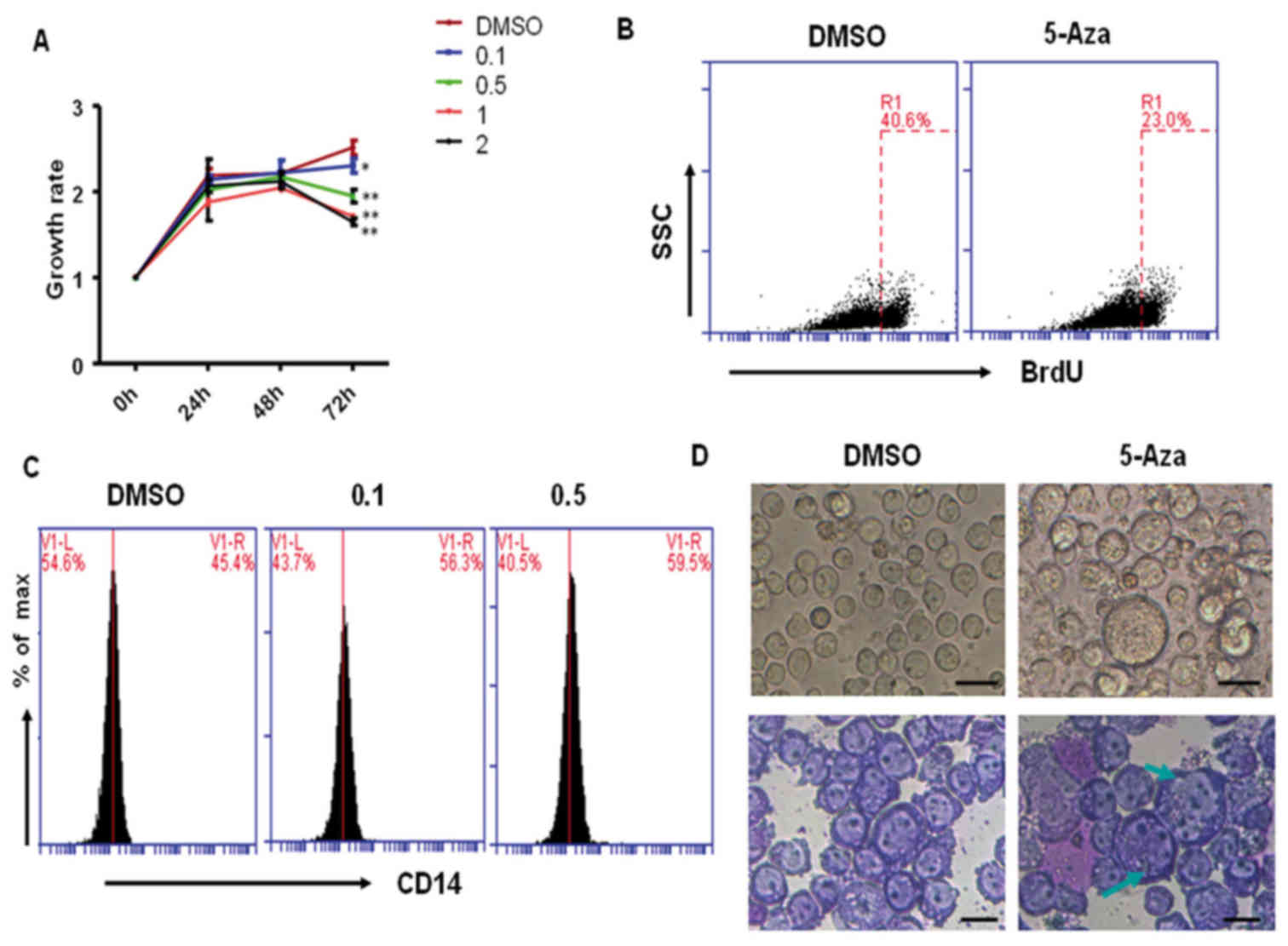
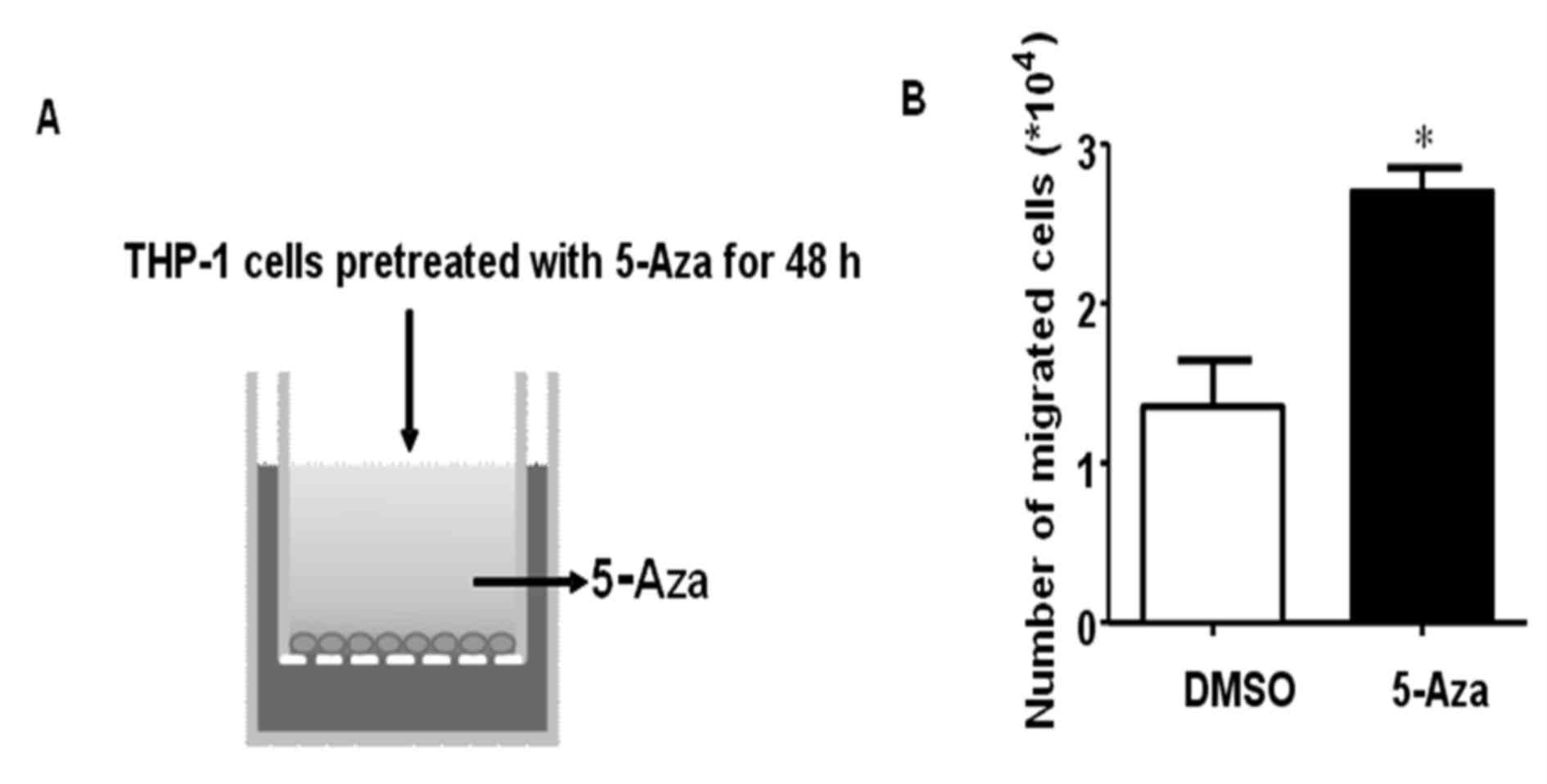
