Activation of liver X receptors with
T0901317 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy in vivo. Eur J Heart Fail.
12:1042–1050. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He Q, Pu J, Yuan A, Lau WB, Gao E, Koch
WJ, Ma XL and He B: Activation of liver-X-receptor α but not
liver-X-receptor β protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Circ Heart Fail. 7:1032–1041. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lei P, Baysa A, Nebb HI, Valen G, Skomedal
T, Osnes JB, Yang Z and Haugen F: Activation of Liver X receptors
in the heart leads to accumulation of intracellular lipids and
attenuation of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol.
108:3232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Son NH, Yu S, Tuinei J, Arai K, Hamai H,
Homma S, Shulman GI, Abel ED and Goldberg IJ: PPARγ-induced
cardiolipotoxicity in mice is ameliorated by PPARα deficiency
despite increases in fatty acid oxidation. J Clin Invest.
120:3443–3454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, Tu H,
Learned RM, Luk A, Hull MV, Lustig KD, Mangelsdorf DJ and Shan B:
Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science.
284:1362–1365. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Swales KE, Korbonits M, Carpenter R, Walsh
DT, Warner TD and Bishop-Bailey D: The farnesoid X receptor is
expressed in breast cancer and regulates apoptosis and aromatase
expression. Cancer Res. 66:10120–10126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK,
Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA, Stimmel JB, Willson TM, Zavacki
AM, Moore DD and Lehmann JM: Bile Acids: Natural ligands for an
orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 284:1365–1368. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Forman BM, Goode E, Chen J, Oro AE,
Bradley DJ, Perlmann T, Noonan DJ, Burka LT, McMorris T, Lamph WW,
et al: Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by
farnesol metabolites. Cell. 81:687–693. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pu J, Yuan A, Shan P, Gao E, Wang X, Wang
Y, Lau WB, Koch W, Ma XL and He B: Cardiomyocyte-expressed
farnesoid-X-receptor is a novel apoptosis mediator and contributes
to myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Eur Heart J.
34:1834–1845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hageman J, Herrema H, Groen AK and Kuipers
F: A role of the bile salt receptor FXR in atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:1519–1528. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bishop-Bailey D, Walsh DT and Warner TD:
Expression and activation of the farnesoid X receptor in the
vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:3668–3673. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ye L, Jiang Y and Zuo X:
Farnesoid-X-receptor expression in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary
arterial hypertension and right heart failure. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 467:164–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao E, Lei YH, Shang X, Huang ZM, Zuo L,
Boucher M, Fan Q, Chuprun JK, Ma XL and Koch WJ: A novel and
efficient model of coronary artery ligation and myocardial
infarction in the mouse. Circ Res. 107:1445–1453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu X, Gao J, Xia Q, Lu T and Wang F:
Increased mortality and aggravation of heart failure in liver X
receptor-α knockout mice after myocardial infarction. Heart
Vessels. 31:1370–1379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pfeffer MA, Pfeffer JM, Fishbein MC,
Fletcher PJ, Spadaro J, Kloner RA and Braunwald E: Myocardial
infarct size and ventricular function in rats. Circ Res.
44:503–512. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang M, Zhong M, Shang Y, Lin H, Deng J,
Jiang H, Lu H, Zhang Y and Zhang W: Differential regulation of
collagen types I and III expression in cardiac fibroblasts by AGEs
through TRB3/MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci.
65:2924–2932. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Woo YJ, Panlilio CM, Cheng RK, Liao GP,
Atluri P, Hsu VM, Cohen JE and Chaudhry HW: Therapeutic delivery of
cyclin A2 induces myocardial regeneration and enhances cardiac
function in ischemic heart failure. Circulation. 114:(1 Suppl).
I206–I213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He K, Chen X, Han C, Xu L, Zhang J, Zhang
M and Xia Q: Lipopolysaccharide-induced cross-tolerance against
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury is mediated by hypoxia-inducible
factor-2α-regulated nitric oxide production. Kidney Int.
85:276–288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cohn JN, Ferrari R and Sharpe N: Cardiac
remodeling-concepts and clinical implications: A consensus paper
from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an
International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol.
35:569–582. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ding L, Dong L, Chen X, Zhang L, Xu X,
Ferro A and Xu B: Increased expression of integrin-linked kinase
attenuates left ventricular remodeling and improves cardiac
function after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 120:764–773.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Q, Xie J, Li R, Shi J, Sun J, Gu R,
Ding L, Wang L and Xu B: Overexpression of microRNA-99a attenuates
heart remodelling and improves cardiac performance after myocardial
infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 18:919–928. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bowers SL, Banerjee I and Baudino TA: The
extracellular matrix: At the center of it all. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
48:474–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chiao YA, Ramirez TA, Zamilpa R, Okoronkwo
SM, Dai Q, Zhang J, Jin YF and Lindsey ML: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 deletion attenuates myocardial fibrosis and
diastolic dysfunction in ageing mice. Cardiovasc Res. 96:444–455.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abbate A, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Bussani R,
Dobrina A, Camilot D, Feroce F, Rossiello R, Baldi F, Silvestri F,
Biasucci LM and Baldi A: Increased myocardial apoptosis in patients
with unfavorable left ventricular remodeling and early symptomatic
post-infarction heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 41:753–760. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Souders CA, Bowers SL and Baudino TA:
Cardiac fibroblast: The renaissance cell. Circ Res. 105:1164–1176.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jourdan-Lesaux C, Zhang J and Lindsey ML:
Extracellular matrix roles during cardiac repair. Life Sci.
87:391–400. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|