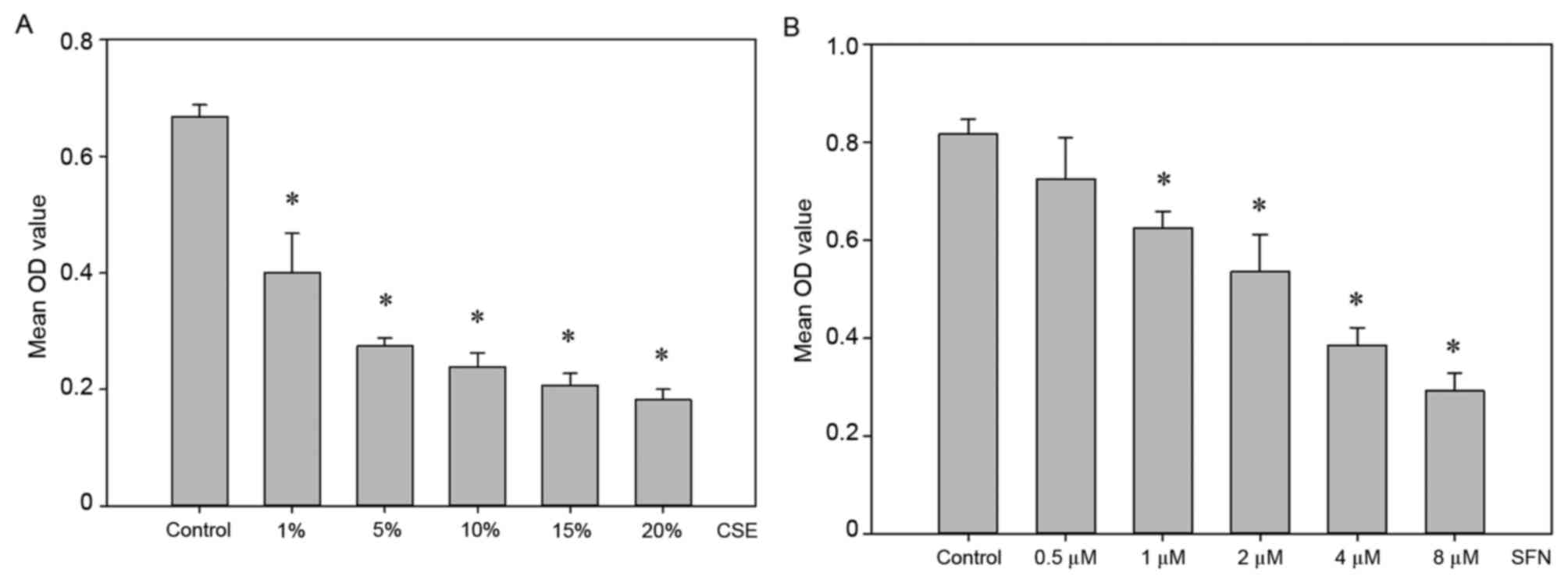
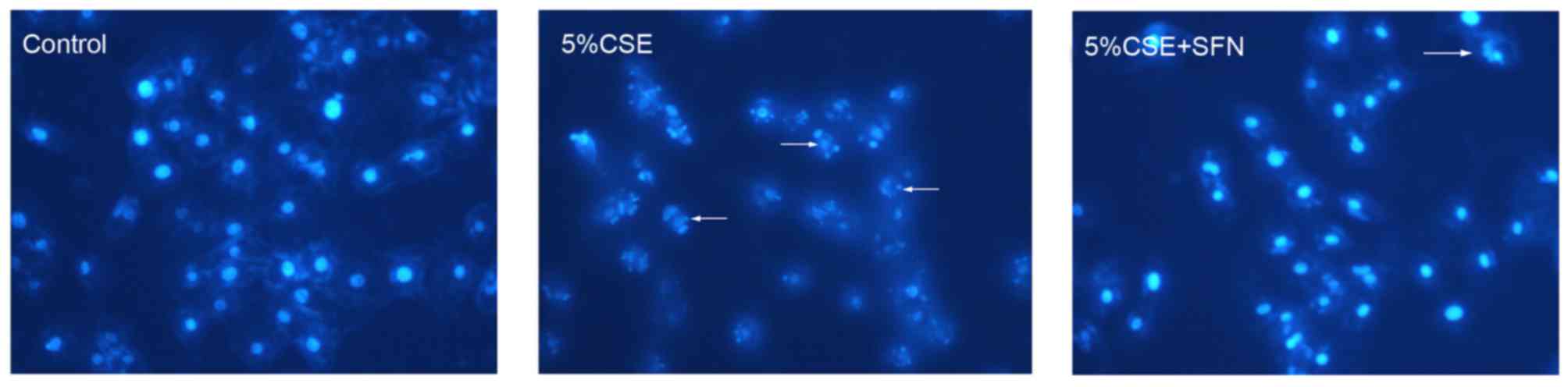
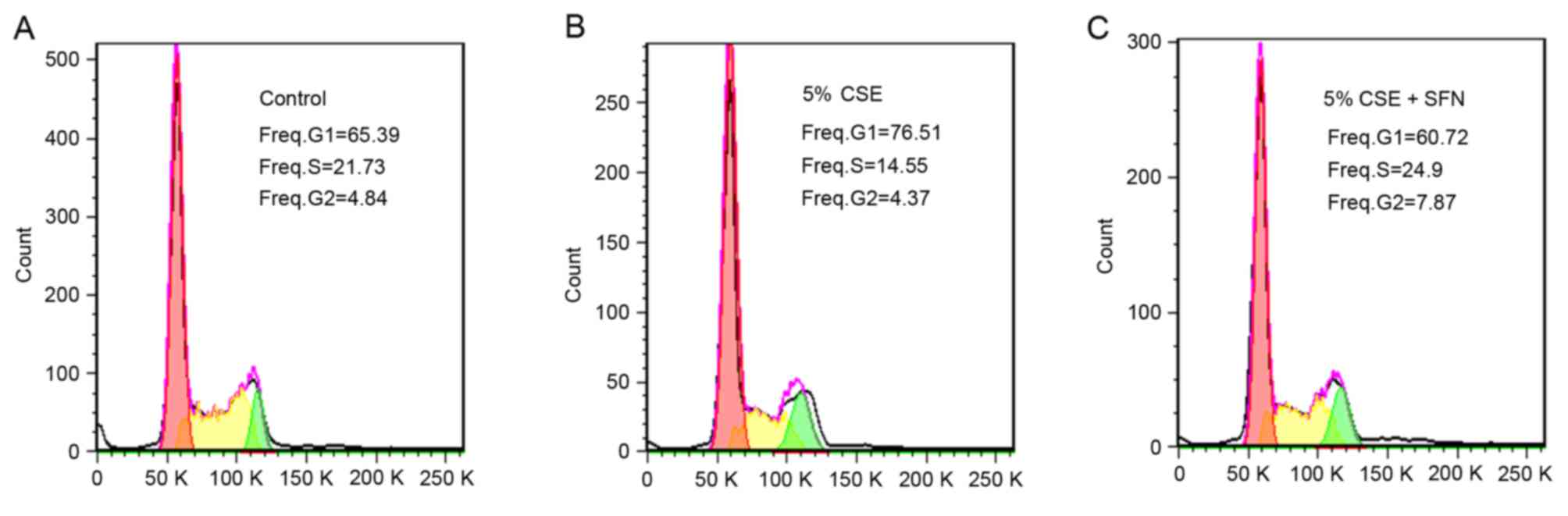
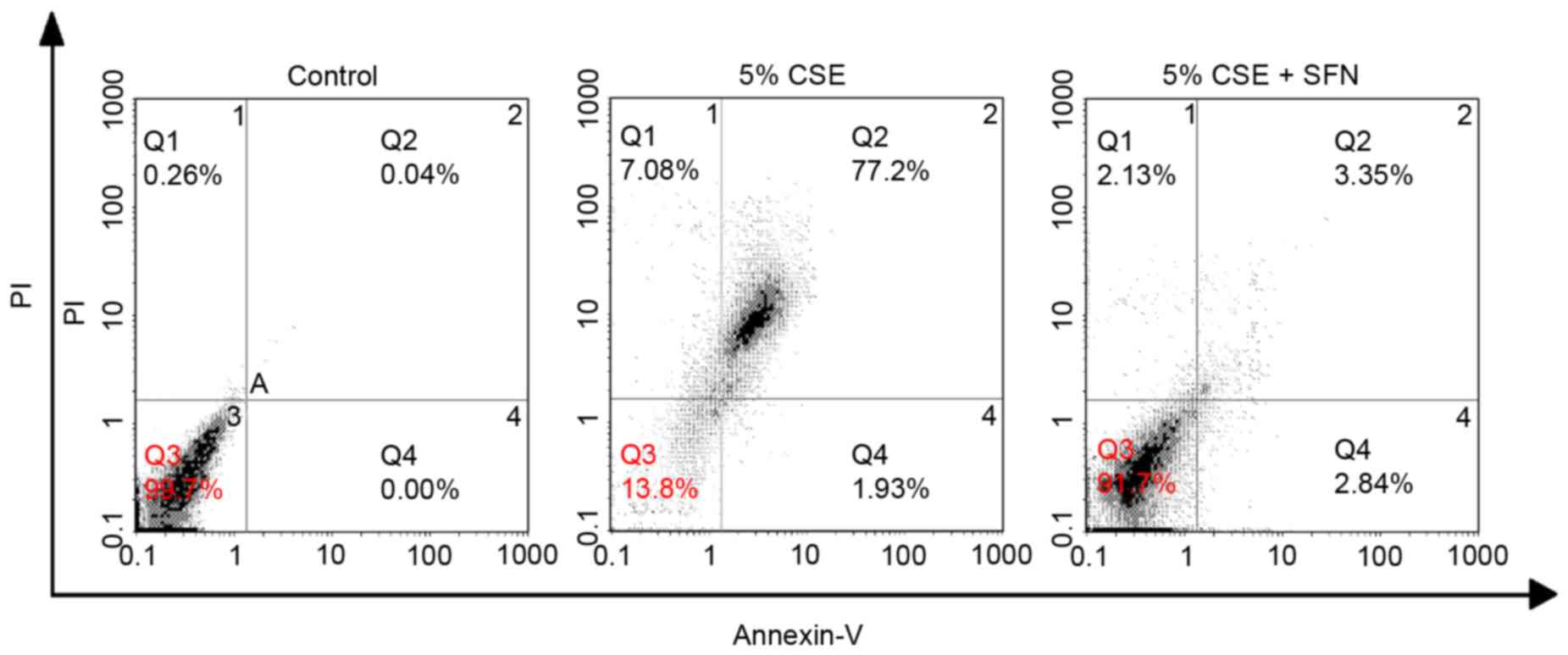
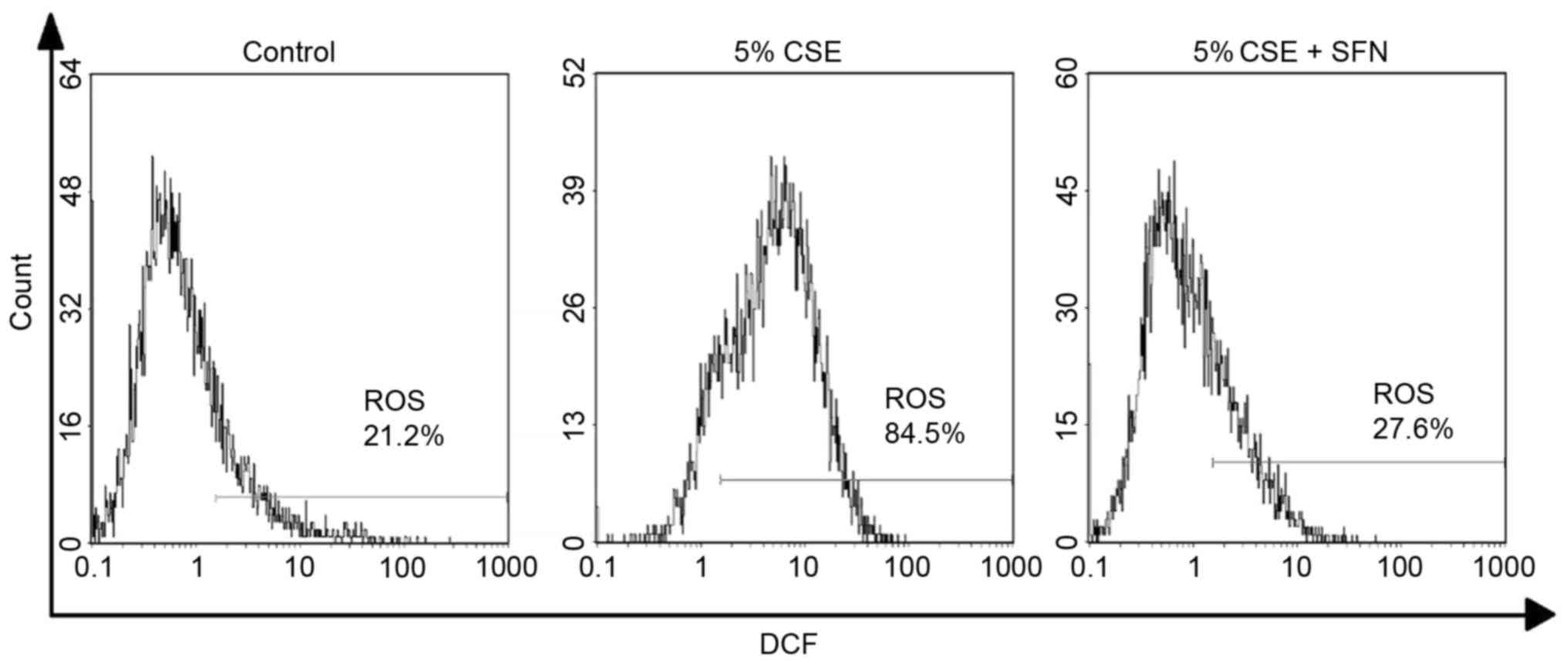
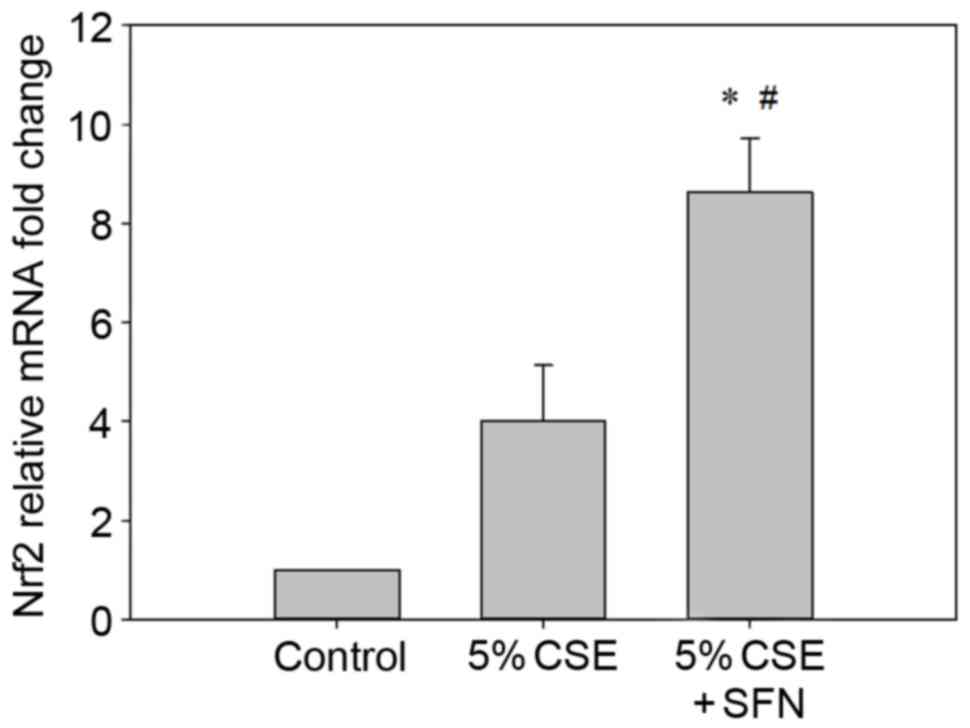
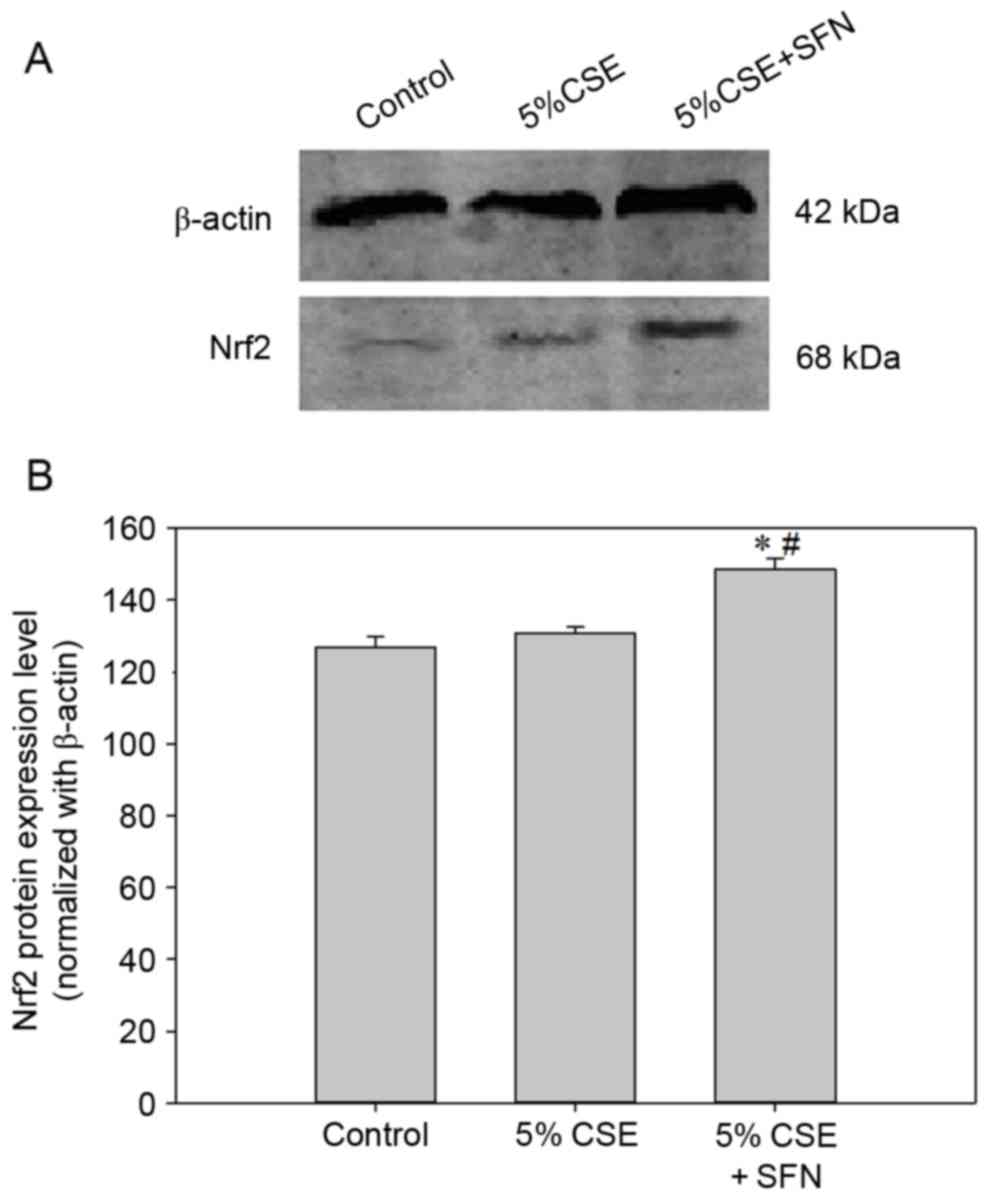
|
1
|
Jansson SA, Backman H, Stenling A,
Lindberg A, Rönmark E and Lundbäck B: Health economic costs of COPD
in Sweden by disease severity-has it changed during a ten years
