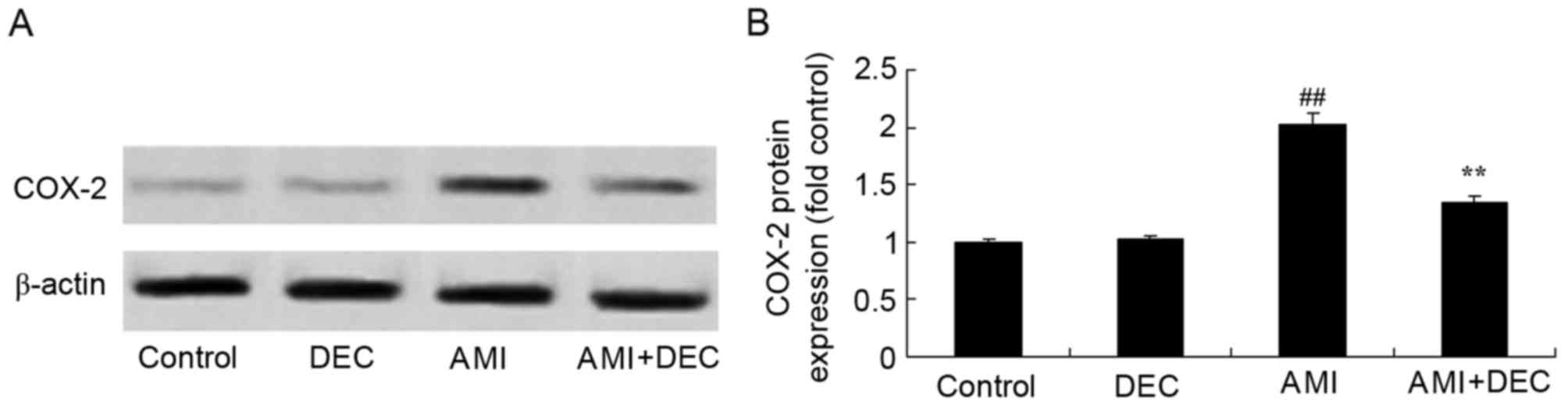
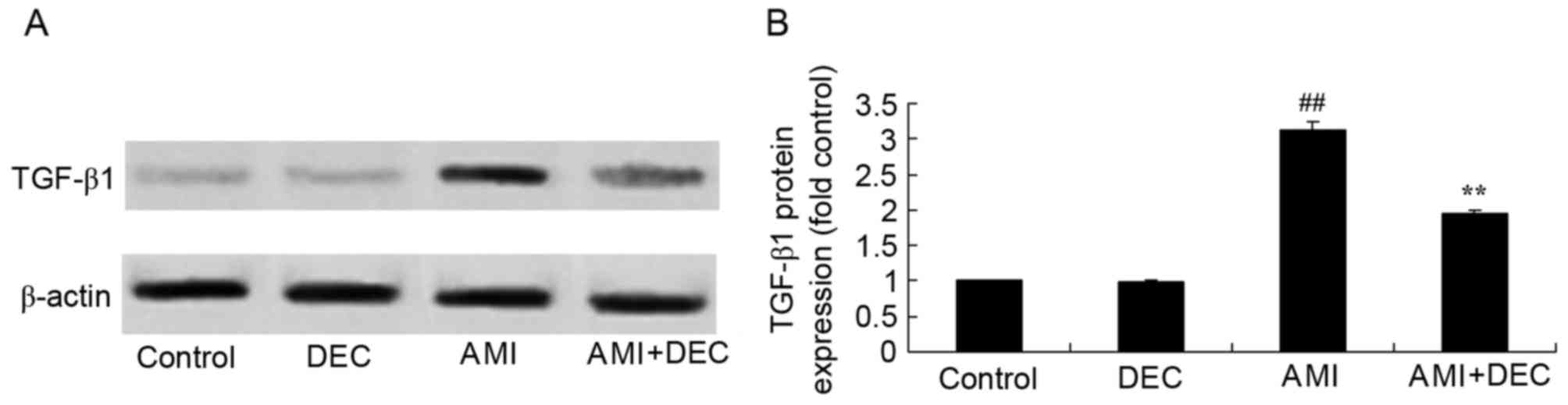
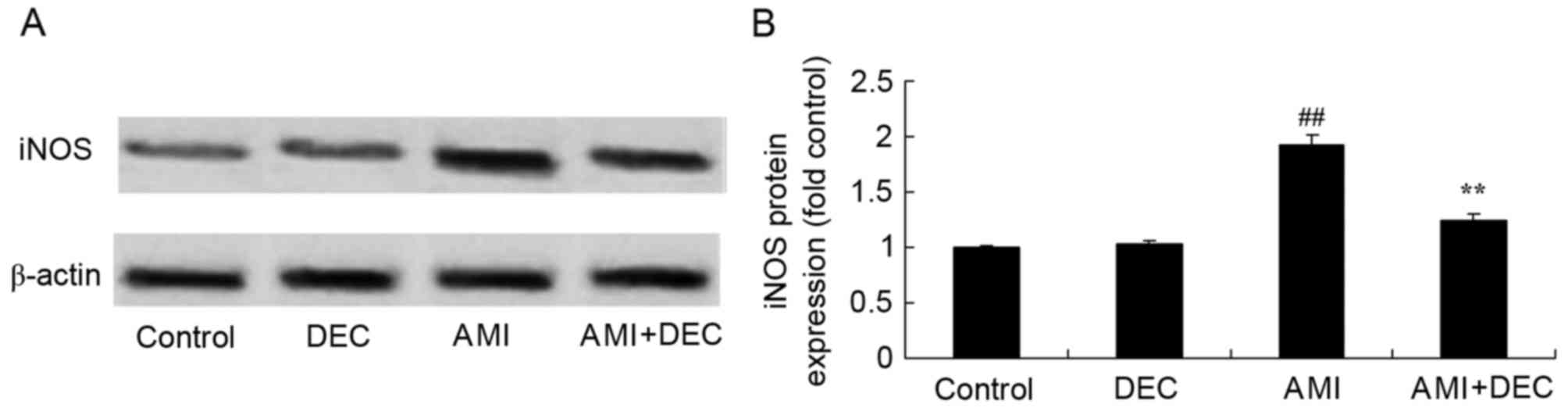
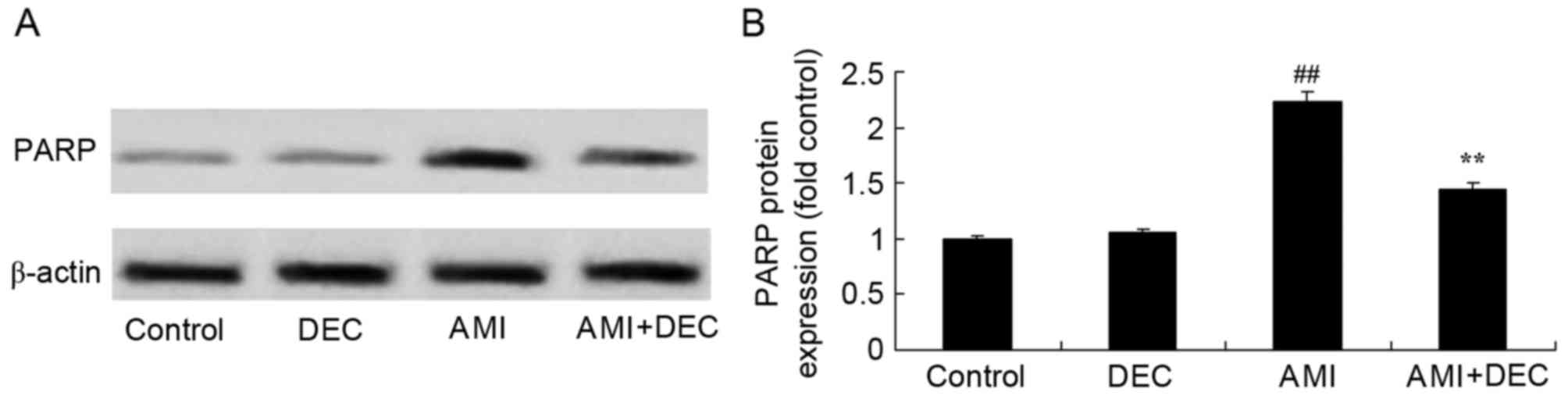
|
1
|
Ritsinger V, Malmberg K, Mårtensson A,
Rydén L, Wedel H and Norhammar A: Intensified insulin-based
glycaemic control after myocardial infarction: Mortality during 20
year follow-up of the randomised Diabetes Mellitus Insulin Glucose
Infusion in Acute Myocardial Infarction (DIGAMI 1) trial. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 2:627–633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suh JW, Yoon YE, Oh IY, Yoon CH, Cho YS,
Youn TJ, Chae IH and Choi DJ: A single-center prospective
randomized controlled trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of
IntraCoronary Erythropoietin delivery BEfore Reperfusion: Gauging
infarct size in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial
infarction. Study design and rationale of the ‘ICEBERG Trial’.
