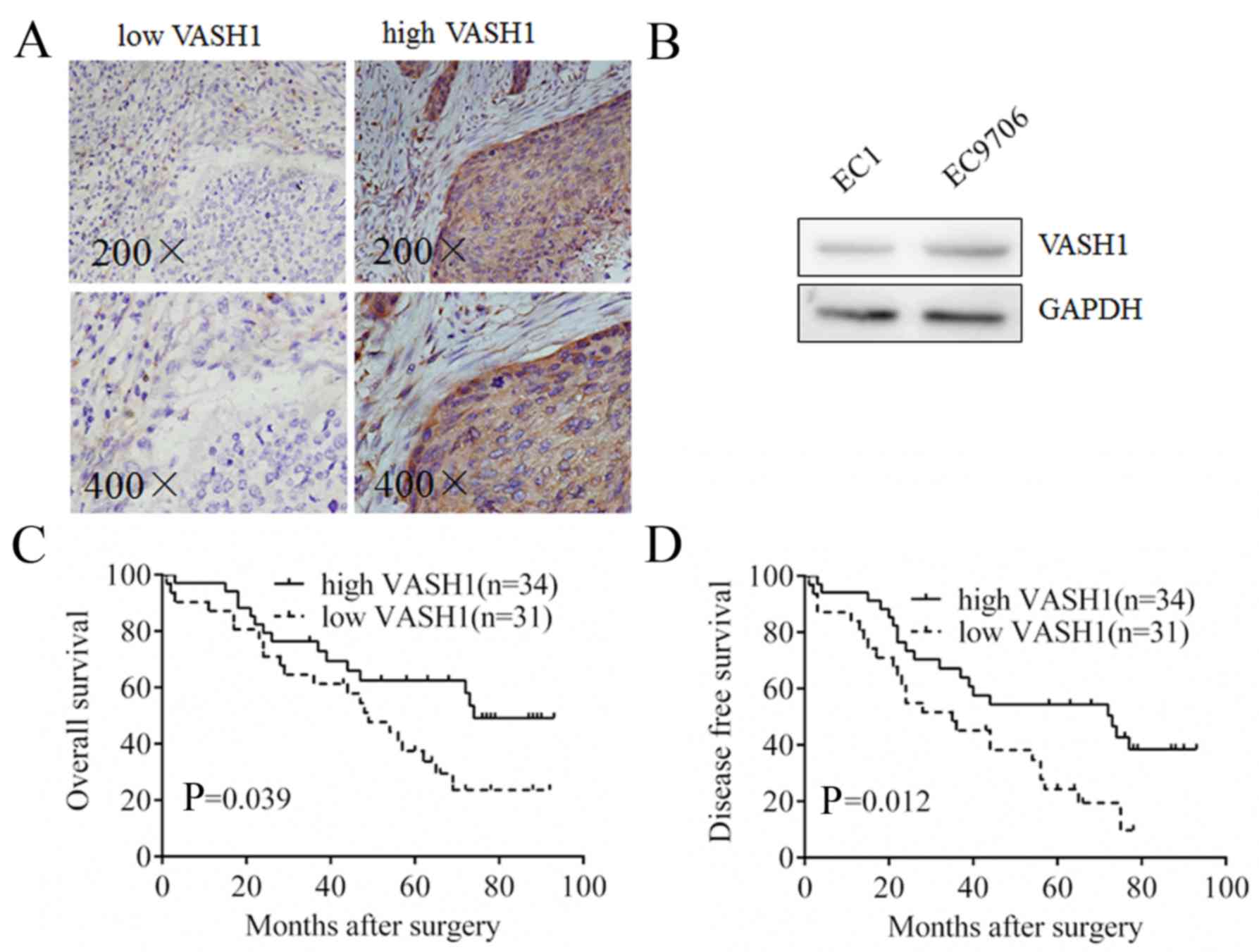
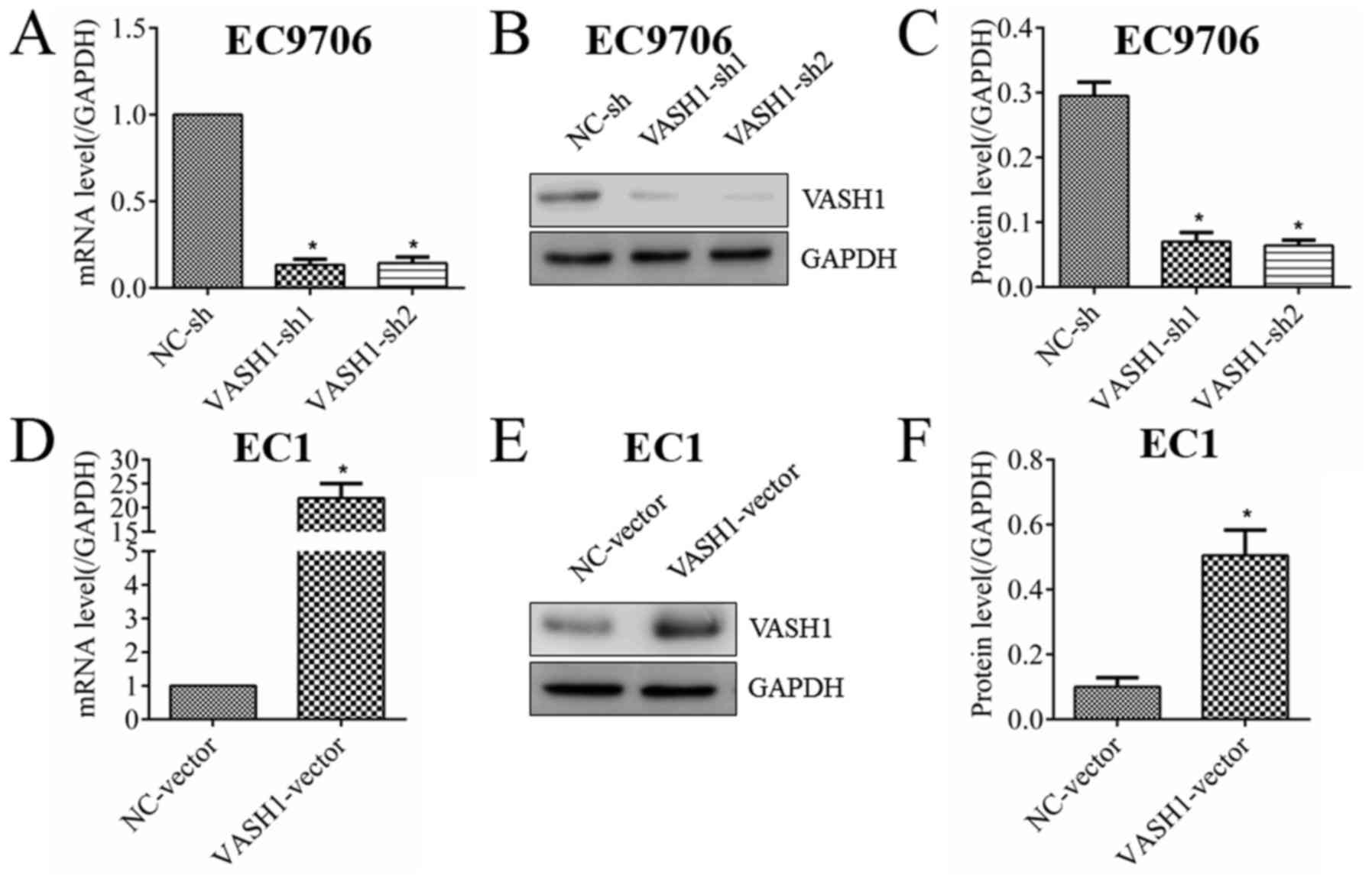
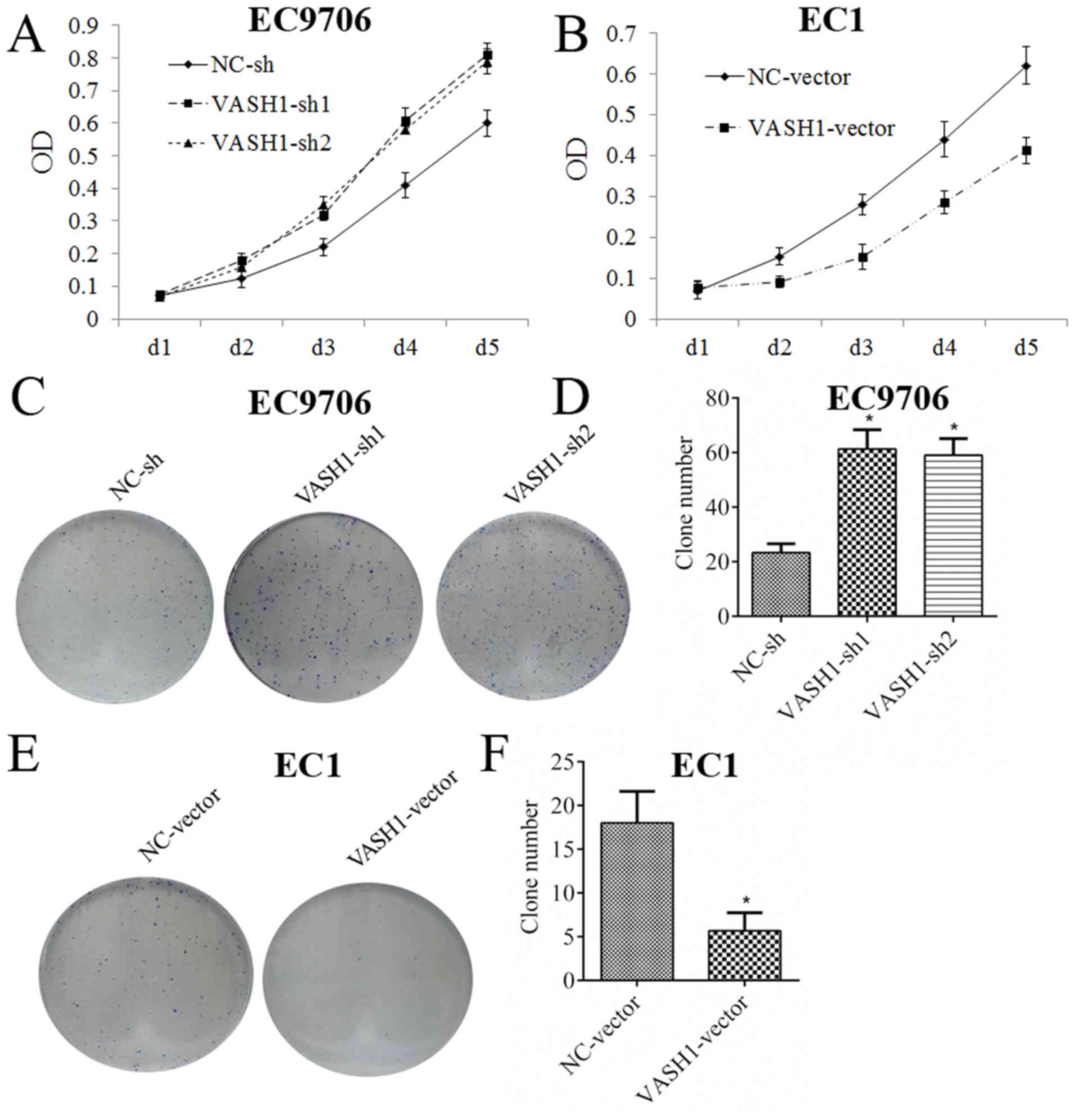
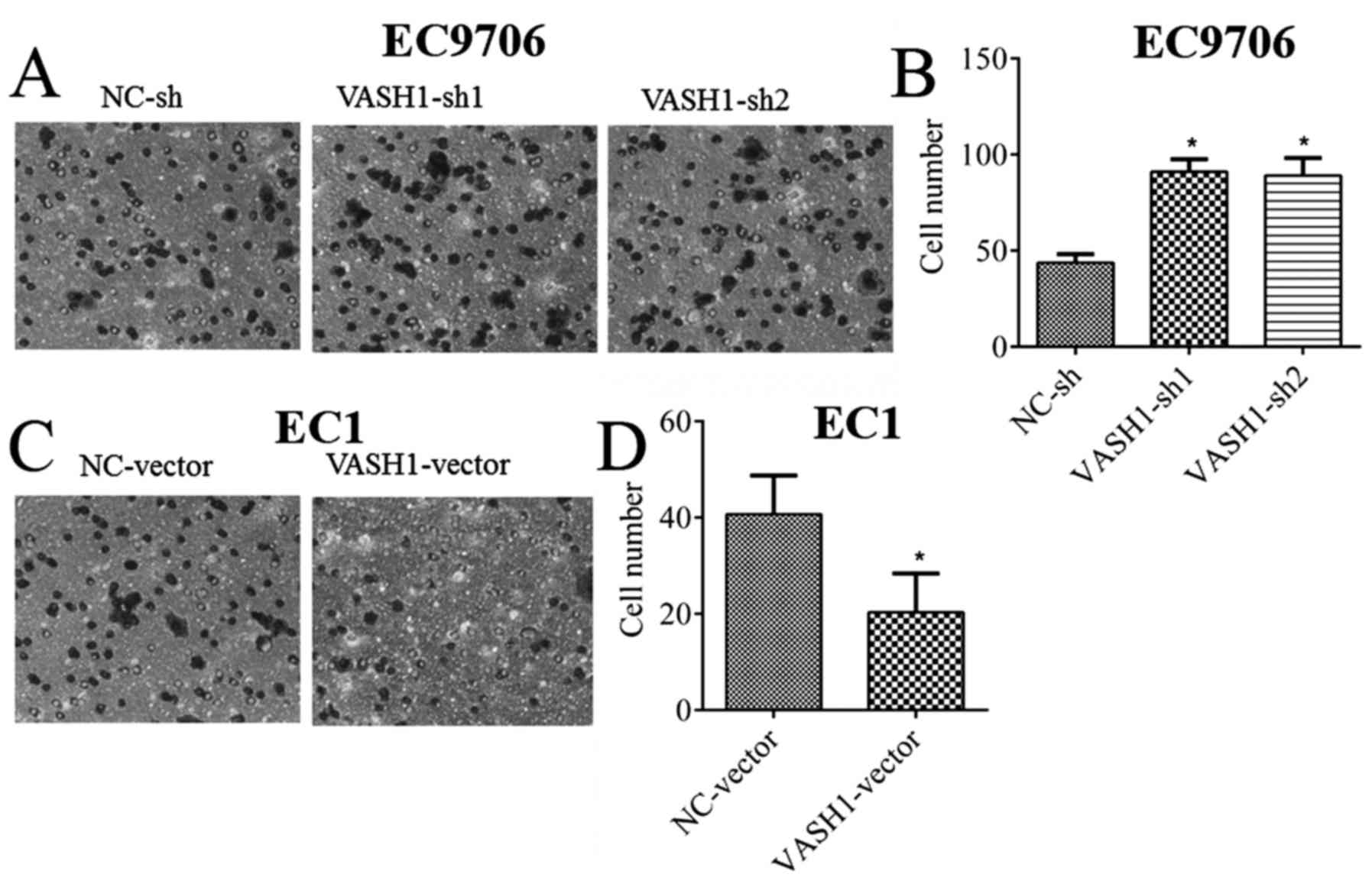
|
1
|
Zhang H, Chen W, Duan CJ and Zhang CF:
Overexpression of HSPA2 is correlated with poor prognosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 11:1412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu YH, Yang F, Zhang SS, Zeng TT, Xie X
and Guan XY: High expression of biglycan is associated with poor
prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:2497–2505. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li M, Yang X, Zhang J, Shi H, Hang Q,
