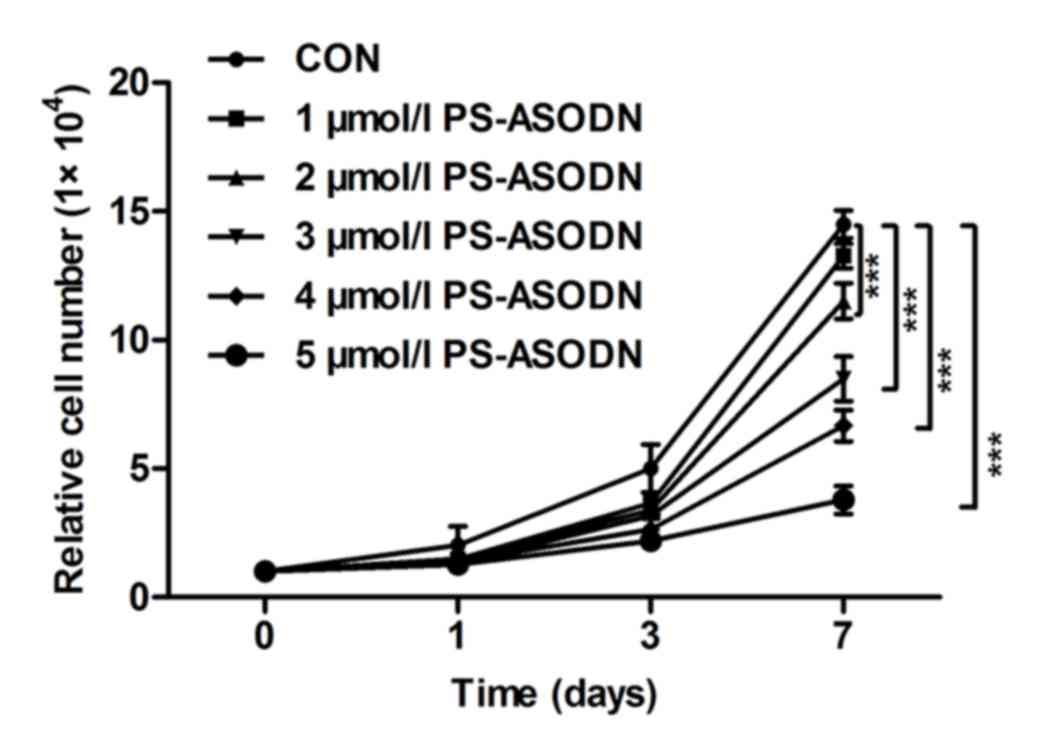
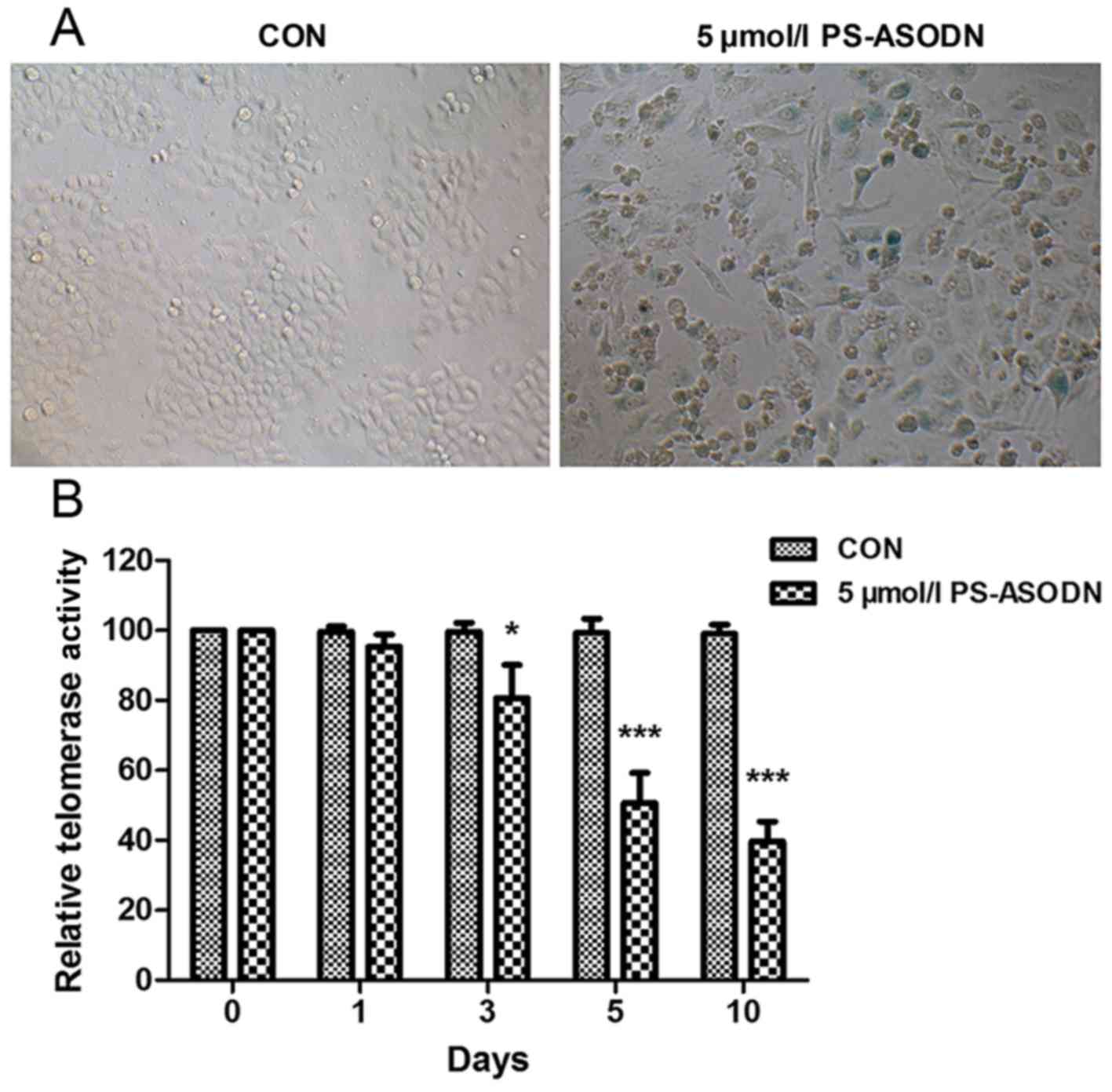
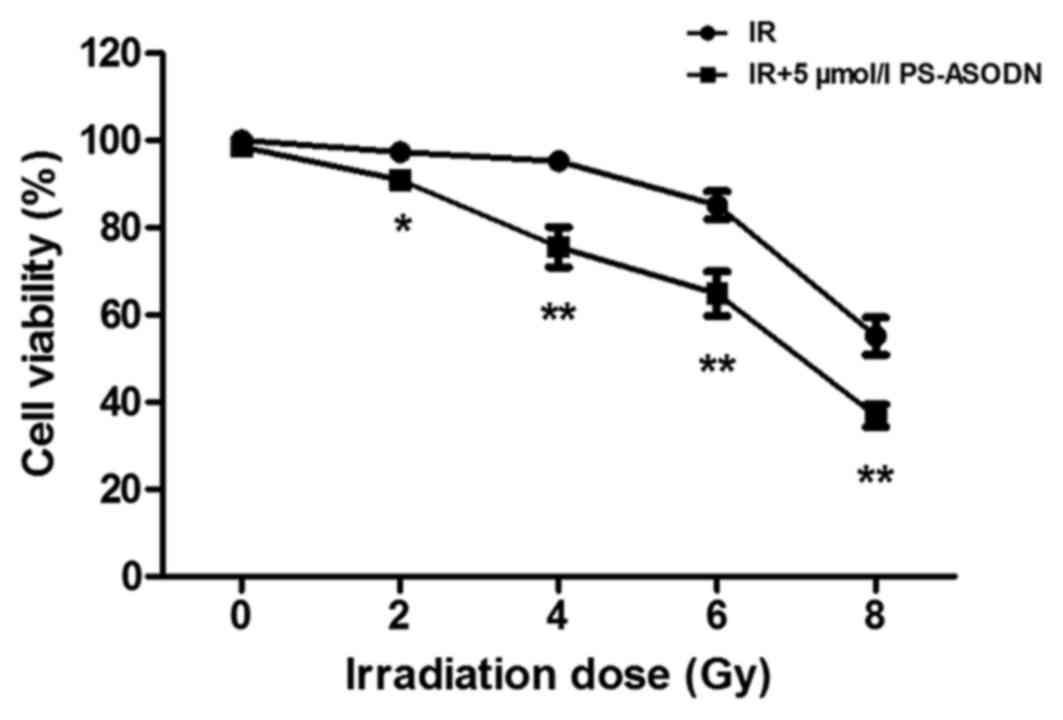
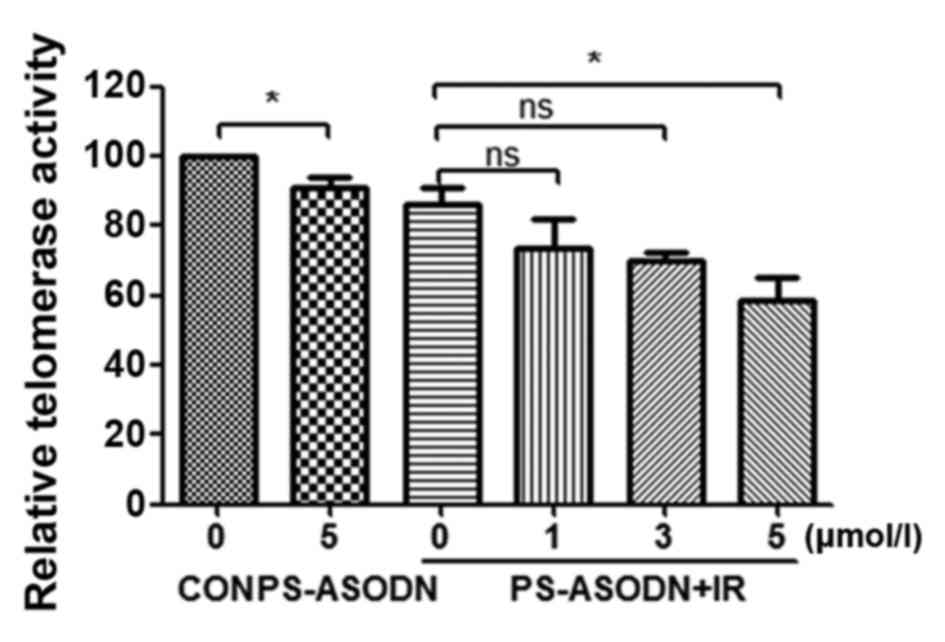
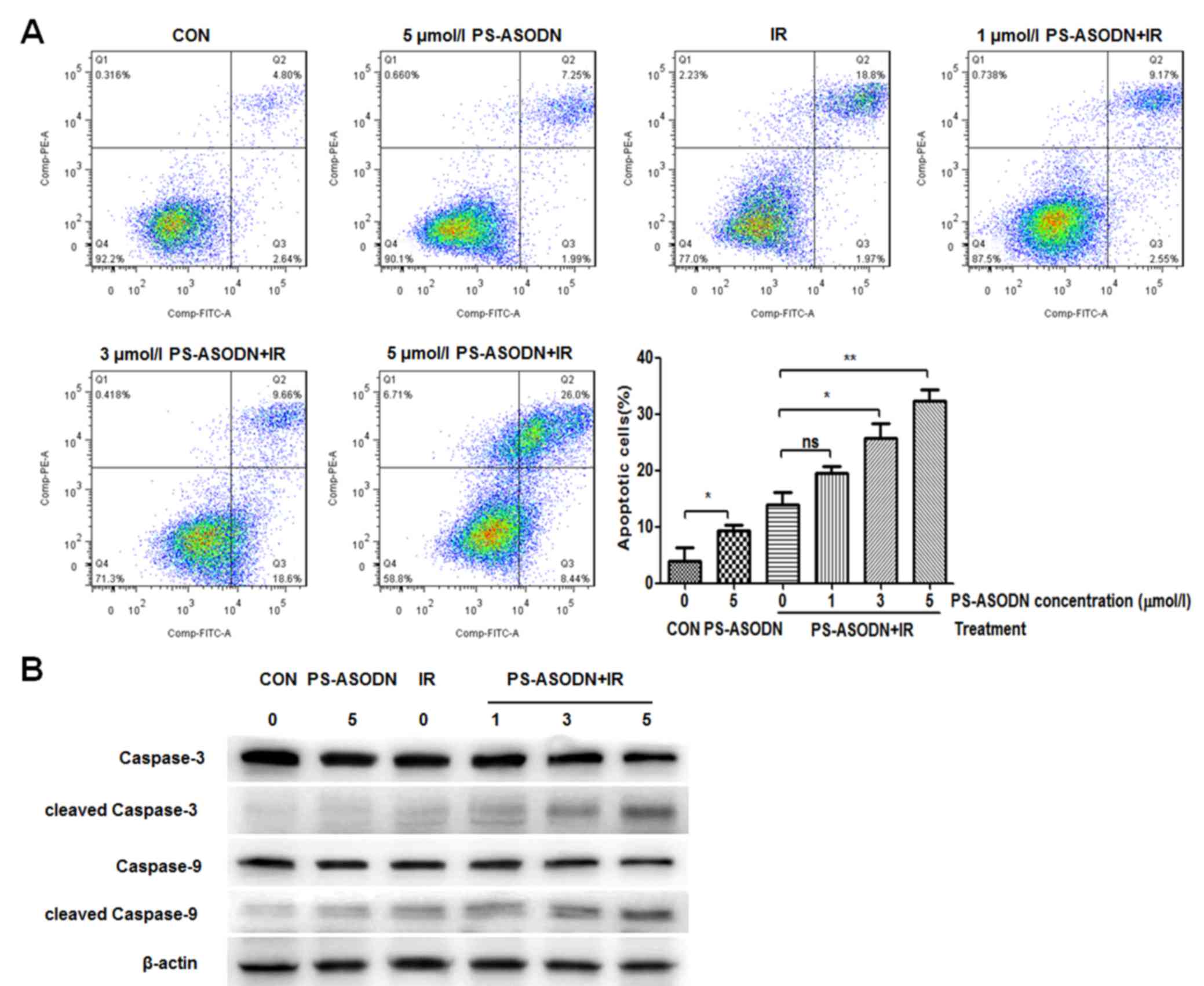
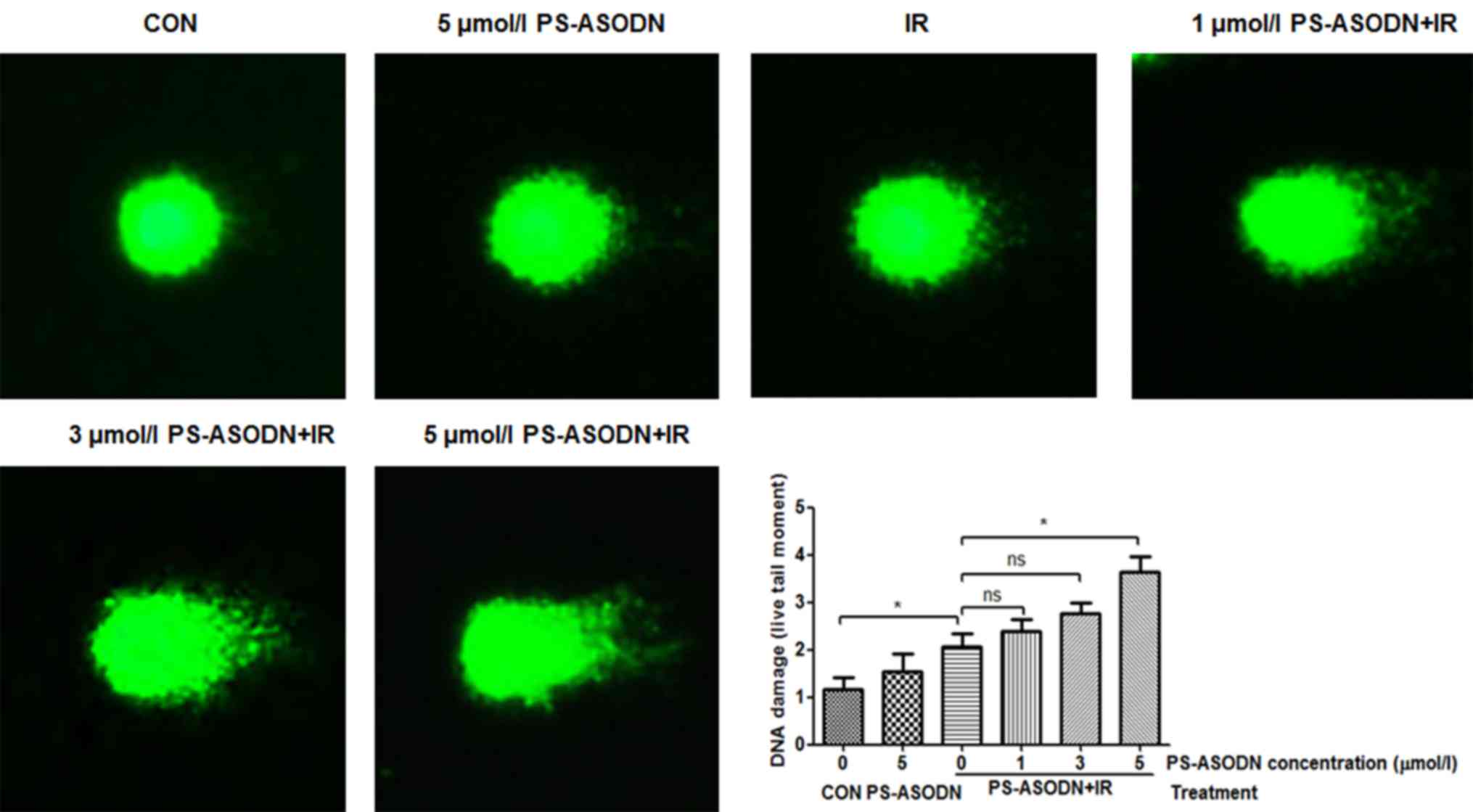
|
1
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lebedeva IV and Stein CA: Antisense
oligonucleotides in cancer: Recent advances. BioDrugs. 13:195–216.