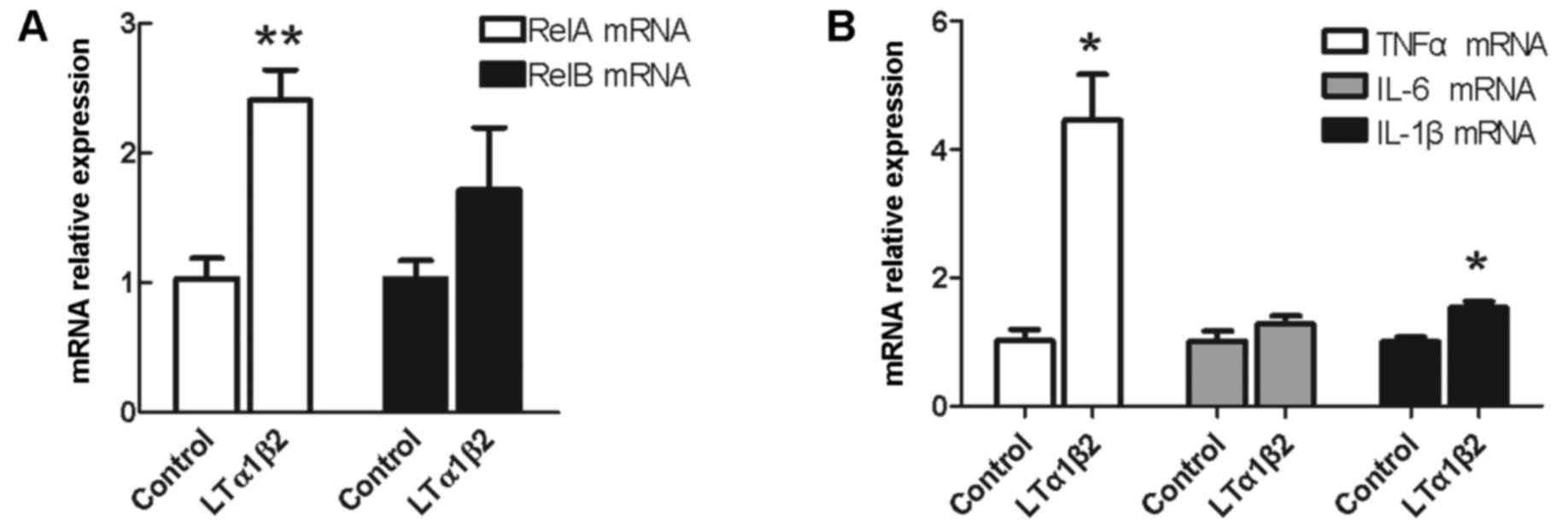
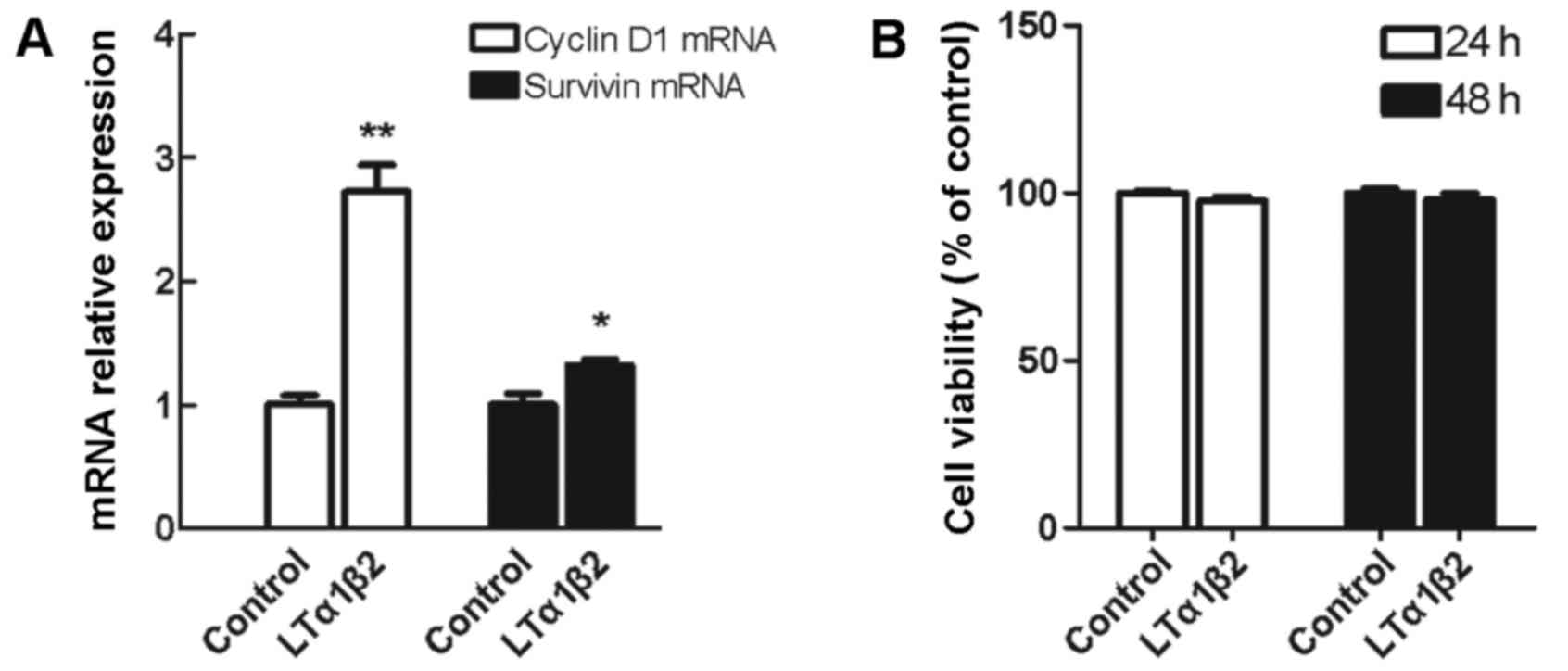
|
1
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Candido J and Hagemann T: Cancer-related
inflammation. J Clin Immunol. 33:(Suppl 1). 79–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Silverman DT, Hartge P, Morrison AS and
Devesa SS: Epidemiology of bladder cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North
Am. 6:1–30. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devesa SS, Grauman DJ, Blot WJ and
Fraumeni JF Jr: Cancer surveillance series: Changing geographic
patterns of lung cancer mortality in the United States, 1950
through 1994. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:1040–1050. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Michaud DS: Chronic inflammation and
bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 25:260–268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Medzhitov R: Origin and physiological
roles of inflammation. Nature. 454:428–435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen M, Zhou LL, Zhou P and Lin XY:
Expression and clinical pathologic significance of CD4~+,CD8~+ and
CD20~+ lymphocytes in tissue of bladder cancer. Chinese J Health
Lab Technol. 25:1112–1114. 2015.
