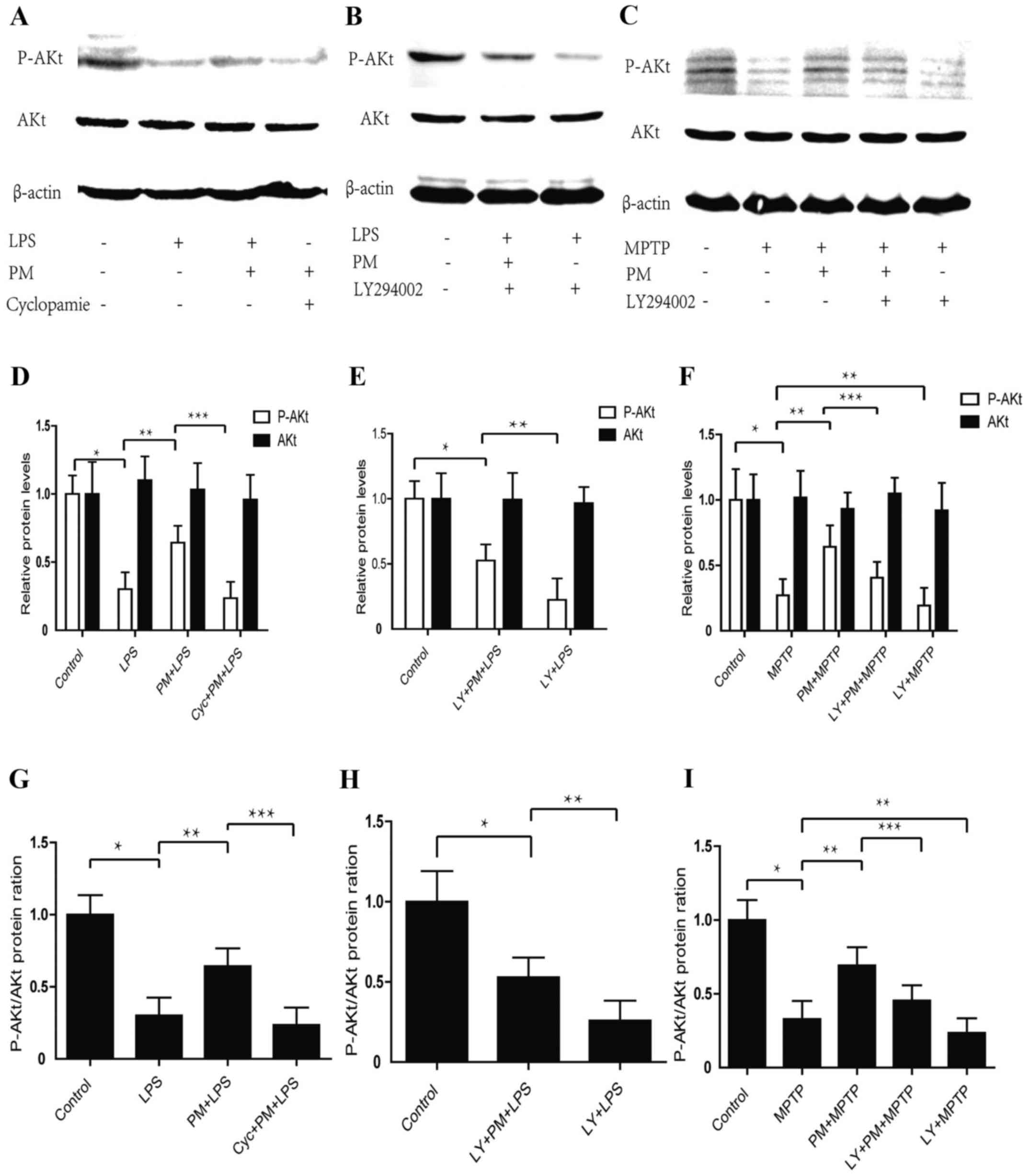
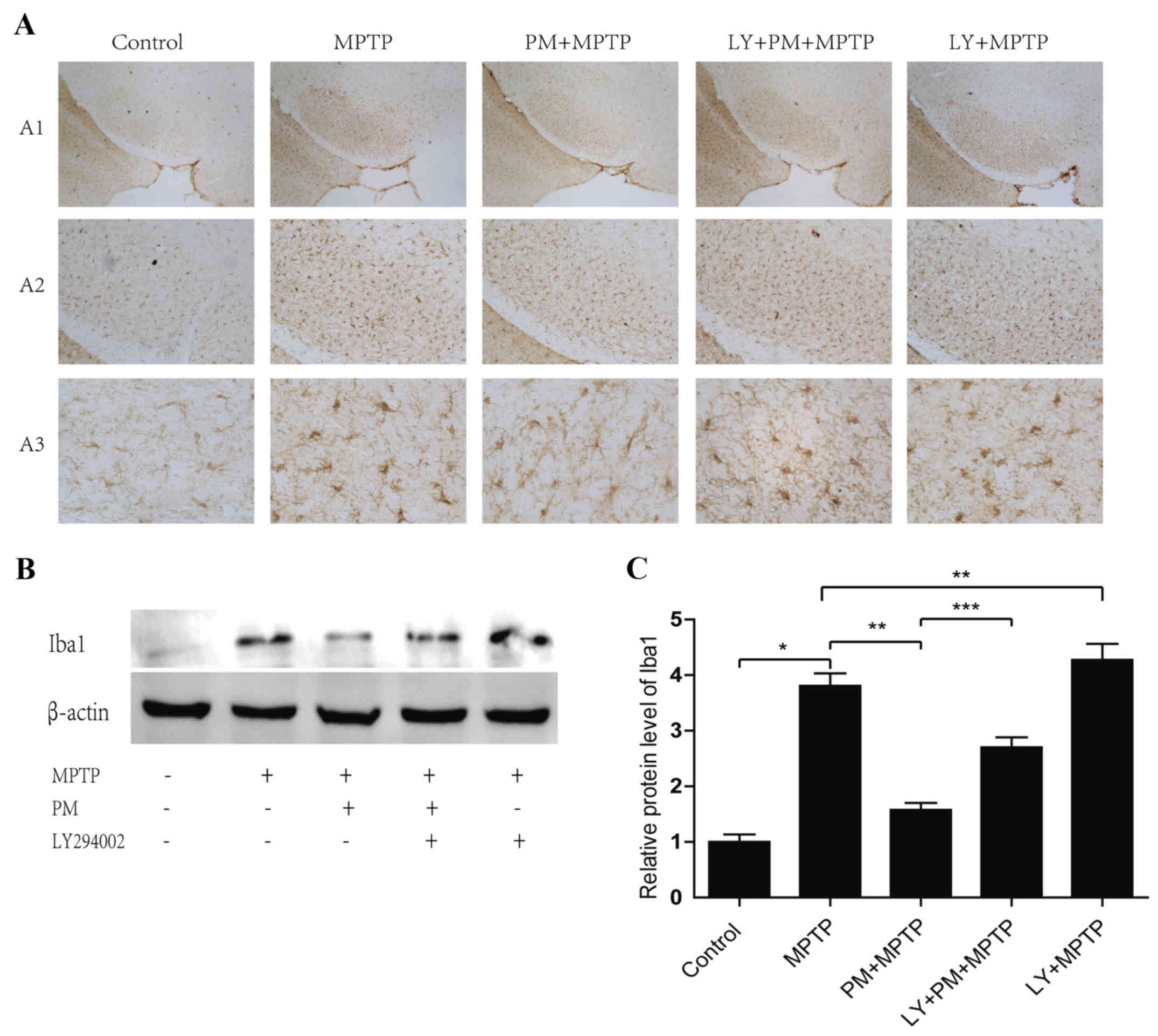
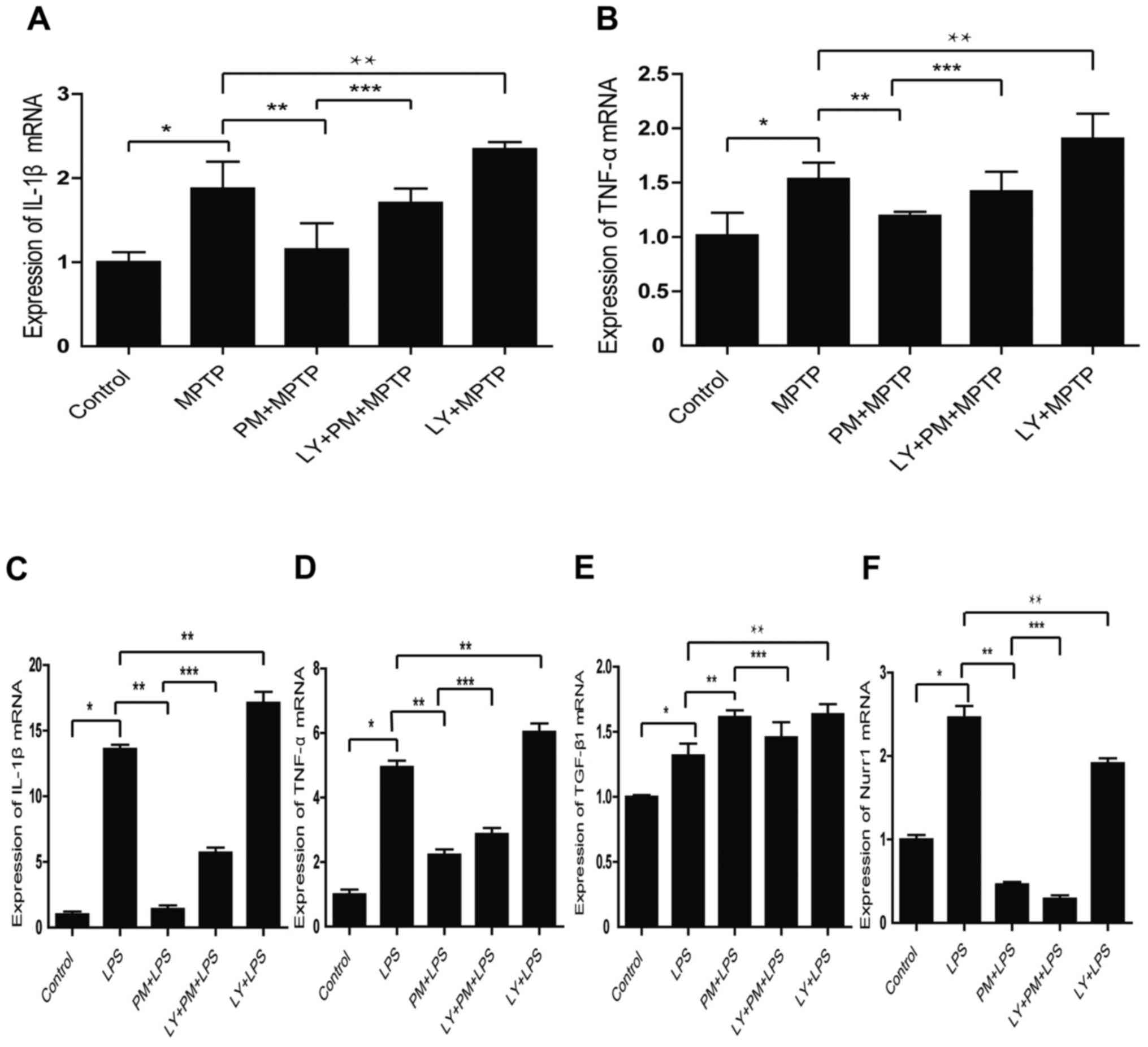
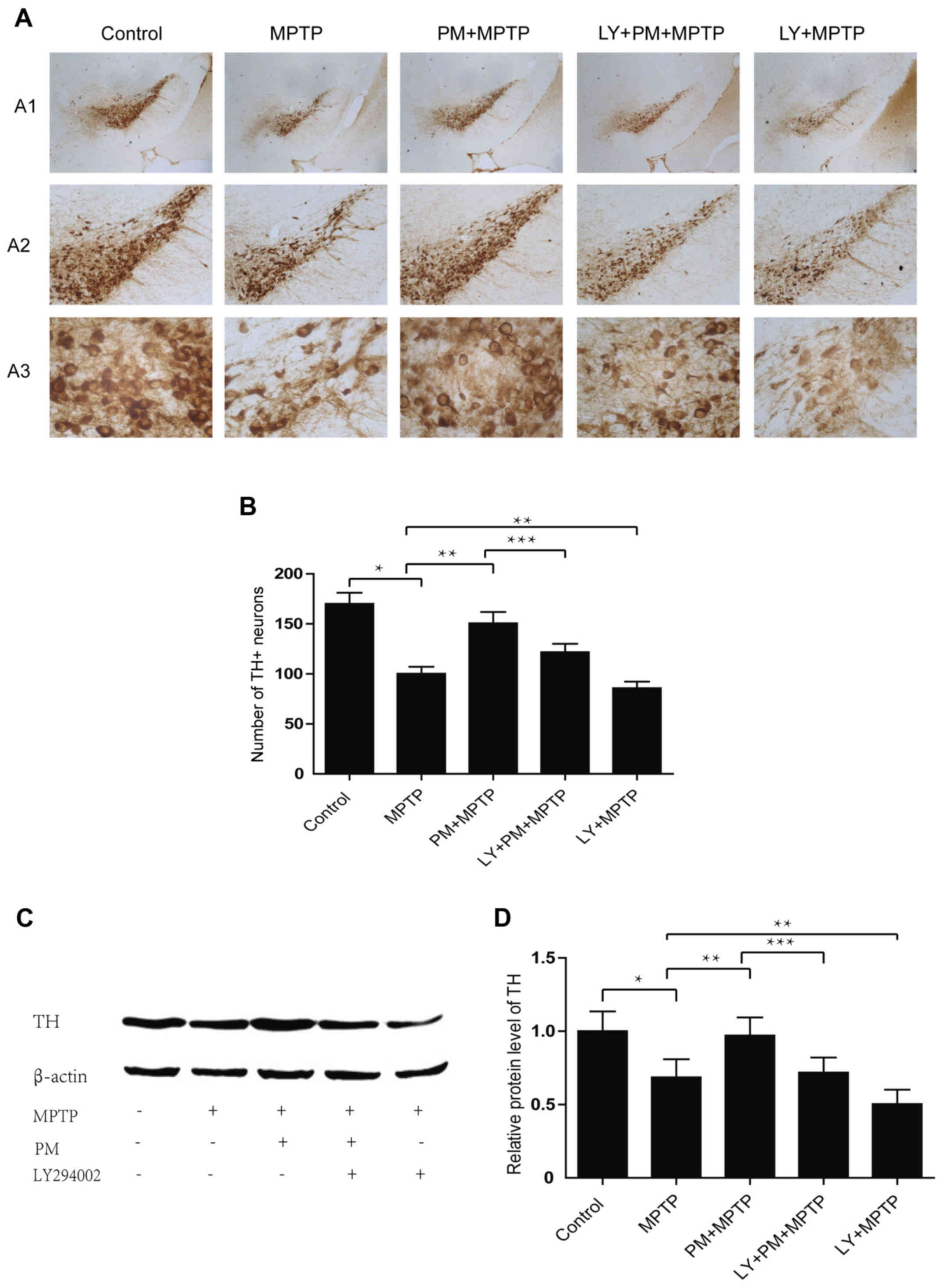
|
1
|
Mullin S and Schapira AH: Pathogenic
mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease. Neurol Clin.
33:1–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berardelli A, Wenning GK, Antonini A, Berg
D, Bloem BR, Bonifati V, Brooks D, Burn DJ, Colosimo C, Fanciulli
A, et al: EFNS/MDS-ES/ENS [corrected] recommendations for the
diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurol. 20:16–34. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Terada T, Yokokura M, Yoshikawa E,