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Walther W and Schlag PM: Current status of
gene therapy for cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:659–664. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nittis T, Guittat L and Stewart SA:
Alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) and chromatin: Is there
a connection? Biochimie. 90:5–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rao YK, Kao TY, Wu MF, Ko JL and Tzeng YM:
Identification of small molecule inhibitors of telomerase activity
through transcriptional regulation of hTERT and calcium induction
pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Bioorg Med Chem.
18:6987–6994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan XK, Yan RH, Li BJ, Chen XM, Wei L and
Wang Z: Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide against human telomerase
reverse transcriptase inhibits the proliferation of Eca-109
esophageal carcinoma cells. Exp Ther Med. 8:1247–1252.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ponnala S, Chetty C, Veeravalli KK, Dinh
DH, Klopfenstein JD and Rao JS: MMP-9 silencing regulates hTERT
expression via β1 integrin-mediated FAK signaling and induces
senescence in glioma xenograft cells. Cell Signal. 23:2065–2075.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Folini M, Brambilla C, Villa R, Gandellini
P, Vignati S, Paduano F, Daidone MG and Zaffaroni N: Antisense
oligonucleotide-mediated inhibition of hTERT, but not hTERC,
induces rapid cell growth decline and apoptosis in the absence of
telomere shortening in human prostate cancer cells. Eur J Cancer.
