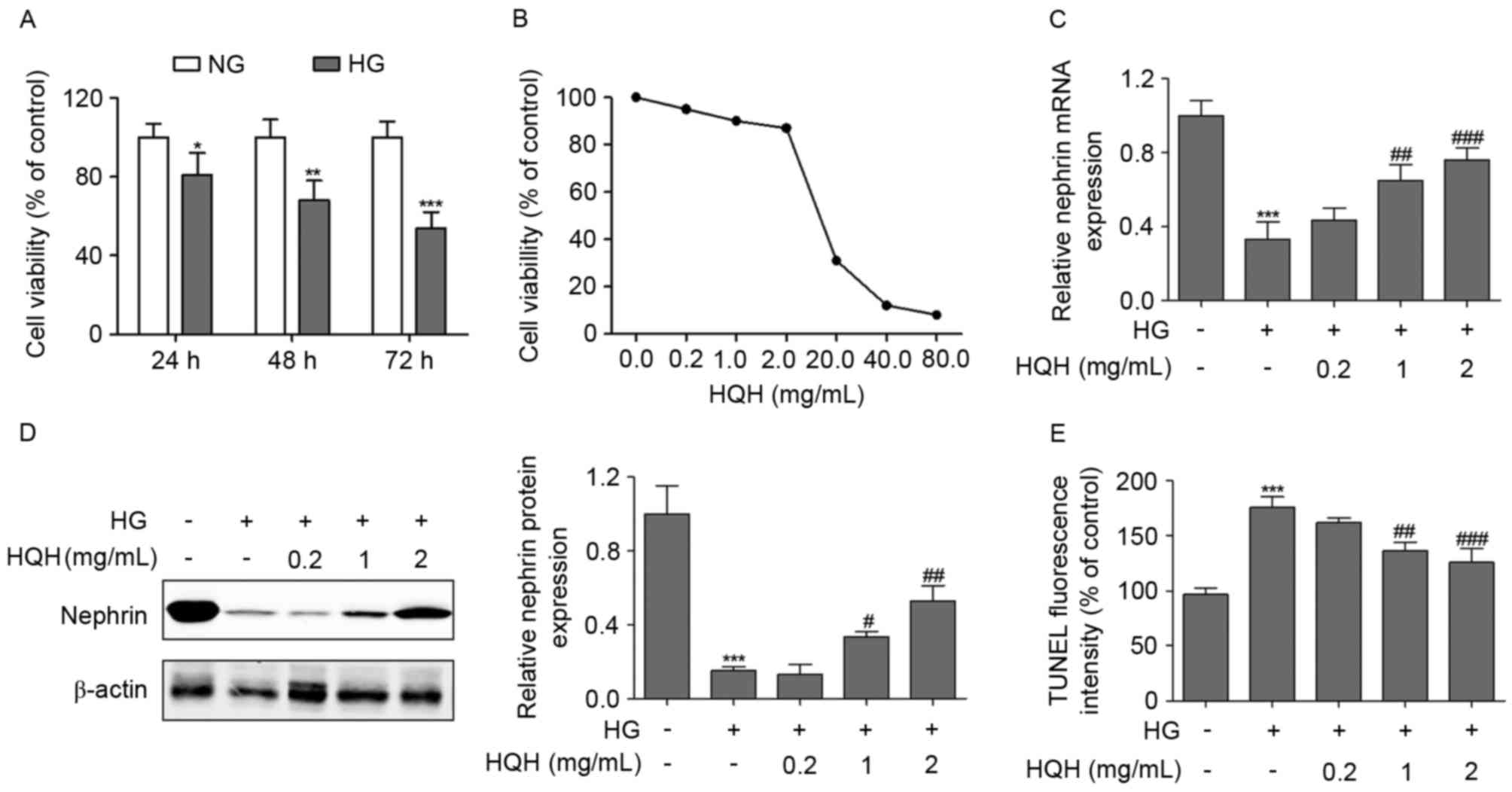
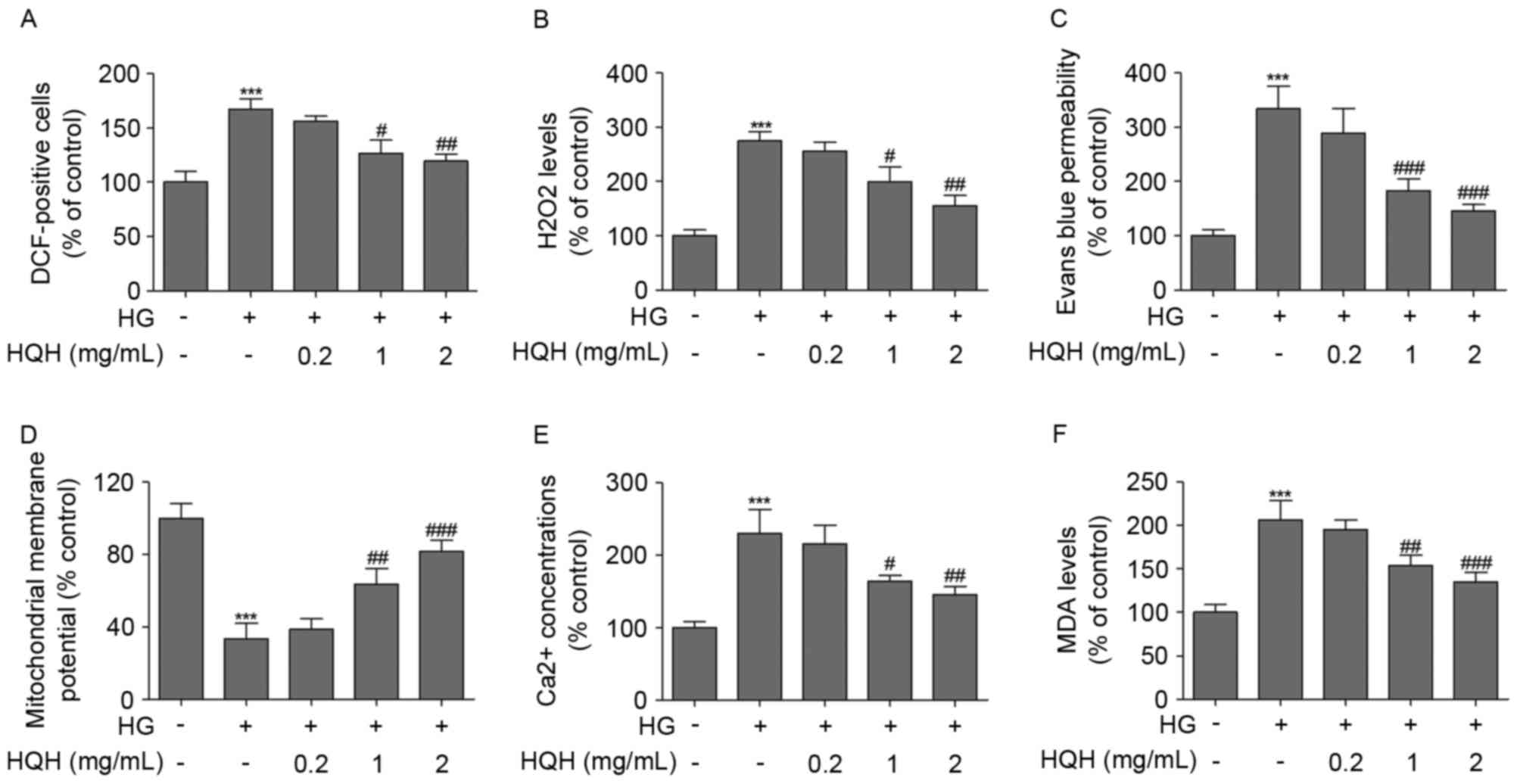
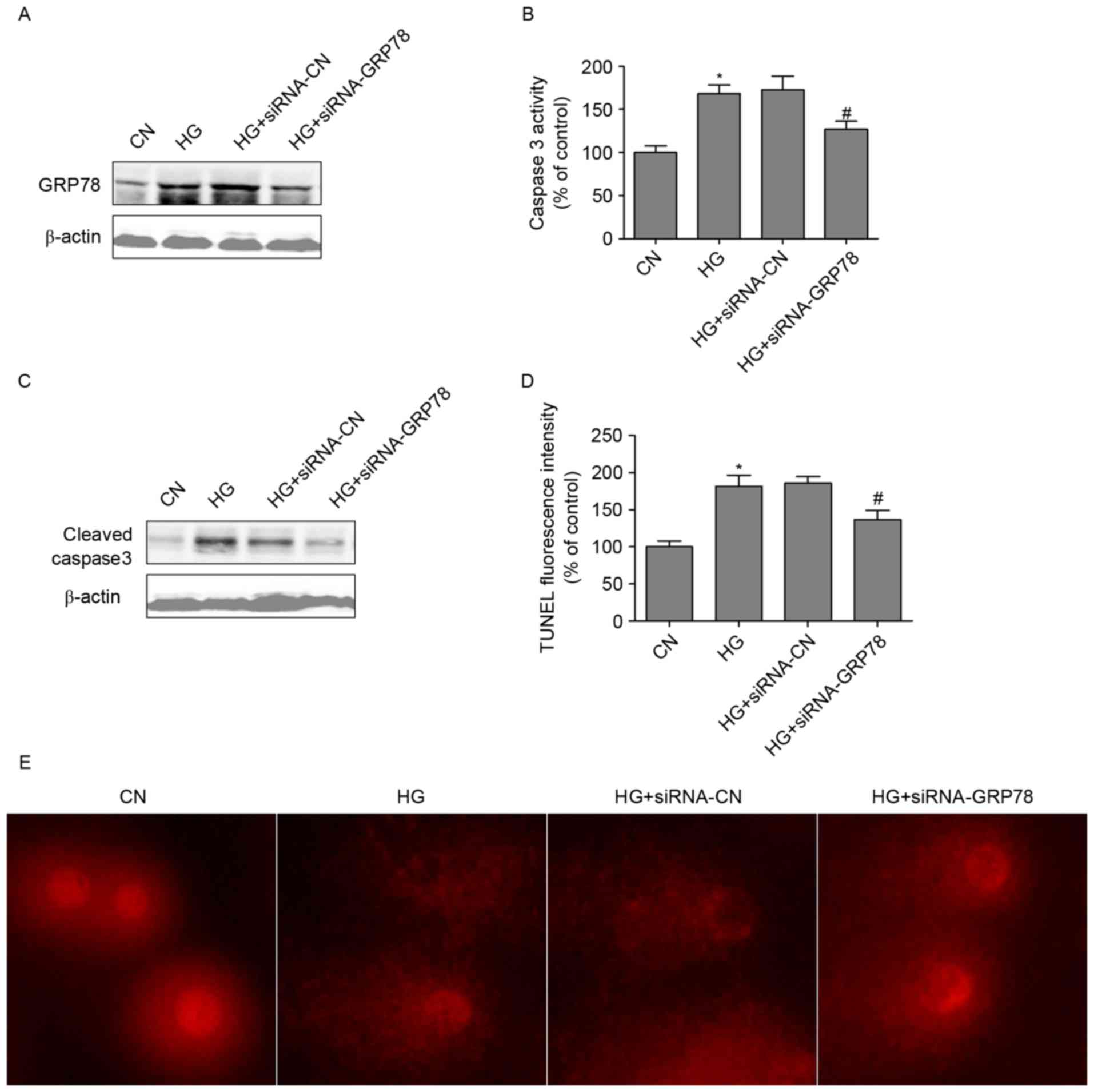
|
1
|
Weir MR: Salt, hypertension, and
proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
2:351–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong C, Zheng H, Huang S, You N, Xu J, Ye
X, Zhu Q, Feng Y, You Q, Miao H, et al: Heme oxygenase-1 enhances
autophagy in podocytes as a protective mechanism against high
glucose-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 337:146–159. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jefferson JA, Shankland SJ and Pichler RH:
Proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease: A mechanistic viewpoint.
Kidney Int. 74:22–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wolf G, Chen S and Ziyadeh FN: From the