|
|
8
|
Wolf MJ, Seleznik GM, Zeller N and
Heikenwalder M: The unexpected role of lymphotoxin beta receptor
signaling in carcinogenesis: From lymphoid tissue formation to
liver and prostate cancer development. Oncogene. 29:5006–5018.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lukashev M, LePage D, Wilson C, Bailly V,
Garber E, Lukashin A, Ngam-ek A, Zeng W, Allaire N, Perrin S, et
al: Targeting the lymphotoxin-beta receptor with agonist antibodies
as a potential cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 66:9617–9624. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen M, Duan X, Zhou P, Zhou W, Wu X, Xu
S, Chen Y and Tao Z: Lymphotoxin β receptor activation promotes
bladder cancer in a nuclear factor-κB-dependent manner. Mol Med
Rep. 11:783–790. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Norris PS and Ware CF: The LT beta R
signaling pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 597:160–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Greten FR and Karin M: The IKK/NF-kappaB
activation pathway-a target for prevention and treatment of cancer.
Cancer Lett. 206:193–199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Haybaeck J, Zeller N, Wolf MJ, Weber A,
Wagner U, Kurrer MO, Bremer J, Iezzi G, Graf R, Clavien PA, et al:
A lymphotoxin-driven pathway to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Cell. 16:295–308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu X, Zimmerman MA, Bardhan K, Yang D,
Waller JL, Liles GB, Lee JR, Pollock R, Lev D, Ware CF, et al:
Lymphotoxin β receptor mediates caspase-dependent tumor cell
apoptosis in vitro and tumor suppression in vivo despite induction
of NF-κB activation. Carcinogenesis. 34:1105–1114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang D, Din UDN, Browning DD, Abrams SI
and Liu K: Targeting lymphotoxin beta receptor with tumor-specific
T lymphocytes for tumor regression. Clin Cancer Res. 13:5202–5210.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Winter H, Van Den Engel NK, Poehlein CH,
Hatz RA, Fox BA and Hu HM: Tumor-specific T cells signal tumor
destruction via the lymphotoxin beta receptor. J Transl Med.
5:142007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Naugler WE and Karin M: NF-kappaB and
cancer-identifying targets and mechanisms. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
18:19–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ammirante M, Luo JL, Grivennikov S,
Nedospasov S and Karin M: B-cell-derived lymphotoxin promotes
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature. 464:302–305. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dejardin E, Droin NM, Delhase M, Haas E,
Cao Y, Makris C, Li ZW, Karin M, Ware CF and Green DR: The
lymphotoxin-beta receptor induces different patterns of gene
expression via two NF-kappaB pathways. Immunity. 17:525–535. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eiró N and Vizoso FJ: Inflammation and
cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg. 4:62–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu S, Rhee KJ, Albesiano E, Rabizadeh S,
Wu X, Yen HR, Huso DL, Brancati FL, Wick E, McAllister F, et al: A
human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation
of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat Med. 15:1016–1022. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Waldner MJ and Neurath MF:
Colitis-associated cancer: The role of T cells in tumor
development. Semin Immunopathol. 31:249–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C
and Mantovani A: Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark
of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis.
30:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vendramini-Costa DB and Carvalho JE:
Molecular link mechanisms between inflammation and cancer. Curr
Pharm Des. 18:3831–3852. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Maeda S and Omata M: Inflammation and
cancer: Role of nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Cancer Sci.
99:836–842. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Blonska M, You Y, Geleziunas R and Lin X:
Restoration of NF-kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor alpha
receptor complex-targeted MEKK3 in receptor-interacting
protein-deficient cells. Mol Cell Biol. 24:10757–10765. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Popivanova BK, Kitamura K, Wu Y, Kondo T,
Kagaya T, Kaneko S, Oshima M, Fujii C and Mukaida N: Blocking
TNF-alpha in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with
chronic colitis. J Clin Invest. 118:560–570. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tu S, Bhagat G, Cui G, Takaishi S,
Kurt-Jones EA, Rickman B, Betz KS, Penz-Oesterreicher M, Bjorkdahl
O, Fox JG and Wang TC: Overexpression of interleukin-1beta induces
gastric inflammation and cancer and mobilizes myeloid-derived
suppressor cells in mice. Cancer Cell. 14:408–419. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hehlgans T, Stoelcker B, Stopfer P, Müller
P, Cernaianu G, Guba M, Steinbauer M, Nedospasov SA, Pfeffer K and
Männel DN: Lymphotoxin-beta receptor immune interaction promotes
tumor growth by inducing angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 62:4034–4040.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|