Contemp Clin Trials. 35:145–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peng Y, Fu X, Li W, Geng W, Xing K, Ru L,
Sun J and Zhao Y: Effect of intracoronary anisodamine and diltiazem
administration during primary percutaneous coronary intervention in
acute myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 25:645–652. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pellaton C, Cayla G, Silvain J, Zeymer U,
Cohen M, Goldstein P, Huber K, Pollack C Jr, Kerneis M, Collet JP,
et al: Incidence and consequence of major bleeding in primary
percutaneous intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction in
the era of radial access: An analysis of the international
randomized Acute myocardial infarction Treated with primary
angioplasty and intravenous enoxaparin or unfractionated heparin to
Lower ischemic and bleeding events at short- and Long-term
follow-up trial. Am Heart J. 170:778–786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamaguchi A, Adachi H, Kawahito K, Murata
S and Ino T: Left ventricular reconstruction benefits patients with
dilated ischemic cardiomyopathy. Ann Thorac Surg. 79:456–461. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Manson A, Poyade M and Rea P: A
recommended workflow methodology in the creation of an educational
and training application incorporating a digital reconstruction of
the cerebral ventricular system and cerebrospinal fluid circulation
to aid anatomical understanding. BMC Med Imaging. 15:442015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu SS, Fan HG, Zheng Z, Feng W, Wang W,
Song YH, Wang LQ, Yuan X and Zhang SJ: Left ventricular
reconstruction with no-patch technique: Early and late clinical
outcomes. Chin Med J (Engl). 123:3412–3416. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vargas-Barron J, Antunez-Montes OY, Roldán
FJ, Aranda-Frausto A, González-Pacheco H, Romero-Cardenas Á and
Zabalgoitia M: Myocardial rupture in acute myocardial infarction:
Mechanistic explanation based on the ventricular myocardial band
hypothesis. Rev Invest Clin. 67:318–322. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao L, Huang K, Huang D, Wang J, Guo H and
Liao Y: Acute myocardial infarction induced increases in plasma
tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 are associated with
the activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase of circulating
mononuclear cell. Int J Cardiol. 123:366–368. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Graziani G and Szabó C: Clinical
perspectives of PARP inhibitors. Pharmacol Res. 52:109–118. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szabó C: Pharmacological inhibition of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in cardiovascular disorders: Future
directions. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 3:301–303. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boerma M, Wang J, Sridharan V, Herbert JM
and Hauer-Jensen M: Pharmacological induction of transforming
growth factor-beta1 in rat models enhances radiation injury in the
intestine and the heart. PLoS One. 8:e704792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Santos LA, Ribeiro EL, Barbosa KP, Fragoso
IT, Gomes FO, Donato MA, Silva BS, Silva AK, Rocha SW, França ME,
et al: Diethylcarbamazine inhibits NF-kB activation in acute lung
injury induced by carrageenan in mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
23:153–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
da Silva BS, Rodrigues GB, Rocha SW,
Ribeiro EL, Gomes FO, E Silva AK and Peixoto CA: Inhibition of
NF-kB activation by diethylcarbamazine prevents alcohol-induced
liver injury in C57BL/6 mice. Tissue Cell. 46:363–371. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lai D, Sun J, Li Y and He B: Usefulness of
ventricular endocardial electric reconstruction from body surface
potential maps to noninvasively localize ventricular ectopic
activity in patients. Phys Med Biol. 58:3897–3909. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Menon SC, Cetta F, Dearani JA, Burkhart
HA, Cabalka AK and Hagler DJ: Hybrid intraoperative pulmonary
artery stent placement for congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol.