period? Respir Med. 107:1931–1938. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Decramer M, Janssens W and Miravitlles M:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 379:1341–1351. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tamimi A, Serdarevic D and Hanania NA: The
effects of cigarette smoke on airway inflammation in asthma and
COPD: Therapeutic implications. Respir Med. 106:319–328. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang H, Shih A, Rinna A and Forman HJ:
Exacerbation of tobacco smoke mediated apoptosis by resveratrol: An
unexpected consequence of its antioxidant action. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 43:1059–1064. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goven D, Boutten A, Leçon-Malas V,
Boczkowski J and Bonay M: Prolonged cigarette smoke exposure
decreases heme oxygenase-1 and alters Nrf2 and Bach1 expression in
human macrophages: Roles of the MAP kinases ERK(1/2) and JNK. FEBS
Lett. 583:3508–3518. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Regoli F and Giuliani ME: Oxidative
pathways of chemical toxicity and oxidative stress biomarkers in
marine organisms. Mar Environ Res. 93:106–117. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tasaki M, Kuroiwa Y, Inoue T, Hibi D,
Matsushita K, Kijima A, Maruyama S, Nishikawa A and Umemura T: Lack
of nrf2 results in progression of proliferative lesions to
neoplasms induced by long-term exposure to non-genotoxic
hepatocarcinogens involving oxidative stress. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
66:19–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cano M, Thimmalappula R, Fujihara M, Nagai
N, Sporn M, Wang AL, Neufeld AH, Biswal S and Handa JT: Cigarette
smoking, oxidative stress, the anti-oxidant response through Nrf2
signaling and Age-related macular degeneration. Vision Res.