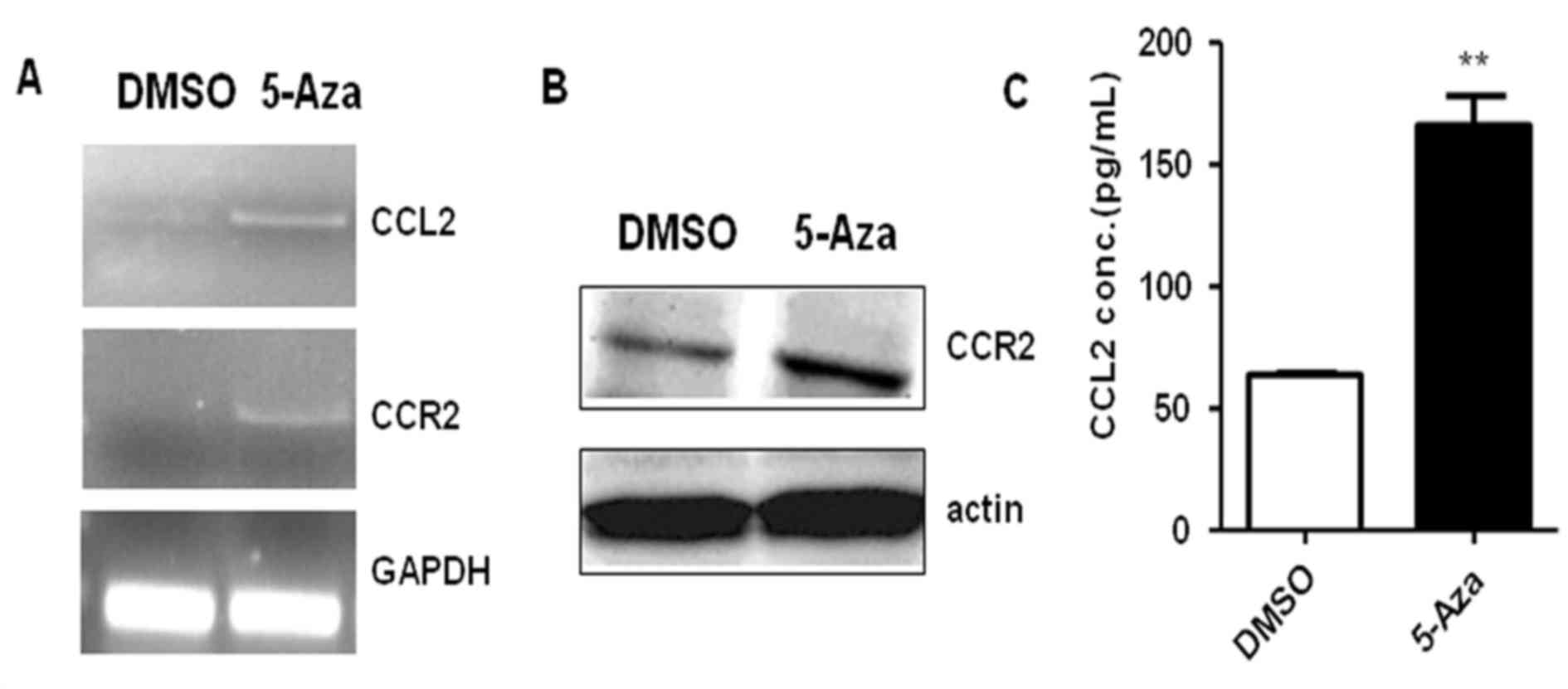
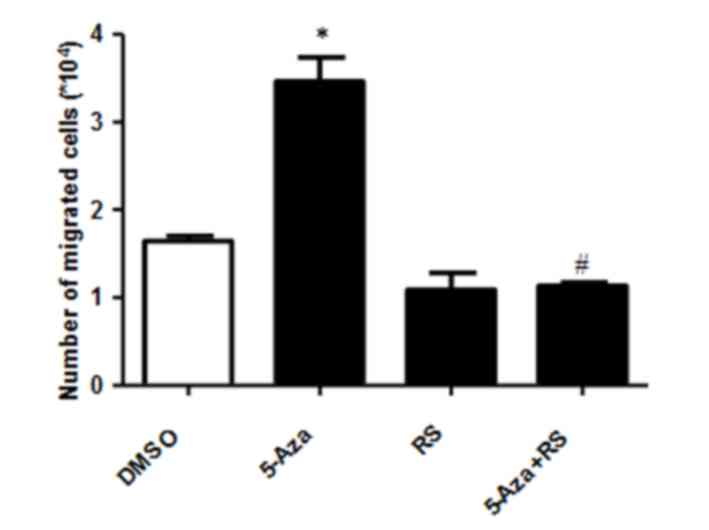
|
1
|
Conway O, Brien E, Prideaux S and
Chevassut T: The epigenetic landscape of acute myeloid leukemia.