periphery of the glomerular capillary wall toward the center of
disease: Podocyte injury comes of age in diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetes. 54:1626–1634. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lemley KV, Lafayette RA, Safai M, Derby G,
Blouch K, Squarer A and Myers BD: Podocytopenia and disease
severity in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 61:1475–1485. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyer TW, Bennett PH and Nelson RG:
Podocyte number predicts long-term urinary albumin excretion in
Pima Indians with Type II diabetes and microalbuminuria.
Diabetologia. 42:1341–1344. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Menini S, Iacobini C, Oddi G, Ricci C,
Simonelli P, Fallucca S, Grattarola M, Pugliese F, Pesce C and
Pugliese G: Increased glomerular cell (podocyte) apoptosis in rats
with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus: Role in the
development of diabetic glomerular disease. Diabetologia.
50:2591–2599. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han SY, Kang YS, Jee YH, Han KH, Cha DR,
Kang SW and Han DS: High glucose and angiotensin II increase beta1
integrin and integrin-linked kinase synthesis in cultured mouse
podocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 323:321–332. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu S, Nam SM, Kim JH, Das R, Choi SK,
Nguyen TT, Quan X, Choi SJ, Chung CH, Lee EY, et al: Palmitate
induces ER calcium depletion and apoptosis in mouse podocytes
subsequent to mitochondrial oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis.
