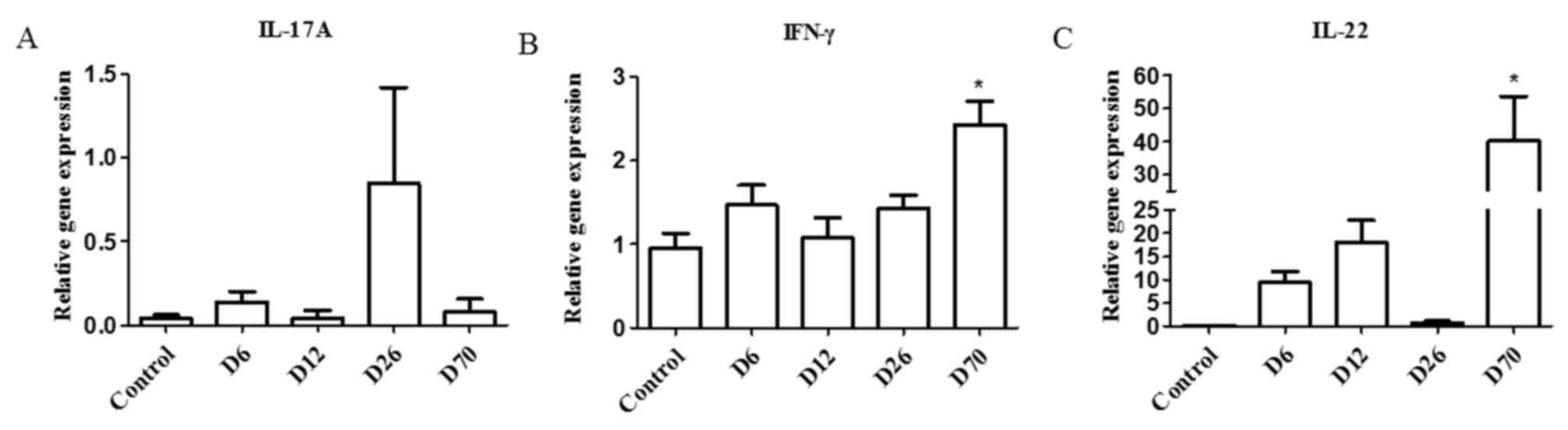
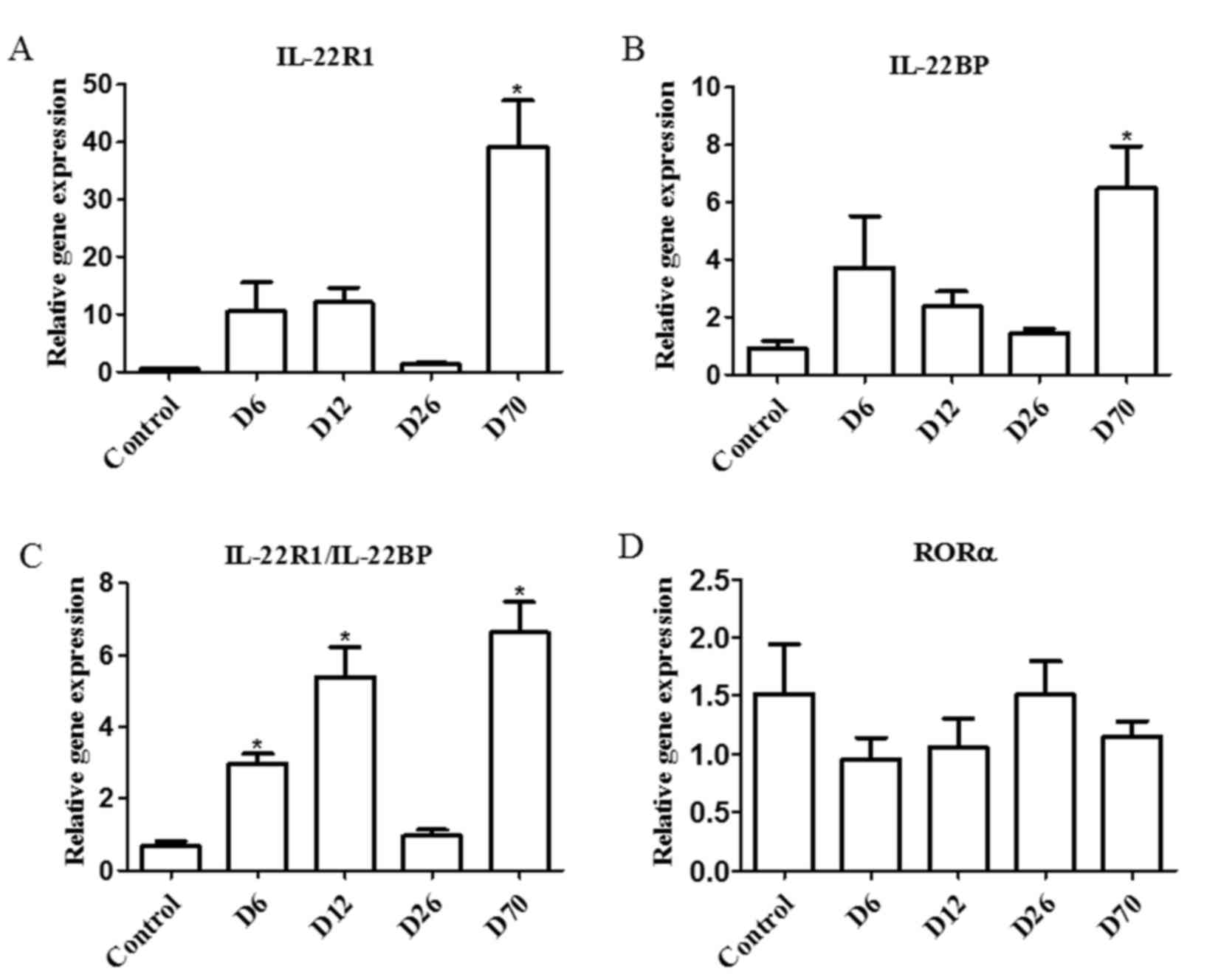
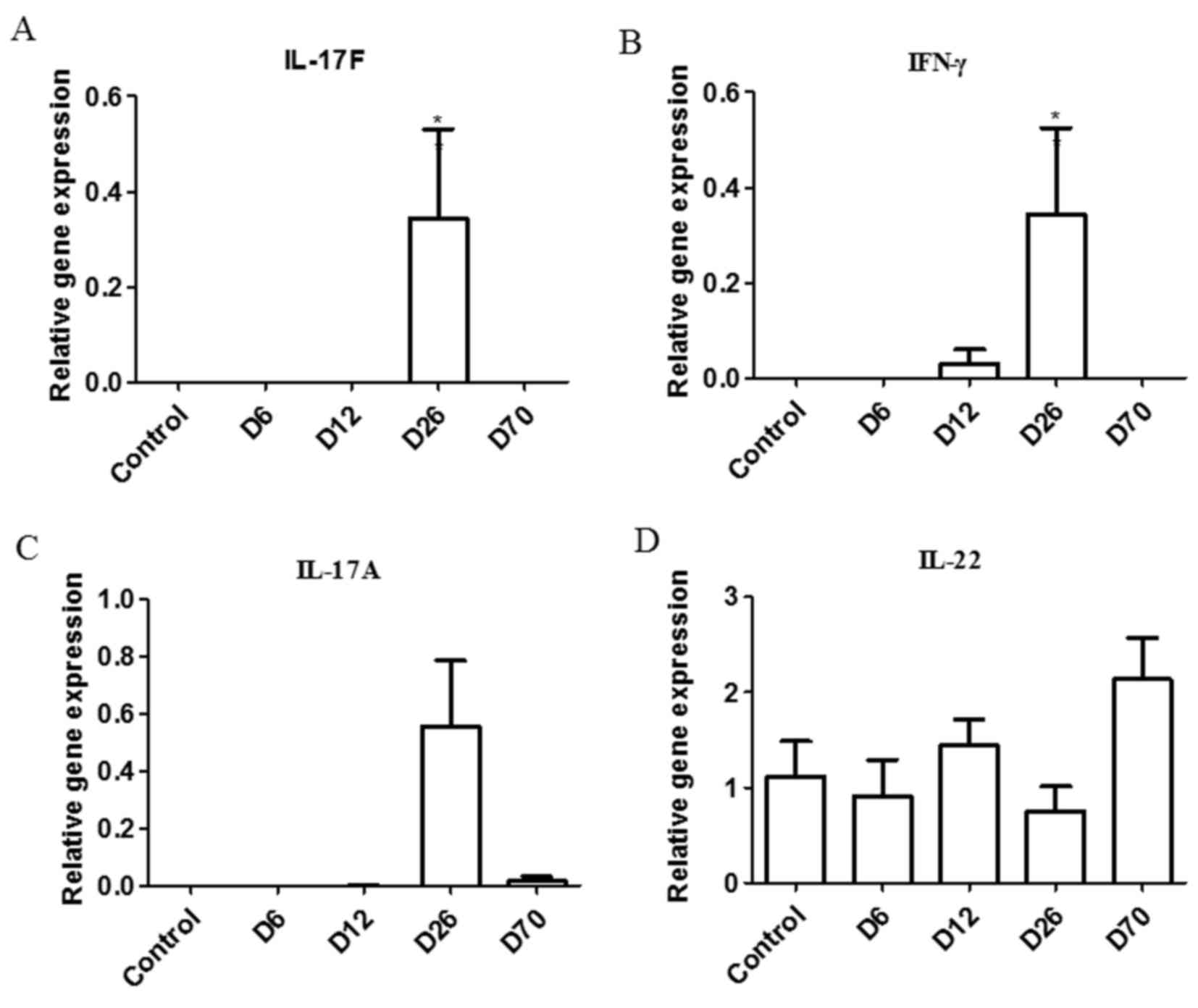
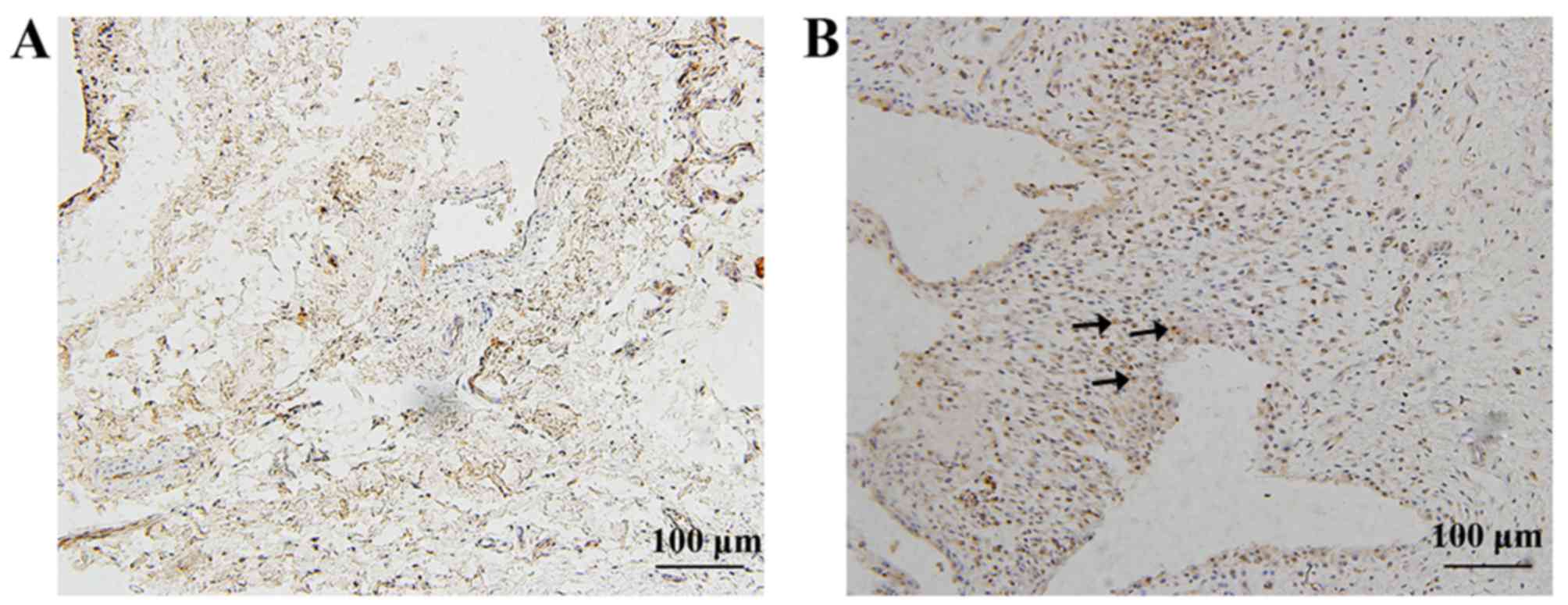
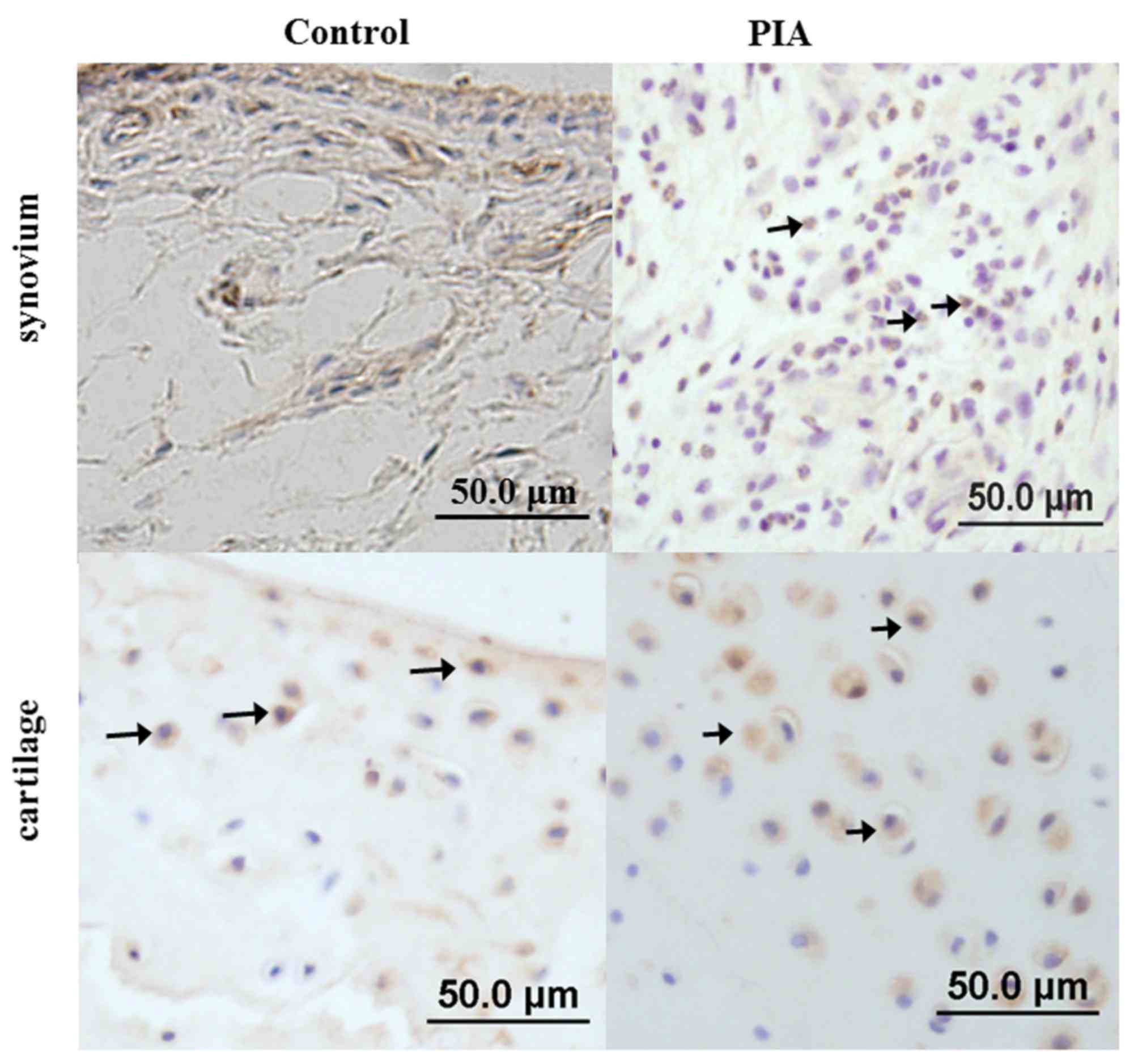
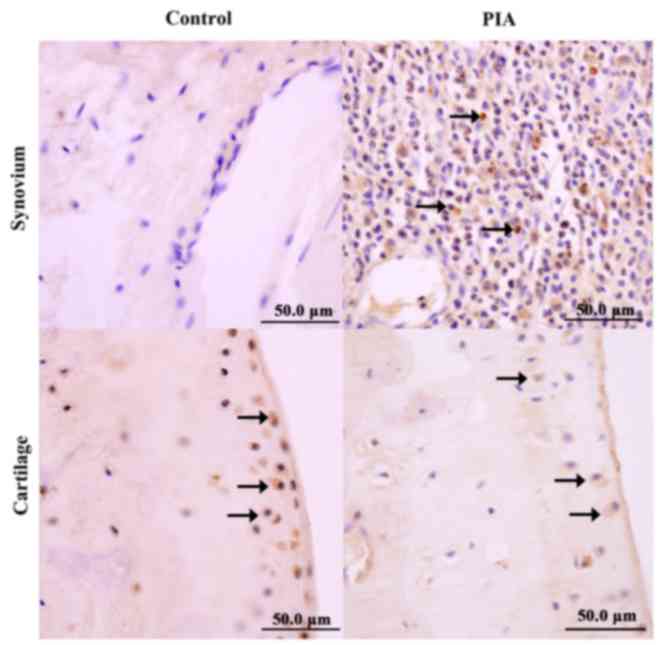
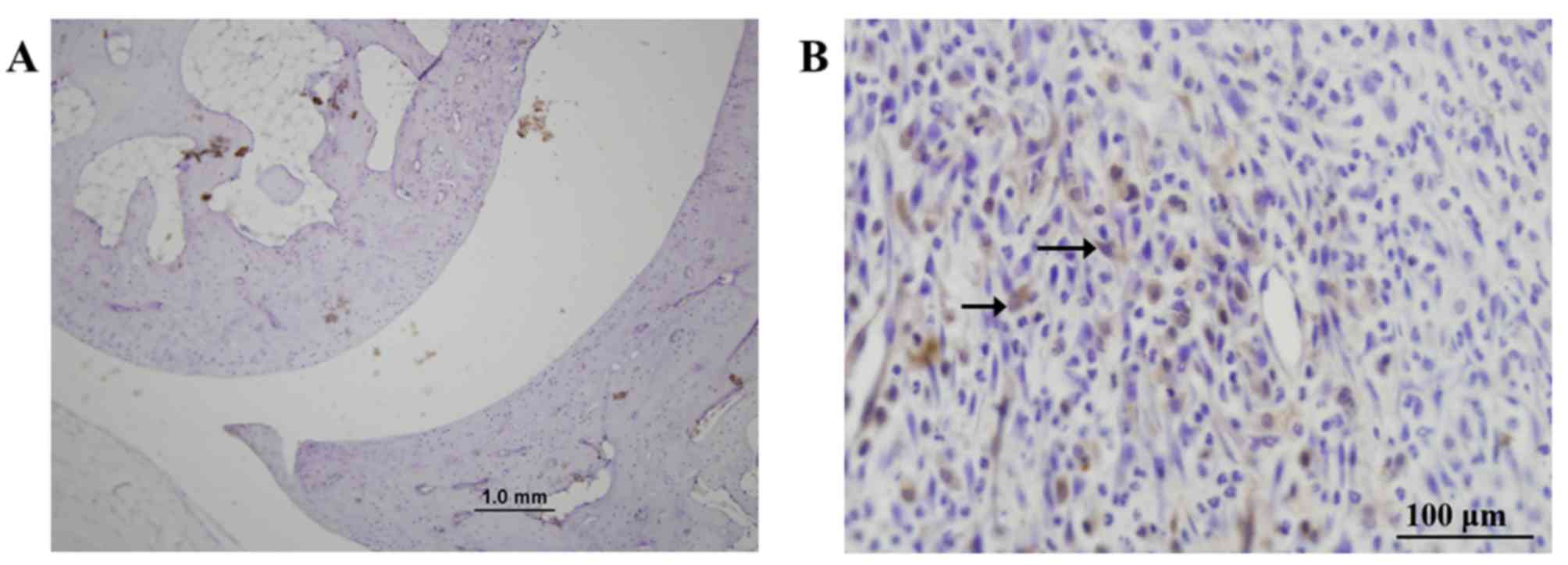
|
1
|
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay
S and Pap T: Synovial fibroblasts: Key players in rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 45:669–675. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Mahony R, Richards A, Deighton C and
