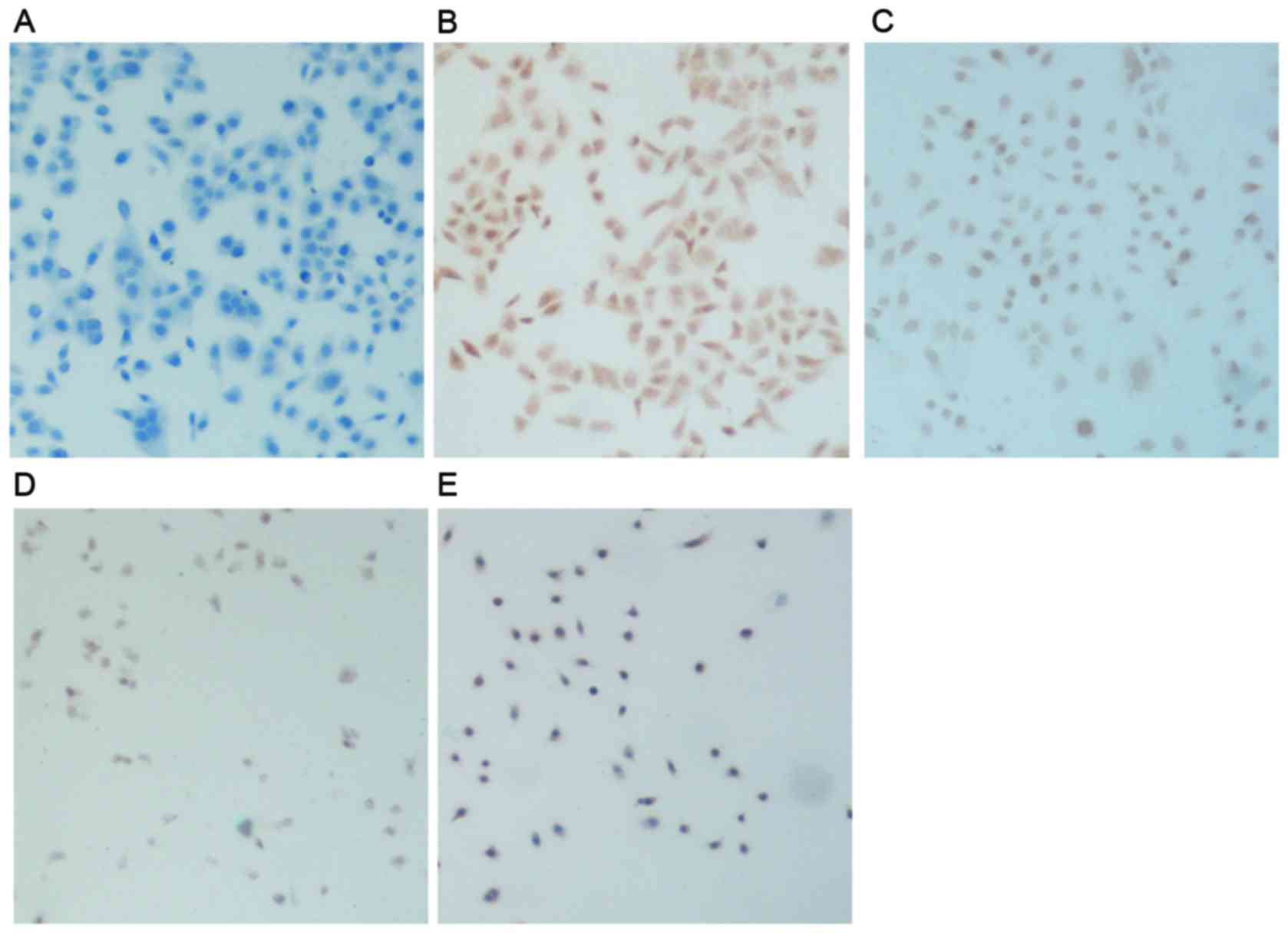
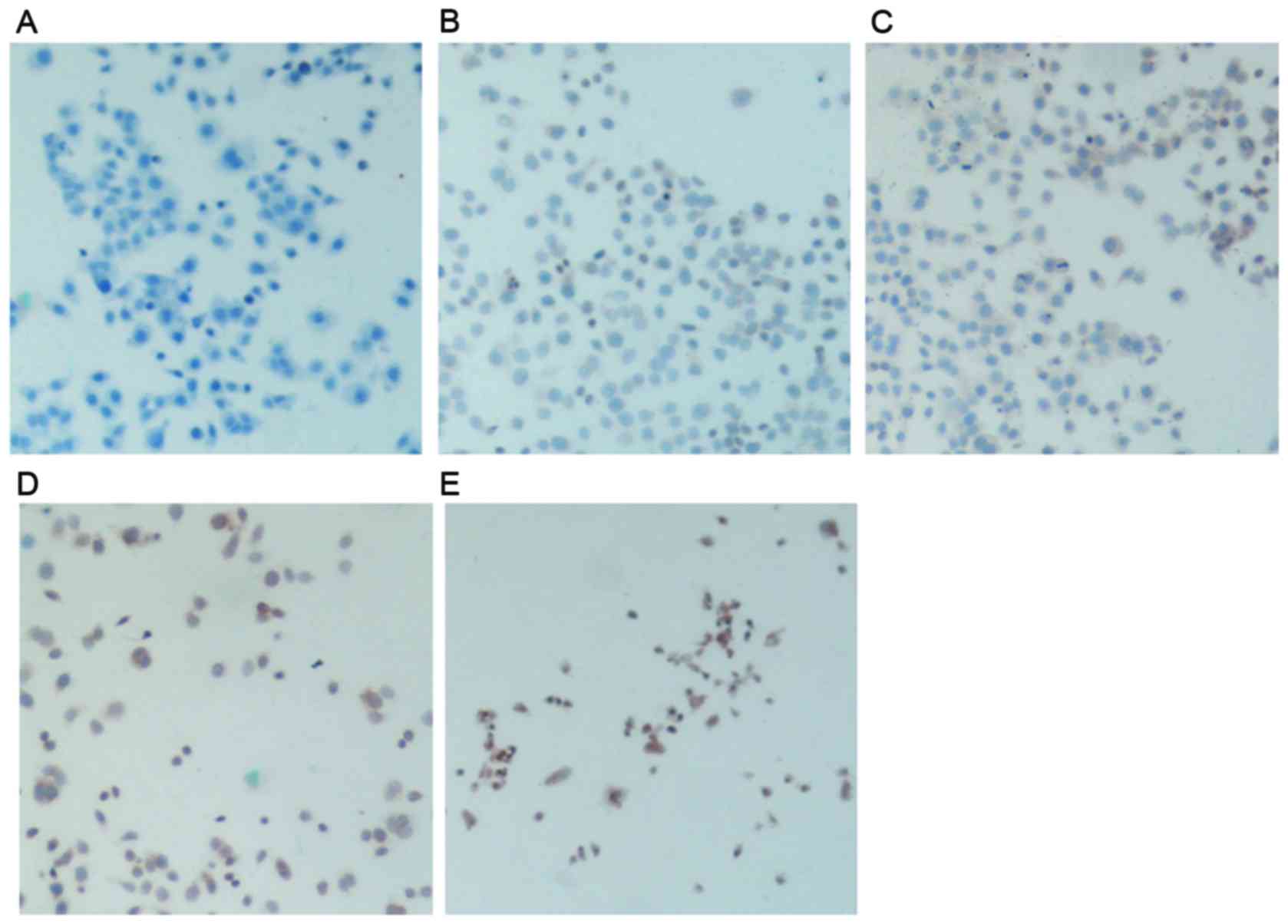
|
1
|
Chen W, Zhang R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Li G, Wu
L and He J: Report of incidence and mortality in China cancer
registries, 2009. Chin J Cancer Res. 25:10–21. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lenz HJ, Lee FC, Haller DG, Singh D,
Benson AB III, Strumberg D, Yanagihara R, Yao JC, Phan AT and Ajani
JA: Extended safety and efficacy data on S-1 plus cisplatin in
patients with untreated, advanced gastric carcinoma in a
multicenter phase II study. Cancer. 109:33–40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li G, Yang F, Gu S, Li Z and Xue M:
MicroRNA-101 induces apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant gastric
cancer cells by targeting VEGF-C. Mol Med Rep. 13:572–578.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen DD, Feng LC, Ye R, He YQ and Wang YD:
miR-29b reduces cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cell by
targeting PI3K/Akt pathway. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao.