6:e19762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pereira ER, Frudd K, Awad W and Hendershot
LM: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and hypoxia response pathways
interact to potentiate hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1)
transcriptional activity on targets like vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF). J Biol Chem. 289:3352–3364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zode GS, Sharma AB, Lin X, Searby CC,
Bugge K, Kim GH, Clark AF and Sheffield VC: Ocular-specific ER
stress reduction rescues glaucoma in murine glucocorticoid-induced
glaucoma. J Clin Invest. 124:1956–1965. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu Q, Guo R, Liu C, Fu D, Liu F, Hu J and
Jiang H: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis
contributing to high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
calcification. J Vasc Res. 52:291–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen YJ, Wu CL, Liu JF, Fong YC, Hsu SF,
Li TM, Su YC, Liu SH and Tang CH: Honokiol induces cell apoptosis
in human chondrosarcoma cells through mitochondrial dysfunction and
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Lett. 291:20–30. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ha TS, Park HY, Seong SB and Ahn HY:
Angiotensin II induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in podocyte,
which would be further augmented by PI3-kinase inhibition. Clin
Hypertens. 21:132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao Y, Hao Y, Li H, Liu Q, Gao F, Liu W
and Duan H: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in apoptosis of
differentiated mouse podocytes induced by high glucose. Int J Mol
Med. 33:809–816. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang ZS, Xiong F, Xie XH, Chen D, Pan JH
and Cheng L: Astragaloside IV attenuates proteinuria in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy via the inhibition of
endoplasmic reticulum stress. BMC Nephrol. 16:442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu H, Sun W, Gu LB, Tu Y, Yu BY and Hu H:
Huaiqihuang Granules () reduce proteinuria by enhancing nephrin
expression and regulating necrosis factor κB signaling pathway in
adriamycin-induced nephropathy. Chin J Integr Med. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Sun W, Zhu Z, Yu J, Wang YH, Xiong M, Gao
X, Zhao ZH and Liu XG: Effects of Chinese herbal medicine
Huaiqihuang Granule on nephrin and podocin expressions in renal
tissues of rats with adriamycin-induced nephrosis. Zhong Xi Yi Jie
He Xue Bao. 9:546–552. 2011.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li CX, Xia M, Han WQ, Li XX, Zhang C,
Boini KM, Liu XC and Li PL: Reversal by growth hormone of
homocysteine-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through
membrane raft-redox signaling in podocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem.
27:691–702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ruotsalainen V, Ljungberg P, Wartiovaara
J, Lenkkeri U, Kestilä M, Jalanko H, Holmberg C and Tryggvason K:
Nephrin is specifically located at the slit diaphragm of glomerular
podocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:7962–7967. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Y, Liu CP, Xu KF, Mao XD, Lu YB, Fang
L, Yang JW and Liu C: Effect of taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic
acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis induced by
advanced glycation end products in cultured mouse podocytes. Am J
Nephrol. 28:1014–1022. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Casalena G, Krick S, Daehn I, Yu L, Ju W,
Shi S, Tsai SY, D'Agati V, Lindenmeyer M, Cohen CD, et al: Mpv17 in
mitochondria protects podocytes against mitochondrial dysfunction
and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
306:F1372–F1380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Daehn I, Casalena G, Zhang T, Shi S,
Fenninger F, Barasch N, Yu L, D'Agati V, Schlondorff D, Kriz W, et
al: Endothelial mitochondrial oxidative stress determines podocyte
depletion in segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Clin Invest.
124:1608–1621. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu C, Xuan X, Che R, Ding G, Zhao M, Bai
M, Jia Z, Huang S and Zhang A: Dysfunction of the
PGC-1α-mitochondria axis confers adriamycin-induced podocyte
injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F1410–F1417. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yuan Y, Huang S, Wang W, Wang Y, Zhang P,
Zhu C, Ding G, Liu B, Yang T and Zhang A: Activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α ameliorates
mitochondrial dysfunction and protects podocytes from
aldosterone-induced injury. Kidney Int. 82:771–789. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zamzami N, Brenner C, Marzo I, Susin SA
and Kroemer G: Subcellular and submitochondrial mode of action of
Bcl-2-like oncoproteins. Oncogene. 16:2265–2282. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R and
Wang X: Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts:
Requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 86:147–157. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yuan Y, Xu X, Zhao C, Zhao M, Wang H,
Zhang B, Wang N, Mao H, Zhang A and Xing C: The roles of oxidative
stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy in
aldosterone/mineralocorticoid receptor-induced podocyte injury. Lab
Invest. 95:1374–1386. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Y, Gui D, Chen J, He D, Luo Y and
Wang N: Down-regulation of PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway by Astragaloside
IV is associated with the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced podocyte apoptosis in diabetic rats. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 33:1975–1987. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tao JL, Wen YB, Shi BY, Zhang H, Ruan XZ,
Li H, Li XM, Dong WJ and Li XW: Endoplasmic reticulum stress is
involved in podocyte apoptosis induced by saturated fatty acid
palmitate. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:3137–3142. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang XZ, Lawson B, Brewer JW, Zinszner H,
Sanjay A, Mi LJ, Boorstein R, Kreibich G, Hendershot LM and Ron D:
Signals from the stressed endoplasmic reticulum induce
C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP/GADD153). Mol Cell Biol.
16:4273–4280. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|