Scott D: Withdrawal of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:1823–1826. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hou W, Meng L, Tian L, Zhu W, Jiang C and
Lu S: A systematic comparison between collagen-induced arthritis
and pristane-induced arthritis in Dark Agouti rats. Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 28:532–538. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vingsbo C, Sahlstrand P, Brun JG, Jonsson
R, Saxne T and Holmdahl R: Pristane-induced arthritis in rats: A
new model for rheumatoid arthritis with a chronic disease course
influenced by both major histocompatibility complex and non-major
histocompatibility. complex genes. 149:1675–1683. 1996.
|
|
5
|
Lu S, Nordquist N, Holmberg J, Olofsson P,
Pettersson U and Holmdahl R: Both common and unique susceptibility
genes in different rat strains with pristane-induced arthritis. Eur
J Hum Genet. 10:475–483. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Holmberg J, Tuncel J, Yamada H, Lu S,
Olofsson P and Holmdahl R: Pristane, a non-antigenic adjuvant,
induces MHC class II-restricted, arthritogenic T cells in the rat.
J Immunol. 176:1172–1179. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR,
Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM and Weaver CT: Interleukin
17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage
distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol.
6:1123–1132. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Solt LA, Kumar N, Nuhant P, Wang Y, Lauer
JL, Liu J, Istrate MA, Kamenecka TM, Roush WR, Vidović D, et al:
Suppression of TH17 differentiation and autoimmunity by a synthetic
ROR ligand. Nature. 472:491–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duhen T, Geiger R, Jarrossay D,
Lanzavecchia A and Sallusto F: Production of interleukin 22 but not
interleukin 17 by a subset of human skin-homing memory T cells. Nat
Immunol. 10:857–863. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wolk K, Witte E, Witte K, Warszawska K and
Sabat R: Biology of interleukin-22. Semin Immunopathol. 32:17–31.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dumoutier L, Lejeune D, Colau D and
Renauld JC: Cloning and characterization of IL-22 binding protein,
a natural antagonist of IL-10-related T cell-derived inducible
factor/IL-22. J Immunol. 166:7090–7095. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sarkar S, Justa S, Brucks M, Endres J, Fox
DA, Zhou X, Alnaimat F, Whitaker B, Wheeler JC, Jones BH and
Bommireddy SR: Interleukin (IL)-17A, F and AF in inflammation: A
study in collagen-induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin
Exp Immunol. 177:652–661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ziolkowska M, Koc A, Luszczykiewicz G,
Ksiezopolska-Pietrzak K, Klimczak E, Chwalinska-Sadowska H and
Maslinski W: High levels of IL-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients:
IL-15 triggers in vitro IL-17 production via cyclosporin
A-sensitive mechanism. J Immunol. 164:2832–2838. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ikeuchi H, Kuroiwa T, Hiramatsu N, Kaneko
Y, Hiromura K, Ueki K and Nojima Y: Expression of interleukin-22 in
rheumatoid arthritis: Potential role as a proinflammatory cytokine.
