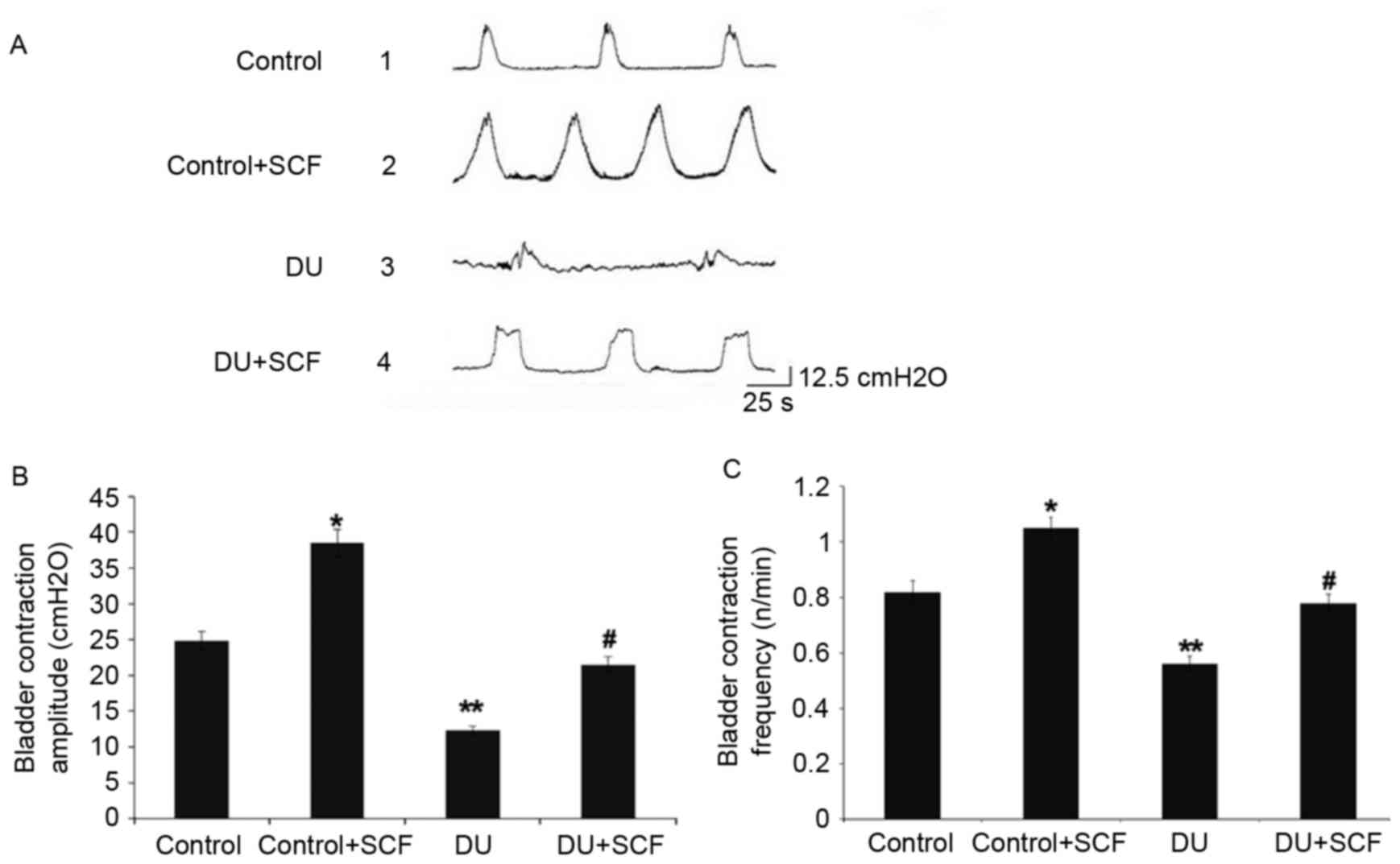
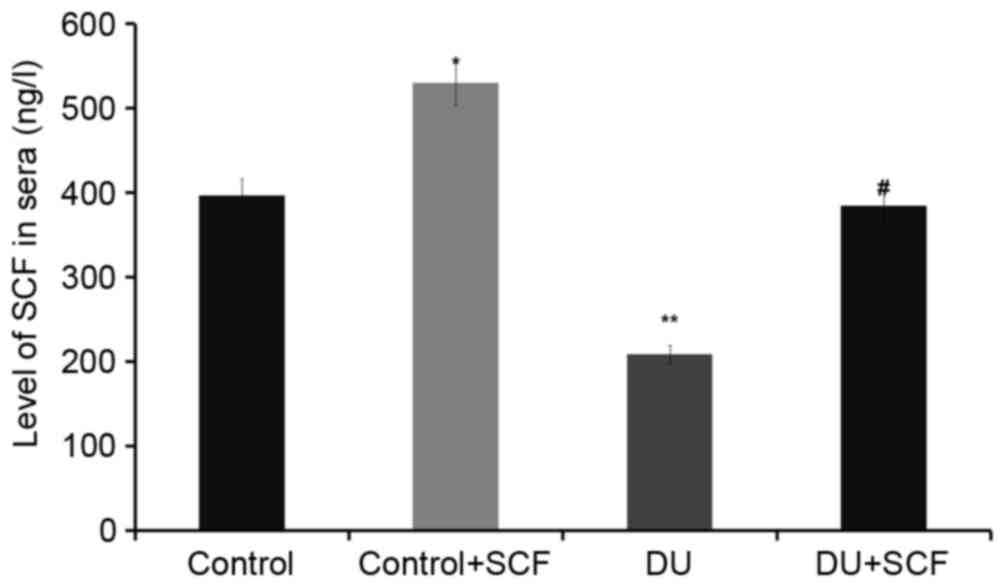
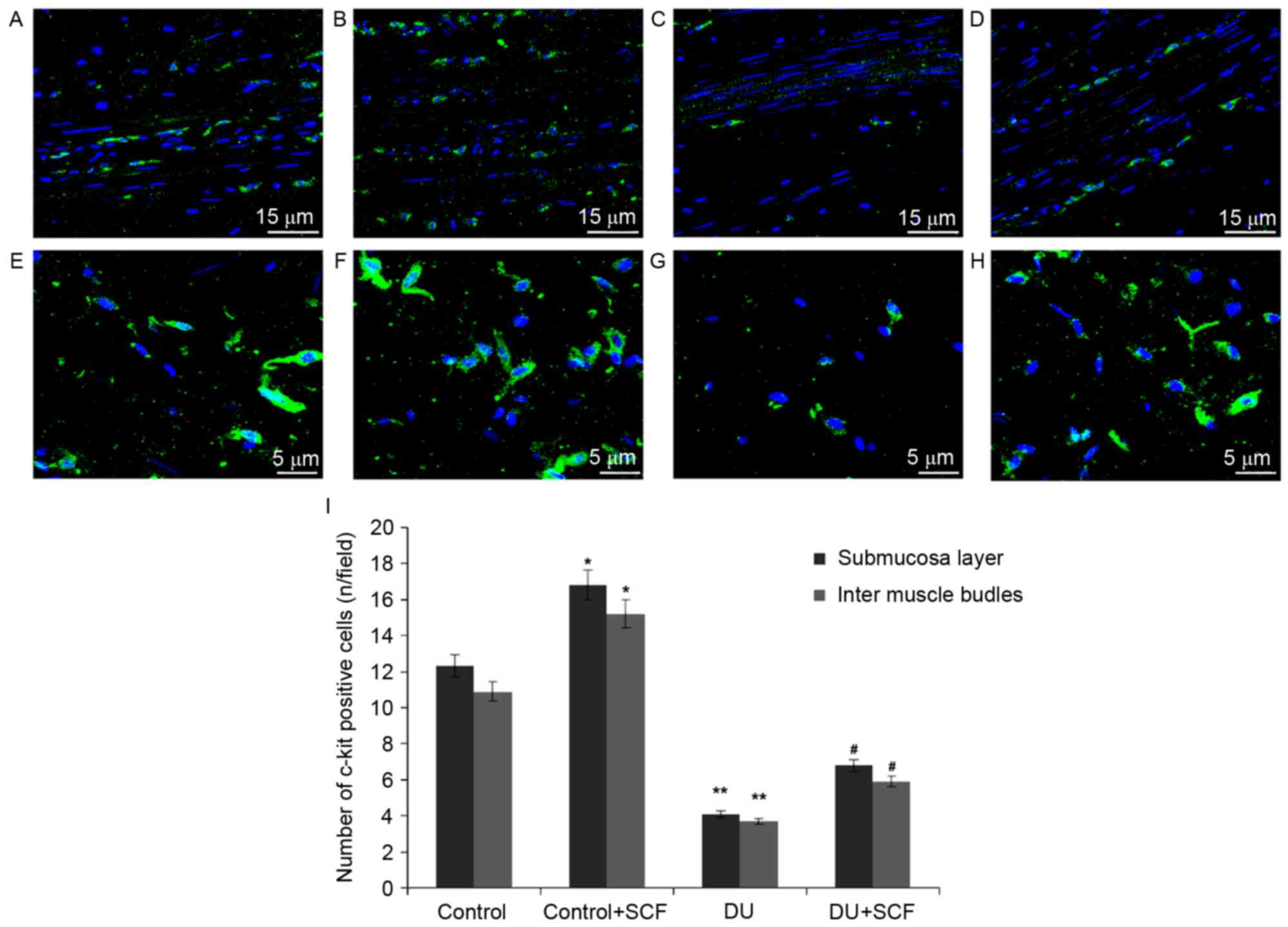
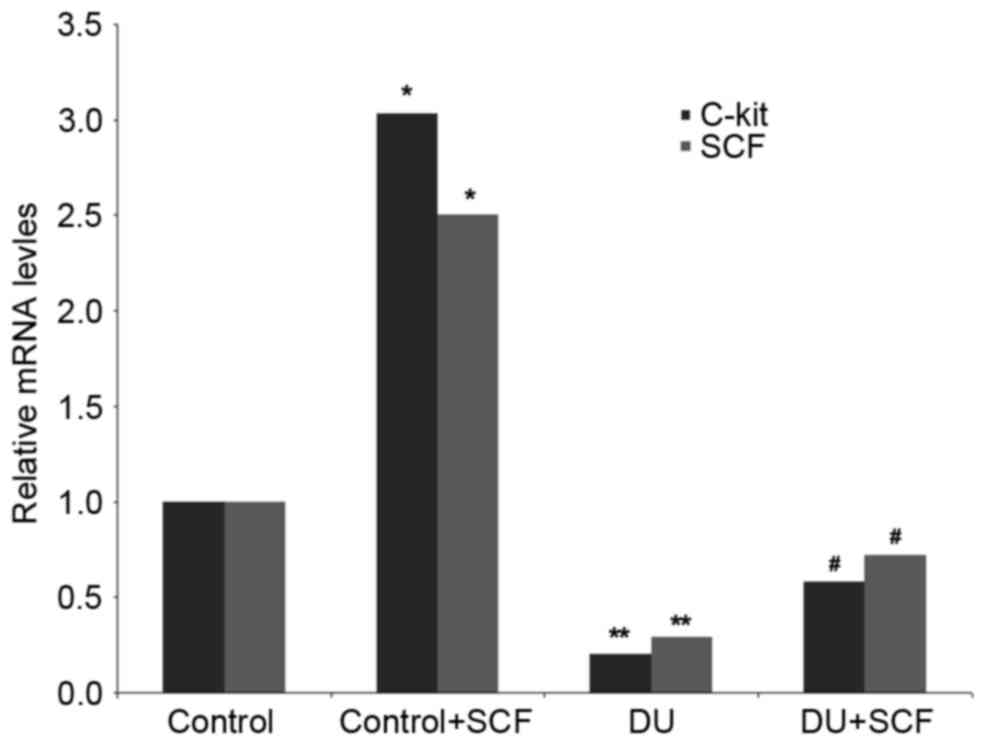
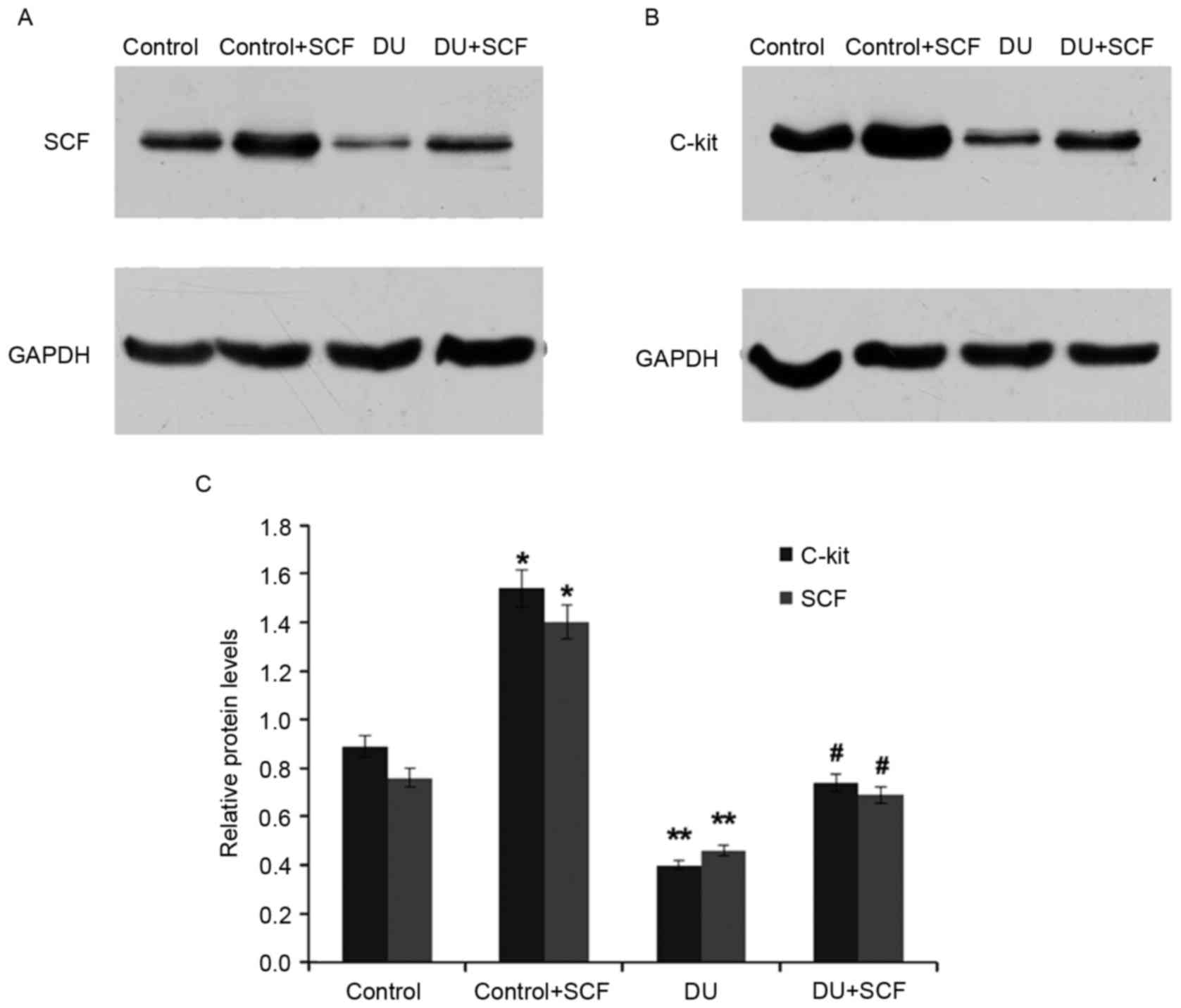
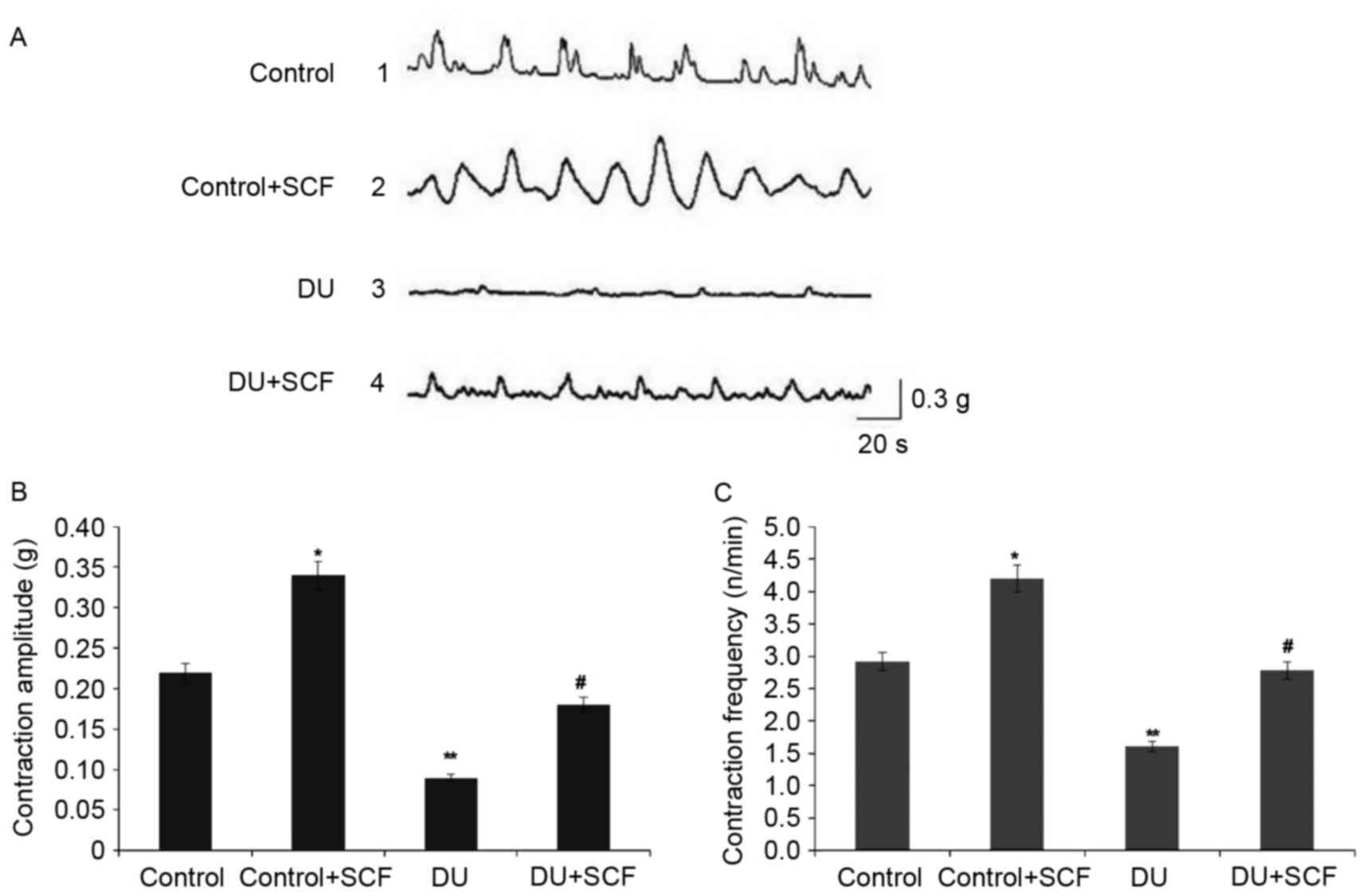
|
1
|
Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D,
Rosier P, Ulmsten U, van Kerrebroeck P, Victor A and Wein A:
Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence
Society: The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract
function: Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the
International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 21:167–178.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Taylor JA III and Kuchel GA: Detrusor
underactivity: Clinical features and pathogenesis of an
underdiagnosed geriatric condition. J Am Geriatr Soc. 54:1920–1932.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lorincz A, Redelman D, Horvath VJ,
Bardsley MR, Chen H and Ordög T: Progenitors of interstitial cells
of cajal in the postnatal murine stomach. Gastroenterology.
134:1083–1093. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Horvath VJ, Vittal H, Lörincz A, Chen H,
Almeida-Porada G, Redelman D and Ordög T: Reduced stem cell factor
links smooth myopathy and loss of interstitial cells of cajal in
murine diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology. 130:759–770. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nishimura M, Koda K, Oda K, Seike K,
Shimizu K and Miyazaki M: Mesenteric transection decreases
expression of interstitial cells of Cajal in an experimental model.