Adv Hematol. 2014:1031752014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luesink M, Pennings JL, Wissink WM,
Linssen PC, Muus P, Pfundt R, de Witte TJ, van der Reijden BA and
Jansen JH: Chemokine induction by all-trans retinoic acid and
arsenic trioxide in acute promyelocytic leukemia: Triggering the
differentiation syndrome. Blood. 114:5512–5521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Radujkovic A, Dietrich S, Bochtler T,
Krämer A, Schöning T, Ho AD, Dreger P and Luft T: Azacitidine and
low-dose cytarabine in palliative patients with acute myeloid
leukemia and high bone marrow blast counts-a retrospective
single-center experience. Eur J Haematol. 93:112–117. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Plimack ER, Kantarjian HM and Issa JP:
Decitabine and its role in the treatment of hematopoietic
malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma. 48:1472–1481. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vispé S, Deroide A, Davoine E, Desjobert
C, Lestienne F, Fournier L, Novosad N, Bréand S, Besse J, Busato F,
et al: Consequences of combining siRNA-mediated DNA
methyltransferase 1 depletion with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in human
leukemic KG1 cells. Oncotarget. 6:15265–15282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang F, Dai X and Wang Y:
5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine induced growth inhibition of leukemia cells
through modulating endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 11:M111.0169152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shin DY, Park YS, Yang K, Kim GY, Kim WJ,
Han MH, Kang HS and Choi YH: Decitabine, a DNA methyltransferase
inhibitor, induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells through
intracellular reactive oxygen species generation. Int J Oncol.
41:910–918. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding B, Wang Z, Jiang X, Li X, Wang C,
Zhong Q, Jiang L, Dai M, Zhang YU, Wei QI and Meng F: Palliative
chemotherapy followed by methylation inhibitor in high-risk acute
myeloid leukemia: An in vitro and clinical study. Mol Clin Oncol.
3:1139–1144. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E,
Santini V, Finelli C, Giagounidis A, Schoch R, Gattermann N, Sanz
G, List A, et al: Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of
conventional care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk
myelodysplastic syndromes: A randomised, open-label, phase III
study. Lancet Oncol. 10:223–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bernal T, Moncada-Pazos A, Soria-Valles C
and Gutiérrez-Fernández A: Effects of azacitidine on matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasia.
