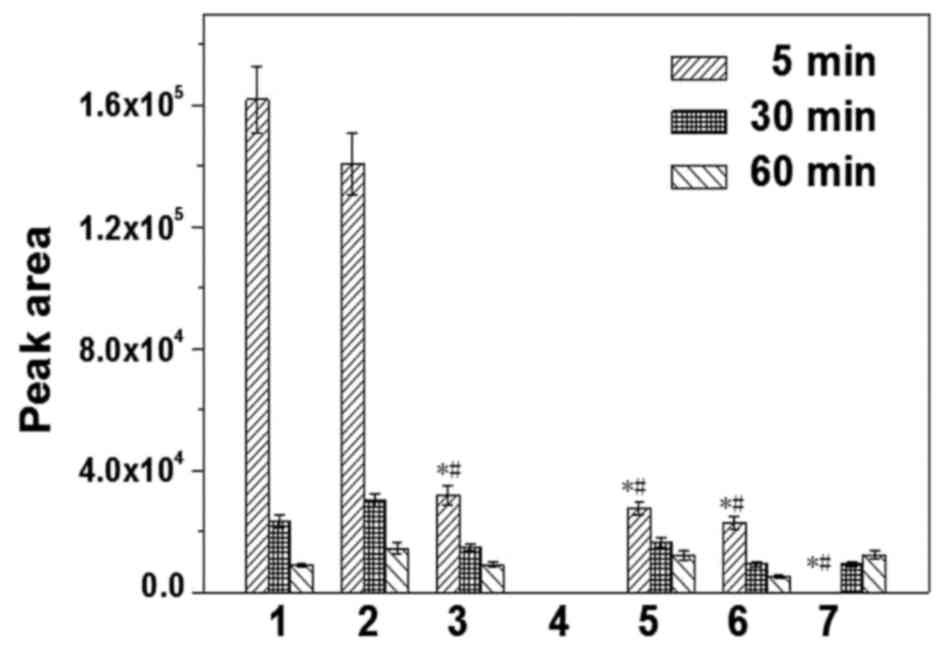
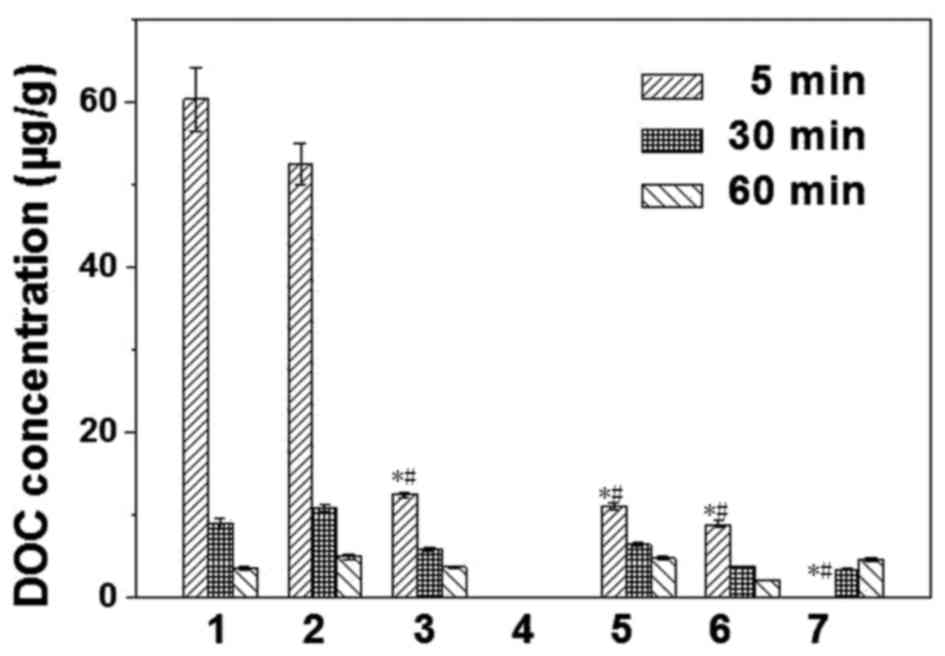
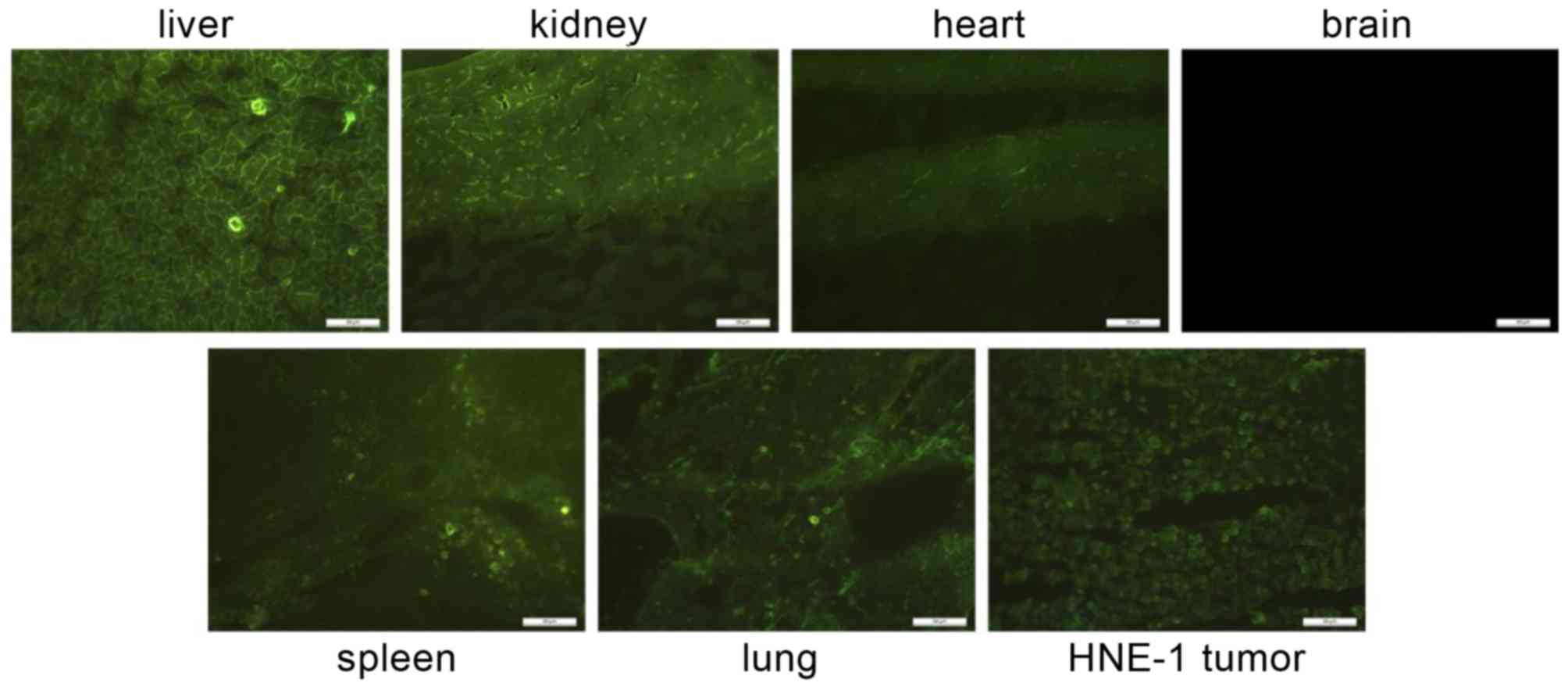
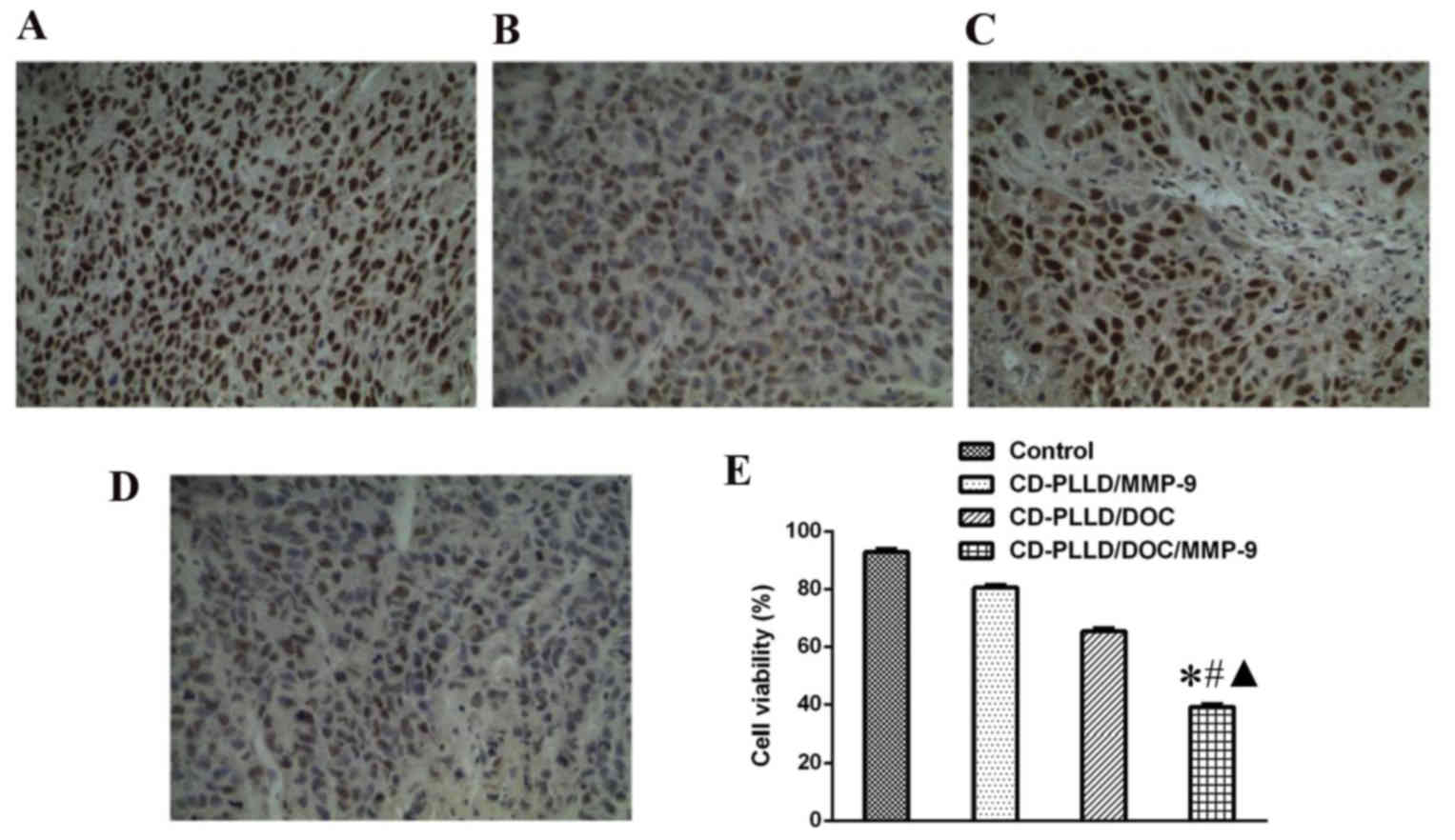
|
1
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chan AT, Hsu MM, Goh BC, Hui EP, Liu TW,
Millward MJ, Hong RL, Whang-Peng J, Ma BB, To KF, et al:
Multicenter, phase II study of cetuximab in combination with
carboplatin in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 23:3568–3576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dai X and Tan C: Combination of microRNA
therapeutics with small-molecule anticancer drugs: Mechanism of
action and co-delivery nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
81:184–197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
He C, Liu D and Lin W: Self-assembled