41:624–634. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kraemer K, Fuessel S, Schmidt U, Kotzsch
M, Schwenzer B, Wirth MP and Meye A: Antisense-mediated hTERT
inhibition specifically reduces the growth of human bladder cancer
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 9:3794–3800. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sekoguchi S, Nakajima T, Moriguchi M, Jo
M, Nishikawa T, Katagishi T, Kimura H, Minami M, Itoh Y, Kagawa K,
et al: Role of cell-cycle turnover and oxidative stress in telomere
shortening and cellular senescence in patients with chronic
hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:182–190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kaul Z, Cesare AJ, Huschtscha LI, Neumann
AA and Reddel RR: Five dysfunctional telomeres predict onset of
senescence in human cells. EMBO Rep. 13:52–59. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley
CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL and Shay
JW: Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal
cells and cancer. Science. 266:2011–2015. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sekaran VG, Soares J and Jarstfer MB:
Structures of telomerase subunits provide functional insights.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:1190–1201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Donate LE and Blasco MA: Telomeres in
cancer and ageing. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 366:76–84.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zvereva MI, Shcherbakova DM and Dontsova
OA: Telomerase: Structure, functions, and activity regulation.
Biochemistry (Mosc). 75:1563–1583. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Agrawal A, Dang S and Gabrani R: Recent
patents on anti-telomerase cancer therapy. Recent Pat Anticancer
Drug Discov. 7:102–117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakhlband A, Barar J, Bidmeshkipour A,
Heidari HR and Omidi Y: Bioimpacts of anti epidermal growth factor
receptor antisense complexed with polyamidoamine dendrimers in
human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cells. J Biomed Nanotechnol.
6:360–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao FJ, Zhang SL, Ma L, Gao H and Zong
ZH: Inhibitory effects of c-erbB-2 antisense oligonucleotide
transfection on uterine endometrial cancer Ishikawa cell lines. Eur
J Gynaecol Oncol. 30:54–59. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Loriot Y, Mordant P, Brown BD, Bourhis J,
Soria JC and Deutsch E: Inhibition of BCL-2 in small cell lung
cancer cell lines with oblimersen, an antisense BCL-2
oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN): In vitro and in vivo enhancement of
radiation response. Anticancer Res. 30:3869–3878. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang KZ, Xu JH, Huang XW, Wu LX, Su Y and
Chen YZ: Curcumin synergistically augments bcr/abl phosphorothioate
antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit growth of chronic myelogenous
leukemia cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:105–110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan Y, Cai H, Yang XJ, Li W, He J, Guo TK
and Chen YR: Liposome-mediated induction of apoptosis of human
hepatoma cells by c-myc antisense phosphorothioate
oligodeoxynucleotide and 5-fluorouracil. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:5529–5533. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Svinareva LV, Glukhov AI, Moskaleva EY and
Shvets VI: Effect of modified DNA and RNA oligonucleotides on
telomerase activity and tumor cell survival in vitro. Appl Biochem
Micro. 47:718–722. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang XS, Wang K, Li X and Fu SB: Effects
of phosphorothioate anti-sense oligodeoxynucleotides on colorectal
cancer cell growth and telomerase activity. World J Gastroenterol.
10:3455–3458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao XD and Chen YR: Inhibition of
telomerase with human telomerase reverse transcriptase antisense
increases the sensitivity of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced
apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Asian J Androl. 9:697–704.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ji XM, Xie CH, Fang MH, Zhou FX, Zhang WJ,
Zhang MS and Zhou YF: Efficient inhibition of human telomerase
activity by antisense oligonucleotides sensitizes cancer cells to
radiotherapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:1185–1191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fan XK, Yan RH, Li BJ, Chen XM, Wei L and
Wang Z: Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide against human telomerase
reverse transcriptase inhibits the proliferation of Eca-109
esophageal carcinoma cells. Exp Ther Med. 8:1247–1252.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|