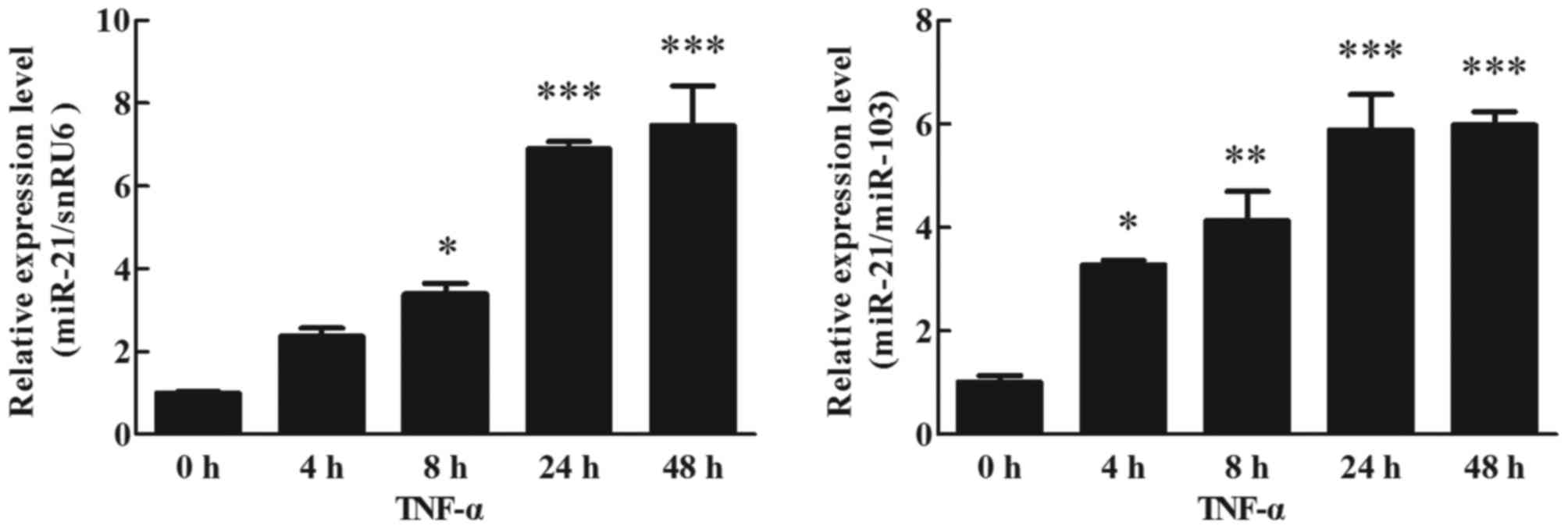
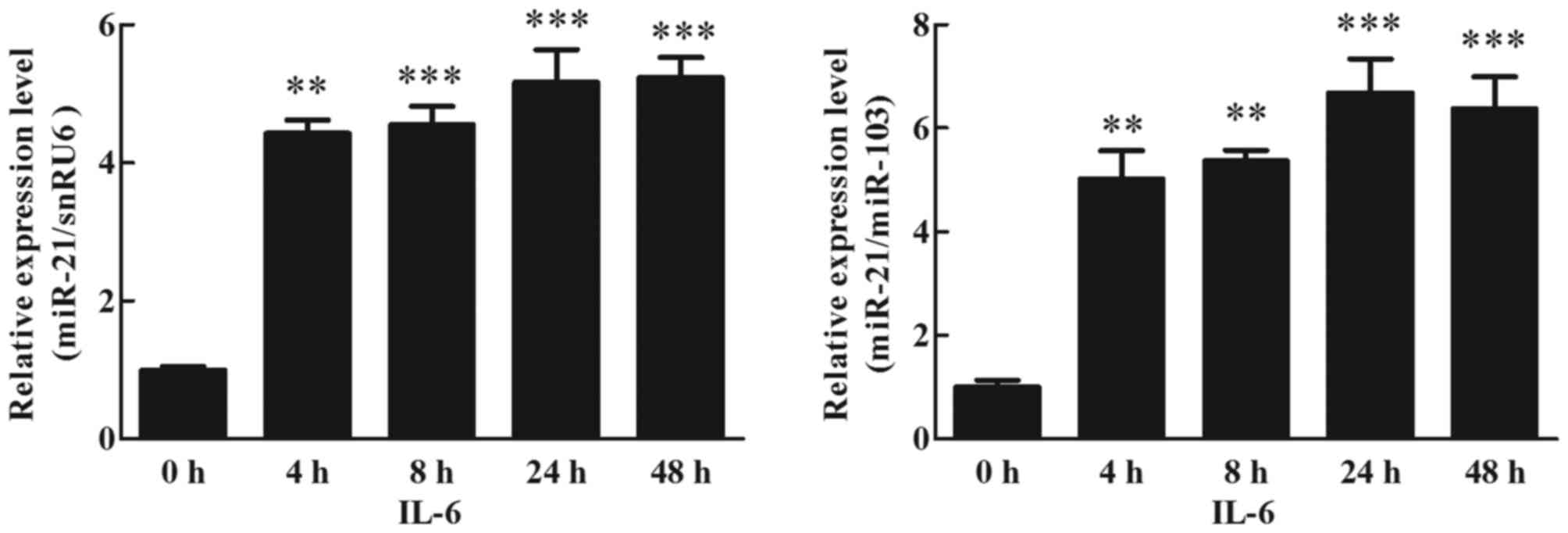
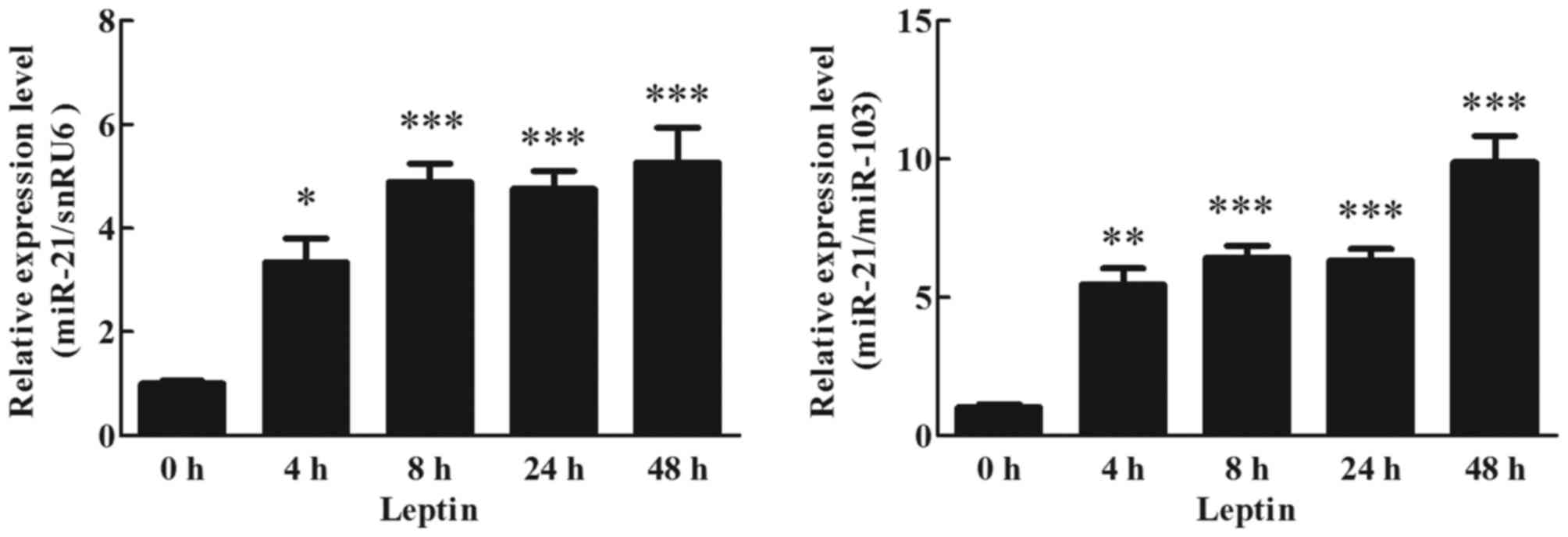
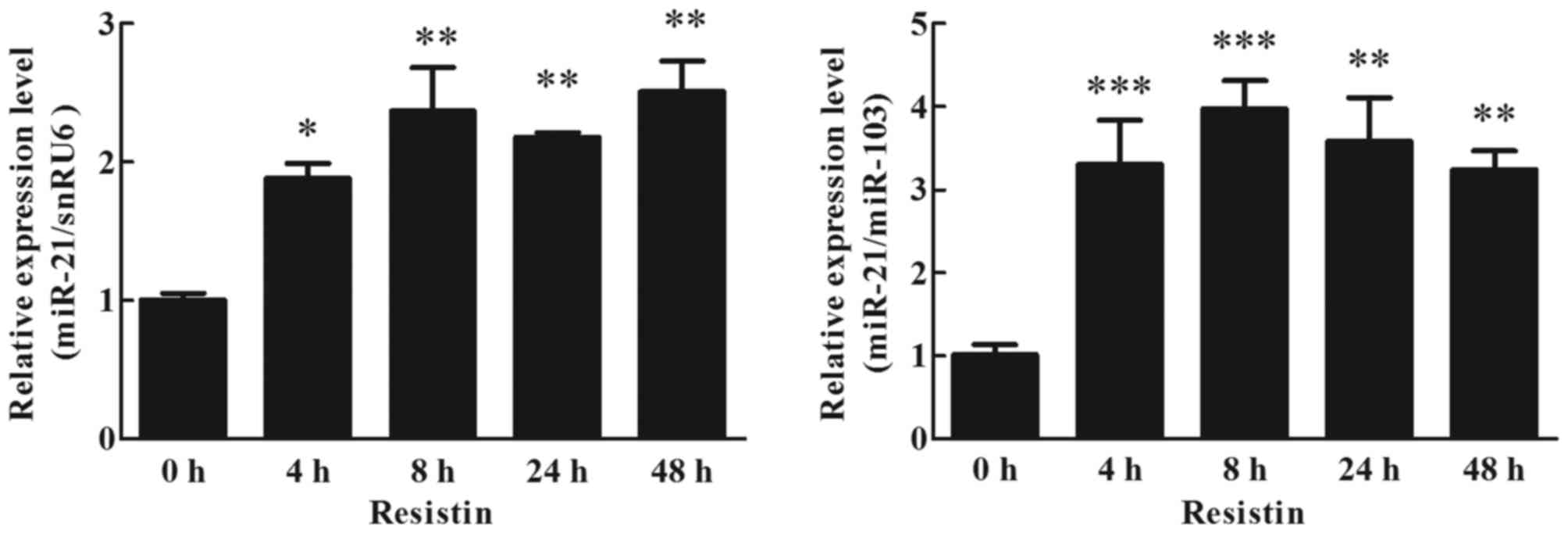
|
1
|
Jeffery RW and Sherwood NE: Is the obesity
epidemic exaggerated? No. BMJ. 336:2452008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galic S, Oakhill JS and Steinberg GR:
Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
316:129–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Haslam DW and James WP: Obesity. Lancet.
366:1197–1209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Boden G: Obesity, insulin resistance and
free fatty acids. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 18:139–143.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parhofer KG: Interaction between glucose
and lipid metabolism: More than diabetic dyslipidemia. Diabetes
Metab J. 39:353–362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deiuliis JA: Micrornas as regulators of
metabolic disease: Pathophysiologic significance and emerging role
as biomarkers and therapeutics. Int J Obes (Lond). 40:88–101. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pfeffer SR, Yang CH and Pfeffer LM: The
role of miR-21 in cancer. Drug Dev Res. 76:270–277. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Beckett EL, Martin C, Choi JH, King K,
Niblett S, Boyd L, Duesing K, Yates Z, Veysey M and Lucock M:
Folate status, folate-related genes and serum miR-21 expression:
Implications for miR-21 as a biomarker. BBA Clin. 4:45–51. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao W, Zhao JJ, Zhang L, Xu QF, Zhao YM,
Shi XY and Xu AG: Serum miR-21 level: A potential diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:14759–14763. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seeger T, Fischer A, Muhly-Reinholz M,
Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S: Long-term inhibition of miR-21 leads to
reduction of obesity in db/db mice. Obesity (Silver Spring).