Huang X, Liu G, Zhu J, He S and Wang H: Effects of EHD2
interference on migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Med Oncol. 30:3962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hasan MR, Sharma R, Saraya A,
Chattopadhyay TK, DattaGupta S, Walfish PG, Chauhan SS and Ralhan
R: Slug is a predictor of poor prognosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma patients. PLoS One. 8:e828462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim SG: What is the next step after
endoscopic resection of superficial esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma? Gut Liver. 9:693–694. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kern J, Steurer M, Gastl G, Gunsilius E
and Untergasser G: Vasohibin inhibits angiogenic sprouting in vitro
and supports vascular maturation processes in vivo. BMC Cancer.
9:2842009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Watanabe K, Hasegawa Y, Yamashita H,
Shimizu K, Ding Y, Abe M, Ohta H, Imagawa K, Hojo K, Maki H, et al:
Vasohibin as an endothelium-derived negative feedback regulator of
angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 114:898–907. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sato Y: The vasohibin family.
Pharmaceuticals. 3:433–440. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tamaki K, Moriya T, Sato Y, Ishida T,
Maruo Y, Yoshinaga K, Ohuchi N and Sasano H: Vasohibin-1 in human
breast carcinoma: A potential negative feedback regulator of
angiogenesis. Cancer Sci. 100:88–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao G, Yang Y, Tang Y, Han R and Sun Y:
Reduced expression of vasohibin-1 is associated with
clinicopathological features in renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol.