50:652–664. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rangasamy T, Cho CY, Thimmulappa RK, Zhen
L, Srisuma SS, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Petrache I, Tuder RM and
Biswal S: Genetic ablation of Nrf2 enhances susceptibility to
cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. J Clin Invest.
114:1248–1259. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suzuki M, Betsuyaku T, Ito Y, Nagai K,
Nasuhara Y, Kaga K, Kondo S and Nishimura M: Down-regulated
NF-E2-related factor 2 in pulmonary macrophages of aged smokers and
patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 39:673–682. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malhotra D, Thimmulappa R, Navas-Acien A,
Sandford A, Elliott M, Singh A, Chen L, Zhuang X, Hogg J, Pare P,
et al: Expression of concern: Decline in NRF2-regulated
antioxidants in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease lungs due to
loss of its positive regulator, DJ-1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
178:592–604. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ping Z, Liu W, Kang Z, Cai J, Wang Q,
Cheng N, Wang S, Wang S, Zhang JH and Sun X: Sulforaphane protects
brains against hypoxic-ischemic injury through induction of
Nrf2-dependent phase 2 enzyme. Brain Res. 1343:178–185. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guerrero-Beltrán CE, Calderón-Oliver M,
Pedraza-Chaverri J and Chirino YI: Protective effect of
sulforaphane against oxidative stress: Recent advances. Exp Toxicol
Pathol. 64:503–508. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bergström P, Andersson HC, Gao Y, Karlsson
JO, Nodin C, Anderson MF, Nilsson M and Hammarsten O: Repeated
transient sulforaphane stimulation in astrocytes leads to prolonged
Nrf2-mediated gene expression and protection from
superoxide-induced damage. Neuropharmacology. 60:343–353. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu R, Hebbar V, Kim BR, Chen C, Winnik B,
Buckley B, Soteropoulos P, Tolias P, Hart RP and Kong AN: In vivo
pharmacokinetics and regulation of gene expression profiles by
isothiocyanate sulforaphane in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
310:263–271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M,
Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K and Yamamoto M: Oxidative stress
sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to
regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol.
24:7130–7139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iida K, Itoh K, Kumagai Y, Oyasu R,
Hattori K, Kawai K, Shimazui T, Akaza H and Yamamoto M: Nrf2 is
essential for the chemopreventive efficacy of oltipraz against
urinary bladder carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:6424–6431. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu C, Huang MT, Shen G, Yuan X, Lin W,
Khor TO, Conney AH and Kong AN: Inhibition of
7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced skin tumorigenesis in
C57BL/6 mice by sulforaphane is mediated by nuclear factor
E2-related factor 2. Cancer Res. 66:8293–8296. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Burkhardt BR, Lyle R, Qian K, Arnold AS,
Cheng H, Atkinson MA and Zhang YC: Efficient delivery of siRNA into
cytokine-stimulated insulinoma cells silences Fas expression and
inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 580:553–560. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oda K, Yumoto R, Nagai J, Katayama H and
Takano M: Mechanism underlying insulin uptake in alveolar
epithelial cell line RLE-6TN. Eur J Pharmacol. 672:62–69. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nadigel J, Audusseau S, Baglole CJ,
Eidelman DH and Hamid Q: IL-8 production in response to cigarette
smoke is decreased in epithelial cells from COPD patients. Pulm
Pharmacol Ther. 26:596–602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thorne D and Adamson J: A review of in
vitro cigarette smoke exposure systems. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
65:1183–1193. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bryan HK, Olayanju A, Goldring CE and Park
BK: The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and -independent
mechanisms of regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:705–717. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kosmider B, Messier EM, Chu HW and Mason
RJ: Human alveolar epithelial cell injury induced by cigarette
smoke. PLoS One. 6:e260592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|