22:2352–2360. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ling HY, Hu B, Hu XB, Zhong J, Feng SD,
Qin L, Liu G, Wen GB and Liao DF: miRNA-21 reverses high glucose
and high insulin induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
through targeting phosphatase and tensin homologue. Exp Clin
Endocrinol Diabetes. 120:553–559. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim YJ, Hwang SH, Cho HH, Shin KK, Bae YC
and Jung JS: MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation of human
adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and high-fat
diet-induced obesity alters microrna 21 expression in white adipose
tissues. J Cell Physiol. 227:183–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim YJ, Hwang SJ, Bae YC and Jung JS:
miR-21 regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation
of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human
adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 27:3093–3102. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spiegelman BM and Flier JS: Obesity and
the regulation of energy balance. Cell. 104:531–543. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wellen KE and Hotamisligil GS:
Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 115:1111–1119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Waterland RA: Epigenetic mechanisms
affecting regulation of energy balance: Many questions, few
answers. Annu Rev Nutr. 34:337–355. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abranches MV, Oliveira FC, Conceição LL
and Peluzio MD: Obesity and diabetes: The link between adipose
tissue dysfunction and glucose homeostasis. Nutr Res Rev.
28:121–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chakraborty C, Doss CG, Bandyopadhyay S
and Agoramoorthy G: Influence of miRNA in insulin signaling pathway
and insulin resistance: Micro-molecules with a major role in type-2
diabetes. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 5:697–712. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arner P and Kulyté A: MicroRNA regulatory
networks in human adipose tissue and obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
11:276–288. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jinwei Z, Yi L, Yuhao W, Liujun H,
Mingzhou L and Xun W: MicroRNA regulates animal adipocyte
differentiation. Yi Chuan. 37:1175–1184. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kilic ID, Dodurga Y, Uludag B, Alihanoglu
YI, Yildiz BS, Enli Y, Secme M and Bostanci HE: MicroRNA-143 and
−223 in obesity. Gene. 560:140–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jordan SD, Krüger M, Willmes DM, Redemann
N, Wunderlich FT, Brönneke HS, Merkwirth C, Kashkar H, Olkkonen VM,
Böttger T, et al: Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143
inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:434–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Olefsky JM and Glass CK: Macrophages,
inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:219–246.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hamada Y, Nagasaki H, Fujiya A, Seino Y,
Shang QL, Suzuki T, Hashimoto H and Oiso Y: Involvement of de novo
ceramide synthesis in pro-inflammatory adipokine secretion and
adipocyte-macrophage interaction. J Nutr Biochem. 25:1309–1316.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Finucane OM, Reynolds CM, McGillicuddy FC
and Roche HM: Insights into the role of macrophage migration
inhibitory factor in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc Nutr Soc.
71:622–633. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thiruvengadam V, Amperayani S, Babu RP and
Uppuluri R: Correlation of childhood obesity and related insulin
resistance with leptin and retinol binding protein 4. Indian J
Pediatr. 82:799–804. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park HK, Qatanani M, Briggs ER, Ahima RS
and Lazar MA: Inflammatory induction of human resistin causes
insulin resistance in endotoxemic mice. Diabetes. 60:775–783. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Medina-Urrutia A, Posadas-Romero C,
Posadas-Sánchez R, Jorge-Galarza E, Villarreal-Molina T,
González-Salazar Mdel C, Cardoso-Saldaña G, Vargas-Alarcón G,
Torres-Tamayo M and Juárez-Rojas JG: Role of adiponectin and free
fatty acids on the association between abdominal visceral fat and
insulin resistance. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|