37:514–519. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou X, Jin W, Jia H, Yan J and Zhang G:
MiR-223 promotes the cisplatin resistance of human gastric cancer
cells via regulating cell cycle by targeting FBXW7. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 34:282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huczyński A: Polyether
ionophores-promising bioactive molecules for cancer therapy. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 22:7002–7010. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyazaki Y, Shibuya M, Sugawara H,
Kawaguchi O and Hirsoe C: Salinomycin, a new polyether antibiotic.
J Antibiot (Tokyo). 27:814–821. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Daugschies A, Gässlein U and Rommel M:
Comparative efficacy of anticoccidials under the conditions of
commercial broiler production and in battery trials. Vet Parasitol.
76:163–171. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Danforth HD, Ruff MD, Reid WM and Miller
RL: Anticoccidial activity of salinomycin in battery raised broiler
chickens. Poult Sci. 56:926–932. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mahmoudi N, de Julián-Ortiz JV, Ciceron L,
Gálvez J, Mazier D, Danis M, Derouin F and García-Domenech R:
Identification of new antimalarial drugs by linear discriminant
analysis and topological virtual screening. J Antimicrob Chemother.
57:489–497. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Naujokat C, Fuchs D and Opelz G:
Salinomycin in cancer: A new mission for an old agent. Mol Med Rep.
3:555–559. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kopp F, Hermawan A, Oak PS, Ulaganathan
VK, Herrmann A, Elnikhely N, Thakur C, Xiao Z, Knyazev P, Ataseven
B, et al: Sequential salinomycin treatment results in resistance
formation through clonal selection of epithelial-like tumor cells.
Transl Oncol. 7:702–711. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim JH, Chae M, Kim WK, Kim YJ, Kang HS,
Kim HS and Yoon S: Salinomycin sensitizes cancer cells to the
effects of doxorubicin and etoposide treatment by increasing DNA
damage and reducing p21 protein. Br J Pharmacol. 162:773–784. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao Z, Sperl B, Ullrich A and Knyazev P:
Metformin and salinomycin as the best combination for the
eradication of NSCLC monolayer cellsand their alveospheres (cancer
stem cells) irrespective of EGFR, KRAS, EML4/ALK and LKB1 status.
Oncotarget. 5:12877–12890. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Antoszczak M, Popiel K, Stefańska J,
Wietrzyk J, Maj E, Janczak J, Michalska G, Brzezinski B and
Huczyński A: Synthesis, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of
new esters of polyether antibiotic - salinomycin. Eur J Med Chem.
76:435–444. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kopp F, Hermawan A, Oak PS, Herrmann A,
Wagner E and Roidl A: Salinomycin treatment reduces metastatic
tumor burden by hampering cancer cell migration. Mol Cancer.
13:162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huczynski A: Salinomycin: A new cancer
drug candidate. Chem Biol Drug Des. 79:235–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moretti M, Bennett J, Tornatore L,
Thotakura AK and Franzoso G: Cancer: NF-κB regulates energy
metabolism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2238–2243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ni M, Xiong M, Zhang X, Cai G, Chen H,
Zeng Q and Yu Z: Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles
conjugated with CD133 aptamers for targeted salinomycin delivery to
CD133+ osteosarcoma cancer stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine.
10:2537–2554. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhi QM, Chen XH, Ji J, Zhang JN, Li JF,
Cai Q, Liu BY, Gu QL, Zhu ZG and Yu YY: Salinomycin can effectively
kill ALDH (high) stem-like cells on gastric cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 65:509–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song SP, Zhang XG, Wang M, et al: Change
and significance of serum creatine kinase and its isoenzyme in
salinomycin poisoning patients. Zhong Guo Wei Sheng Jian Yan Za
Zhi. 21:28–29. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Cai Z, Tchou-wong KM and Rom WN: NF-kappaB
in lung tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel). 3:4258–4268. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Varfolomeev E, Goncharov T, Maecker H,
Zobel K, Kömüves LG, Deshayes K and Vucic D: Cellular inhibitors of
apoptosis are global regulators of NF-κB and MAPK activation by
members of the TNF family of receptors. Sic Signal. 5:ra222012.
|
|
26
|
Majdalawieh A and Ro HS: Regulation of
IkappaBalpha function and NF-kappaB signaling: AEBP1 is a novel
proinflammatory mediator in macrophages. Mediators Inflamm.