nanoscale coordination polymers carrying siRNAs and cisplatin for
effective treatment of resistant ovarian cancer. Biomaterials.
36:124–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Liu R, Yang J, Ma G, Zhang Z and
Zhang X: Dual sensitive and temporally controlled camptothecin
prodrug liposomes codelivery of siRNA for high efficiency tumor
therapy. Biomaterials. 35:9731–9745. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang Y, Yang K, Wei P, Huang S, Pei Y,
Zhao W and Pei Z: Cationic vesicles based on amphiphilic pillar
[5]arene capped with ferrocenium: A redox-responsive system for
drug/siRNA co-delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 53:13126–13130.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma D, Zhang HB, Tu K and Zhang LM: Novel
supramolecular hydrogel/micelle composite for co-delivery of
anticancer drug and growth factor. Soft Matter. 8:3665–3672. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang AT, Liang DS, Liu YJ and Qi XR: Roles
of ligand and TPGS of micelles in regulating internalization,
penetration and accumulation against sensitive or resistant tumor
and therapy for multidrug resistant tumors. Biomaterials.
53:160–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu Q, van Gaal EV, Brundel P, Ippel H,
Hackeng T, Rijcken CJ, Storm G, Hennink WE and Prakash J: A novel
approach for the intravenous delivery of leuprolide using
core-cross-linked polymeric micelles. J Control Release.
205:98–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma D, Zhang HB, Chen YY, Lin JT and Zhang
LM: New cyclodextrin derivative containing poly(L-lysine) dendrons
for gene and drug co-delivery. J Colloid Interface Sci.