Futatsubashi M, Kono S, Konishi T, Miyajima H, Hashizume T and
Ouchi Y: Extrastriatal spreading of microglial activation in
Parkinson's disease: A positron emission tomography study. Ann Nucl
Med. 30:579–587. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka S, Ishii A, Ohtaki H, Shioda S,
Yoshida T and Numazawa S: Activation of microglia induces symptoms
of Parkinson's disease in wild-type, but not in IL-1 knockout mice.
J Neuroinflamm. 10:1432013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tang Y and Le W: Differential roles of M1
and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol.
53:1181–1194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Varnum MM and Ikezu T: The classification
of microglial activation phenotypes on neurodegeneration and
regeneration in Alzheimer's disease brain. Arch Immunol Ther Exp
(Warsz). 60:251–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim BW, Koppula S, Kumar H, Park JY, Kim
IW, More SV, Kim IS, Han SD, Kim SK, Yoon SH and Choi DK: α-Asarone
attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation by inhibiting NF
kappa B activation and mitigates MPTP-induced behavioral deficits
in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Neuropharmacology.
97:46–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rubin LL and de Sauvage FJ: Targeting the
Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:1026–1033. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Sauvage F: The HH signaling pathway in
cancer. Bull Mem Acad R Med Belg. 162:219–223. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Banerjee SB, Rajendran R, Dias BG,
Ladiwala U, Tole S and Vaidya VA: Recruitment of the Sonic hedgehog
signaling cascade in electroconvulsive seizure-mediated regulation
of adult rat hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci.
22:1570–1580. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sims JR, Lee SW, Topalkara K, Qiu J, Xu J,
Zhou Z and Moskowitz MA: Sonic hedgehog regulates
ischemia/hypoxia-induced neural progenitor proliferation. Stroke.