Br J Surg. 94:483–490. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Wershil BK: The c-kit
receptor, stem cell factor, and mast cells. What each is teaching
us about the others. Am J Pathol. 142:965–974. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Torihashi S, Nishi K, Tokutomi Y, Nishi T,
Ward S and Sanders KM: Blockade of kit signaling induces
transdifferentiation of interstitial cells of cajal to a smooth
muscle phenotype. Gastroenterology. 117:140–148. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu JJ, Rothman TP and Gershon MD:
Development of the interstitial cell of Cajal: Origin, kit
dependence and neuronal and nonneuronal sources of kit ligand. J
Neurosci Res. 59:384–401. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Forrest A, Huizinga JD, Wang XY, Liu LW
and Parsons M: Increase in stretch-induced rhythmic motor activity
in the diabetic rat colon is associated with loss of ICC of the
submuscular plexus. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
294:G315–G326. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamamoto T, Watabe K, Nakahara M, Ogiyama
H, Kiyohara T, Tsutsui S, Tamura S, Shinomura Y and Hayashi N:
Disturbed gastrointestinal motility and decreased interstitial
cells of Cajal in diabetic db/db mice. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
23:660–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kubota M, Kanda E, Ida K, Sakakihara Y and
Hayashi M: Severe gastrointestinal dysmotility in a patient with
congenital myopathy: Causal relationship to decrease of
interstitial cells of Cajal. Brain Dev. 27:447–450. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomsen L, Robinson TL, Lee JC, Farraway
LA, Hughes MJ, Andrews DW and Huizinga JD: Interstitial cells of
Cajal generate a rhythmic pacemaker current. Nat Med. 4:848–851.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin L, Xu LM, Zhang W, Ge YB, Tang YR,
Zhang HJ, Li XL and Chen JD: Roles of stem cell factor on the
depletion of interstitial cells of Cajal in the colon of diabetic
mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:G241–G247. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lang RJ, Tonta MA, Zoltkowski BZ, Meeker
WF, Wendt I and Parkington HC: Pyeloureteric peristalsis: Role of
atypical smooth muscle cells and interstitial cells of Cajal-like
cells as pacemakers. J Physiol. 576:695–705. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pezzone MA, Watkins SC, Alber SM, King WE,
de Groat WC, Chancellor MB and Fraser MO: Identification of
c-kit-positive cells in the mouse ureter: The interstitial cells of
Cajal of the urinary tract. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
284:F925–F929. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang X, Zhang Y and Hu J: The expression
of Cajal cells at the obstruction site of congenital pelviureteric
junction obstruction and quantitative image analysis. J Pediatr
Surg. 44:2339–2342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McCloskey KD and Gurney AM: Kit positive
cells in the guinea pig bladder. J Urol. 168:832–836. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davidson RA and McCloskey KD: Morphology
and localization of interstitial cells in the guinea pig bladder:
Structural relationships with smooth muscle and neurons. J Urol.
173:1385–1390. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim SO, Song SH, Ahn KY and Kwon DD:
Distribution of interstitial cells of cajal in menopausal rat
urinary bladder showing detrusor overactivity. Int Neurourol J.
14:48–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kubota Y, Kojima Y, Shibata Y, Imura M,
Sasaki S and Kohri K: Role of KIT-positive interstitial cells of
Cajal in the urinary bladder and possible therapeutic target for
overactive bladder. Adv Urol. 2011:8163422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sutherland RS, Baskin LS, Kogan BA and
Cunha G: Neuroanatomical changes in the rat bladder after bladder
outlet obstruction. Br J Urol. 82:895–901. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Fang Q, Lu Y, Song B, Li W and Li
L: Effects of mechanical stretch on interstitial cells of Cajal in
guinea pig bladder. J Surg Res. 164:e213–e219. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim SO, Oh BS, Chang IY, Song SH, Ahn K,
Hwang EC, Oh KJ, Kwon D and Park K: Distribution of interstitial
cells of Cajal and expression of nitric oxide synthase after
experimental bladder outlet obstruction in a rat model of bladder
overactivity. Neurourol Urodyn. 30:1639–1645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kubota Y, Hashitani H, Shirasawa N, Kojima
Y, Sasaki S, Mabuchi Y, Soji T, Suzuki H and Kohri K: Altered
distribution of interstitial cells in the guinea pig bladder
following bladder outlet obstruction. Neurourol Urodyn. 27:330–340.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nakahara M, Isozaki K, Vanderwinden JM,
Shinomura Y, Kitamura Y, Hirota S and Matsuzawa Y: Dose-dependent
and time-limited proliferation of cultured murine interstitial
cells of Cajal in response to stem cell factor. Life Sci.
70:2367–2376. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tong W, Jia H, Zhang L, Li C, Ridolfi TJ
and Liu B: Exogenous stem cell factor improves interstitial cells
of Cajal restoration after blockade of c-kit signaling pathway.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 45:844–851. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|