102:1737–1741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ka SM, Chao L Kuoping, Lin JC, Chen ST, Li
WT, Lin CN, Cheng JC, Jheng HL, Chen A and Hua KF: A low toxicity
synthetic cinnamaldehyde derivative ameliorates renal inflammation
in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and its related signaling
pathways. Free Radic Biol Med. 91:10–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mezzaroma E, Toldo S, Farkas D, Seropian
IM, van Tassell BW, Salloum FN, Kannan HR, Menna AC, Voelkel NF and
Abbate A: The inflammasome promotes adverse cardiac remodeling
following acute myocardial infarction in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:19725–19730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mezzaroma E, Toldo S and Abbate A: Role of
NLRP3 (cryopyrin) in acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
99:225–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Altaf A, Qu P, Zhao Y, Wang H, Lou D and
Niu N: NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood monocytes of acute
coronary syndrome patients and its relationship with statins. Coron
Artery Dis. 26:409–421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alestalo K, Miettinen JA, Vuolteenaho O,
Huikuri H and Lehenkari P: Bone marrow mononuclear cell
transplantation restores inflammatory balance of cytokines after ST
segment elevation myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 10:e01450942015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ruparelia N, Digby JE, Jefferson A, Medway
DJ, Neubauer S, Lygate CA and Choudhury RP: Myocardial infarction
causes inflammation and leukocyte recruitment at remote sites in
the myocardium and in the renal glomerulus. Inflamm Res.
62:515–525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zaitone SA and Abo-Gresha NM: Rosuvastatin
promotes angiogenesis and reverses isoproterenol-induced acute
myocardial infarction in rats: Role of iNOS and VEGF. Eur J
Pharmacol. 691:134–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Das B and Sarkar C: Is preconditioning by
oxytocin administration mediated by iNOS and/or mitochondrial
K(ATP) channel activation in the in vivo anesthetized rabbit heart?
Life Sci. 90:763–769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ørn S, Ueland T, Manhenke C, Sandanger Ø,
Godang K, Yndestad A, Mollnes TE, Dickstein K and Aukrust P:
Increased interleukin-1b levels are associated with left
ventricular hypertrophy and remodelling following acute ST segment
elevation myocardial infarction treated by primary percutaneous
coronary intervention. J Intern Med. 272:267–276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li S, Fan Q, He S, Tang T, Liao Y and Xie
J: MicroRNA-21 negatively regulates Treg cells through a
TGF-β1/Smad-independent pathway in patients with coronary heart
disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:866–878. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rocha SW, de França ME, Rodrigues GB,
Barbosa KP, Nunes AK, Pastor AF, Oliveira AG, Oliveira WH, Luna RL
and Peixoto CA: Diethylcarbamazine reduces chronic inflammation and
fibrosis in carbon tetrachloride- (CCl4-) induced liver injury in
mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:6963832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Davies NM, Smith GD, Windmeijer F and
Martin RM: COX-2 selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and
risk of gastrointestinal tract complications and myocardial
infarction: An instrumental variable analysis. Epidemiology.
24:352–362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Varas-Lorenzo C, Castellsague J, Stang MR,
Perez-Gutthann S, Aguado J and Rodriguez LA: The use of selective
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and the risk of acute myocardial
infarction in Saskatchewan, Canada. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf.
18:1016–1025. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Metcalfe C, Wheeler BW, Gunnell D and
Martin RM: International regulatory activity restricting COX-2
inhibitor use and deaths due to gastrointestinal haemorrhage and
myocardial infarction. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 19:778–785.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ribeiro EL, Barbosa KP, Fragoso IT, Donato
MA, Gomes FO, da Silva BS, e Silva AK Soares, Rocha SW, da Silva
Junior VA and Peixoto CA: Diethylcarbamazine attenuates the
development of carrageenan-induced lung injury in mice. Mediators
Inflamm. 2014:1051202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dong F, Yang XJ, Jiang TB and Chen Y:
Ischemia triggered ATP release through Pannexin-1 channel by
myocardial cells activates sympathetic fibers. Microvasc Res.
104:32–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|