29:3325–3334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Q, Tian X, Zhang C and Wang Q:
Upregulation of vasohibin-1 expression with angiogenesis and poor
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgery. Med
Oncol. 29:2727–2736. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kosaka T, Miyazaki Y, Miyajima A, Mikami
S, Hayashi Y, Tanaka N, Nagata H, Kikuchi E, Nakagawa K, Okada Y,
et al: The prognostic significance of vasohibin-1 expression in
patients with prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 108:2123–2129. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kimura H, Miyashita H, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi
M, Watanabe K, Sonoda H, Ohta H, Fujiwara T, Shimosegawa T and Sato
Y: Distinctive localization and opposed roles of vasohibin-1 and
vasohibin-2 in the regulation of angiogenesis. Blood.
113:4810–4818. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shen Z, Seppänen H, Kauttu T, Vainionpää
S, Ye Y, Wang S, Mustonen H and Puolakkainen P: Vasohibin-1
expression is regulated by transforming growth factor-β/bone
morphogenic protein signaling pathway between tumor-associated
macrophages and pancreatic cancer cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
33:428–433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang YX, Du ZM, Jiao L, Shao Q, Fu S,
Shao JY, Zhu XF, Ernberg I and Li YH: Inhibition of MiR-155
suppresses cell migration in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through
targeting ZDHHC2. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:8472–8484. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y and Lin Q: MicroRNA-145 inhibits
migration and invasion by down-regulating FSCN1 in lung cancer. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:8794–8802. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang T, Yu TT, Zhang DM, Hou XM, Liu XJ,
Zhao D and Shan L: Vasohibin-1 expression detected by
immunohistochemistry correlates with prognosis in non-small cell
lung cancer. Med Oncol. 31:9632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yan Y, Shen Z, Ye Y, Jiang K, Zhang H,
Shen C, Mustonen H, Puolakkainen P and Wang S: A novel molecular
marker of prognosis in colorectal cancer: Vasohibin-1. Med Oncol.
31:8162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miyashita H, Watanabe T, Hayashi H, Suzuki
Y, Nakamura T, Ito S, Ono M, Hoshikawa Y, Okada Y, Kondo T and Sato
Y: Angiogenesis inhibitor vasohibin-1 enhances stress resistance of
endothelial cells via induction of SOD2 and SIRT1. PLoS One.
7:e464592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyashita H, Suzuki H, Ohkuchi A and Sato
Y: Mutual balance between vasohibin-1 and soluble VEGFR-1 in
endothelial cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 4:782–793. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Lv ZD, Zhang L, Liu XP, Jin LY, Dong Q, Li
FN, Wang HB and Kong B: NKD1 down-regulation is associated with
poor prognosis in breast invasive ductal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:4015–4021. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen Y, Zhang F, Lan H, Chen K, Zhang Q,
Xie G, Teng L and Jin K: FRZB up-regulation is correlated with
hepatic metastasis and poor prognosis in colon carcinoma patients
with hepatic metastasis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4083–4090.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Strong AL, Ohlstein JF, Biagas BA, Rhodes
LV, Pei DT, Tucker HA, Llamas C, Bowles AC, Dutreil MF, Zhang S, et
al: Leptin produced by obese adipose stromal/stem cells enhances
proliferation and metastasis of estrogen receptor positive breast
cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 17:1122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pathak R, Philizaire M and Mujtaba S:
Dichotomy in the Epigenetic Mark Lysine Acetylation is Critical for
the Proliferation of Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers (Basel).
7:1622–1642. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu S, Han B, Zhang Q, Dou J, Wang F, Lin
W, Sun Y and Peng G: Vasohibin-1 suppresses colon cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:7880–7898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rusckowski M, Wang Y, Blankenberg FG,
Levashova Z, Backer MV and Backer JM: Targeted scVEGF/(177)Lu
radiopharmaceutical inhibits growth of metastases and can be
effectively combined with chemotherapy. EJNMMI Res. 6:42016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vanajothi R and Srinivasan P: An
anthraquinone derivative from Luffa acutangula induces apoptosis in
human lung cancer cell line NCI-H460 through p53-dependent pathway.
J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 36:292–302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qiu K, Huang Z, Huang Z, He Z and You S:
miR-22 regulates cell invasion, migration and proliferation in
vitro through inhibiting CD147 expression in tongue squamous cell
carcinoma. Arch Oral Biol. 66:92–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen JS, Li HS, Huang JQ, Dong SH, Huang
ZJ, Yi W, Zhan GF, Feng JT, Sun JC and Huang XH: MicroRNA-379-5p
inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting FAK/AKT
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 375:73–83.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|