Exp Hematol. 41:172–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Poplineau M, Schnekenburger M, Dufer J,
Kosciarz A, Brassart-Pasco S, Antonicelli F, Diederich M and
Trussardi-Régnier A: The DNA hypomethylating agent,
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine, enhances tumor cell invasion through a
transcription-dependent modulation of MMP-1 expression in human
fibrosarcoma cells. Mol Carcinog. 54:24–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hassan HT, Veit A and Maurer HR:
Synergistic interactions between differentiation-inducing agents in
inhibiting the proliferation of HL-60 human myeloid leukaemia cells
in clonogenic micro assays. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 117:227–231.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S and Sawaya
BE: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uenogawa K, Hatta Y, Arima N, Hayakawa S,
Sawada U, Aizawa S, Yamamoto T and Takeuchi J: Azacitidine induces
demethylation of p16INK4a and inhibits growth in adult T-cell
leukemia/lymphoma. Int J Mol Med. 28:835–839. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Su Y, Xu H, Xu Y, Yu J, Xian Y and Luo Q:
Azacytidine inhibits the proliferation of human promyelocytic
leukemia cells (HL60) by demethylation of MGMT, DAPK and p16 genes.
Hematology. 17:41–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kimura S, Kuramoto K, Homan J, Naruoka H,
Ego T, Nogawa M, Sugahara S and Naito H: Antiproliferative and
antitumor effects of azacitidine against the human myelodysplastic
syndrome cell line SKM-1. Anticancer Res. 32:795–798.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ufkin ML, Peterson S, Yang X, Driscoll H,
Duarte C and Sathyanarayana P: miR-125a regulates cell cycle,
proliferation, and apoptosis by targeting the ErbB pathway in acute
myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 38:402–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao XN, Lin J, Li YH, Gao L, Wang XR, Wang
W, Kang HY, Yan GT, Wang LL and Yu L: MicroRNA-193a represses c-kit
expression and functions as a methylation-silenced tumor suppressor
in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene. 30:3416–3428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nishi M, Eguchi-Ishimae M, Wu Z, Gao W,
Iwabuki H, Kawakami S, Tauchi H, Inukai T, Sugita K, Hamasaki Y, et
al: Suppression of the let-7b microRNA pathway by DNA
hypermethylation in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia with MLL
gene rearrangements. Leukemia. 27:389–397. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koschmieder S, Agrawal S, Radomska HS,
Huettner CS, Tenen DG, Ottmann OG, Berdel WE, Serve HL and
Müller-Tidow C: Decitabine and vitamin D3 differentially affect
hematopoietic transcription factors to induce monocytic
differentiation. Int J Oncol. 30:349–355. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen HM, Zhang P, Voso MT, Hohaus S,
Gonzalez DA, Glass CK, Zhang DE and Tenen DG: Neutrophils and
monocytes express high levels of PU.1 (Spi-1) but not Spi-B. Blood.
85:2918–2928. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aoyama S, Nakano H, Danbara M, Higashihara
M, Harigae H and Takahashi S: The differentiating and apoptotic
effects of 2-aza-5′-deoxycytidine are dependent on the PU.1
expression level in PU.1-transgenic K562 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 420:775–781. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alberich-Jordà M, Wouters B, Balastik M,
Shapiro-Koss C, Zhang H, Di Ruscio A, Radomska HS, Ebralidze AK,
Amabile G, Ye M, et al: C/EBPγ deregulation results in
differentiation arrest in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest.
122:4490–4504. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chuang LP, Chen NH, Lin SW, Chang YL, Liao
HR, Lin YS, Chao IJ, Lin Y and Pang JH: Increased C-C chemokine
receptor 2 gene expression in monocytes of severe obstructive sleep
apnea patients and under intermittent hypoxia. PLoS One.
9:e1133042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang J, Lv X, Chen J, Xie C, Xia W, Jiang
C, Zeng T, Ye Y, Ke L, Yu Y, et al: CCL2-CCR2 axis promotes
metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by activating ERK1/2-MMP2/9
pathway. Oncotarget. 7:15632–15647. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Udaka K and
Yokoyama A: Simultaneous inhibition of DNA methyltransferase and
histone deacetylase induces p53-independent apoptosis via
down-regulation of Mcl-1 in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leuk
Res. 35:932–939. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi YJ, Yoon JH, Cha SW and Lee SG:
Ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the invasion and migration of THP-1 acute
monocytic leukemia cells via inactivation of the MAPK signaling
pathway. Fitoterapia. 82:911–919. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|