40:3618–3636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hung HC, Hsiao YH and Gean PW: Sonic
hedgehog signaling regulates amygdalar and extinction of fear
memory. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 25:1723–1732. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hung HC, Hsiao YH and Gean PW: Learning
induces sonic hedgehog signaling in the amygdala which promotes
neurogenesis and long-term memory formation. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 18:pyu0712015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Dass B, Iravani MM, Jackson MJ, Engber TM,
Galdes A and Jenner P: Behavioural and immunohistochemical changes
following supranigral administration of sonic hedgehog in
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated common
marmosets. Neuroscience. 114:99–109. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Dong W, Guo S, Zhao S, He S,
Zhang L, Tang Y and Wang H: Lentivirus-mediated delivery of sonic
hedgehog into the striatum stimulates neuroregeneration in a rat
model of Parkinson disease. Neurol Sci. 35:1931–1940. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schabbauer G, Tencati M, Pedersen B,
Pawlinski R and Mackman N: PI3K-Akt pathway suppresses coagulation
and inflammation in endotoxemic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 24:1963–1969. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim SN, Kim ST, Doo AR, Park JY, Moon W,
Chae Y, Yin CS, Lee H and Park HJ: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway mediates acupuncture-induced
dopaminergic neuron protection and motor function improvement in a
mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Int J Neurosci. 121:562–569.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao Y, Zhang Q, Xi J, Xiao B, Li Y and Ma
C: Neuroprotective effect of fasudil on inflammation through
PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin dependent pathways in a mice model of
Parkinson's disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2354–2364.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dai R, Xia Y, Mao L, Mei Y, Xue Y and Hu
B: Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in the neuroprotective effect of
Sonic hedgehog on cortical neurons underoxidative stress. J
Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 32:856–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xia YP, Dai RL, Li YN, Mao L, Xue YM, He
QW, Huang M, Huang Y, Mei YW and Hu B: The protective effect of
sonic hedgehog is mediated by the phosphoinositide [corrected]
3-kinase/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway in cultured rat astrocytes under
oxidative stress. Neuroscience. 209:1–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo Z, Xu S, Du N, Liu J, Huang Y and Han
M: Neuroprotective effects of stemazole in the MPTP induced acute
model of Parkinson's disease: Involvement of the dopamine system.
Neurosci Lett. 616:152–159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuribara H, Higuchi Y and Tadokoro S:
Effects of central depressants on rota-rod and traction
performances in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol. 27:117–126. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ouchi Y, Yoshikawa E, Sekine Y,
Futatsubashi M, Kanno T, Ogusu T and Torizuka T: Microglial
activation and dopamine terminal lossin early Parkinson's disease.
Ann Neurol. 57:168–75. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ouchi Y, Yagi S, Yokokura M and Sakamoto
M: Neuroinflammation in the living brain of Parkinson's disease.
Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 15 Suppl 3:S200–S204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cappellano G, Carecchio M, Fleetwood T,
Magistrelli L, Cantello R, Dianzani U and Cormi C: Immunity and
inflammation in neurodegenerative disease. Am J Neurodegener Dis.
21:89–107. 2013.
|
|
26
|
Gonzalez-Reyes LE, Verbitsky M, Blesa J,
Jackson-Lewis V, Paredes D, Tillack K, Phani S, Kramer ER,
Przedborski S and Kottmann AH: Sonic hedgehog maintains cellular
and neurochemical homeostasis in the adult nigrostriatal circuit.
Neuron. 75:306–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gordon R, Singh N, Lawana V, Ghosh A,
Harischandra DS, Jin H, Hogan C, Sarkar S, Rokad D, Panicker N, et
al: Protein kinase Cd upregulation in microglia drives
neuroinflammatory responses and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in
experimental models of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis.
93:96–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim BW, Koppula S, Park SY, Kim YS, Park
PJ, Lim JH, Kim IS and Choi DK: Attenuation of neuroinflammatory
responses and behavioral deficits by Ligusticum officinale (Makino)
Kitag in stimulated microglia and MPTP-induced mouse model of
Parkinson's disease. J Ethnopharmacol. 164:388–397. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou X, Liu Z, Jang F, Xiang C, Li Y and
He Y: Autocrine Sonic hedgehog attenuates inflammation in
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice via upregulation of
IL-10. PLoS One. 7:e441212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Haas SJ, Zhou X, Machado V, Wree A,
Krieglstein K and Spittau B: Expression of Tgfβ1 and inflammatory
markers in the 6-hydroxydopamine mouse model of Parkinson's
disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 9:72016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Quesada A, Lee BY and Micevych PE: PI3
kinase/Akt activation mediates estrogen and IGF-1 nigral DA
neuronal neuroprotection against a unilateral rat model of
Parkinson's disease. Dev Neurobiol. 68:632–644. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim CH, Han BS, Moon J, Kim DJ, Shin J,
Rajan S, Nguyen QT, Sohn M, Kim WG, Han M, et al: Nuclear receptor
Nurr1 agonists enhance its dual functions and improve behavioral
deficits in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 112:8756–8761. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maguire-Zeiss KA and Federoff HJ: Future
directions for immune modulation in neurodegenerative disorders:
Focus on Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna).
117:1019–1025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|