405:305–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li M, Zhou X, Zeng X, Wang C, Xu J, Ma D
and Xue W: Folate-targeting redox hyperbranched poly(amido amine)s
delivering MMP-9 siRNA for cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B.
4:547–556. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Luo K, Li C, Li L, She W, Wang G and Gu Z:
Arginine functionalized peptide dendrimers as potential gene
delivery vehicles. Biomaterials. 33:4917–4927. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma D, Lin QM, Zhang LM, Liang YY and Xue
W: A star-shaped porphyrin-arginine functionalized poly(L-lysine)
copolymer for photo-enhanced drug and gene co-delivery.
Biomaterials. 35:4357–4367. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pang JD, Zhuang BX, Mai K, Chen RF, Wang J
and Zhang LM: Click modification of helical amylose by
poly(l-lysine) dendrons for non-viral gene delivery. Mater Sci Eng
C Mater Biol Appl. 49:485–492. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma D, Liu ZH, Zheng QQ, Zhou XY, Zhang Y,
Shi YF, Lin JT and Xue W: Star-shaped polymer consisting of a
porphyrin core and poly(L-lysine) dendron arms: Synthesis, drug
delivery, and in vitro chemo/photodynamic therapy. Macromol Rapid
Commun. 34:548–552. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu T, Xue W, Ke B, Xie MQ and Ma D:
Star-shaped cyclodextrin-poly(L-lysine) derivative co-delivering
docetaxel and MMP-9 siRNA plasmid in cancer therapy. Biomaterials.
35:3865–3872. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Creixell M and Peppas NA: Co-delivery of
siRNA and therapeutic agents using nanocarriers to overcome cancer
resistance. Nano Today. 7:367–379. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liotta LA, Steeg PS and Stetler-Stevenson
WG: Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: An imbalance of positive
and negative regulation. Cell. 64:327–336. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rao JS, Bhoopathi P, Chetty C, Gujrati M
and Lakka SS: MMP-9 short interfering RNA induced senescence
resulting in inhibition of medulloblastoma growth via p16(INK4a)
and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cancer Res.
67:4956–4964. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ajani JA: Chemotherapy for advanced
gastric or gastroesophageal cancer: Defining the contributions of
docetaxel. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 7:1627–1631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bouvier E, Thirot S, Schmidt F and
Monneret C: First enzymatically activated Taxotere prodrugs
designed for ADEPT and PMT. Bioorg Med Chem. 12:969–977. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sánchez-Moreno P, Boulaiz H,
Ortega-Vinuesa JL, Peula-García JM and Aránega A: Novel drug
delivery system based on docetaxel-loaded nanocapsules as a
therapeutic strategy against breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci.
13:4906–4919. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cortes J, Rodriguez J, Aramendia JM,
Salgado E, Gurpide A, Garcia-Foncillas J, Aristu JJ, Claver A,
Bosch A, Lopez-Picazo JM, et al: Front-line paclitaxel/cisplatin
based chemotherapy in brain metastases from non-small-cell lung
cancer. Oncology. 64:28–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng SS and Chien S: Chemotherapeutic
engineering: Application and further development of chemical
engineering principles for chemotherapy of cancer and other
diseases. Chem Eng Sci. 58:4087–4114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhao Y, Zhai D, Chen X, Yu Q, He H, Sun Y,
Gao Z, Wang L, Wang H, Han D and Ji H: Determination of nimodipine
in human plasma by HPLC-ESI-MS and its application to a
bioequivalence study. J Chromatogr Sci. 48:81–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ju P, Liu Z, Jiang Y, Zhao S, Zhang L,
Zhang Y, Gu L, Tang X, Bi K and Chen X: Determination of a novel
anticancer c-Met inhibitor LS-177 in rat plasma and tissues with a
validated UPLC-MS/MS method: Application to pharmacokinetics and
tissue distribution study. Biomed Chromatogr. 29:1103–1111. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sledge GW Jr and Miller KD: Exploiting the
hallmarks of cancer: The future conquest of breast cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 39:1668–1675. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Teicher BA: Molecular targets and cancer
therapeutics: Discovery, development and clinical validation. Drug
Resist Updat. 3:67–73. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brannon-Peppas L and Blanchette JO:
Corrigendum to ‘Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer
therapy’ Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 56(2004)1649–1659. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 61:3642009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kato K, Kawashiri S, Yoshizawa K, Kitahara
H, Okamune A, Sugiura S, Noguchi N and Yamamoto E: Expression form
of p53 and PCNA at the invasive front in oral squamous cell
carcinoma: Correlation with clinicopathological features and
prognosis. J Oral Pathol Med. 40:693–698. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|