Arthritis Rheum. 52:1037–1046. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sarkar S, Zhou X, Justa S and Bommireddy
SR: Interleukin-22 reduces the severity of collagen-induced
arthritis in association with increased levels of interleukin-10.
Arthritis Rheum. 65:960–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Olofsson P and Holmdahl R:
Pristane-induced arthritis in the rat. Methods Mol Med.
136:255–268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Geboes L, Dumoutier L, Kelchtermans H,
Schurgers E, Mitera T, Renauld JC and Matthys P: Proinflammatory
role of the Th17 cytokine interleukin-22 in collagen-induced
arthritis in C57BL/6 mice. Arthritis Rheum. 60:390–395. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pinto LG, Talbot J, Peres RS, Franca RF,
Ferreira SH, Ryffel B, Aves-Filho JC, Figueiredo F, Cunha TM and
Cunha FQ: Joint production of IL-22 participates in the initial
phase of antigen-induced arthritis through IL-1β production.
Arthritis Res Ther. 17:2352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fossiez F, Djossou O, Chomarat P,
Flores-Romo L, Ait-Yahia S, Maat C, Pin JJ, Garrone P, Garcia E,
Saeland S, et al: T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to
produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J Exp Med.
183:2593–2603. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jovanovic DV, Di Battista JA,
Martel-Pelletier J, Jolicoeur FC, He Y, Zhang M, Mineau F and
Pelletier JP: IL-17 stimulates the production and expression of
proinflammatory cytokines, IL-beta and TNF-alpha, by human
macrophages. J Immunol. 160:3513–3521. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Katz Y, Nadiv O and Beer Y: Interleukin-17
enhances tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced synthesis of
interleukins 1,6 and 8 in skin and synovial fibroblasts: A possible
role as a ‘fine-tuning cytokine’ in inflammation processes.
Arthritis Rheum. 44:2176–2184. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N,
Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, Saito S, Inoue K, Kamatani N,
Gillespie MT, et al: IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with
rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis.
J Clin Invest. 103:1345–1352. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jovanovic DV, Di Battista JA,
Martel-Pelletier J, Jolicoeur FC, He Y, Zhang M, Mineau F and
Pelletier JP: IL-17 stimulates the production and expression of
proinflammatory cytokines, IL-beta and TNF-alpha, by human
macrophages. J Immunol. 160:3513–3521. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N,
Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, Saito S, Inoue K, Kamatani N,
Gillespie MT, et al: IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with
rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis.
J Clin Invest. 103:1345–1352. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chabaud M, Garnero P, Dayer JM, Guerne PA,
Fossiez F and Miossec P: Contribution of interleukin 17 to synovium
matrix destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. 12:1092–1099.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Benderdour M, Tardif G, Pelletier JP, Di
Battista JA, Reboul P, Ranger P and Martel-Pelletier J: Interleukin
17 (IL-17) induces collagenase-3 production in human osteoarthritic
chondrocytes via AP-1 dependent activation: Differential activation
of AP-1 members by IL-17 and IL-1beta. J Rheumatol. 29:1262–1272.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koshy PJ, Henderson N, Logan C, Life PF,
Cawston TE and Rowan AD: Interleukin 17 induces cartilage collagen
breakdown: Novel synergistic effects in combination with
proinflammatory cytokines. Ann Rheum Dis. 61:704–713. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grassi W, de Angelis R, Lamanna G and
Cervini C: The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J
Radiol. 27 Suppl 1:S18–S24. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Marijnissen RJ, Koenders MI, Smeets RL,
Stappers MH, Nickerson-Nutter C, Joosten LA, Boots AM and van den
Berg WB: Increased expression of interleukin-22 by synovial Th17
cells during late stages of murine experimental arthritis is
controlled by interleukin-1 and enhances bone degradation.
Arthritis Rheum. 63:2939–2948. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|