2010:8238212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee HJ, Seo HS, Kim GJ, Jeon CY, Park JH,
Jang BH, Park SJ, Shin YC and Ko SG: Houttuynia cordata Thunb
inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines through
inhibition of the NFκB signaling pathway in HMC-1 human mast cells.
Mol Med Rep. 8:731–736. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ferreiro DU and Komives EA: Molecular
mechanisms of system control of NF-kappaB signaling by
IkappaBalpha. Biochemistry. 49:1560–1567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen S, Dong Y, Xu C, Jiang L, Chen Y,
Jiang C, Hou W and Li W: Involvement of a chromatin modifier in
response to mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP)-induced Sertoli
cell injury: Probably an indirect action via the regulation of
NF-κB/FasL circuitry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 440:749–755.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Travert M, Ame-Thomas P, Pangault C,
Morizot A, Micheau O, Semana G, Lamy T, Fest T, Tarte K and
Guillaudeux T: CD40 ligand protects from TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
follicular lymphomas through NF-kappaB activation and up-regulation
of c-FLIP and Bcl-xL. J Immunol. 181:1001–1111. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang L, Zhao S, Wang HX and Zou P:
Inhibition of NF-kappa B can enhance Fas-mediated apoptosis in
leukemia cell line HL-60. Front Med China. 4:323–328. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Strasser A, Jost PJ and Nagata S: The many
roles of FAS receptor sig-naling in the immune system. Immunity.
30:180–192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mahmood Z and Shukla Y: Death receptors:
Targets for cancer therapy. Exp Cell Res. 316:887–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen L, Park SM, Tumanov AV, Hau A, Sawada
K, Feig C, Turner JR, Fu YX, Romero IL, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
CD95 promotes tumour growth. Nature. 465:492–496. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kong FC, Zhang JQ, Zeng C, Chen WL, Ren
WX, Yan GX, Wang HX, Li QB and Chen ZC: Inhibitory effects of
parthenolide on the activity of NF-κB in multiple myeloma via
targeting TRAF6. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 35:343–349.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Diab S, Fidanzi C, Léger DY, Ghezali L,
Millot M, Martin F, Azar R, Esseily F, Saab A, Sol V, et al:
Berberis libanotica extract targets NF-κB/COX-2, PI3K/Akt and
mitochondrial/caspase signalling to induce human erythroleukemia
cell apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 47:220–230. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gmeiner WH, Jennings-Gee J, Stuart CH and
Pardee TS: Thymineless death in F10-treated AML cells occurs via
lipid raft depletion andFas/FasL co-localization in the plasma
membrane with activation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Leuk
Res. 39:229–235. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu W, Lin YT, Yan XL, Ding YL, Wu YL,
Chen WN and Lin X: Hepatitis B virus core protein inhibits
Fas-mediated apoptosis of hepatoma cells via regulation of
mFas/FasL and sFas expression. FASEB J. 29:1113–1123. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li L, Yao YC, Fang SH, Ma CQ, Cen Y, Xu
ZM, Dai ZY, Li C, Li S, Zhang T, et al: Pigment epithelial-derived
factor (PEDF)-triggered lung cancer cell apoptosis relies on p53
protein-driven Fas ligand (Fas-L) up-regulation and Fas protein
cell surface translocation. J Biol Chem. 289:30785–30799. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
An H, Kim JY, Lee N, Cho Y, Oh E and Seo
JH: Salinomycin possesses anti-tumor activity and inhibits breast
cancer stem-like cells via an apoptosis-independent pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 466:696–703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu PP, Zhu JC, Liu GX, Shui CX and Li XM:
Salinomycin enhances the apoptosis of T-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia cell line jurkat cells induced by vincristine. Zhongguo
Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 23:653–657. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Parajuli B, Shin SJ, Kwon SH, Cha SD,
Chung R, Park WJ, Lee HG and Cho CH: Salinomycin induces apoptosis
via death receptor-5 up-regulation in cisplatin-resistant ovarian
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 33:1457–1462. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|